Cerebral encephalopathy in adults is a rather complex disease. Treatment of encephalopathy involves the simultaneous use of several methods of restorative medicine.
Brain Clinic specialists have extensive experience in treating cerebral encephalopathy in adults of various origins, and will be able to correctly and safely restore its functioning without any side or negative effects on the body.
Call and make an appointment! Our treatment helps even with the most severe cases, when other treatments did not help!
| Initial consultation and examination 2,500 | Therapeutic and restorative neurometabolic therapy from 5000 |
Treatment of encephalopathy
Treatment of encephalopathy is based on treating the underlying disease that led to brain damage, as well as eliminating its symptoms.
Typically, drugs are used that prevent the development of seizures, improve blood supply to the brain and reduce intracranial pressure.
Among the newest treatment methods:
- Intradermal administration of vascular drugs that have a long period of action. They reduce dizziness and headaches.
- Electroneurostimulation “Cefaly” is stimulation of deep brain structures using electromagnetic impulses. This method allows you to relieve the patient from depression and anxiety, and effectively treats chronic and acute headaches.
- Carboxytherapy - a small amount of carbon dioxide is injected subcutaneously, which leads to dilation of blood vessels at the injection site, which can significantly improve blood circulation, reduce pain in the neck and back of the head, relaxes the back muscles, and reduces tinnitus.
- Botulinum therapy with Botox and Dysport helps to effectively treat various types of headaches.
Additional methods in the treatment of this disease are: breathing exercises, reflexology and physiotherapy.
Diagnostic criteria
First of all, a symptomatic diagnosis is carried out, in which the doctor must collect a complete medical history and determine the development of the main symptoms and the presence of somatic pathologies. It is also necessary to conduct a physical examination, which consists of measuring blood pressure, counting the pulse, and listening to heart sounds. Neurological tests are necessary.
To identify cerebral circulatory deficiency, a screening examination is performed. This diagnostic method should include activities such as:
- listening to the carotid arteries;
- neuropsychological testing;
- neuroimaging;
- Ultrasound examination of the central arteries of the head.
According to doctors, it is believed that cerebral circulatory deficiency is diagnosed in 80% of patients with stenotic lesions of the main cephalic arteries.
To establish the reason why vascular encephalopathy develops, laboratory tests are carried out. Patients must undergo a clinical blood test, blood biochemistry, coagulation test and blood glucose level.
To determine areas of pathology in the brain, examinations such as electroencephalography, MRI, etc. are performed. It is also possible to conduct auxiliary examination methods: ultrasound and electrocardiography, which determine the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Our specialists
Tarasova Svetlana Vitalievna
Expert No. 1 in the treatment of headaches and migraines. Head of the Center for the Treatment of Pain and Multiple Sclerosis.
Somnologist.
Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Doctor of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.Derevianko Leonid Sergeevich
Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Vertebrologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 23 years.
Palagin Maxim Anatolievich
The doctor is a neurologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 6 years.
Romanova Tatyana Alexandrovna
Pediatric neurologist. Experience: 24 years.
Temina Lyudmila Borisovna
Pediatric neurologist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 46 years.
Zhuravleva Nadezhda Vladimirovna
Head of the center for diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Experience: 16 years.
Mizonov Sergey Vladimirovich
The doctor is a neurologist. Chiropractor. Osteopath. Physiotherapist. Experience: 8 years.
Bezgina Elena Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 24 years.
Drozdova Lyubov Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist. Vertebroneurologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 17 years.
Development mechanism
With external hydrocephalus, cerebrospinal fluid accumulates outside the cerebral hemispheres, in the subarachnoid spaces. Excessive amounts of cerebrospinal fluid compress the cerebral cortex. External non-occlusive hydrocephalus of the brain occurs as a result of hypersecretion or malabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid.
Internal hydrocephalus can be congenital or acquired. Congenital hydrocephalus develops during intrauterine exposure to the fetus, acquired hydrocephalus develops during life. Mixed hydrocephalus is a separate form of the disease in which cerebrospinal fluid accumulates both in the ventricles and under the meninges.
Read also
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is a type of acute cerebrovascular accident, which is characterized by the effusion of blood into the brain with the development of neurological deficit, often leading...
Read more
Swelling of the legs
Causes of Swelling in the Legs The legs are common sites for swelling due to the effect of gravity on the fluids in the human body. However, fluid retention is not the only cause of leg swelling. Injuries...
More details
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, which manifests itself in the form of various clinical symptoms. This disease is diagnosed at different times...
More details
Chronic cerebral ischemia
One of the most common diagnoses at an appointment with a neurologist for patients in the older age group is chronic cerebral circulatory failure, discirculatory encephalopathy. According to…
More details
Atherosclerosis
What is atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries caused by the formation of plaque. As a person gets older, fat and cholesterol can accumulate in the arteries and form plaque. Accumulation…
More details
Encephalopathy of the brain in adults
General information about cerebral encephalopathy
The set of symptoms that occur as a result of the death of neurons in the brain is called encephalopathy. This happens due to poisoning, cessation of blood flow or lack of oxygen, which arise due to the presence of a pathological condition or various diseases.
Encephalopathy is divided into types depending on the period in which it arose.
It can be either congenital, resulting from the death of brain cells in the fetus due to a violation of intrauterine development, or acquired, resulting from the influence of various diseases and other pathologies acquired after birth.
Congenital encephalopathy of the brain
The appearance of congenital encephalopathy occurs due to various malformations of the central nervous system, as well as changes in metabolic processes due to genetic failures. In addition, congenital encephalopathy can begin if the child is exposed to a variety of injuries, such as birth injuries to the brain or hypoxia.
The acquisition of encephalopathy after birth occurs due to the impact of a number of damaging factors on the brain. Most often, encephalopathy develops at a fairly low speed, but sometimes it can appear suddenly, for example, with the malignant progression of hypertension or severe kidney damage.
Encephalopathy together with chronic ischemia are among the most common vascular diseases of the human brain. Because of these diseases, brain stroke most often occurs. As a result, a huge number of people die and become disabled every year. Due to encephalopathy, the quality of life suffers greatly and the body’s performance decreases. We can conclude that prevention together with treatment are one of the primary tasks of medicine and are of great importance.
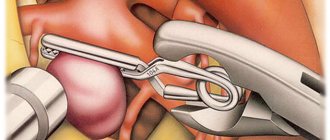
The need for surgery
When the lumen of the vessels is significantly narrowed, angioencephalopathy of the brain continues to progress, surgery is recommended. There are two ways to improve blood circulation with this diagnosis: stenting or bypass surgery. In the first case, the walls of the vessels are expanded and strengthened, and in the second, the diseased vessel is replaced with an artificial one. The decision about which type of surgery to use is made by the doctor. At the same time, it takes into account the severity of the disease and the presence of concomitant health problems.
Stages
Based on the severity of symptoms, DEP is divided into three stages:
- In the first case, mild cognitive impairment is noticeable, the neurological status is not changed. Most patients at this stage subjectively assess the manifestations of the disease, their quality of life remains virtually unchanged. The patient may complain of general weakness, fatigue, dizziness, insomnia, decreased performance, become tearful and irritable, and develop depression.
- At the second stage, obvious cognitive and motor disorders appear; the emotional sphere suffers the most. A person may hear and see worse, memory lapses and incoordination of movements appear. Gradually, the patient’s personality deteriorates, and the level of irritability and anxiety increases.
- The third stage is considered vascular dementia, it can have varying degrees of severity, mental and motor disorders occur. A person cannot live a full life and needs care. In the last stage, dementia often develops.
The symptoms are stronger the older the person is at the time the disease is diagnosed. In addition, its course depends on the general state of health and the presence of other diseases.
Symptoms and severity
According to clinical manifestations, external hydrocephalus in an adult is divided into 3 degrees: mild, moderate and severe. With mild hydrocephalus, the body can independently restore the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Neurologists distinguish the following types of hydrocephalus:
- open external hydrocephalus in adults;
- closed hydrocephalus;
- replacement (non-occlusive) hydrocephalus of the brain in an adult;
- moderate (mild) hydrocephalus of the brain in adults;
- hypotrophic hydrocephalus;
- hypersecretory hydrocephalus.
Severe external hydrocephalus of the brain is accompanied by destruction of brain tissue, which becomes unable to absorb cerebrospinal fluid, the production of which is not impaired. Closed hydrocephalus is characterized by blockage or difficulty in the movement of cerebrospinal fluid and its accumulation in the brain tissue. Obstacles blocking the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid include neoplasms, hematomas, blood clots, and adhesions caused by inflammatory processes.
The patient complains of slight malaise, headache, dizziness, and short-term darkening of the eyes. The average degree of hydrocephalus is manifested by intense signs of brain damage. Patients experience the following symptoms:
- Severe pain in the head, aggravated by physical activity;
- Pressing pain in the eyeballs, the appearance of colored circles of flashes when closing the eyes;
- Feeling of heaviness in the skull;
- Nausea independent of food intake;
- Vomiting without relief.
Sweating occurs periodically. An ophthalmological examination reveals swelling of the optic nerve head. Patients note swelling of the face, weakness, lethargy, and increased fatigue.
External hydrocephalus of the brain in an adult is accompanied by neurological symptoms:
- Decreased visual acuity;
- Strabismus;
- Impaired visual perception: double vision, blurred images;
- Paralysis or paresis of the limbs;
- Numbness of the face;
- Decreased sensitivity;
- Impaired coordination.
Patients have speech impairment, difficulty pronouncing sounds and perceiving spoken speech. With severe external hydrocephalus, epileptic and convulsive seizures, frequent fainting, and coma occur. The patient loses memory, intellectual abilities, and his self-care skills decrease.
The clinical picture of chronic hydrocephalus consists of three pathognomonic symptoms: dementia, gait disturbance and urinary incontinence. Dementia is manifested by a decrease in the level of wakefulness, rapid exhaustion of the patient, disorientation in time, the development of severe intellectual disorders, and decreased criticism. Patients become unsure when walking and develop paresis of both lower extremities. The most recent symptom of hydrocephalus is urinary incontinence. This symptom of the disease is more common in men after 50-60 years of age.
Based on the intensity of the manifestation of hydrocephalus, a distinction is made between a moderate form of the disease, which occurs with minor symptoms, and a severe form - the accumulation of a large volume of cerebrospinal fluid provokes the manifestation of acute neurological symptoms.
External non-occlusive hydrocephalus occurs when the process of cerebrospinal fluid absorption is disrupted. Atrophic (replacement) hydrocephalus develops most often in older people and is accompanied by the death of brain cells.
Prevention methods
Now you know the main causes and symptoms of cerebral angioencephalopathy, what it is. Is it possible to prevent the development of the disease?
First of all, doctors advise undergoing a medical examination once a year to identify pathology at the initial stage. In this case, no specific therapy is prescribed, but constant monitoring by specialized specialists is required.
If you are at risk, you should pay special attention to your own health. You need to establish a sports regime and regularly do exercises for the collar area. The therapist should tell you more about them. Some people benefit from physical therapy sessions. At the same time, one should not forget about proper nutrition. You will need to exclude excessively salty and peppery foods from your diet.
Possible complications
Patients with angioencephalopathy must be prescribed background therapy with antiplatelet medications to stabilize blood pressure. Untimely treatment of vascular pathologies of the brain can lead to complications such as oxygen starvation, disruption of the integrity of blood vessels and hemorrhage. Over time, such patients develop fits of laughter, followed by hysteria. There is a coordination disorder and manifestations of oral automatism. Against the background of damage to the occipital zone of the brain, a decrease in vision and even its complete loss cannot be ruled out.
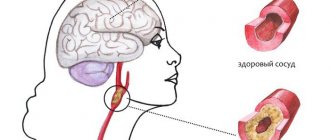
Main reasons
Angioencephalopathy develops in the presence of concomitant pathologies of the vascular system. The disease occurs in people suffering from:
- vascular atherosclerosis;
- hypertension;
- low pressure;
- hormonal imbalances;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- thrombosis;
- increased blood viscosity;
- systemic vasculitis;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- diabetes mellitus;
- kidney pathologies;
- malformations of the cervical spine.
Among all the causes of cerebral angioencephalopathy, atherosclerosis and hypertension are especially worth noting. It is these disorders that in most cases lead to circulatory problems.
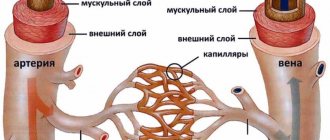
With atherosclerosis, plaques form on the inner walls of blood vessels throughout the body. They reduce the lumen of the bloodstream, and in some cases even completely block it. As a result, the area supplied by this vessel begins to experience a deficiency of useful microelements and oxygen. The medulla shows extreme sensitivity to the lack of these components. Just a few minutes of oxygen deprivation can trigger the death of neurons.
The vessels of the brain have the property of independent regulation of tone. Thanks to it, an increase in blood pressure in the body does not affect the increase in these parameters in the structures of the head. The blood flow remains virtually unchanged. However, long-term progressive hypertension leads to depletion of the compensatory capabilities of blood vessels. As a result, they become sclerotic and lose their tone and elasticity.
Treatment and prevention of hydrocephalus
For patients with mild external hydrocephalus, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe drug therapy. Taking medications that block production and accelerate the release of cerebrospinal fluid can reduce intracranial pressure. For this purpose, patients are prescribed osmotic and loop diuretics (urea, mannitol, furosemide) and sauletics (diacarb). Taking corticosteroids can quickly relieve swelling and inflammation.
Nootropic drugs (vasotropil, cavinton, noofen) and venotonics (actovegin, glivenol) improve brain functioning. Panangin and asparkam restore the concentration of potassium in the blood, which is excreted from the body in large quantities when taking diuretics. For severe headaches, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs that have an analgesic effect (nimesulide, ketorolac, diclofenac) are prescribed.
If drug treatment does not eliminate the signs of external hydrocephalus, the treatment is considered ineffective. In such cases, patients at the Yusupov Hospital are consulted by a neurosurgeon. At a meeting of the expert council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category, a collegial decision is made regarding the advisability of performing surgical intervention.
In the acute form of hydrocephalus and severe symptoms of the disease, conservative therapy is ineffective. The main treatment method in this case is bypass surgery. During surgery, a special system is installed in the brain cavity through which cerebrospinal fluid is drained into the abdominal or thoracic cavity, occipital cistern, atrium or pelvis.
Complications may develop after bypass surgery:
- Hypodrenage;
- Hyperdrainage;
- Breakdown of the shunt system;
- Sepsis.
If complications occur, neurosurgeons replace the shunt. Despite the presence of certain risks of developing negative consequences of shunting, surgery is the only method that can improve the quality of life for patients with hydrocephalus.
Less traumatic are endoscopic operations that are performed in partner clinics:
- Endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy of the floor of the third ventricle;
- Septostomy;
- Ventriculocystocysternostomy;
- Endoscopic removal of tumors inside the ventricles;
- Aqueductoplasty.
The essence of endoscopic operations for hydrocephalus is that the neurosurgeon inserts endoscopic instruments with a miniature video camera into the skull through a miniature hole. The doctor sees the cavity of the ventricles of the brain and monitors the progress of the intervention. The endoscopic method allows you to create an outflow path for cerebrospinal fluid. Most often, neurosurgeons perform ventriculocisternostomy of the floor of the third ventricle. After surgery, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricular system occurs into the cisterns of the brain.
Conservative treatment of external hydrocephalus in adults
In the presence of mild hydrocephalus of the brain in adults, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital provide drug therapy. Patients are prescribed the following medications:
- diuretics;
- plasma replacement solutions;
- barbiturates;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- analgesics.
The rehabilitation clinic provides physiotherapeutic procedures and physical therapy. During treatment, it is important for the patient to adhere to a special diet with low fatty foods.
Neurosurgical operations for hydrocephalus
Neurosurgeons perform palliative interventions in the presence of open hydrocephalus and the impossibility of performing radical surgery for closed hydrocephalus. Doctors perform spinal and ventricular puncture. After taking 100 ml of cerebrospinal fluid, the patient's condition temporarily improves.
Ventriculoperitoneal shunting is a radical neurosurgical operation. Using a valved system, a catheter diverts cerebrospinal fluid into the abdominal cavity, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream. During the Küttner-Wenglovsky operation, a drain is placed through which the cerebrospinal fluid passes from the ventricle of the brain into the subdural space.
In order to reduce the release of cerebrospinal fluid, the choroidal components of the cerebral ventricle are removed during a neurosurgical operation. If there is a speck, they are dissected. Fluid also drains from the posterior wall of the ventricle into the spinal canal.
Prevention of hydrocephalus consists of timely and adequate treatment of the pathologies that cause the disease. For patients with arterial hypertension, cardiologists at the Yusupov Hospital select optimal antihypertensive drugs and adjust drug doses. Patients with infectious diseases of the brain are prescribed the latest generation of antibacterial drugs. When the initial stage of hydrocephalus is detected, regular examination is carried out and computed tomography is performed.
If you have symptoms of external hydrocephalus of the brain, call the Yusupov Hospital. Contact center specialists will offer a time convenient for the patient to consult a neurologist. After a comprehensive examination, the doctor will determine the severity of the disease and prescribe treatment depending on the severity of symptoms, the presence of indications and contraindications for surgical intervention.