Hydrocephalus in adults is a pathological condition that is characterized by excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cerebrospinal fluid spaces of the brain. Hydrocephalus can be an independent disease or a consequence of various pathological processes in the brain. Long-term hydrocephalus can lead to disability or death. Effective treatment of hydrocephalus in adults is carried out by neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital.
Causes of hydrocephalus
With this disease, the balance between the formation, circulation and absorption of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted. The causes of hydrocephalus have not been fully elucidated.
Hydrocephalus in a child is usually the result of inherited genetic abnormalities and congenital disorders of the brain and spinal cord. It can also occur after premature birth, during which hemorrhage occurred in the ventricles of the newborn’s brain.
Hydrocephalus of the brain in an adult can have the following causes:
- meningitis;
- brain tumors;
- traumatic brain injury;
- subarachnoid hemorrhage;
- other conditions that impede the release of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles into the cisterns of the brain.
Hydrocephalus of the brain in the elderly
Hydrocephalus in older people occurs when excess fluid accumulates in the brain due to impaired production or absorption of cerebrospinal fluid or blockage of the pathways through which cerebrospinal fluid flows out. Excessive cerebrospinal fluid can press brain tissue against the skull, causing brain tissue damage. At the Yusupov Hospital, professors and doctors of the highest category make diagnoses using modern research methods. Neurologists determine the cause and extent of the disease and apply individual treatment regimens to patients.
The substance of the brain and spinal cord is constantly washed by cerebrospinal fluid. It protects the brain from damage and provides nutrients. The circulation of cerebrospinal fluid occurs in the subarachnoid space between the pia mater and the choroid along the surface of the cerebral hemispheres and the cerebellum. Under the base of the brain there are cisterns in which cerebrospinal fluid accumulates. They connect to the subarachnoid space.
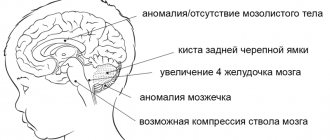
Liquor is concentrated in the three ventricles of the brain. They communicate with the fourth ventricle, which is located between the brain stem and the cerebellum. From the fourth ventricle, cerebrospinal fluid enters the spinal canal through two lateral openings and spreads down to the lumbar region. When the cerebrospinal fluid outflow pathways are blocked, hydrocephalus develops.
In the presence of increased intracranial pressure, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe diacarb, mannitol and mannitol to older people in combination with furosemide or lasix. These drugs have a diuretic effect, removing excess fluid from the body. Diacarb temporarily blocks the production of cerebrospinal fluid. To correct potassium levels in the body, use asparkam or panangin. Nutrition of brain tissue in elderly patients improves after using Cavinton, Actovegin, Cerebrolysin, and Semax.
Neurosurgeons at partner clinics of the Yusupov Hospital perform the following endoscopic operations on elderly people:
- aqueductoplasty;
- endoscopic ventriculocisternostomy of the floor of the third ventricle;
- removal of intraventricular brain tumor;
- septostomy;
- endoscopic installation of a shunt system.
After the operation, the patient's condition improves, and neurological symptoms reverse. Elderly people with hydrocephalus restore their ability to self-care and adapt to social life.
Classification of the disease
There are three main forms of pathology:
- occlusive hydrocephalus, or internal, is a condition in which fluid does not flow from the ventricles, while the space around the brain is compressed;
- non-occlusive hydrocephalus, or external, - fluid can enter from the ventricles into the space between the brain and its membranes, while they expand and compress the nervous tissue from the outside;
- mixed hydrocephalus is a combination of several blocks of cerebrospinal fluid outflow pathways.
External replacement hydrocephalus is a severe form in which the substance of the cerebral cortex atrophies, and excess fluid takes its place. A synonym for this condition is atrophic hydrocephalus.
The disease is also divided depending on its causes into post-traumatic, post-infectious and post-hemorrhagic forms. Hydrocephalus can be progressive (active) or chronic (compensated). It is accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure.
Diagnosis of hydrocephalus in adults
Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital diagnose hydrocephalus using computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. These methods make it possible to determine the size and shape of the ventricles, brain cisterns, and subarachnoid space. If doctors at a neurology clinic detect early signs of hydrocephalus on an MRI, they prescribe medication to stop the progression of the disease. X-ray of the cisterns at the base of the brain allows us to clarify the type of hydrocephalus and assess the direction of the cerebrospinal fluid flow.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital use the following methods for diagnosing atrophic hydrocephalus:
- magnetic resonance or computed tomography, which allows you to determine the size and shape of the cisterns of the brain, ventricles and subarachnoid space;
- radiography of the tanks, with the help of which the type of hydrocephalus is clarified and the direction of the cerebrospinal fluid flow is determined;
- diagnostic test spinal puncture with collection of 40-55 ml of cerebrospinal fluid, accompanied by a short-term improvement in the patient’s condition;
- ultrasound examination of cerebral vessels to determine the state of arterial and venous blood flow.
After analyzing the results of a comprehensive study, individual treatment is prescribed. The tactics for managing patients with severe hydrocephalus are developed at a meeting of the expert council with the participation of professors and doctors of the highest category. Neurosurgeons determine indications for surgical intervention.
A trial diagnostic lumbar puncture with removal of 30-50 ml of cerebrospinal fluid is carried out to diagnose the disease. After the procedure, the patient’s condition temporarily improves due to the restoration of blood supply to ischemic brain tissue against the background of a decrease in intracranial pressure. In acute hydrocephalus, lumbar puncture is not performed due to the high risk of brainstem herniation and the development of dislocation syndrome.
To clarify the diagnosis, neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe craniography, ultrasound, and angiography. The results of the examination are discussed at a meeting of the expert council, where tactics for managing a patient with hydrocephalus are developed.
Symptoms and signs of hydrocephalus
External hydrocephalus is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- a disproportionately large skull in a child, divergence of sutures, enlargement of the fontanel;
- nausea and vomiting;
- intense headache;
- decreased intelligence, memory, hearing, vision;
- drowsiness;
- speech disorders.
Moderate external hydrocephalus appears gradually, and its symptoms are often mild. Only as the disease progresses does replacement hydrocephalus occur with severe consequences:
- mental disorders;
- violation of motor functions, balance;
- disturbance of mental activity.
Hydrocephalus in adults is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- intense, untreatable headache;
- vestibular disorders;
- loss of visual fields;
- paralysis of limbs;
- lack of skin sensitivity.
Internal hydrocephalus mainly affects the structures of the cerebellum: gait is disrupted, coordination of movements is lost, handwriting becomes uneven and large.
Symptoms of hydrocephalus require urgent medical attention, as this disease can cause irreversible consequences.
Classification of hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus can be congenital or acquired. It is generally accepted that the disease is diagnosed in children, but there is an increasing increase in cases of dropsy in adult patients.
According to the nature of the course, hydrocephalus can be:
- Acute - this form of the disease is characterized by a rapid course, the signs become obvious literally within three days.
- Subacute – symptoms increase and develop within one month.
- Chronic – the pathology develops for more than one month.
Treatment of hydrocephalus
For this disease, medications are ineffective. Hydrocephalus is treated surgically. During the operation, the doctor installs a shunt system that allows cerebrospinal fluid to flow normally from the cavities of the brain into the abdominal cavity, and less often into the heart chamber or pleural cavity. The shunt system is equipped with a valve that prevents liquid backflow.
In some patients, ventriculostomy may be used. This is an endoscopic operation during which the surgeon makes a small hole in the wall of the 3rd ventricle of the brain. The normal outflow of cerebrospinal fluid then occurs through it.
Folk remedies for hydrocephalus have limited use. You can use tinctures of mint, lemon balm, cornflower, astragalus, calamus, and buckthorn berries.
Examination and treatment
Hydrocephalus, or “water on the brain,” is a serious and often incurable disease. It is characterized by the accumulation of fluid in the brain. The lack of fluid outflow negatively affects not only the mental, but also the physical development of the patient, whose appearance becomes specific - the head becomes enlarged while maintaining the normal parameters of the rest of the body.
Get diagnosed with hydrocephalus of the brain at Clinic No. 1
- X-ray
- Craniogram
- Ophthalmoscopy (as prescribed by a doctor)
- Angiography
For one-time payment for services - 20% discount
Call
Prevention and consequences of hydrocephalus
The prognosis for this disease is difficult to determine. It largely depends on how early treatment is started and the extent of irreversible brain damage.
The consequences of hydrocephalus include delayed physical and mental development. However, with the right rehabilitation program, many children with this diagnosis can lead normal lives with minor limitations.
With a progressive form of pathology, the prognosis is unfavorable.
On the other hand, even bypass surgery is not always accompanied by complete recovery. The factors on which this depends have not been fully established.
Therefore, disease prevention is important:
- if necessary, genetic counseling for expectant mothers;
- protection against infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- prevention of traumatic brain and birth injuries;
- vaccination against pneumococcus, which protects against meningitis;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases causing hydrocephalus in adults.
Will an MRI show hydrocephalus?
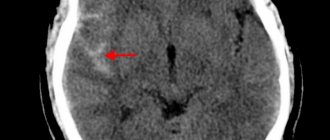
With magnetic resonance imaging, layer-by-layer images of the anatomical area being studied are obtained. When examining the scans, the doctor sees the brain matter and identifies abnormalities. MRI clearly shows hydrocephalus. The method is informative in the early stages of the disease, even if the patient does not have characteristic symptoms. Detailed images allow doctors to identify dropsy of the brain, determine the type, and diagnose concomitant diseases.
Hydrocele of the brain on coronal MRI scanning
Why should you contact the Mama Papa Ya clinic?
The network of family clinics “Mama Papa Ya” has a wide network of branches in Moscow and other cities and offers medical services]at affordable prices[/anchor]:
- consultation with a pediatrician to identify symptoms of pathology in the child;
- consultation with a neurologist and ophthalmologist;
- observation and rehabilitation after surgical treatment of hydrocephalus;
- accurate instrumental diagnosis of the state of the brain;
- the possibility of treating both children and adults in one clinic.
If you suspect such a pathology, we invite you to sign up for a consultation at the nearest branch by phone or on our website.
Reviews
Good clinic, good doctor!
Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and clearly explain what the problem is. If something is wrong, she speaks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don’t regret that I ended up with her. Anna
I would like to express my gratitude to the staff of the clinic: Mom, Dad, and me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, a very friendly and cheerful team and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish your clinic prosperity.
Anonymous user
Today I had a mole removed on my face from dermatologist I.A. Kodareva. The doctor is very neat! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Yulia Borshchevskaya is friendly and accurately fulfills her duties.
Belova E.M.
Today I was treated at the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and attention. Many thanks to them and continued prosperity.
Anonymous user
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Iratyev V.V.
We visited the “Mama Papa Ya” Clinic with our child. A consultation with a pediatric cardiologist was needed. I liked the clinic. Good service, doctors. There was no queue, everything was the same price.
Evgeniya
I liked the first visit. They examined me carefully, prescribed additional examinations, and gave me good recommendations. I will continue treatment further; I liked the conditions at the clinic.
Christina
The doctor carefully examined my husband, prescribed an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis. She gave recommendations on our situation and ordered additional examination. No comments so far. Financial agreements have been met.
Marina Petrovna
I really liked the clinic. Helpful staff. I had an appointment with gynecologist E.A. Mikhailova. I was satisfied, there are more such doctors. Thank you!!!
Olga
Hydrocephalic syndrome in children
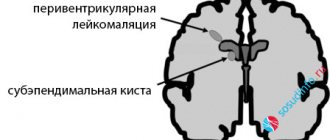
Hydrocephalus occurs in children and adults of any age. Most often, hydrocephalic syndrome occurs in children. If the cerebrospinal fluid begins to collect before the skull bones have fused, then the circumference of the child’s head increases and the skull becomes deformed, which can be seen with the naked eye.
At the same time, atrophy or arrest of tissue development of the cerebral hemispheres is recorded. Therefore, the pressure inside the skull with hydrocephalic syndrome in children does not increase too much. If the process continues for a long time, normal pressure hydrocephalus is formed, in which the ventricles are large and dilated, and atrophy of the medulla is pronounced.
Gradually developing hydrocephalus in children is characterized by progressive atrophy of brain tissue. The child is diagnosed with movement disorders due to conduction disturbances. When the paraventricular part of the pyramidal tract is affected, lower paraparesis is detected in children.
Typical symptoms are visual disturbances. There may be endocrine disorders. ICP increases, and long-term ischemia of brain tissue occurs. The child has intellectual-mnestic and mental disorders. A patient diagnosed with hydrocephalic syndrome has a typical appearance. His head is increased in size, especially in the sagittal direction, but his face remains small.
The skin on the surface of the head is stretched, therefore it is very thin, atrophic, you can see every wreath. There is thinning of the skull bones, with increased spaces between them. The anterior and posterior fontanelles are tense, dilated, sometimes protruded, there is no pulsation. Sutures that have not yet ossified may slowly diverge. If doctors tap the brain part of the head, there may be a sound of a cracked pot.
With the diagnosis under consideration, there is a violation of the motor innervation of the eyeball. The gaze is directed downward, convergent strabismus develops, visual acuity decreases, the final form of which can be absolute blindness. Hyperkinesis can develop in parallel with movement disorders.
With hydrocephalic syndrome in newborns, cerebellar symptoms appear a little later:
- impaired motor coordination
- violation of statics
- inability to sit
- inability to hold your head up
- the child cannot stand
Next, a gross deficit of mnestic functions arises; the child’s intelligence is greatly reduced. Also in some cases the following behavioral symptoms appear:
- irritability
- excitability
- indifference to the environment
- adynamia
Neurological symptoms:
- shrill scream
- headache
- drowsiness
- vomit
- decreased vision
- strabismus
- bulging fontanelle (only in infants)
Papilledema does not occur immediately as a manifestation of increased ICP levels. Due to increased pressure inside the skull, the following symptoms appear:
- disturbance in the acquisition and processing of information
- attention disorder
- Puberty is too early in girls
- dysfunction of the organization (difficulty with summarizing, presenting, justifying, etc.)
- memory problems
Consequences of hydrocephalic syndrome in children:
- Weakness in the muscles of the arms and legs
- Hearing and vision loss
- Dysregulation of body temperature
- Violation of fat and carbohydrate metabolism
- Risk of death
If the operation is performed in a timely manner, the patient recovers, there is a possibility of both stable remission and absolute recovery. With implanted shunts, the disease no longer bothers the person. The shunt is removed only after 3-4 years, if symptoms of hydrocephalic syndrome do not appear.