Encephalopathy is a complex of neurological and mental disorders associated with focal damage to the brain. Depending on the etiology, several forms of this disease are distinguished: dyscirculatory, which is caused by circulatory pathology and is more common in old age, traumatic, which usually occurs in athletes after repeated traumatic brain injuries, hypoxic, etc. Encephalopathy of toxic origin develops due to direct damaging effects on the brain of various toxic substances. Pathology can occur at any age, including in children, but the clinical course and prognosis largely depend on the general state of health and timely initiation of treatment. Is this pathology treatable? Doctors at Leto clinics are convinced that with rapid detoxification and elimination of the toxin, the chance of complete restoration of the functioning of the central nervous system (CNS) is very high.
Toxic encephalopathy of the brain: what kind of disease, main causes
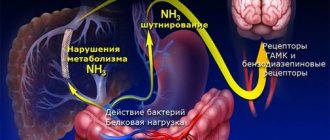
The toxicogenic effect of most neurotropic poisons is based on their negative impact directly on neuronal membranes and the mechanisms of nerve impulse transmission. Violations of energy and plastic metabolism play an important role in the pathogenesis of the disease. In addition, some toxins inhibit the hematopoietic and circulatory systems, breathing, which also causes toxic hypoxic encephalopathy. Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, cells localized in the cerebral cortex, cerebellum and hippocampus are especially sensitive to the influence of pathological factors, which causes the clinical manifestations of the disease.
Major neurotoxins
The main causes of toxic encephalopathy include:
alcohol and volatile solvents: destroy cell membranes, receptors, cause changes (irreversible with long-term exposure) in energy metabolism;- psychoactive substances (opiates, cannabinoids, amphetamines, cocaine, ephedrine, hallucinogens, some drugs, etc.): pathologically affect the reuptake system and the production of norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin
- heavy metals (mercury, lead, manganese, arsenic, thallium, etc.): have a direct destructive effect on the structures of the central nervous system and also affect the functioning of the peripheral nervous system.
Accordingly, the risk of toxic brain encephalopathy is especially high among people working in hazardous industries. These are, for example, chemical, construction, metallurgy, and agriculture, where insecticides and pesticides are used. The disease is often diagnosed in alcoholism and drug addiction. The pathology is less common among artists; those who use neurotoxic paint solvents are at risk.
Signs of encephalopathy
Conventionally, all signs of the disorder can be divided into three main groups:
- Neuropsychological . The patient's intellectual abilities decrease. It is difficult for him to focus on anything, and he has difficulty solving simple problems. The person becomes emotionally disinhibited. He has a dominant depressive mood.
- Vegetative . Urination is impaired and problems with speech arise.
- Motor . The step shortens, the gait becomes shaky, the posture becomes unstable.
These signs indicate that encephalopathy should be treated as soon as possible. Delay leads to a worsening of the patient’s condition, so it is unacceptable.
Clinical manifestations of toxic encephalopathy
The signs of the disease and the course of the disease largely depend on the neurotoxin that caused this condition. Depending on the severity and duration of symptoms, the disease can be acute or chronic. But even the acute form rarely goes away without any consequences. Residual effects persist for a long time (and in some cases throughout life). Typically this is:
- regular headaches with dizziness;
- general weakness, increased fatigue;
- irritability;
- sleep disturbances (difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings, nightmares);
- autonomic dysfunction syndrome, which is manifested by increased sweating, tremor of the fingers of outstretched arms, and decreased muscle tone;
- cognitive disorders: deterioration of memory and attention; often the patient experiences difficulties even with reading fiction and watching TV shows and films.
After acute toxic encephalopathy, hypothalamic crises may periodically occur, accompanied by:
- increased headache;
- rise in blood pressure;
- pain syndrome in the chest area;
- chills with trembling;
- attacks of anger and irritability.
Symptoms of the acute form of the disease
This type of illness is typical for poisoning with heavy metals and volatile solvents; it is relatively rare in alcoholism and drug addiction, usually against the background of an already existing deficiency or disturbances in thiamine metabolism.
Clinical manifestations of the pathology include:
- oculomotor disorders (eye paralysis, strabismus, decreased response to light stimuli);
- astasia and abasia (loss of the ability to move without support and assistance);
- generalized convulsive syndrome;
- amnesia, and often the patient replaces events that he does not remember with fictitious ones;
- oral automatisms;
- repeated vomiting;
- severe headache;
- increase or decrease in body temperature;
- tachycardia;
- acute psychosis.
Without timely medical care, there is a high risk of death due to cerebral edema, stroke, and acute respiratory failure.
Symptoms of chronic toxic encephalopathy
With a prolonged course, there are 5 stages of the disease:
- Prodromal. Signs of the disease can only be visible to the patient’s loved ones. Pay attention to lack of concentration, absent-mindedness and forgetfulness.
- First. Apathy develops, coordination of movements decreases, mild tremors are possible, sleep disturbances, loss of appetite, and weight loss are typical. Various emotional disorders are noted: feelings of internal tension and anxiety, fear.
- Second. Personality and behavioral disorders come to the fore, which many take to be the initial symptoms of dementia.
- Third. Speech disorders, severe disorientation, and a decrease in almost all reflexes are characteristic.
- Fourth. Toxic encephalopathy of the most severe degree: coma develops with loss of all neurological functions.
Very often the disease is complicated by concomitant acute and chronic somatic pathologies. Thus, in addition to neurological symptoms, manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system are often noted. As a rule, the immune system suffers greatly, which leads to a decrease in resistance to various bacterial, viral and fungal infections. And in such cases, the negative influence of waste products of pathogenic microflora “joins” the action of the neurotropic poison - infectious-toxic encephalopathy develops.
Symptoms
There are many reasons for the appearance of cerebral encephalopathy, and therefore its manifestations differ. They depend on why it develops, where it is localized in the brain and what the nature of the lesion is. However, a common feature is a slow or rapid change in mental status.
For example, hepatitis contributes to a mild change: the patient cannot draw simple designs, that is, he develops apraxia - the inability to make complex movements, purposeful actions. But brain anoxia is a sharp lack of oxygen that leads to death within a few minutes.
Symptoms of encephalopathy include poor coordination of movements, inability to concentrate, inattention, as well as more serious manifestations:
- tremor of the limbs;
- lethargy;
- breathing disorder – it becomes periodic;
- muscle pain, twitching;
- convulsions;
- numbness of the nose, lips, fingertips;
- fainting, dizziness;
- persistent headaches or acute attacks;
- noise in the head;
- sleep disturbance;
- decreased thinking abilities, memory;
- sudden change of mood;
- decreased sex drive;
- apathy;
- fatigue and constant weakness;
- depression;
- sluggishness of speech;
- irritability;
- nausea, vomiting;
- coma.
If treatment is not started in time, the symptoms will intensify, hallucinations, delusions, disorders of consciousness, psychosis, etc. may appear, and there is a risk of death.
Diagnostic principles
The diagnosis is based on objective symptoms, results of laboratory and instrumental examinations and anamnesis. In addition to the mandatory examination by a therapist and neurologist, the following are indicated:
- general clinical analysis of blood and urine;
- biochemical blood test with determination of glucose, ALT, AST, bilirubin, urea, creatinines and electrolytes;
- according to indications: analysis to determine immunospecific status, neurospecific factors;
- CT, MRI, angiography;
- specific tests to detect heavy metals and narcotic substances in the body.
If symptoms indicate damage to internal organs, additional research or consultation with specialized specialists may be required. Differential diagnosis is carried out with other forms of encephalopathies and neurodegenerative diseases.
Read also
Alzheimer's disease
47,000,000 people suffer from dementia in the world.
Doctors call Alzheimer's disease the most common cause of dementia. Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease accompanied by... Read more
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
What it is? Why is this happening? Is this condition dangerous? What to do if doctors make such a diagnosis? These questions are always asked by patients who come to see a neurologist. According to classification...
More details
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is a type of acute cerebrovascular accident, which is characterized by the effusion of blood into the brain substance with the development of neurological deficit, often leading...
More details
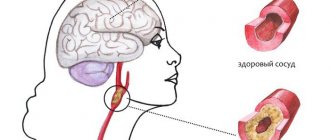
Atherosclerosis
What is atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries caused by the formation of plaque. As a person gets older, fat and cholesterol can accumulate in the arteries and form plaque. Accumulation…
More details
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, which manifests itself in the form of various clinical symptoms. This disease is diagnosed at different times...
More details
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 6,000 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 7,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 30,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 60,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL | |
| Ward for 4 persons | 10,000 rub./day |
| Ward for 3 persons | 13,000 rub./day |
| Ward 1 bed VIP | 23,000 rub./day |
| Individual post | 5,000 rub. |
| PETE | 15,000 rub./day |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!
Treatment
Considering the variety of factors causing encephalopathy, treatment should be carried out in the following areas:
- Eliminating the cause of the disease.
- Improving blood supply to the brain.
- Prescription of drugs that protect nerve cells from damage.
For encephalopathy, the following groups of drugs are prescribed:
- Neuroprotective drugs. These drugs are highly effective in treating encephalopathy disorders. They improve trophic processes in nerve cells, provide protection and restoration of cell membranes from damage. The most commonly prescribed drugs are: Cerebrolysin, Nootropil, Encephabol, Cortexin.
- Improving blood microcirculation in the vessels of the brain is achieved by prescribing drugs such as Actovegin and Kurantil.
- Hypotensive (blowing blood pressure). Preference is given to drugs with a long action (about 24 hours) in order to avoid hypertensive crises. If one drug is insufficient, a combination of drugs is prescribed. The most commonly used are ACE inhibitors (Enalapril, Lisinopril, Fosinopril), beta blockers (Nebilet, Metoprolol, Bisoprolol), diuretics (Hypothiazide), Indapamide, Spironolactone. .
- Statins are drugs that lower blood lipid levels. Typically prescribed are Atorvastatin (Atoris), Simvastatin (Simvacard), and Rosuvastatin (Rozart). In addition, to correct lipid levels, you must adhere to a low-calorie diet.
- Antioxidants - these drugs protect the cell from pathological oxidation processes and the effects of toxic free radicals. The use of the drug Mexicor for encephalopathy is effective.
- Antiplatelet agents - by reducing platelet aggregation, blood circulation in small vessels improves. Usually medications such as Aspirin and Clopidogrel are prescribed.
- Monitoring glucose levels is mandatory for diabetes mellitus.
- Detoxification - promotes the removal of toxic metabolites from the body; this therapy is especially effective for alcoholic and hepatic encephalopathy. In cases of severe intoxication, plasmapheresis (hardware purification of blood plasma from toxins) may be required.
After drug treatment, special attention should be paid to the patient’s rehabilitation:
- Compliance with the work and rest regime.
- Normalization of sleep.
- Maintaining a diet if necessary (for obesity, diabetes).
- Dosed physical activity.
- Spa treatment.
Encephalopathy is very insidious, since the initial manifestations of the disease are very nonspecific and can be regarded by a person as chronic fatigue. In addition, it is sometimes very difficult to determine which factor leads to brain damage.
Encephalopathy often develops as a result of several causes affecting the body at once. This means that the boundaries of each type of encephalopathy are very blurred. That is why in the treatment of this condition it is justified to prescribe several groups of drugs with different mechanisms of action.
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://mir.ismu.baikal.ru/src/downloads/2581419b_uchebnoe_posobie_distsirkulyatornaya_entsefalopatiya.pdf 2. https://dep_ninh.pnzgu.ru/files/dep_ninh.pnzgu.ru/hronicheskaya_nedostatochnost_mozgovogo_krovoobrascheniya.pdf
Rate, How helpful was the article?
4.2 25 people voted, average rating 4.2
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Clinical guidelines for the treatment of toxic encephalopathy
The basic principles of disease treatment are as follows:
- restoration and maintenance of the full functioning of internal organs and systems;
- stopping further entry of the neurotoxin into the body (limiting work activity, giving up alcohol and/or drugs, etc.);
- speeding up metabolism to eliminate poison as quickly as possible, using specific antidotes;
- symptomatic treatment.
In the acute period, therapy is carried out strictly in a hospital setting under round-the-clock medical supervision. As the patient’s well-being improves, the patient is transferred to an outpatient regimen. For a long course the following is prescribed:
- nootropic drugs;
- drugs that improve metabolic processes in the brain;
- neuropeptides;
- antioxidants;
- means for normalizing the tone of cerebral vessels;
- vitamins and dietary supplements (group B, nicotinamide, riboxin, succinic, ascorbic acid, glycine, etc.);
- if necessary, tranquilizers from the group of benzodiazepines, antidepressants, sleeping pills.
Symptoms of toxic encephalopathy are a mandatory indication for contacting a neurologist. No treatment with folk remedies - only comprehensive, individually selected therapy in combination with physical procedures, dietary correction, and lifestyle changes. Don't hesitate to start therapy! To make an appointment or call a specialized specialist at home, call us 24/7 at 8(969)060-93-93.
Stages of encephalopathy
The disease has three degrees of severity:
- The first one . There are no external signs, but instrumental diagnostics demonstrate diffuse changes in the brain tissue.
- Second . Brain activity is impaired, but symptoms occur only occasionally.
- Third . Negative symptoms are pronounced. There is a high risk of disability for the patient.
A disease detected at the first stage is more treatable.