What is a coma during a stroke? This is a dangerous condition in which a person is literally on the verge between life and death. This complication is characterized by damage and, as a consequence, disruption of the brain, which leads to a complete shutdown of physiological systems.
Coma is considered a protective reaction of our body in order to preserve the remnants of a functioning system; it is for this reason that recovery from a coma after a stroke is possible. Let's take a closer look at this condition.
Causes of coma
The state of coma causes apoplexy, as a result of which hemorrhage develops in the brain, and this causes a certain state of unconsciousness. Coma after a stroke is very common.
The following factors can lead to this phenomenon:
- Severe bleeding into the brain is considered the most common factor in the development of coma.
- Ischemia. This factor is characterized by insufficient or completely absent blood flow to the brain.
- Brain swelling. This factor can lead to the above factors.
- Atheroma. This factor is characterized by severe degeneration of the vessel walls.
- Intoxication. A coma state can be caused by severe intoxication due to chemicals or other substances, depending on how much of the substance was consumed.
- Callagenosis. The condition is characterized by significant changes in connective tissue.
- Angiopathy. A condition in which a specific protein begins to accumulate in the blood vessels of the brain.
- An extremely rare factor is acute vitamin deficiency.
- Infectious, autoimmune blood diseases.
In addition, ischemic stroke is also divided into types, they depend on the cause of ischemia itself. Let's look at them too:
- Stroke caused by atherosclerosis in the cerebral veins. During the process of plaque growth, its tearing off, or the formation of a blood clot on the plaque itself. This leads to the closure of the lumen of the artery and, accordingly, to a serious circulatory disorder.
- Stroke caused by cardioembolism. It develops due to a blood clot formed in the heart entering the brain. Blood clots may well grow in the chambers of the heart or ventricles, but the detachment of a blood clot most often occurs due to disturbances in the frequency and rhythm of the heart.
- Lacunar stroke. It occurs as a result of deformation of small vessels in the brain, most often this occurs as a complication of other diseases, such as diabetes mellitus (mainly type 2) or hypertension.
- Stroke caused by hemodynamic disturbances. It is most often caused by some kind of organic damage to the blood vessels of the brain in combination with labile blood pressure (blood pressure), all of which causes perfusion disturbances.
Ischemic strokes do not often cause a coma, but it often happens that patients come out of it on their own. But the state of coma with hemorrhagic hemorrhage is more common, and this type is also very dangerous, as it causes severe tissue necrosis in the brain. Let's talk about this type in more detail.
How is it determined that coma has turned into death?
Modern medicine is able to maintain breathing, cardiac activity and provide nutrition for a long time to a person in a deep coma. Death is declared when blood flow to the brain stops and irreversible pathological changes occur.
These changes are diagnosed using computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging. The absence of any brain activity is determined by electroencephalography methods, and cessation of cerebral circulation is recorded angiographically.
Based on the totality of the obtained indicators, death is diagnosed and, in agreement with relatives, life support equipment is turned off.
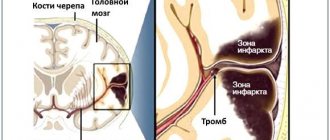
Hemorrhagic cerebral stroke
This type of stroke is characterized by extensive bleeding in the brain. Bleeding can begin after damage to the vessel (due to external mechanical trauma), due to rupture of an aneurysm, or damage by a blood clot. In addition, there are often cases when there is a congenital pathology in which the permeability of the vessel is increased. Naturally, with this type of stroke, the prognosis is greatly worsened, since the consequences are very serious, and the rehabilitation period increases. It is also worth noting that with a hemorrhagic stroke, coma is very severe.
With any type of stroke, coma can develop, but with hemorrhagic stroke it appears most often, it develops faster and has a number of complications and aggravating factors.
Definition of coma
One of the common questions is the length of time a person remains in a coma after a stroke. The average duration of coma ranges from several days to two weeks, provided that emergency medical care was provided and cerebral edema was eliminated.
If there were any additional factors, then the coma state could last up to several years.
Who can predict, now we will tell you the main symptoms of the onset of coma:
- Very quiet speech, most often the person cannot connect even a couple of words.
- Specific delirium and confusion.
- The patient does not respond to external stimuli; this symptom develops quite quickly.
- Nausea or vomiting itself.
- It's hard to feel the pulse.
- The respiratory rate (respiratory rate) decreases to critical levels.
- Body temperature decreases, leading to acute heat exchange disturbances.
- There are rare cases when a patient experiences uncontrollable urination and defecation.
- Noticeable dilation of the pupils, which do not react in any way to changes in light in the environment.
All the symptoms described above develop individually, sometimes with their appearance, a person continues to do something at the level of instincts or basic reflexes. Reflexes such as breathing remain (most often, rare, shallow breathing remains, which may not be enough and the patient is connected to specialized equipment) and swallowing reflexes (thanks to which feeding with tubes can be eliminated).
It is not uncommon for convulsions, shudders, and small movements to occur during a coma.
Coma develops instantly, it is almost impossible to predict it, except for the coma that is caused by an ischemic stroke. Such serious consequences of a stroke can be noticed provided that the patient has the following symptoms:
- Severe dizziness that does not go away for a long time.
- A sharp decrease in visual acuity, complete loss of vision is possible.
- Severe and unhealthy drowsiness, the patient can fall asleep almost on the go.
- The consciousness of such patients is extremely confused.
- There is severe numbness of the extremities and a slight loss of skin sensitivity.
- Coordination of movements is severely impaired; the patient sometimes cannot stand on his feet.
Such symptoms continue for quite a long time, although people sometimes do not even pay attention to them.
Knowing these symptoms, you can contact a specialist for help in time, thereby improving the prognosis or even preventing the development of the disease.
On the verge of mysticism
Denis Nikolaevich! I recently read the most interesting novel by Evgeny Vodolazkin “The Aviator”. Not a fantasy novel. The realities of the early and late nineties of the last century. Its hero Innokenty went through hellish torture during the years of Stalinist repressions in a concentration camp. He ended up in a special laboratory where prisoners (instead of death) were frozen. It remained frozen for decades. We learned how to defrost. Innocent was also unfrozen... According to his passport, he is almost a hundred years old. But in essence he was born again. He is young, he is an advertising hero, he is in love and loved, he is waiting for the birth of a child. He is recognized as man of the year. It’s just that the past doesn’t let go. He remembers the horrors of the camp, remembers the executioners. The main thing, and this is noticed by the doctor who observes and knows Innocent, his wife notices, and he himself: not only is it becoming more and more difficult to walk, his memory is fading, his consciousness begins to become confused. And this is irreversible: the process of death of body cells is underway.
I understand that “Aviator” is the author’s brilliant fantasy. But freezing is not akin to a coma? Don't you always come out of a coma? And if they go out, does she leave any traces? Does the person fully recover? How long can you be in a coma? Why is the patient sometimes put into this state? Finally, what is coma? There is no insurance against it.
Denis Protsenko:
Let me start with the fact that coma and cryotechnology (that same freezing) are fundamentally different things. Therefore, as a doctor and specialist in the field of critical care medicine, I will talk about the present and more studied. Coma is a complex disorder of important body functions. This is a pathological condition in which there is no consciousness and the patient lies with his eyes closed, despite various external stimuli. He does not open his eyes when he hears pain or shouts. And this is one of the main signs of coma. With closed ones at any depth of unconsciousness, that is, coma.
So he still hears and feels pain? Doesn't he just open his eyes?
Denis Protsenko:
Yes. This is, if you like, an axiom: a person in a coma always lies with his eyes closed. But much depends on the depth of the coma and its classification. There are several such classifications. The reason for the development of coma is also important. Most often, coma occurs as a result of acute cerebrovascular accident. And in young people, the cause is often traumatic brain injury or poisoning.
How long can a person be in a coma?
Denis Protsenko:
From a few minutes to decades. There are such isolated observations, even descriptions in specialized literature.
Do you mean and to whom General Anatoly Aleksandrovich Romanov, who was wounded in 1995? He has been in a coma for a quarter of a century.
Denis Protsenko:
Not quite in a coma! As far as I understand his medical history, Anatoly Alexandrovich began to emerge from his coma after two weeks. He began to open his eyes. However, coming out of a coma also goes through certain stages. Unfortunately, his recovery stalled at a very early stage and he is still in a vegetative state. He opens his eyes. But he has no other signs of higher nervous activity.
A person can be in a coma from a few minutes to decades
Does he have the so-called “locked-in man” syndrome? This is when a person lies motionless, but his gaze is fixed on external stimuli.
Denis Protsenko:
Indeed, the “locked-in person” syndrome is one of the phases of recovery from a coma. But as far as I monitor media data about General Romanov, he never reached this phase.
In addition to the “man locked up” phase, there is also a phase that you call the phase of gross psychoorganic disorders...
Denis Protsenko:
This is not what I call. This is a generally accepted classification. And it consists of a combination of three characteristics: sloppiness, gluttony and hypersexuality. It is believed that coma is a protective reaction of the body when the brain does not want to remember negative information when it wants to rest. That is why most patients who survived a coma and recovered consciousness do not remember this period. Unlike the hero of the novel Vodolazkin, with whom we began our conversation.
But since we remembered it, let’s continue. For those who are in a coma, for those who survived it, do some body cells die off? First of all, the brain?
Denis Protsenko:
It depends on the cause of the coma. If the cause was damage to the brain substance (trauma, cerebral hemorrhage), then the brain cells die. And in a coma, which is a consequence of poisoning, brain cells are restored.
Why are some patients put into a coma? And how is this done?
Denis Protsenko:
This is done with the help of medications. At one time they tried to treat mental illness this way. Now this has actually been abandoned.
But you can often hear from doctors that the patient was put into an artificial coma...
Denis Protsenko:
We use the term “induced coma” to explain to relatives of patients one of the methods for treating cerebral edema, which is essentially a deep, drug-induced sleep.
How long can it last? Does the brain and other organs of the body suffer?
Denis Protsenko:
This method of treatment is carried out only in an intensive care unit. The patient is under close supervision of medical personnel and special monitors. This guarantees a combination of effectiveness and safety of this treatment approach.
What about diabetic, hepatic coma?
Denis Protsenko:
The cause of coma may be metabolic disorders. And these disorders occur both in diabetes and liver diseases. Manifestations of the same coma are the same closed eyes and other clinical signs.
— Can a person who has survived a coma recover completely?
Denis Protsenko:
I will answer as a person who survived a coma 20 years ago as a result of a car accident: it did not stop me from giving you this interview today.
Forecast
It is impossible to say with complete certainty what prognosis awaits this or that person; it all depends on additional factors that existed before or after the coma. Let's consider the factors that can lead to the death of a patient:
- Creatine. With an increased concentration of creatine in the blood (up to 1.5 mg/dL), the chances of an unfavorable outcome increase.
- Severe convulsions that can remain intense and strong for up to three days or more.
- Complete loss of all reflexes, especially breathing and swallowing.
- Age. Naturally, the older a person is, the more difficult it is for him to get out of a comatose state. People whose age exceeds 70 years have virtually no chance of rehabilitation.
- Negative indications for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies.
A fairly common occurrence in which coma gives way to a vegetative existence.
Positive prognoses depend only on the degree of damage to the brain and central nervous system (CNS), as well as on additional factors, let’s consider them:
- Information about the cause of the disease will have a positive impact on the quality of treatment, and therefore on the period of rehabilitation.
- Provide first aid.
- Compensatory ability of the central nervous system.
With a gradual recovery from a coma, the degree of brain damage can be determined. They can manifest themselves in the form of speech impairment, severe loss of sensitivity, loss of vision and other complications caused by the coma state.
Recovery after a coma
Rehabilitation after a coma becomes extremely important: a set of measures that can help you get closer to or return to your previous way of life. Everything is subject to calculation - from the load level to the program itself. The Clinical Brain Institute has been successfully dealing with these problems for quite a long time. We are ready to offer effective rehabilitation programs developed with special care, which are selected individually for each patient. Our specialists, being professionals in their field, are also very responsive and attentive people, which is something that patients so often lack!
Treatment
Treatment begins with stabilizing the respiratory rate (respiratory rate), and it is also very important to restore all functions of the cardiovascular system. The development of a treatment plan should begin only after all necessary research has been completed. It is very important to quickly replace all vital functions with artificial ones. For example, supplying oxygen to the body, stabilizing body temperature, and providing nutrition are very important.
Hemorrhagic stroke is treated only with surgery. With this operation, bleeding in the brain is eliminated and the aneurysm, which was the causative agent of the bleeding, is clogged. After all these manipulations, the swelling begins to rapidly subside. Such an operation requires a highly qualified neurosurgeon.
Stages of medical care for patients in a coma after a stroke
Patients in a state of coma that has developed as a result of a stroke are provided with medical care at the prehospital stage by emergency physicians:
- restore airway patency;
- provide oxygen through an air duct or transfer the patient to artificial ventilation;
- prevent aspiration (foreign bodies entering the respiratory tract).
When there is a sharp decrease in blood pressure, drugs are used that have a vasopressor effect (alpha-adrenergic agonists) and improve myocardial contractility (cardiac glycosides), drugs that replenish the volume of circulating fluid (crystalloid solutions and low molecular weight dextrans). If the patient develops seizures, tranquilizers and antipsychotics are used. If necessary, barbiturates and inhalation anesthesia are used.
When a patient is admitted to the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, doctors take emergency measures:
- maintaining an optimal level of oxygen supply;
- monitoring of blood pressure and correction of cardiac activity;
- administration of pressor amines (1 ml of 1% mesotone solution intramuscularly or subcutaneously, caffeine, corticosteroids;
- constant monitoring and correction of acid-base balance in the body;
- control of swallowing (in the presence of dysphagia, a nasogastric tube is inserted to prevent aspiration bronchopneumonia and ensure adequate nutrition for the patient);
- control of the condition of the bladder and intestines.
There are currently no specific drug treatments for hemorrhagic stroke. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital are taking measures aimed at reducing the usually high intracranial pressure. At the same time, they normalize blood pressure, the state of the blood coagulation system and the permeability of the vascular wall, and support the activity of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. In the absence of contraindications, surgical interventions are performed at partner clinics. In the case of an ischemic stroke, patients are brought out of a coma and the restoration of lost functions is immediately begun using methods of drug therapy and physical rehabilitation.
If signs of coma appear, the patient should be placed on a horizontal surface, turn his head to the side and call an ambulance. Call and alert the clinic staff about the current situation. The Yusupov Hospital employs professors and doctors of the highest category who use modern equipment and medications that allow them to do everything possible to bring a patient out of a coma after a stroke.
Caring for a patient in a coma
A patient in a comatose state after a stroke needs good care. Daily observation is required, as well as proper, professional care. After a person is admitted to intensive care, the first step is to connect all the necessary equipment that will support the person’s life.
The diet should consist of nutrients, but to avoid stomach problems, it is sometimes worth giving regular food prepared at home, of course, within the limits of a healthy diet.
Prevention of bedsores is necessary, since the patient lies for days. The patient's hygiene must be maintained, and bed linen must be changed when soiled or once a week.
Prevention
The most important prevention of coma is the prevention of stroke. Prevention lies in the basic principles, let's look at them in detail:
Always worried about your health, you need to undergo regular medical examinations, and also adhere to the right lifestyle in order to avoid any complications or pathologies.
It is necessary to literally memorize the main symptoms of a stroke; it is worth mentioning that at the slightest suspicion you should immediately go to a specialist for advice.
As a result, we realized that stroke and coma are very related to each other. Coma is just a developed vegetative state. That is why rehabilitation depends on all extraneous factors that literally fall on a person. Coming out of a coma is possible, but it requires a lot of effort. We hope we were able to answer your question, how many days does a coma last and what to do about it.
Main symptoms and signs of coma
The process of coma development can be either almost instantaneous or gradual. This can be a time period from several minutes to several days. Symptoms of comatose states may vary depending on the underlying disease. A very important point is the timely recognition of the condition preceding the onset of coma. In some cases, in addition to loss of consciousness, symptoms include changes in the color of the skin, the presence of unusual odors in the air exhaled by the patient, a decrease or increase in body temperature, as well as pressure. X-ray, laboratory and instrumental examinations make it possible to clarify the diagnosed coma.