Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine
This disease is very common today.
People who have sedentary jobs are especially susceptible to it. With this pathology, the nerve endings extending from the spine are compressed, which causes pain under the left rib. It often radiates to the back, buttock, and even thigh; it can be encircling in nature, accompanied by numbness and tingling. The fact that the cause of pain is osteochondrosis may also be indicated by a decrease in the mobility of the thoracic region. “Shots” occur not only when inhaling, but also during movements and sudden turns of the body. In most cases, they overtake a person after being in an uncomfortable position for a long time. They often happen during sleep.
Pain under the left rib behind
Such localization of pain may lead the doctor to think about the presence of kidney disease. To confirm the diagnosis, a general blood test and ultrasound examination are prescribed. Sometimes pain under the ribs at the back indicates the presence of lumbar or thoracic osteochondrosis. X-rays, CT scans, and blood tests may be needed to make a diagnosis.
Pain in the left intestine
Other reasons can cause such pain, namely:
- pericarditis;
- pneumothorax;
- pleurisy;
- renal colic;
- acute pancreatitis;
- myocardial infarction.
Intercostal neuralgia
Intercostal neuralgia is another very common factor that causes pain under the ribs on the left. The latter is very similar to the heart, which can cause real panic. The reasons may be:
- osteochondrosis;
- unsuccessful rotation of the body;
- hypothermia;
- draft;
- cold;
- enlarged uterus (during pregnancy).
An attack of intercostal neuralgia is often accompanied by numbness of the upper extremities, muscle twitching, increased sweating, and pallor of the skin. The pain intensifies not only when breathing, but also when coughing, sneezing, yawning, turning the body, and can last from several hours to a couple of days. Often a person is forced to remain immobilized all this time, since every movement brings him pain.
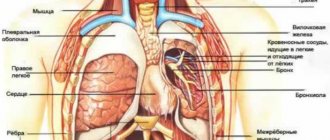
Splenic rupture
This is an organ located in the hypochondrium on the left side. The spleen is a kind of storage facility for red blood cells. It is involved in immune processes and is involved in cleansing liquid connective tissue from harmful substances.
When the spleen ruptures, a stabbing pain occurs when inhaling on the left side under the ribs. The abdominal cavity is damaged and blood leaks into it. Against this background, the pain when inhaling on the left under the ribs on the side increases significantly. Over time, it covers the entire abdomen. It becomes extremely difficult for a person to swallow air.
In addition to pain when inhaling under the rib on the left, the following symptoms are observed:
- cyanosis of the skin in the area where the spleen is located;
- chills;
- nausea turning into vomiting;
- high body temperature;
- arterial hypotension.
If there are signs of organ rupture, you must immediately call an ambulance. But even with timely intervention by doctors, the spleen can be saved only in 1% of cases. Therefore, the main treatment for this condition is complete removal of the organ.
Heart diseases
Pain in the left hypochondrium may well be caused by heart diseases, such as ischemia, angina, cardiomyopathy and others. The most serious of them is myocardial infarction. Pain in this case is accompanied by both the development of the pathology and the condition preceding it.
Associated signs indicating a heart attack:
- dyspnea;
- chills;
- cold clammy sweat;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- sharp pallor of the face (even to the point of cyanosis) and puffiness;
- numbness of hands.
Pain on the left side can radiate to the shoulder blade, shoulder, or neck. It is sharp, burning (and not aching, as, for example, with colitis), accompanied by heaviness behind the sternum. If you have such symptoms, you should immediately call an ambulance, as this is a life-threatening condition.
Pathologies of the diaphragm
This is the main respiratory muscle, which conditionally separates the chest and abdominal cavity. As a rule, the cause of pain on the left under the ribs in front when inhaling is a diaphragmatic hernia, during the development of which the lower part of the stomach moves upward due to an increase in the lumen of the esophagus.
This pathological condition can occur against the background of:
- regular high-intensity physical activity;
- pregnancy;
- chronic constipation;
- excess body weight;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory diseases.
Diaphragmatic hernia is a serious illness, the danger of which is that over time the functioning of the digestive system, heart and lungs is increasingly disrupted.
Main symptoms of the disease:
- Aching pain on the left under the ribs when inhaling air. It is permanent.
- Frequent episodes of regurgitation (almost after every meal).
- Heartburn.
- Belching air.
- Difficulty swallowing food.
- Bloating.
- Cough.
- Tachycardia.
Treatment of pathology involves the use of surgical methods, during which the surgeon returns the stomach to its place and sutures the lumen of the esophagus. Conservative therapy in this case is ineffective. Medications only temporarily reduce the severity of symptoms.
Lung cancer
With cancer of the left lung, when the tumor grows into the pleura, pain appears in the chest. They usually appear at a late stage. The pain radiates to the neck, arm and stomach. It can be sharp and stabbing. Often has a girdling character.
This symptom is accompanied by others characteristic of lung cancer:
- This is primarily a cough.
- The patient suffers from lack of appetite and rapidly loses weight.
The signs of this pathology are in many ways similar to dry pleurisy. And pain in the left side when inhaling is one of the common symptoms. Pleurisy is often the first and only manifestation of tuberculosis, occurring at its initial stage. It is diagnosed when there are foci of disease in the lungs or lymph nodes.
Tuberculous pleurisy can be purulent. Accompanied by fever, increased sweating, shortness of breath, chills. A person suddenly loses weight.
Lung pain
Since the lungs do not have pain-sensing nerves, there is no pain in the lungs. Symptoms of pulmonary diseases are characterized by coughing and difficulty breathing. The only part of the lungs that can cause pain is the pleura, trachea and large bronchi. In the differential diagnostic plan, assessment of pain intensity , its localization, connection with breathing and cough, the appearance of shortness of breath, and the effectiveness of pain-relieving drug therapy . Intense pain in the lungs indicates an acute disease and, as a rule, it is combined with shortness of breath, intensifies with breathing, this is pleural pain. In acute tracheitis, the pain is localized behind the sternum and is intense, aggravated by coughing.
Chest pain accompanied by shortness of breath is a serious sign, especially if it is difficult to treat. You should always clarify the dependence of pain on the position of the patient’s body and the effect of movement on the intensity of pain. This pain occurs with the following diseases:
- intercostal neuralgia;
- pathologies of the thoracic spine;
- radiculitis;
- muscle diseases;
- pleurisy.
You should also remember about projected and radiated pain. Chest pain occurs with the following diseases:
- pericarditis;
- aortic diseases;
- pulmonary embolism, gastric and duodenal ulcers;
- pancreatitis;
- subphrenic abscess.
Pain behind the sternum, in the heart area, in the left half of the chest, between the shoulder blades, often radiating to the left arm, is characteristic of coronary heart disease.
Causes of pain in the lungs
Dry pleurisy develops during a tuberculous process in the lungs. Pleurisy also occurs with the following diseases:
- pneumonia;
- lung abscess;
- pulmonary infarction;
- tumors affecting the pleura;
- echinococcosis, with chest injuries;
- rheumatism;
- diffuse connective tissue diseases (collagenosis);
- uremia, blood diseases.
Chest pain is usually one-sided, stabbing, worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or changing body position. The most typical location is the lower and lateral parts of the chest. In the position on the affected side, the pain subsides, which is associated with a decrease in the movements of the pleura, so the patient instinctively takes this position.
Exudative pleurisy
In most cases, the cause of exudative pleurisy is tuberculosis, but it can also be a consequence of other diseases. At the beginning of pleural exudation, there is pain in the side, limited respiratory mobility of the affected side of the chest, pleural friction noise, and a dry, painful cough occurs. As the effusion accumulates, the pain in the side disappears, a feeling of heaviness appears, some bulging and smoothing of the intercostal spaces on the painful side appears. Lobar pneumonia is an acute infectious disease of the lungs, affecting one or more lobes. The most common pathogen is pneumococcus. The disease begins with the appearance of stabbing pain in the chest, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- a sharp rise in temperature;
- chills;
- increasing symptoms of intoxication;
- cheek hyperemia;
- herpes on the lips;
- shortness of breath, cyanosis.
A dry, painful cough is also characteristic, followed by a cough with the release of rusty sputum, a viscous consistency mixed with blood.
With spontaneous pneumothorax, air enters the pleural cavity until the pressure in it reaches atmospheric pressure or the lung collapses. Spontaneous pneumothorax can develop in the following diseases:
- chest injury;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- suppurative lung diseases;
- lung cancer;
- bullous emphysema;
- breakthrough of echinococcal bladder and air cyst.
There are open, closed and valve pneumothorax. With an open pneumothorax, the pleural cavity communicates with atmospheric air constantly, both during inhalation and exhalation. Closing the perforation leads to the establishment of negative pressure in the pleural cavity . The most dangerous is valvular pneumothorax, in which air enters the pleural cavity during inhalation, and during exhalation the hole closes and the air is retained. As air accumulates, the pressure in the pleural cavity increases, the mediastinum shifts to the healthy side, the lung on the affected side collapses, and hemodynamic disturbances occur.
Spontaneous pneumothorax occurs mainly in young men and is manifested by sudden sharp pain in the chest, aggravated by breathing, talking, and physical stress. The pain is usually long-lasting and is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- severe pallor of the skin;
- weakness;
- cold sweat with low rapid pulse;
- drop in blood pressure.
The patient is bothered by severe shortness of breath and dry cough. Tachycardia and cyanosis appear. Patients prefer to be in a sitting position. Respiratory movements of the chest are superficial. There is a lag in breathing and often an expansion of the corresponding half of the chest. There is no vocal tremor on the affected side.
With lung cancer, chest pain may occur late in the disease. Chest pain may occur late in the disease. Other clinical symptoms depend on the location of the tumor, its proximity to the bronchial tree, the rate of tumor growth and the involvement of nearby organs in the process. If the inflammatory perifocal process in lung cancer reaches the pleura, then hemorrhagic exudative pleurisy develops.
The nature of the pain is different: acute, stabbing, girdling, aggravated by coughing and breathing. The pain can cover a certain area or half of the chest, and it can radiate to the arms, neck, and abdomen. The pain becomes especially intense and excruciating when the tumor grows into the ribs or spine with compression of the nerve roots. There is a special form of lung cancer (Penkosta) with painful plexitis.
Pain may be in the spine and limbs, which is associated with tumor metastasis. In the late stage, the following symptoms characteristic of the development of the disease appear:
- dyspnea;
- cough;
- hemoptysis;
- fever;
- increasing weakness;
- weight loss.
The patient's condition is extremely serious. Decreased breathing is heard with a large number of moist fine rales.
For pain of bone origin, the following pathological processes may be the cause:
- injury;
- inflammatory diseases:
- osteomyelitis of the ribs and sternum;
- swelling;
- hyperemia;
- fluctuation.
Palpation of the ribs is sharply painful. Fistulas may form. As a rule, the process is accompanied by an increase in temperature and signs of intoxication.
Tuberculosis of the ribs (the result of hematogenous dissemination), which is characterized by a more sluggish course, typically the formation of a cold abscess, and subsequently a fistula.
Actinomycosis of the ribs , developing as a complication of actinomycosis of the lungs; characterized by a hard deep infiltrate, fistulas, pus on the skin surface.
Pain appears only when the tumor is significant. Chondrosarcoma is usually localized in the posterior rib. Rarer forms include myeloma, Ewing endothelioma, fibrosarcoma, and neurosarcoma.
Pain in the lungs is also affected by metastatic bone damage and metastases of the lungs , breast, and prostate gland. In addition, pain in the lungs is caused by:
- tumor-like processes;
- dystrophic processes;
- osteoporosis;
- osteomalacia of bones.
The above diseases are most often observed in endocrine diseases and as a complication of corticosteroid therapy.
arthritis of a rheumatic and infectious-allergic nature can be causes of chest pain More common are arthritis of infectious-metastatic origin, developing with osteomyelitis, tuberculosis, actinomycosis and syphilis. The following symptoms are characteristic:
- hyperemia;
- swelling of the joints;
- severe pain on movement and palpation of the joints;
- arthrosis;
- joint tumors.
The cause of pain of muscle origin is often myositis and the following diseases:
- acute infections (influenza, gonorrhea, typhoid fever);
- chronic infections (tuberculosis, syphilis);
- metabolic diseases (diabetes mellitus, gout);
- muscle fatigue, injury.
Characteristic symptoms are swelling, induration, and soreness of the affected muscle during movement and palpation. Pain in the left side of the chest may occur with excessive hypertrophy of the anterior scalene muscle.
Gas pain
The large intestine reaches the level of the chest. Passing through the upper part of the abdominal cavity behind the stomach, it reaches the upper point behind the lower left part of the chest. This turn is located behind the spleen, which is why it is called the splenic flexure of the large intestine. Gases tend to rise upward, so they accumulate at this top point.
Compressed by the powerful muscles of the colon, the trapped gases cause severe pain; this happens so often that the phenomenon has received its own name - air (gas) accumulation syndrome in the splenic flexure. It happened that people with this syndrome were brought to hospitals with suspected heart attacks or kidney stones.
After finding out the true cause of the pain, patients experienced great moral relief, while doctors who made an incorrect diagnosis felt just as much embarrassment and shame. Pain from gas accumulation syndrome in the splenic flexure of the large intestine manifests itself to the left of the sternum or in the left upper part of the abdominal cavity, and an experienced doctor in this case will immediately make the correct diagnosis. But do not self-diagnose if the pain is severe and acute.
Stomach ulcer
With a perforated stomach ulcer, pain may also occur under the left rib in front. This symptom is preceded by signs characteristic of colitis (flatulence, bloating). Then the person is overtaken by pain, it is dagger-like and strong. Sometimes tolerable, and sometimes capable of causing loss of consciousness, it can shift slightly to the right.
Often pain occurs after eating. Accompanied by other symptoms: nausea, loss of appetite, vomiting, belching with an unpleasant aftertaste. If cutting, stabbing pain occurs and there is a history of a stomach ulcer, urgent hospitalization is necessary.
Gastritis
When there is periodic pain in the upper left side, gastritis can be suspected. Discomfort is also felt in the stomach. The pain is not acute - aching, radiating under the shoulder blade. It usually occurs after eating and then subsides. It often does not bring much discomfort to a person, so many do not attach importance to it for a long time. Meanwhile, the disease progresses.
Painful sensations with gastritis are accompanied by periodic nausea, heartburn, unpleasant belching, vomiting, problems with stool (constipation or diarrhea), weakness, and pale skin. When moving, turning the body, as well as taking a deep breath, the pain in the stomach area and above may intensify. Many manifestations are similar to signs of colitis, so gastritis is differentiated from this disease first of all.
Osteochondrosis
Currently, this is the most common spinal disease. During its development, degenerative-dystrophic changes in bone and cartilage tissue occur. According to statistics, about 90% of the world's population suffers from osteochondrosis.
The main reasons for the development of the disease:
- improper formation of the spine during intrauterine development;
- hereditary predisposition;
- the natural aging process of the body;
- disturbance of phosphorus and calcium metabolism;
- unbalanced diet;
- inactive lifestyle or, on the contrary, high-intensity physical activity;
- vibrations that are long-lasting or regular (for example, when driving);
- excess body weight;
- smoking;
- various types of injuries;
- weakness of muscle tissue in the back;
- scoliosis;
- flat feet;
- infectious diseases;
- constantly being in a state of stress;
- living in unfavorable environmental conditions;
- wearing uncomfortable shoes, including high-heeled models;
- pregnancy.
If, when you inhale, there is a stabbing sensation in the left side under the ribs, this is considered a symptom of thoracic osteochondrosis. In addition, a person may experience a feeling of numbness in the area of the heart and stomach. Often the pain radiates to the left shoulder blade or shoulder. The patient also experiences rapid onset of fatigue even with minimal mental and physical exertion.
In most cases, the treatment regimen for osteochondrosis includes the following points: medication, physical therapy, physiotherapy, massage, traction, kinesiotaping, diet.
Pancreatic diseases
The pancreas is located on the left side, and with pathologies of this organ, pain in the hypochondrium often occurs. This is one of the most typical symptoms of pancreatitis. The pain is girdling in nature. It is unsharp, aching, and often quite strong. The intensity increases as you inhale. A person has to “fold” in half to alleviate the condition.
Pain usually occurs after a feast. Especially abundant and with the use of strong drinks. Inflammation of the pancreas is accompanied by nausea, vomiting with bile, and heartburn. The urine becomes dark, and the stool becomes abnormally light in color. During acute attacks, the temperature may rise significantly.
Pathologies of the spleen
Another organ located on the left is the spleen. It is closest to the surface of the body, so any abnormal processes occurring in it immediately make themselves felt. Problems with the spleen often occur after or during infectious diseases, since this organ is responsible for filtering blood from dead red blood cells. It greatly increases in size, fighting the virus, which explains the discomfort.
Sometimes the spleen is damaged by the ribs as a result of injury. It breaks. In such cases, pain appears not only when sighing or moving, but also on its own. It can be very strong, difficult to bear, and it radiates to the back.
Pathologies of the spleen are often accompanied by increased body temperature, inflammation of regional lymph nodes, headaches, and enlarged liver. When an organ ruptures, the skin in the navel area turns blue. If such symptoms are present, you should immediately seek medical help.
Acute pyelonephritis
If your left side hurts under the ribs when you inhale, this may indicate kidney pathology. The term “acute pyelonephritis” refers to an inflammatory process in which the pyelocaliceal system and intermediate tissue of the organ are involved.
The main reason for the development of the disease is the spread of infection to the kidneys from the lower urinary tract. This occurs in the presence of one or more provoking factors.
These include:
- intestinal dysbiosis;
- vaginal dysbiosis, an increase in its acidity;
- hormonal imbalance;
- frequent change of sexual partners (for women);
- increased intrarenal pressure;
- ureteral strictures;
- prostate adenoma or cancer;
- stones in the ducts through which urine is excreted from the body;
- hypothermia;
- diabetes;
- pregnancy;
- overwork;
- viral infections;
- hypovitaminosis.
If the left side of the organ is affected, the disease can be suspected if the following signs are present:
- The urge to urinate becomes more frequent. In this case, urine is not released.
- When inhaling, the left side hurts under the ribs, the unpleasant sensations radiate to the abdominal cavity.
- General health worsens.
- Body temperature rises.
- A feverish state appears.
- Sweating increases.
Gradually, the pain with a deep breath on the left (under the ribs) reaches its maximum peak. Its severity decreases somewhat as you exhale. Coughing, sneezing, any physical activity - all this increases the intensity of painful sensations so much that a person may lose consciousness.
The key to successful treatment is timely provision of medical care. The prognosis is considered favorable if the disease subsides while taking medications. According to statistics, in 30% of patients the disease becomes chronic. At the same time, the risk of developing pathologies that pose a threat to the patient’s life remains.
What to do if such pain occurs
When a person experiences pain in the left hypochondrium when inhaling, it is recommended not to waste time and contact a medical facility to determine its correct cause. The following doctors diagnose this condition:
- endocrinologist;
- cardiologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- gynecologist;
- surgeon.
Self-medication is strictly prohibited, because it will worsen the general condition and provoke the emergence of various complications. You need to know when to go to a medical facility. There are situations when pain cannot be ignored. An ambulance should be called in the following cases:
- aching pain that lasts for an hour;
- dull pain accompanied by coughing and vomiting (often with blood);
- stabbing pain that does not go away for more than half an hour and gets worse;
- sudden sharp pain.
So, we have looked at the most common situations in which pain occurs in the left hypochondrium when taking a deep breath. It can also occur with movement, coughing, sneezing, and even at rest. In most cases, the cause of pain is serious dysfunction of vital organs: heart, stomach, lungs, pancreas, spleen.
And sometimes we are talking about critical conditions when a person needs help urgently. Therefore, if there is pain in the left chest, you cannot endure it and wait for it to go away on its own. You need to contact a doctor as quickly as possible, establish the cause and eliminate it before unwanted complications and consequences appear.
Heart pathologies
In the human body, the diaphragm is closely connected with the central circulatory organ. That is why, in the presence of cardiac pathologies, the process of inhaling air can be accompanied by pronounced painful sensations.
As a rule, patients in this case are diagnosed with one of the forms of cardiomyopathy. The most dangerous is considered to be dilation, in which the heart becomes flabby and cannot fully perform its function. The causes of this pathology are unknown.
In addition to pain when breathing on the left under the ribs, patients complain of shortness of breath after performing any physical activity, dizziness, a constant feeling of weakness, swelling of the lower extremities, sleep disturbances, and frequent episodes of fainting.
For cardiomyopathy, symptomatic treatment is carried out. The prognosis for the presence of the disease is usually unfavorable. Until recently, the only option for patients was a donor organ transplant. But the difficulty is that the queue of patients is extremely impressive. However, finding a donor heart is almost impossible. Currently, the stem cell treatment method is used in practice.