Failures in myocardial function leading to heart failure occur at any age. The disorders are accompanied by a different clinical picture, can be asymptomatic for many years, and cause acute pain and mild discomfort in the chest. Often pathological changes in the structures of one of the main organs of the body lead to irreparable consequences. That is why it is important to promptly seek medical support, assess the condition, find out the diagnosis, and take therapeutic measures.
In fact, there is no single disease “heart disease”. This is a general name for a whole group of pathologies, the nature of which is associated with persistent congenital, acquired disorders.
Heart defect is
Defects in the walls, septa, and entire valve apparatus, which negatively affect hemodynamics, clearly characterize and generalize all cardiac defects. Pathologies occur in a chronic form, have a slow course, and can be eliminated through surgery.
The problem is manifested by errors in blood circulation, in which hypoxia of individual organs and tissues is noticeable. Cardiopathy occurs in pediatrics and in adult patients of both sexes; they differ in prognosis, clinical picture and causes.
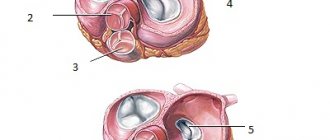
The myocardium has two halves:
- The first starts and controls the small blood circle. Here the blood from the veins is filled with oxygen particles.
- The second deals with a large circle, nutrition of the whole body.
The central septum is a barrier, so that blood from the veins and arteries does not mix. The heart muscle has 2 ventricles, a pair of atria, and a unique valve system. Together, all these elements are responsible for orderly blood movement in a single direction. Just one defect and the device fails. Unpleasant symptoms develop, oxygen starvation of tissues occurs, and a diagnosis of “heart disease” is made.
Causes
To determine the fact that influenced the formation of damage, it is important not to forget that cardiac pathology can be congenital (CHD) and acquired (APS).
The causes of congenital heart disease are often considered to be:
- Adverse habits of parents, mothers in particular. This is alcohol abuse, drug use, smoking, and addiction to medications.
- Chronic maternal diseases (coagulation disorders, diabetes, systemic connective tissue diseases).
- Mutations of genes, chromosomes.
- Infections during pregnancy, when the fetus is affected by cytomegalovirus, Varicella-Zoster (chickenpox), RNA virus (rubella).
- Ionizing radiation.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions. Poisoning with chemicals, teratogenic medications.
Congenital heart disease is not always diagnosed in childhood. According to statistics, congenital heart disease is found in one baby out of 125.
The causes of PPP are often considered to be:
- Complications of rheumatic disease. The disease can affect valves and other internal structures.
- Infectious lesions leading to endocarditis.
- Atherosclerosis of blood vessels, when the pathological process spreads to the valves.
- Complications of hypertension, ischemia, cardiomyopathy, and other pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Only a doctor can determine the factor that triggered the pathological process. It is pointless to look for a cardiac problem without consultation and diagnostic procedures. The cause of the heart defect will be clear only after collecting anamnesis, assessing the condition, and analyzing research results.
Clinical picture
The symptoms of this pathology are extremely varied. It all depends on what kind of defect occurs, its hemodynamic significance and the presence of other diseases of the cardiovascular system in the patient. However, there are a number of nonspecific signs that may indicate the presence of a defect.
Most often, patients complain of shortness of breath, which occurs during physical exertion. The severity and level of stress that causes it depend on the type of defect and the state of the cardiovascular system. Due to volume overload of the systemic circulation, patients experience swelling of the lower extremities and abdominal wall.
Note! In the case of a defect with blood discharge from right to left, the patient’s skin will have a bluish, cyanotic tint. This is a consequence of hypoxia, which is caused by the mixing of venous and arterial blood.
Since very often heart defects do not have specific symptoms, examining the patient in a hospital setting is important. That is why it is imperative to consult a doctor if you have complaints from the cardiovascular system or if your condition worsens. This way you can identify the problem in the early stages, when it has not yet become the cause of serious organic changes in the myocardium and peripheral organs.
- Heart scintigraphy in Moscow
Classification
There are combined, complex and simple structural cardiac disorders. According to the level of oxygen starvation - white (pale) and blue. According to the classification information of the Association of New York Cardiac Surgeons, there are 4 classes of complexity:
- First . There are no serious anatomical changes in the myocardium; surgical intervention is not recommended.
- Second . The pathology is not advanced, the processes are reversible. Thanks to surgery, 100% recovery is possible. The systems and organs (except the heart muscle) are not damaged against the background of the defect.
- Third . Irreversible cardiac defects are observed. Pathological changes in the body caused by deformities are reversible.
- Fourth . The most dangerous class, often leading to death. All violations are irreversible.
Is surgery necessary for heart defects? What medications should I take and what should I not do? Only the attending physician can give answers to all these questions. There is no point in looking for an answer on the Internet. To cope with the problem and find an exceptionally error-free solution, make an appointment with a qualified cardiologist.
Treatment
When treating heart disease, a regimen of limited physical activity is prescribed. The following are used as drug treatments:
- antihypertensive drugs;
- β-blockers;
- anticoagulants.
Most often, the most effective treatment option for heart disease is surgery. It is aimed at completely eliminating the cause of disturbances in the functioning of the heart. This can be either an organ-preserving operation or prosthetics of the affected anatomical structure.
How to determine a heart defect?
Based on my own feelings, having familiarized myself with the relevant literature, it is impossible to accurately establish that there is myocardial damage. The diagnosis is made by a competent physician. Only a specialist with experience and knowledge, using innovative diagnostic techniques, is able to announce the name of the disease, if any.
Symptoms, external signs
The clinical picture is ambiguous for patients of different age categories. For babies who were born relatively recently, the following signs are characteristic:
- cyanosis in the area of the nasolabial triangle;
- low physical activity, retardation of movements;
- low body weight that does not correspond to age.
In adults, symptoms are specific. May concern:
- swelling of the lower extremities and other tissues (especially in the evening);
- angina attacks that occur quite often;
- heavy breathing when lying down;
- sleep disturbances, shortness of breath, pain between the shoulder blades;
- fatigue, dizziness, fainting;
- discomfort under the ribs on the right side (problems with the liver, gall bladder).
Symptoms of heart disease may be specific, reflecting a specific pathology:
- when the skin on the face is pale and the blush is pronounced, mitral stenosis is suspected;
- with false athleticism, when the muscle tissue of the lower body is not physically developed enough, a narrowing of the aorta is possible;
- protrusion of the sternum is characteristic of cardiac pathology of the septum.
You won’t be able to simply read the list of signs and determine the type of myocardial disease. Many of the above-mentioned points are also suitable for describing other diseases and malfunctions in the body. Therefore, it is not advisable to try to make predictions on your own.
Diagnostics in the clinic
There is a basic set of manipulations recommended for suspected simple, complex, or combined heart disease:
- at the first stage of communication, an anamnesis is collected, complaints are clarified, the age, gender of the applicant, and the presence of chronic problems are taken into account;
- a visual inspection, palpation, and listening to rhythms are performed;
- X-ray of the sternum, electrocardiogram, ultrasound.
Only a doctor has the right to make a diagnosis based on a survey, test results, and ultrasound examination. No decoding of analyzes on the Internet will give 100% accuracy results. Contact doctors at a successful medical center so as not to experiment with your own health.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is established on the basis of complaints and objective examination data. During the examination, the doctor may pay attention to a lagging pulse in one of the arms, the presence of pathological noises when listening to the heart, and the presence of chest deformities. To confirm this disease, a number of instrumental studies are carried out:
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- ECG and echocardiography of the heart;
- X-ray examination;
- MSCT and MRI of the heart;
- phonography.
When diagnosing congenital heart defects, examination of a pregnant woman is of great importance. To do this, they also resort to ultrasound and invasive prenatal diagnostic methods, such as amniocentesis. If a defect is suspected, the child is immediately transferred to a specialized department after birth.
Congenital heart defects
CHD is formed due to abnormal development, abnormal growth of the myocardium during fetal maturation (approximately 3-8 weeks of pregnancy). The reasons are varied, ranging from external negative factors to hereditary predisposition. Sometimes congenital heart disease develops in the first 60 days of a child’s life, when erroneous changes occur during the restructuring of blood circulation. The baby's vascular system is not capable of independent functioning.
Modern medicine has about 35 varieties, including:
- Atrial septal defect (ASD).
- Ventricular septal defect (VSD).
- Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA).
- Coarctation of the aorta (CA) and others.
When a congenital heart defect is diagnosed, treatment is attempted taking into account the age characteristics of the patient.
Acquired heart pathologies
PPS are formed during human life. Usually these are valvular disorders. Common defects include narrowing and incomplete closure of the aortic, mitral, tricuspid, and pulmonary valves. More than 75% of all cases are aortic lesions.
Cardiopathy can develop due to various circumstances:
- systematic overload of the heart chambers;
- complications of rheumatism, certain infectious lesions, for example, endocarditis;
- mechanical injuries;
- changes of atherosclerotic type, etc.
It is important to detect the problem in a timely manner. Acquired heart defects in the initial stages of development, class 1 and 2 disorders are easily treated. The main thing is to find a good cardiologist.
Therapy Options for Adults
Congenital heart defects continue to be treated not only in childhood, but also in adulthood. The tactics are chosen by the doctor depending on the patient’s condition.
“If complications occur, the main treatment method is cardiac surgery. If symptoms of heart failure develop and surgical treatment is impossible, drug therapy is prescribed,” says Dmitry Karpenko. And here it is important to understand that you cannot self-medicate, just as you cannot independently adjust the therapy prescribed by a doctor. This can lead to serious consequences.
Related news
A cardiologist tells how to reduce high blood pressure in hot weather
What is the difference between VPS and PPS
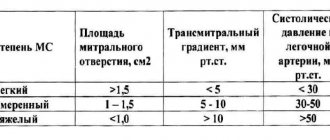
Cardiopathy acquired at one of the life stages and congenital cardiopathy have significant differences. And the difference concerns not only the nature of the formation of defects. Here it is important to pay attention to the nuances, signs of pathology, and the mechanics of disorders. It is best to evaluate the difference between the two options by looking at the table.
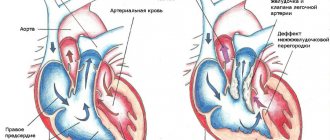
| Variety | Name | Clinic (picture) | Failure of blood movement, that is, hemodynamics |
| Without bluing of the integument (VPS) | Damage to the partitions between the ventricles and atria. | Systolic murmur in the left side of the chest, protrusion of the anterior wall. | Blood is dumped from left to right. Reflex arterial spasm leads to an increase in pulmonary pressure. The left ventricle is overloaded. |
| PDA when the duct is not closed. | A systolic-diastolic murmur is heard in the left side of the chest. | In the small circle, blood flow increases. The left side parts are overloaded. Discharge occurs from the aorta to the pulmonary artery. | |
| Stenosis (heart disease). Narrowing of the lumen of the pulmonary artery. | There is a rough systolic murmur over the PA valve. | The right ventricle receives a high load, the pulmonary blood flow is pooled. | |
| Narrowing of the lumen – coarctation. | High blood pressure, murmurs along the left thoracic border. | The left ventricle receives a high load; insufficient lumen interferes with normal blood flow. | |
| With blue discoloration (VPS) | TMS – vascular transposition. | Hypoxia, quite pronounced. | The nutrition of the organs is disrupted. |
| One ventricle. | Systolic murmurs at the top, hypoxia. | Venous and arterial blood mix, the speed of its movement increases. | |
| Fallot | This is a notebook | Blood is dumped from right to left | |
| Mitral valve related PPS | Failure. | Systolic murmur at the apex. | Reverse blood flow into the atrium on the left side. |
| Stenosis. | Diastolic murmur at the apex. | The atrium on the left side is overloaded, dilated, hypertrophied. | |
| AVR (aortic heart disease) | Valve insufficiency. | The carotid arteries pulsate noticeably. Blood pressure is increased (pulse). | The left ventricle is distended due to backflow. |
| Narrowing of AK. | Fainting, pain similar to angina pectoris. | The release of blood into the aorta is impaired. | |
| PKLA | PA valve insufficiency. | On the valve, tone II is weakened. | When moving, the blood is again thrown into the ventricle on the right. |
| LA narrowing. | The ventricle on the right side is noticeably pulsating. | Release into the pulmonary artery is difficult. | |
| Tricuspid valve injuries | Failure. | There is a systolic murmur. | Rejection of blood into the right atrium. |
| Stenosis. | Tone I is strengthened. | The right atrium becomes overloaded and expands. Hypertrophy is observed. |
Treatment of heart defects
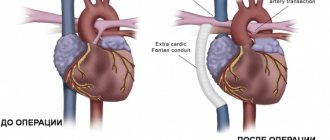
It is impossible to completely get rid of complex cardiac defects using pharmaceutical products. At the moment, there is no drug that eliminates defects. Mild forms of pathology, including congenital ones, are eliminated through surgery. An exception to the rule is considered to be arterial heart disease, which is treated pharmacologically in the first day after birth. Therapy involves the use of anti-inflammatory drugs.
When cyanosis is visible, intervention is carried out promptly in the surgery department. The event can be postponed only if there are no obvious symptoms, the patient does not complain, and the cardiac disease was discovered by chance during instrumental diagnostics. During the procedure, anesthesia is administered. The defect in the open organ is removed by connecting the circulatory system to artificial equipment. The violation is subject to incomplete suturing, sometimes closing with a special patch made of pericardium.
Modern cardiology centers not only in Russia offer special minimally invasive procedures. The intervention is carried out under the control of ultrasound scanning and x-rays. A miniature catheter is inserted into the cavity of the femoral vein and passed to the right atrium. An occluder is inserted here, which should become a closing element. It is made from nickel-titanium wire. Only a cardiologist who has diagnosed heart defects and collected the patient’s medical history can decide what therapy is needed in a particular case with congenital heart disease.
With teaching staff, things are slightly different. Here it is necessary to determine and control the accuracy of information about the causes of the development of the disorder. Therapeutic protocols often include:
- diuretics and ACE inhibitors;
- aldosterone antagonists and beta-blockers;
- antiarrhythmic drugs to stabilize pulsation.
Antibiotics are appropriate in the presence of an infectious agent, for example, when there is rheumatism and heart disease is a consequence. A penicillin series that suppresses streptococci is recommended.
Severe types of PS are corrected through operations. Prosthetics and organ reconstruction are relevant. The second option is valvotomy, plastic surgery, commissurotomy. Valve prostheses are either artificial or biological. There is a difference. When a mechanical element is installed, anticoagulants are prescribed not for a while, but for life. Patients with a biological replacement option should take therapy with drugs that inhibit the process of blood clotting for 70-100 days (during the recovery period). The type of suitable valve device is selected individually. It is noteworthy that mechanical models are more durable than biological ones.
5.2. Peculiarities of parental attitude towards children who have undergone surgery for congenital heart disease under the age of 3 years
Congenital heart defects (CHD) are serious diseases that entail serious impairments in physical and, in some cases, mental development. CHD is a group of diseases united by the abnormal position and morphological structure of the heart and large vessels. The latter arise as a result of disruption or incompleteness of their prenatal development. With many congenital heart disease, pathological hemodynamic conditions arise, sometimes so severe that they threaten the very life of the patient. Statistics show that about 40% of children with severe defects die before the age of 5 without surgical intervention. The average life expectancy of non-operated patients is 30-40 years with disability.
A child is usually diagnosed with congenital heart disease immediately after birth or in infancy. Of the two types of defects (blue and white), the most severe are the blue type defects, in which more pronounced disturbances of hemodynamics and gas exchange, and arterial hypoxia are observed. These defects are often accompanied by a lag in physical and mental development (Kovalev V.V., 1974).
The current level of development of cardiac surgery makes it possible to successfully correct congenital heart disease surgically. The subsequent development of the child is largely determined by the influence of two biological factors: a) persistent hemodynamic disturbances resulting from organic compensation of the defect and not correctable even after surgery; b) the biological hazards of the operation itself, performed under conditions of artificial circulation, deep hypothermia (although such surgical technology has sharply increased the effectiveness of treatment of congenital heart disease).
The development of children who have undergone surgery for congenital heart disease at an early age is currently the subject of many works both in our country (mainly psychiatric) and abroad. A significant part of them is devoted to assessing the development of intelligence in children. A number of researchers, studying the level of mental development of children 3-7 years after surgery (Barret-Boyes, Neutre, Clarkson et al, 1976; Satanieni, 1979), showed that their level of development does not differ from the level of healthy children (Egerton, Kay, 1964 ; Sanderland, Matarasso etal, 1973; Whitman, Drotar etal, 1973; Silbert, Kenneth, 1977 and others). It has also been shown that neuropsychiatric complications after surgery correlate with the surgical method used (Wada, Jakawashi, Matsui, 1982).
Domestic studies also indicate that a decrease in the level of mental development does not occur after surgery (Ilyin, Wenger, 1979; Amosov, Bendet, Morozov, 1980; Morozov, 1978, 1980) if it is performed at an early age. However, children operated on after 8 years of age exhibit a number of personality characteristics that are more likely associated with a defective parenting style (Amosov et al., 1980). Many works are devoted to the analysis of the influence of the type of defect on the mental development of the child and the problem of choosing the optimal age for surgery (Litasova, Valykov et al., 1983).
The problem of social adaptation of children who underwent surgery at different ages is specially discussed in the literature (Bendet, Morozov, Skumin, 1980; Morozov, 1980; Baer, Freedman 1984; Tolpykin, 1985). According to the authors, the basis for maladjustment in children is often the behavior of parents, who, even after surgery, continue to treat their children as sick. It is the special living conditions (gentle regime at school, overprotection, parental fear, etc.) that lead to the formation of such characteristics as irritability, emotional instability, infantilism, which become especially noticeable in adolescence (Kremneva, 1975; Litasova, Valykov, 1983 ). The authors pay special attention to the immaturity of the emotional-volitional sphere in combination with a high level of intellectual development. Considering the combination of features of a primary and secondary defect in children with congenital heart disease, researchers (Kovalev, 1974) point to the possibility of the latter appearing due to the assessment by others of the children’s disease as “more severe.” However, the dynamics and patterns of formation of such deficiency remain a research problem until recently (Lebedinsky V.V., 1985).
Based on a comparison of literary data and some general psychological principles, it is possible to outline the range of problems that arise when studying the characteristics of the mental development of adolescents who have undergone surgery to eliminate congenital heart disease in early childhood.
The condition of adolescents who underwent surgery for congenital heart disease in childhood, their mental development and personal characteristics are insufficiently studied issues. Solving them is extremely necessary, since curing a child from such a serious somatic illness does not mean eliminating the secondary one - a social defect, changing the attitude of the people around him towards the child. Consequently, even without being chronically ill (especially if the defect is not accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the somatic condition and if its elimination is carried out in early childhood), a child can become a “social chronicler”. Thus, it is the study of a secondary social defect, and then its neutralization, that are the most important tasks of a psychologist when working with children and adolescents who have had severe somatic illnesses, and in particular, congenital heart defects.
The features of mental development and personality formation of adolescents during the elimination of congenital heart disease in early childhood are determined, as mentioned above, by the interaction and mutual influence of three types of harm: 1) the harm of the defect, 2) the harm of the operation, 3) the harm of the distorted social situation of development. For example, mental development disorders that arose due to the harmful effects of a defect and surgery can, presumably, be fully compensated due to optimal upbringing. And, conversely, with a successful outcome of the operation, complete recovery, due to overprotection and improper parenting style, manifestations of social maladjustment and mental development disorders are possible. This moment can manifest itself especially clearly in adolescence. At the same time, the question arises about the possibility and necessity of diluting the influence of the three named harmful factors.
Experiencing illness – previous | next – Development situation
Personality features in borderline disorders and somatic diseases
Consultation with a psychologist for family problems
Consequences of pathology
It all depends on the form and well-formed medical prescriptions. If you detect the danger in a timely manner, contact a medical professional, undergo a thorough examination, and determine the pathology, you can significantly improve your quality of life. Mild types of lesions are usually not fatal. By taking medications, you can feel quite healthy, be careful, but engage in various types of activities.
It is convenient to obtain accurate information on a specific case from the treating cardiologist-specialist. The doctor will analyze the existing features and give a prognosis and tell you about the possible consequences.
Prevention
A healthy lifestyle is the main option for preventing rheumatic heart disease and other types of cardiac defects. Thanks to proper nutrition, an even distribution of physical activity, and the absence of stress, you can strengthen the immune system and increase the regenerative capabilities of the body, especially in the case of traumatic injuries. Cardiologists advise:
- Eat only healthy food, do not forget about vitamins, important microelements, add more fresh fruits, vegetables, low-fat fish and herbs (dill, cilantro, parsley, onions, lettuce) to your diet.
- Monitor your blood pressure, constantly use a tonometer, and if your condition worsens, take medications prescribed by your cardiologist.
- Avoid depressive disorders and stressful situations. It is important to create coziness and comfort around you from a psychological point of view, not to get nervous about little things, to devote more time to hobbies, to communicate with pleasant people and friends.
- Monitor your health and well-being, monitor the activity of organs and systems of the body, monitor the behavior of the thyroid gland, liver, and symptoms characteristic of these organs.
Prevention of the development of major heart defects, which are considered congenital, depends on the future parents. During the planning period, during conception, in the first trimester of pregnancy, it is important that the expectant mother:
- I gave up bad habits, smoking, drinking alcohol, and taking drugs.
- She was examined for infections, or more precisely for herpes and cytomegalovirus.
- I did not get vaccinated during pregnancy, but took care of the prevention of rubella, chicken pox, measles, polio and mumps in advance.
It is strictly forbidden to take medications that can harm the fetus. If you use tablets, drops, syrups, sprays, check whether you can continue to do this when planning a child or becoming pregnant.
FAQ
There are a huge number of questions that users most often ask on the Internet. The answers should be reviewed in detail in order to collect useful information in one place and publish explanations for people interested in myocardial defects.
How long do people live with heart disease?
It all depends on the disease, its course, and the age of the patient. You can live up to 100 years. The fact is that mild forms of defects do not interfere with blood flow. Pathological changes in blood vessels and other organs do not occur. Therefore, with the first class of disorders, you can live happily and long without any special signs of a cardiac problem.
Severe stages of cardiac defects can lead to death. It is problematic to say exactly how long a person is destined to live. Too many factors have a direct influence on the formation of this information. It is better to ask your doctor how long people with a similar diagnosis live with heart disease.
Is it possible to play sports with a heart defect?
It is not prohibited to engage in sports training or practice sets of exercises if physical activity does not disrupt the functioning of the myocardium. Without fanaticism, it is permissible to do exercises, get involved in yoga, and other simple practices. Each case of cardiac disease is individual, therefore, advice from a doctor is needed. The doctor will assess the condition, take into account the nuances, and tell you what can and cannot be done.
Typically, people with heart valve disease lead a sedate lifestyle, engage in equestrian sports, that is, horse riding, swimming, water aerobics, and figure skating. Classes should not be aimed at professionals. There is no talk of participating in competitions.
Fly on a plane?
Not all cardiovascular diseases allow you to decide to fly. For example, after a heart attack, access to airplanes is closed for 6 months. With vices, things are not so categorical. Patients with mild forms are allowed to use air transport. But at the same time, it is important to take the medications prescribed by the cardiologist in a timely manner, monitor your own condition, evaluate your sensations, and take immediate action if they worsen.
Before flying, consult with your attending cardiologist. A specialist will assess the situation and tell you what is the best course of action, whether it is worth choosing air transportation, whether there are risks or health hazards.
Drive?
Driving vehicles with mitral heart disease and other types of pathology is possible if the patient does not complain of severe symptoms and does not lose consciousness while driving. Professional drivers driving taxis, cargo, public, and special vehicles must periodically undergo a comprehensive and thorough examination. In some situations, the commission is able to prohibit driving a vehicle if there is a risk of an emergency on the road.
Drink alcohol or energy drinks?
Doctors advise not only people suffering from congenital and acquired heart pathologies to give up alcohol-containing drinks and energy drinks. Alcohol and substances from energy drinks enter the bloodstream, increasing blood pressure and contraction frequency, at least up to 130 beats per minute. There is a violation of metabolic processes and organ nutrition. Therefore, even small doses are contraindicated for men, women and children with diseases of the cardiovascular system accompanied by insufficiency.
Please note that, by and large, the causes of acquired heart defects do not play a role, that is, chronic heart patients should not drink the above-mentioned products under any circumstances.
Go to the bathhouse or sauna?
Baths and saunas are associated with healing the body, but not everyone benefits from such hot events. At elevated ambient temperatures, blood vessels dilate, blood flow accelerates, pulse and blood pressure increase. This is useful for a healthy person, but for a heart patient it can turn into a real disaster. It is not recommended to go to the bathhouse and sauna with cardio defects of classes 2, 3 and 4. Hot air overloads the heart muscle, which can lead to malnutrition of the organ.
Steam rooms are acceptable for patients with first class lesions. It is important to prepare your body for the change in temperature in advance, that is, take a warm shower. Don't delay your visit. Limit yourself to 5-10 minutes.
Are people with heart defects allowed into the army?
The decision of the military commissariat commission depends on numerous factors. The presence/absence of insufficiency, the degree of blood outflow, well-being, and medical history are taken into account. Sometimes heart problems are not considered contraindications for service in units where there is no great physical activity. Certain categories of persons with complications of heart disease, pathology that belongs to the third and fourth class, can receive exemption. Guys with congenital defects of myocardial valves and interatrial septum are not accepted into the army. They are usually kept in reserve, meaning they can easily be mobilized in the event of war.
| To the list of articles | Infective endocarditis |
Basic definitions
Heart disease is a congenital or acquired morphological change in the valve apparatus, partitions between the departments and large vessels extending from them. There are many types of such pathologies. The underlying causative factors are also different for each group.
The development mechanism for congenital and acquired defects is similar. It is based on the inability of the myocardium to provide adequate blood flow due to anatomical defects. The result of such processes is a reflex expansion of the cavities of the heart. The consequence of increased physical activity is an increase in the muscle layer of the chambers and blood vessels - hypertrophy.
In the later stages of the defect, signs of disturbances in the systemic and pulmonary circulation appear with the development of chronic heart failure. Pulmonary hypertension develops. Its development indicates a severe course of the disease and determines how long people live with heart disease.
1 What is heart disease
- Heart defects: classification, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
The term “heart disease” refers to any pathologies that represent anatomical disorders of the structures of valves, septa, heart muscle, and large vessels. With such pathologies, the heart cannot cope with its functions, the organs experience oxygen starvation, which exposes them to serious danger. There are two main types of heart defects – congenital and acquired.
We recommend
Cardiac stenting – how long do patients live after surgery?