Periodic or constant pain in the chest when swallowing can be a sign of many problems and diseases - from a cold to a foreign body in the human body. The main reason is a pathological process in the digestive system. Any problems with the gastrointestinal tract most often arise and develop unnoticed and practically asymptomatic. But if, when swallowing, it hurts in the middle of the chest or radiates to other areas, you cannot ignore it. Trying to relieve pain and self-medicating is not recommended. It is better to consult a general practitioner
who will determine the exact cause and prescribe the correct treatment. Everything should happen under the supervision of a specialist.
Chest pain when swallowing: causes
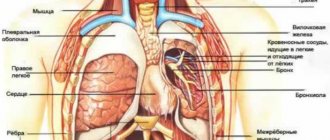
Painful discomfort can be associated with various disorders in the body. Pain when swallowing is caused by viruses and colds, allergies, foreign bodies in the throat or esophagus, as well as diseases of various systems and internal organs. If you experience pain while eating or swallowing, then most likely there are problems with the esophagus, and the pain radiates to the sternum. The problem may be associated with disturbances in the contractions of the esophagus, with the emergence and development of pathologies, with the passage of food into the stomach, with inflammation or erosion of the mucous membrane, etc. What do you need to remember? If, when swallowing food, pain appears in the chest area (on the left, right or in the middle), then this rarely indicates problems and diseases of the chest - more often there is a symptom of gastrointestinal tract pathologies, including oncological ones.
What examinations are necessary to undergo for an accurate diagnosis?
If you feel discomfort in the heart area during or after eating, seek help from a doctor - a cardiologist or gastroenterologist. Mandatory priority examinations: general and biochemical blood tests, ECG, echocardiography to detect abnormalities in the structure of the heart. In addition, the gastrointestinal tract is also diagnosed: they do an ultrasound of the abdominal organs, fibrogastroduodenoscopy to identify pathologies of the stomach lining, and contrast radiography to exclude a hiatal hernia. For the purpose of differential diagnosis, medications are prescribed (proton pump inhibitors, which reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid).
All research methods are prescribed only by a doctor after carefully collecting a medical history, examination, palpation and auscultation data. If gastrocardial syndrome is suspected, endoscopic examinations are contraindicated, since vagal stimulation and sudden cardiac arrest are possible.
Possible diseases
What led to the pain and how serious the problem is, only a specialist can say. Therefore, if it is difficult and painful for you to swallow, do not delay visiting a doctor, because you risk missing the onset of a serious illness and worsening your health condition.
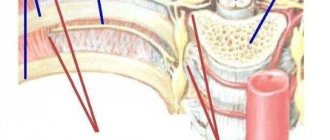
Esophageal diverticula
Diverticulum is a dangerous disease that can lead to a large number of suppurations and ulcers in the neck and the development of pneumonia. It all starts with the fact that the walls of the esophagus are stretched due to the occurrence of hernial formations. They interfere with normal swallowing of food and cause severe pain. The first signs of the disease are bad breath, sore throat and further painful swallowing.
Esophagitis
This is an inflammatory process in the esophageal mucosa that causes pain when eating. Pain syndrome occurs in separate parts of the esophagus, or it hurts entirely. The intensity and nature of the pain resembles an attack of angina pectoris and responds with pain behind the sternum.
Esophagospasm
A disease of esophageal motility, in which painful sensations appear both when eating and drinking water, and at rest (for example, during sleep) or under severe stress when a person is worried. Pathology develops when the nerve plexuses are disrupted or when the mucous membrane is damaged.
Cardiospasm
Pathology develops when a narrowing and subsequent expansion occurs in the lower part of the esophagus. When the situation worsens, the patient develops anemia and vitamin deficiency, as well as constant belching and nausea.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
This is a chronic disease that manifests itself in the form of hydrochloric acid from the stomach entering higher parts of the digestive tract. In this case, the mucous membrane of the esophagus is constantly injured, and the person experiences more and more pain when swallowing. The pathology is accompanied by a severe cough and constant sore throat. The disease can be recognized if heartburn torments every day for several hours a day and for several months in a row. If left untreated, the disease will lead to the development of ulcers and possibly esophageal cancer.
Action tactics
If the patient experiences pain in the heart area while eating, it is advisable to stop eating and take a comfortable body position.
When a patient has such an attack for the first time and it is accompanied by pressure or burning in the chest, tachycardia, shortness of breath, they seek medical help.
Some patients know that vomiting alleviates the condition, so they induce it artificially.
To prevent recurrent attacks, regardless of the cause of pain, stick to a diet, eat small portions, but more often. Food should be thermally processed and neutral; it is important to chew food thoroughly. Depending on the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes medications: antispasmodics, proton pump blockers, antibiotics if Helicobacter pylori infection is detected. For organic lesions of the esophagus, surgical treatment is recommended.
Esophageal injuries
If a patient comes to the doctor asking why there is pain in the middle of the chest when swallowing, then the doctor must determine the cause. This is often associated with trauma to the esophagus, which may be:
- received due to various types of damage: gunshots, stab wounds, incised wounds, etc.;
- associated with internal pathological processes: neoplasms, narrowing, expansion in different areas (neck, thoracic region, etc.);
- associated with various pathologies of body systems, for example, damage to large vessels;
- received due to damage during surgical treatment, for example, during intubation, neck injuries, etc.
The type and duration of treatment depends on the type of injury and the severity of the damage.
Feeling of a lump in the stomach
Gastritis
14371 21 August
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Feeling of a lump in the stomach: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
The feeling of a coma in the stomach is described when one experiences a feeling of heaviness, discomfort and fullness in the stomach, even when it is only slightly filled. Sometimes patients find it difficult to determine the exact location of the coma and point to the lower third of the sternum or solar plexus. In some cases, a feeling of a lump and cramps in the stomach may occur on an empty stomach.
Types of feeling of a coma in the stomach
A feeling of heaviness or coma in the stomach can be an independent symptom, but may be accompanied by other unpleasant sensations. Sometimes it is heartburn, sour belching, bloating, constipation.
In some cases, a feeling of a lump appears when swallowing
, making it difficult for chewed food to pass through.
In addition, patients may complain that food did not enter the stomach, but stopped in the esophagus.
In such patients, vomiting of unchanged food is possible. When describing symptoms, you should pay attention to the time of onset of discomfort - before
or
after eating
.
The patient may feel heaviness in the stomach with pain or heartburn, on an empty stomach or after eating, and night pain also occurs.
Sometimes the sensation of a lump in the stomach occurs
regardless of food intake
.
In such cases, they complain of stomach spasms
, sometimes accompanied by a feeling of a lump in the throat.
What diseases cause a sensation of a lump in the stomach?
Eating more than your usual amount of food
, accompanied by a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the stomach. This condition is not a manifestation of the disease and goes away on its own after some time.
It should be noted that stomach capacity varies depending on eating habits.
People who are small or
have undergone gastric resection
can eat a small portion, otherwise they will not only experience a feeling of heaviness or fullness in the stomach, but also vomiting.
A sensation of coma may occur when consuming foods that cause excess gas.
, as well as
food that is difficult to digest
(salads with mayonnaise, fatty, fried and smoked dishes) and
highly carbonated drinks
.
When eating dry and hastily,
an unpleasant sensation in the epigastric region is caused by poor processing of the food bolus with saliva and insufficient secretion of gastric juice.
However, a feeling of coma or discomfort in the stomach, or more precisely, in the epigastric region, may appear after eating even a small amount of food
.
This condition can be caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract or other reasons.
First of all, they assume indigestion, or functional dyspepsia. Its symptoms most often include pain and discomfort immediately after eating, a feeling of heaviness and fullness in the stomach, heartburn, belching, nausea, sometimes vomiting, reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus, bloating and bowel dysfunction.
Dyspepsia can be a symptom of both functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and organic diseases.
Functional causes of dyspepsia are often caused by errors in diet and medications.
Iron ions have an irritating effect on the gastric mucosa, which is most pronounced when taking medications based on ferrous iron. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, which are systematically taken for rheumatic and non-rheumatic diseases of the musculoskeletal system, also cause undesirable effects: heaviness and discomfort in the stomach, nausea, vomiting, and dyspeptic disorders.
Neurological disorders
(neuroses, depression), psychological trauma almost always affects the state of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to impaired motility.
Functional dyspepsia is not accompanied by erosive or ulcerative lesions of the stomach; its symptoms disappear when the general state of health is normalized.
One of the common causes of discomfort in the stomach immediately after eating is
gastritis
. It is accompanied by functional and inflammatory processes that have a negative effect on the gastric mucosa. Symptoms of gastritis include heaviness and pain in the stomach, indigestion, nausea, heartburn, sour belching and bloating when eating any food. The inflammatory process leads to atrophy of the mucous membrane and disruption of the glands that secrete gastric juice.
Insufficient gastric juice and weak peristalsis of the stomach and intestines make it difficult to digest food.
Gastritis is often accompanied by dyspepsia. In addition to a feeling of heaviness and aching pain in the epigastric region after eating, poor appetite, weakness, fatigue, and irritability are noted. When pressing on the abdomen, a dull pain appears in the projection of the stomach.
Impaired motor-evacuation functions
upper digestive tract is always accompanied by a feeling of coma or a feeling of heaviness in the stomach. Disorders of esophageal motility are usually caused by incoordination of the esophageal sphincters. Uncoordinated work of the esophageal muscles can lead to a delay in the bolus of food on the way to the stomach, the reflux of food particles into the respiratory tract, and reflux (return of stomach contents into the esophagus). Impaired gastric motility leads to slow emptying, which is accompanied by a feeling of heaviness and fullness even with a small amount of food consumed, pain in the epigastric region, heartburn, nausea and vomiting.
Motility disorders of the esophagus and stomach may be associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, tumors and stenoses (narrowings), metabolic disorders (hyperkalemia, hypercalcemia), postoperative complications of gastrectomy, taking certain medications (opiates, antidepressants, hormones), alcohol and nicotine .
Peristalsis worsens with a sedentary lifestyle and with age.
Stomach cancer can also cause symptoms such as a feeling of heaviness or a lump in the stomach. Moreover, depending on the location of the tumor, its manifestations vary. If the tumor is located closer to the esophagus, problems with swallowing food occur. This is accompanied by increased salivation, nausea, vomiting, and pain in the epigastric region. When the tumor is localized in the lower parts of the stomach, closer to the duodenum, a prolonged feeling of heaviness after eating and bloating is characteristic. When burping, a putrid odor may be felt.
Which doctors should you contact if you feel a lump in your stomach?
If there is a constant feeling of a lump in the stomach or a feeling of heaviness, it is necessary to contact or to make a preliminary diagnosis. The gastroenterologist may also refer the patient to an oncologist. A consultation may also be required.
Diagnosis and examination if you feel a lump in the stomach
First of all, clinical blood and stool tests are necessary for differential diagnosis.
Symptoms
The pathology has quite varied symptoms, which largely depend on the type of damage, causes, concomitant diseases and duration of the disease. The main symptoms include:
- bad breath, burning, heartburn, cough, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing;
- sharp pain (most often behind the sternum);
- low pressure;
- decreased appetite, weakened immune system, gastrointestinal problems;
- pale skin color, blue mucous membranes, etc.
The first and most obvious symptom is problems with swallowing.
conclusions
Do not neglect the importance of the symptom when your heart hurts after eating. This can be a signal of serious illness or interfere with normal life activities. If discomfort occurs in the chest while eating, consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary examinations and offer the correct solution to the problem with the help of medication or surgical treatment. Diet and psychotherapy have a significant effect. If you are worried about tachycardia after eating, we recommend that you read our expert’s article on this topic.
Diagnostics
The doctor will determine which examinations will be needed during the initial consultation. To do this you need to see a therapist
who will give recommendations and directions, or you can immediately go to
a gastroenterologist
who will prescribe an endoscopy of the stomach and esophagus.
X-rays (with and without contrast agent), ultrasound
of certain internal organs, checking the functioning of the cardiovascular system and additional studies and tests (for each specific case) may also be prescribed.