Chest pain is a rather unpleasant sensation that can be life-threatening. It is important to react in time to prevent a disaster. The main causes of chest pain: heart, respiratory organs, problems with muscles and bones. Let's look at all possible options.
When pain is deadly
The cause of chest pain is the heart
Why else can you feel chest pain?
Useful VIDEO on chest pain
Diagnosis of chest pain
Spinal problems
Chest pain when inhaling often appears due to pathologies of the spinal column. The fact is that the spine contains a huge number of nerve endings, inflammation and/or infringement of which can lead to pain radiating into the chest, causing pain when inhaling.
Osteochondrosis
It is a serious disease that affects the cartilage tissue of the spinal column. The intervertebral discs thin out and become less durable, resulting in a decrease in the distance between the vertebrae. Because of this, nerve tissue is pinched, which leads to pain. If the pain intensifies when you inhale, this may indicate that the thoracic spine is affected.
Intercostal neuralgia
Sharp acute pain in the chest when inhaling occurs when compression or irritation of the nerve roots that are located between the ribs occurs. This condition can last literally a couple of minutes or drag on for a day, preventing the person from taking a deep breath and causing significant discomfort. The pain can come on suddenly, for no apparent reason, and often makes a person worry and think that the heart is stabbing, although the reason is completely different.
Fractured ribs
If you have recently been injured and experience pain in your chest when you inhale, you may suspect a rib fracture. This is a dangerous condition, and with a visit to a traumatologist
/
the surgeon
cannot hesitate, since, among other things, you may have damage to internal organs. The fracture itself, depending on its severity, can provoke additional damage.
When should you see a doctor?
Pain in the heart area is a dangerous symptom that always requires additional diagnostics and a search for its causes. It is important to understand that diseases of all organs and systems require appropriate attention and treatment. But in some cases, you can independently determine the danger of a developing condition.
For the first time in life, an acute attack of pain in the heart area always requires contacting emergency medical services. The same applies to people with previously diagnosed angina pectoris (a form of angina in which pain occurs only against the background of a trigger and is eliminated by taking nitroglycerin) if taking a previously effective dose of nitrates did not relieve the pain within 15 minutes of taking the drug.
The absence of a serious danger may be indicated by pain or discomfort behind the sternum, which occurs immediately after a sharp turn or tilt of the body, eating or taking a horizontal position after eating. This also includes short-term attacks of mild pain that occur against the background of strong experiences or stressful situations. In such cases, a scheduled visit to the doctor is recommended.
Important! Regardless of the characteristics of the pain, the presence or absence of radiation, other symptoms or provoking factors, diagnosis is necessary. Only a doctor's examination, laboratory tests, ECG and other studies can help accurately determine the origin of pain and exclude life-threatening conditions.
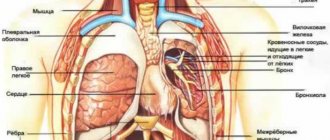
Diseases and pathologies of the heart
Often, when inhaling, pain appears in the left chest if there is a heart problem. In this case, there may be quite a few reasons, and only an experienced pulmonologist
.
Pericarditis
Pericarditis is an inflammation of the heart sac - the outer lining of the heart, which is called the “pericardium”. The nature of such a disease can be infectious, rheumatic, or result from a heart attack. With pericarditis, not only does pain appear when inhaling on the right or left side of the chest; the condition is often accompanied by severe weakness, as well as shortness of breath if fluid leaks between the layers of the pericardium. Pericarditis with effusion can develop into suppuration and cause compression of the heart by accumulated secretions.
Pulmonary embolism
This is the name of the condition when the pulmonary arteries stop passing blood, i.e. clogged. This is a consequence of a blood clot (thrombus), drops of fat, bone marrow, catheter element or other foreign body entering the arterial bed. In this case, when inhaling, pain occurs in the left side of the chest, and the person needs urgent medical attention.
Sources
- Trukhan D.I., Davydov E.L. “Chest pain: current issues in clinical diagnosis and treatment of angina” // Consilium Medicum – No. 17(10) – 2015.
- Yu. V. Vasiliev “Pain behind the sternum: differential diagnosis, treatment” // Cardiology - 2006.
- Ruigomez A., Rodriguez LA, Wallander MA et al “Chest pain in general practice: incidence, comorbidity and mortality” // Fam. Pract. – Vol. 23 – 2006
- A.N. Belovol, I.I. Knyazkova “Clinical approaches to the diagnosis of chest pain” // Current preparations and technologies – No2 (78) – 2011 r.
- Nilsson S., Scheike M., Engblom D. et al. “Chest pain and ischemic heart disease in primary care” // Br. J.Gen. Pract. – Vol. 53 – 2003.
Pulmonary pathologies
There are many causes of pain in the sternum during inspiration, which are associated with pathologies of the respiratory system. It is worth considering some cases when pain may appear when inhaling.
Pneumothorax
It is an accumulation of gas in the pleural cavity, which leads to the collapse of lung tissue, from which the process occurs. In this case, the mediastinum shifts towards the healthy organ, the blood vessels are compressed, which leads to respiratory disorders, and blood circulation is also impaired. Often pneumothorax is traumatic, and can also be a consequence of spontaneous disruption of tissue integrity.
Pleuropneumonia
If chest pain appears when taking a deep breath, this may indicate progressive pulmonary pneumonia, when the pleura is involved in the pathological process. This disease is very dangerous; Along with pain when inhaling, a person notes the inability to take a deep breath and general weakness.
Pleurisy
Inflammation of the serous membrane of the lungs is called pleurisy and may be accompanied by pain when inhaling. In this case, a person not only has pain in the chest area when inhaling, but also shortness of breath, cough, pulmonologist
notes pleural friction noise when listening to breathing, and the temperature also rises.
Lungs' cancer
Pain in the middle of the chest when inhaling can occur if a malignant neoplasm has developed in the lungs. Pain syndrome is a consequence of tissue proliferation and compression of neighboring structures. To determine why your chest begins to hurt when you inhale and move, first consult a neurologist
, who, after a survey and examination, will refer you to a specialist.
Prevention
Prevention of pain in the heart area when inhaling is complex and is aimed at strengthening the entire body as a whole and the cardiovascular system in particular. First of all, this is a healthy lifestyle: a rational schedule of work and rest, proper nutrition and moderate physical activity. Cardio training and yoga help control breathing and strengthen the heart muscle.
However, if you have concomitant diseases, it is important to coordinate all your actions with your doctor. For example, the doctor will help you control the level of fat and cholesterol you consume. This is important because they are part of cell membranes, and completely avoiding their consumption can be harmful.
What tests to do if your lungs hurt?
The main examination to determine the cause of lung pain is a history and x-ray. An imaging test in the form of a chest x-ray is then usually performed, as well as an ECG and arterial oxygen saturation (saturation measurement) using a small device called a pulse oximeter. If reflux or other digestive system diseases are suspected, your doctor may order an upper endoscopy or gastroscopy. Based on the research results, further measures are planned and therapy is selected.
Diagnostics
Tingling in the chest has dozens of etiological factors, so a detailed examination is necessary to clarify them. Several specialists are involved in the diagnostic search: neurologist, cardiologist, therapist, etc. To determine the cause of stabbing pain in various parts of the chest, a set of laboratory and instrumental methods is selected, which includes:
- Electrocardiography.
ECG is used to diagnose rhythm disturbances: extrasystoles, blockades. The cardiogram also shows signs of ischemic heart disease, myocarditis, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. To assess the functional class of angina, cardiology specialists prescribe a stress test (ECG with dosed exercise). - Ultrasonography.
If abnormalities are detected during electrocardiography, echocardiography is performed. Ultrasound of the pleural cavity is informative for detecting pleurisy. For unclear tingling in the lower chest, sonography of the abdominal organs is performed to identify an inflammatory process or signs of an ulcerative defect. Ultrasound screening is the first stage in diagnosing breast diseases. - X-ray methods
. Chest radiography is a standard method that visualizes pathological changes in the pulmonary parenchyma, pathognomonic changes in the configuration of the heart. If joint damage is suspected, an x-ray of the ribs is indicated. To clarify the diagnosis, a chest MRI is done. - Blood tests.
The hemogram can reveal anemia and nonspecific signs of inflammation. Biochemical blood tests help diagnose coronary diseases (based on specific changes in the lipid spectrum). If there is a strong stabbing sensation in the heart area, it is advisable to examine myocardial markers.
Considering that a common cause of tingling in the chest is disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, the patient is recommended to undergo a complete neurological examination with a check of the vegetative status. In rare cases, electrophysiological methods are prescribed: EEG, electroneuromyography (ENMG). According to indications, a psychiatrist is involved in the diagnostic search, who can identify signs of masked depression.
Consultation with a therapist for tingling in the chest
Why does my chest hurt?
Cardioneurosis
Tingling in the left half of the chest, especially in the projection of the heart, most often occurs with neuroses.
Uncomfortable sensations in the chest are provoked by mental fatigue, stress, and are occasionally observed during physical exertion. Patients tend to talk in detail about their condition: they select many words to describe the pain (stabbing, aching, squeezing). Simultaneously with the tingling sensation, a sinking heart, chills or hot flashes are felt. As a rule, a person mistakes the symptoms of cardioneurosis for signs of a serious cardiac disease. There is increased anxiety and fear of death, which aggravate the course of the disease. Stitching sensations bother the patient several times a day, last no more than 1 hour, and are of mild or moderate intensity. Tingling attacks can disappear as suddenly as they begin.
Somatized depression
For mental disorders, tingling and cardialgia with a pinching feeling in the chest (“precardiac melancholy”) are pathognomonic. Symptoms often appear in the morning, immediately after waking up, but as depression progresses, the diurnal periodicity is lost. Tingling is complemented by autonomic changes: hyperhidrosis, bradycardia or tachycardia. The psycho-emotional state is characterized by irritability, fatigue, and apathy.
Cardiovascular diseases
Tingling on the left side of the chest is observed in organic and functional cardiac diseases. Usually it is the first symptom of pathology. The intensity of the sensations varies depending on the cause. With organic damage, there are strong “lumbago”, forcing the person to freeze and put his hand to the pre-cardiac region. Typical cardiac factors for chest tingling:
- Arrhythmias.
Rhythm interruptions are manifested by mild and short-term stabbing sensations, which are clearly localized in the chest. Against their background, the patient experiences freezing or, conversely, too fast heartbeat. Symptoms have no clear provoking factors and can appear at any time of the day. - Cardiac ischemia.
IHD is characterized by intense stabbing pain, which is felt behind the sternum or in the entire left half of the chest, radiating to the shoulder blade and arm. The attack lasts 5-10 minutes and is quickly stopped by taking nitrates. If the symptoms give way to excruciating burning or pressing pain, there is a risk of unstable angina, progressing to myocardial infarction. - Inflammatory processes.
Tingling in the chest of moderate strength, which does not have a clear localization, is typical of myocarditis, endocarditis, pericarditis. The symptom may be related to a bacterial or viral infection suffered a couple of weeks ago. Patients also complain of shortness of breath, increased fatigue, and fever. - Cardiomyopathies.
Non-inflammatory myocardial damage is characterized by a long-term, asymptomatic course. A person occasionally notices tingling in the precordial area, shortness of breath during physical exertion, and interruptions in heart function. Stitching sensations do not radiate and are mild or moderate. - Heart defects.
Tingling in the chest occurs in pathologies with unchanged or partially altered blood circulation, which is not critical for the condition. In addition, shortness of breath, attacks of tachycardia or cardiac arrest, cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle and fingertips are noted.
Tingling in the chest
Anemia
A stabbing sensation in the chest on the left is one of the components of anemic syndrome caused by a lack of hemoglobin and insufficient oxygen saturation of tissues. Discomfort is most pronounced during physical activity, and with moderate and severe anemia it also occurs at rest. In addition to tingling, there is pale skin, frequent attacks of dizziness and tinnitus, and fatigue.
Respiratory diseases
Strong stabbing sensations are typical for pleural pain, which develops against the background of dry pleurisy, pneumothorax, and carcinomatosis. The tingling is one-sided, sometimes radiating to the interscapular area. The pain is aggravated by coughing and laughing. Therefore, the patient lies on his side on the affected side, trying not to move for longer. The symptom is accompanied by shortness of breath, lag of half of the chest in breathing.
Tuberculosis
In the presence of a primary tuberculosis complex and involvement of the intrathoracic lymph nodes, patients feel a slight tingling sensation on the side of the active process or in the center of the chest. The symptom is supplemented by night sweats, cough with scanty sputum. When tuberculosis is complicated by pleurisy, sharp stabbing pain occurs on one side of the chest. The pain intensifies with a deep breath and bending the body in the opposite direction.
Intercostal neuralgia
When the intercostal nerves are damaged, a person experiences a sharp tingling and shooting pain, which is localized in one place in the chest or spreads along the ribs. The stabbing sensation sharply intensifies when palpating the intercostal spaces, taking deep breaths and turning the body. The attack lasts a couple of minutes, during which time the patient freezes and tries not to breathe for fear of worsening the pain.
The clinical picture of intercostal neuralgia is complemented by paresthesia (“crawling”) and numbness on the affected side of the chest. Skin hyperemia and local hyperhidrosis are less common. Tingling attacks that occur on the left side of the chest resemble cardiac pain. Middle-aged and elderly patients often try to relieve discomfort with nitroglycerin, but it has no effect.
Fibromyalgia
This disease is characterized by tingling of varying intensity throughout the chest. Pain is also felt in the abdomen, arms and legs - patients complain that “it hurts everywhere.” Symptoms appear for no apparent reason and last for several weeks or even months. On the skin of the chest, a feeling of “crawling”, numbness, and burning may occur. With fibromyalgia, pain is complemented by weakness and malaise, insomnia, and depression.
Inflammatory diseases of the ribs
Tingling may be one of the manifestations of Tietze syndrome. Stitching sensations occur near the sternum, usually on one side. They begin suddenly and become more severe with awkward movements, coughing and sneezing. Symptoms persist for several years with alternating periods of exacerbations and remissions. Tingling in the chest also occurs with aseptic periostitis and osteomyelitis of the ribs.
Gastrointestinal pathologies
With lesions of organs located in the upper abdomen, tingling in the lower, less often middle, parts of the chest is often disturbing, which is due to the peculiarities of innervation. A stabbing sensation in the middle of the chest, above the epigastrium, is characteristic of hyperacid gastritis, gastric ulcer. With cholecystitis and hepatitis, tingling is observed in the chest on the right. There is a clear connection between discomfort and food intake and errors in diet.
Breast diseases
With mastopathy, a woman complains of pain and tingling in one or both mammary glands. Unpleasant sensations intensify before menstruation, during which time the breasts become very sensitive. Sometimes the stabbing pain has a clear localization, which is typical for the focal form of the disease. Similar symptoms occur with a cyst or fibroadenoma of the mammary gland.
Diseases that cause pain in the lungs
Pain in the lungs is most often a manifestation of a certain disease, and ignoring such symptoms means not worrying about your health. People feel pain in different ways: sometimes they cut, sometimes they prick, sometimes they press. The location of the pain is also an important factor. By summing up all the symptoms of pain in the lungs, it is possible to make a correct diagnosis, since there are many diseases in which pain in the lungs is felt.
Diseases in which a person experiences pain in the lungs:
- Pneumonia;
- Bronchitis;
- Acute tracheitis;
- Lobar pneumonia;
- Pleurisy;
- Spontaneous pneumothorax;
- Lungs' cancer;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Pain of bone, joint or muscle origin;
- Heart diseases;
- Pericarditis;
- Pulmonary embolism;
- Aortic diseases;
- Pancreatitis;
- Stomach and duodenal ulcers;
- COPD