Home → Information about diseases → Hydrocephalus (hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome of HHS)
Absolutely all people have a small amount of fluid in the cranial cavity that washes the brain. This liquid is called “liquor”. Liquor is constantly produced and absorbed (renewed). If a person produces more cerebrospinal fluid than is absorbed, it begins to accumulate in the cranial cavity, and intracranial pressure increases. Excess fluid begins to put pressure on the brain, causing various disruptions to its functioning. This is called hydrocephalus (increased intracranial pressure, hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome or “dropsy of the brain”).
Manifestations of hydrocephalic syndrome in newborns:
As a result of disturbances in liquorodynamics and changes in pressure inside the skull, the discomfort of the nervous system in a newborn child increases. In accordance with this, disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system occur, which can be general or local in nature:
- The child is restless and has difficulty sleeping
- Baby sucks poorly
- Frequent, profuse regurgitation
- Impaired muscle tone
- Decreased innate reflexes
- Possible manifestations of trembling and tremor of the limbs and chin
- Increase in head size
- The opening of the sutures of the skull is more than 0.5 cm, tension of the fontanelles
- Graefe's sign, setting sun sign, convergent strabismus and intermittent horizontal nystagmus
- When examining the fundus, swelling of the optic discs may be observed.
Clinical manifestations of HGS in children
In children, manifestations of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome may include headache, frequent nausea and vomiting. In this case, the headache is often aching, dull, and can be compared to a feeling of fullness and pressure. Sometimes children complain that it is difficult for them to raise their eyes or tilt their heads.
Manifestations of HGS in children also include hyperactivity, decreased concentration and attention, and poor performance at school.
Anatomy of the central nervous system of newborns
The central nervous system is the main part of the nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, located in the cranial cavity and the spinal canal. The central nervous system is responsible for controlling all vital processes in the body, thinking, speech, coordination, and the functioning of all senses.
The brain consists of the following sections:
- cerebral hemispheres (left and right)
- diencephalon
- midbrain
- bridge
- cerebellum
- medulla
Ultrasound examination of these sections allows us to assess the condition of the gray and white matter of the brain and exclude the presence of congenital pathology in the fetus (hemorrhages, tumors, malformations, cysts, hydrocephalus, dislocations, etc.), as well as possible changes associated with childbirth.
The liquor system consists of:
Internal liquor spaces
- Lateral ventricles of the brain (right and left)
- Third ventricle of the brain
- Fourth ventricle of the brain
External liquor spaces
- Subarachnoid space
- Interhemispheric fissure
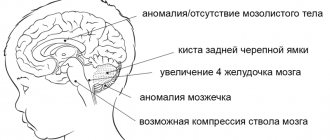
In accordance with this, hydrocephalus can be external - when the size of the interhemispheric fissure increases; internal - with expansion of the lateral ventricles (VLD, VLS), third and fourth ventricles (V3, V4); and mixed.
Each ventricle contains a choroid plexus (Plexus chorioidei). These plexuses play an important role in the production of cerebrospinal fluid - a fluid that circulates in the ventricles of the brain, the subarachnoid space of the brain and spinal cord, and the cerebrospinal fluid ducts. Overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid leads to hydrocephalus and an increase in the size of the cerebrospinal fluid containing spaces.
Normal values for sizes V3, V4, MS, MD, VLS, VLD, m/p gap, bone/marrow diastasis, see below
Osteopath for hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus (“dropsy of the brain”, or hydrocephalic syndrome) occurs as a result of the accumulation of fluid in the cavities of the brain in excess. Hypertension is an increase in blood pressure that occurs due to fluid pressure on the brain.
Often, hydrocephalic syndrome in children is combined with increased intracranial pressure, resulting in the development of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome .
Hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome is one of the most common brain lesions in the clinic, caused by excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricles of the brain and under its membranes, resulting from obstruction of outflow, excessive formation and impaired reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid. In order to better understand the essence of this process, let's take a closer look at the anatomy (structure) of the brain and the mechanisms of fluid outflow from it. The human brain has several cavities called ventricles (4 large ones), they are connected to each other and filled with a special liquid (cerebrospinal fluid), which is produced by special structures - the choroid plexuses from the blood flowing through the arteries. Then the cerebrospinal fluid is absorbed into the venous vessels, replaced by new fluid. The brain, given its high need for oxygen, needs increased blood supply, therefore, blood flows into it through four large arteries and flows back through the veins. For the proper functioning of the brain, good movement of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricles and between the membranes of the brain, good absorption into the venous network and outflow of blood from the brain through the veins are required.
If there is a disturbance in any part of the cerebrospinal fluid dynamics, the outflow of excess fluid becomes difficult; it accumulates in the ventricles of the brain, expanding them, between the membranes. The veins fill with blood, and in a child of the first year of life, not only the size of the ventricles of the brain increases, but also the size of the head. The large fontanelle increases in size, bulges, pulsates, and the sagittal suture diverges, but this is precisely what helps the child compensate for the excess accumulation of fluid for a long time.
It should be noted that this syndrome can occur both as a result of organic damage to the brain (“mechanical” blockage of the outflow of fluid by a tumor or hematoma), and inorganic damage associated with a decrease in vascular tone, in particular venous tone, which leads to difficulty in the outflow of excess fluid and overflow ventricles of the brain.
Signs
In children older than one year (with closed fontanelles), signs of intracranial hypertension can develop very quickly; they manifest themselves as severe, paroxysmal headaches, often in the morning, with vomiting that does not bring relief. The behavior of children changes, at first they are restless, they are irritated by any external irritant (bright light, loud sound, etc.), then the children become lethargic and inactive. Sometimes there is a fixed position of the head and a pained expression on the face. Congestion and decreased visual acuity are observed in the fundus.
It should be noted that children of any age may experience so-called transient (transient) fluctuations in cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Headache, nausea, dizziness and other symptoms can be a manifestation of a variety of functional disorders of the brain, as well as various tumors (both benign and malignant), abscesses, hematomas, infectious and other diseases. Depending on the causes of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, treatment will be different - from medication, aimed at improving the outflow of fluid, to surgery, eliminating the cause of occlusion (blockage) of the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
Diagnostics
In order to establish the true cause of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive clinical examination of the child.
To clarify the cause of the disease, it is necessary to conduct the following hardware examination:
- echoencephalography (EchoEG) is a method for diagnosing intracranial lesions using ultrasound, has no contraindications, provides high accuracy, and can be used in children almost from birth;
- rheoencephalogram (REG) - examines the venous outflow of brain vessels, performed in children from birth;
- radiography of the skull - more informative for long-term disease, more often used in children over one year of age;
- computed tomography (CT) - allows you to most accurately determine the area of cerebrospinal fluid outflow occlusion, the size of the ventricles, and so on;
- electroencephalography (EEG) - determination of brain activity processes using electrical impulses.
Examinations by such specialists as an ophthalmologist, a neurologist, a psychiatrist (long-term hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome can lead to atrophy of the cerebral cortex and, subsequently, to delayed mental development), and a neurosurgeon are necessary.
Treatment
Treatment, depending on the causes of the disease, can be medicinal (dehydration therapy with diacarb in combination with vascular drugs, massage and physiotherapy) and surgical (removal of a formation that interferes with the outflow of fluid or, if it is impossible to carry out such an operation, bypass surgery of the ventricles of the brain is indicated - inserted a shunt is a special tube) with the help of which cerebrospinal fluid flows from the ventricles of the brain directly into the lower part of the spinal canal.
Let us return to the description of brain damage syndromes, since hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome is rarely isolated, but is often combined with depression or coma syndrome.
The depression syndrome is manifested by lethargy, physical inactivity, decreased spontaneous activity, general muscle hypotonia, suppressed reflexes of newborns, decreased sucking and swallowing reflexes. This syndrome characterizes the course of the acute period of perinatal encephalopathy and usually disappears by the end of the first month of life. But it can be a harbinger of cerebral edema and the development of coma.
Comatose syndrome is a manifestation of an extremely serious condition of a newborn (such children have 1-4 points on the Apgar scale). The clinical picture includes lethargy, adynamia, decreased muscle tone to atony, congenital reflexes are not detected, the pupils are constricted, the reaction to light is insignificant or absent at all, “floating” movements of the eyeballs, and there is no reaction to painful stimuli. Breathing is arrhythmic, with frequent apneas (stops), bradycardia (decrease in heart rate), muffled heart sounds, arrhythmic pulse, low blood pressure, no sucking and swallowing reflexes.
This condition of a newborn requires emergency treatment and is extremely uncertain in terms of the development and health of the child.
The success of treatment depends on early diagnosis and the correct drug regimen.
OSTEOPATHY AND TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION-HYDROCEPHAL SYNDROME
In cases where hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome is clearly expressed, prompt surgical treatment is required.
If you or your child have been diagnosed with this, but the situation is actually far from critical and does not require surgical intervention, and there is only a slight increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, then osteopathy will be very useful. In many cases, we have been able to help patients improve their quality of life, get rid of headaches and poor sleep, by removing obstacles to the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid and normalizing cerebrospinal fluid pressure. For this, osteopathic doctors use special techniques that have been developed and verified over decades to work on the structures of the skull, the membranes of the brain, blood vessels, etc. Thanks to the manipulations of an osteopath, many patients managed to avoid taking medications that are fraught with side effects, and recover in the most natural and safe way.
Osteopathy is also good after surgical treatment or a course of drug therapy. It helps to neutralize possible complications and consolidate a positive result.
Causes of hydrocephalus
The causes of hydrocephalus can be those that were affected during the period of intrauterine development of the child (congenital) and after childbirth (acquired).
Congenital causes include:
- The course of pregnancy with complications
- Difficult birth
- Premature birth
- Late labor
- Brain hypoxia
- Birth injury
- Congenital pathologies of brain development
Acquired causes include:
- Volumetric formations of the brain (abscesses, cysts, hematomas)
- Traumatic damage to the bones of the skull and brain (fractures, indentations, injuries)
- Infectious diseases
- Vascular disorders
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus consists of several stages:
History, follow-up, parent survey
For diagnosis, it is necessary to know the baby’s behavioral characteristics, his problems, and also monitor the growth dynamics of the child’s head circumference in the first months of life. Particular attention should be paid if the size of the head increases by more than 2-3 cm per month, divergence of the seams and bulging of the fontanelles are determined.
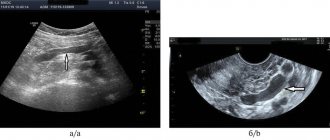
Neurosonography (ultrasound of the brain) of newborns and children
Neurosonography (or ultrasound examination of the brain is carried out in the maternity hospital, at 1st, 3-4 months of life).
Neurosonography (ultrasonography, ultrasound of the brain, NSG) is an ultrasound method for studying the state of the brain. The method is used to identify congenital pathologies that have not previously been diagnosed in the fetus, as well as possible changes associated with childbirth and adaptation to new conditions.
It is optimal to perform NSG for all children in the neonatal period (the first 28 days of life), as well as at the 3-4th month of life. In addition, NSG is performed according to the indications of the attending physician, if indicated, or to assess the dynamics during treatment.
During an ultrasound examination, it is important to establish a correspondence between the results of the study and the proper values of brain structures. Deviation from normal neurosonography values requires the attention of both the doctor and the patient. Therefore, it is important to know what neurosonography describes. To do this, let's briefly look at the anatomy of the brain.
Normal values and interpretation of NSG indicators
V3 – size of the 3rd ventricle of the brain (N 4.8 +/- 1.2 mm)
V4 – size of the fourth ventricle of the brain (up to 8 mm)
MD (MS) – median D (median S) – measurement of the displacement of the median structures (subtract the smaller from the larger value and divide by 2). Normally no more than 2mm. (N < 2 mm)
VLD, VLS – body of the lateral ventricle at the level of the fusion of the choroid plexuses (normally up to 15 mm)
V/r left (right)
M/n fissure – interhemispheric fissure (N < 3-4 mm, can be closed)
Diastasis k/m – diastasis bone-marrow (N < 4 mm)
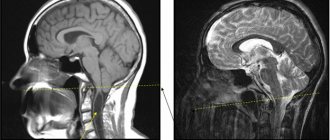
X-ray of the skull, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging
These methods of radiation examination are used in cases of suspected hydrocephalus and allow a more accurate assessment of the condition of the brain and the cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the skull.
Osteopathic diagnosis of hydrocephalus and hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome
When examining a newborn child, a child of the 1st year of life and older children, an experienced osteopathic doctor evaluates the shape of the skull, the condition of the sutures of the skull and fontanel, identifying signs of hypertension. In addition, by assessing the mobility of the bones and membranes of the skull, a pediatric osteopath can notice disturbances in the ventricular system of the brain and determine hypertension in the child.
Complications and prognosis
Complications of hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome are possible at any age:
- delayed mental and physical development;
- blindness;
- deafness;
- coma;
- paralysis;
- bulging fontanel;
- epilepsy;
- urinary and fecal incontinence;
- death.
The prognosis is most favorable for hydrocephalic syndrome in infants. This is because they experience transient increases in blood pressure and cerebrospinal fluid, which stabilize with age.
In older children and adults, the prognosis is relatively favorable and depends on the cause of HGS, the timeliness and adequacy of treatment.
Treatment of hydrocephalus and hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome with osteopathy
The brain is a vital organ and needs protection and proper metabolism. These are the functions performed by cerebrospinal fluid, the fluid that washes the brain and spinal cord. This fluid is produced in the lateral ventricles of the brain for 24 hours, almost continuously.
Due to the fact that cerebrospinal fluid is produced continuously and is renewed 6 times during the day, drug therapy in the form of diuretics does not give the expected effect.
Osteopathic treatment in this situation is most effective. Imagine the cerebrospinal fluid system as a network of communicating vessels. On the one hand, a lot is produced, on the other hand, there are barriers along the way. With the help of osteopathic techniques, it becomes possible to eliminate barriers along the path of cerebrospinal fluid by freeing the membranes of the brain, improve the functioning of the nerve cell and stop the development of the pathological reflex of overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid, which ultimately eliminates the cause of hypotension-hydrocephalic syndrome and normalizes intracranial pressure.
Treatment methods for hydrocephalus
The surgical method of treating hydrocephalus is used only in extreme cases (decompensated forms of internal hydrocephalus), excess fluid is drained from the cranial cavity into the abdominal cavity using a tube (shunt), this operation, like any other, is quite traumatic; in the future, several more surgical operations may be required interventions to replace and check the operation of the shunt.
A medicinal method of treating hydrocephalus - the use of diuretics, such as Diacarb, is often used by neurologists in outpatient practice. Diakarb removes fluid not only from the cranial cavity, but also from the body as a whole, at the same time a loss of microelements occurs, the effect of this treatment method is temporary, after its cessation, the fluid begins to accumulate again and intracranial pressure increases.
Herbal medicine - the use of diuretic herbs (horsetail, fennel, lingonberry leaf), does not cause addiction and loss of microelements. It is used, as a rule, for preventive purposes: to avoid exacerbation of hydrocephalus during colds, when changing climatic zones, in the autumn-spring period with pronounced changes in weather conditions.
Massage is an effective method for children with motor impairments (increased muscle tone, delayed motor development), and is mainly aimed at relaxing tense muscles. It is advisable to use only in complex treatment, since massage does not affect the main cause of the disease - hydrocephalus and hypoxia of the cerebral cortex.
MICROCURRENT REFLEXOTHERAPY - the method is effective in children with various manifestations of hydrocephalus, it allows you to eliminate not only external manifestations (hysterics, developmental delays, etc.), but also treat hydrocephalus itself, that is, it has a complex therapeutic effect on the body. The effect of treatment is stable and does not stop after the end of treatment.
Advantages of treatment at the Neonatus Sanus Osteopathy Clinic
Our clinic of osteopathy and neurology on Vasilyevsky Island “Neonatus Sanus” - health from birth, has extensive practical experience in the prevention and treatment of newborns, infants and infants.
We know how and love to work with young children!
Our clinic employs experienced osteopathic doctors and neurologists. A lot of attention is paid to each child in order to understand the child, accurately assess his condition, give recommendations to parents and, if necessary, carry out effective osteopathic treatment.
In our center you can get the best examination, treatment and recommendations from leading specialists in St. Petersburg.