A microstroke is a pinpoint injury to the structure of the brain. They mean a tiny cerebral hemorrhage. Unfortunately, due to the fact that it is not large in scale and is practically invisible, patients rarely give it due importance and do not go to the hospital.
Symptoms rarely make themselves felt longer than 24 hours. After this, it goes away on its own, and it is very easy to attribute it to fatigue, weather dependence or similar phenomena. Moreover, at subsequent scheduled visits to a neurologist, if you do not report the incident, it is impossible to identify signs of a microstroke in women.
The Yusupov Hospital welcomes specialists of the highest category, doctors and candidates of medical sciences, whose specialization is pathology of the nervous system. They resort to innovative methods, including neuroimaging. This method combines several techniques, thanks to which it is possible to assess the functions, structure and biochemical characteristics of the brain. Thus, it is possible to use equipment to record which areas are already damaged and which are at risk of necrosis in the future.
The difference between a stroke and a microstroke
The clinical pictures for ischemic stroke and microstroke are similar, but differ in scale. Doctors distinguish two forms of stroke. In one version, a heart attack occurs: a section of the brain dies due to disruption of blood flow in the brain due to a blockage of a vessel. In the second situation, the death of part of the brain structures occurs due to the rupture of one of the arteries.
Unlike ischemic stroke, with a microstroke a very small area dies. Symptoms of stroke and mini-stroke differ in women, so if they do not know how this disease progresses, they may ignore health changes. If you miss the initial warning signs, then one attack on your feet can lead to a series of repeated ones.
Expert opinion
Author: Polina Yuryevna Vakhromeeva
Neurologist
A microstroke manifests itself in the form of neurological disorders, the nature of which depends on the area of the brain affected. In general, attacks of minor and major strokes are similar. Possible manifestations: numbness of half the face, inability to smile, acute headache and dizziness, nausea and vomiting, loss of coordination.
After an attack of a micro-stroke, patients do not always immediately feel a deterioration in their general condition. Symptoms regress within 24 hours, and the neurological deficit is completely leveled. However, without follow-up therapy, the risk of a recurrent attack increases significantly. Treatment must be provided immediately and in full.
Depending on the cause of the stroke, drug therapy is prescribed individually for each patient. According to indications, vasodilating, antihypertensive, thrombolytic, decongestant and nootropic drugs are used. You cannot start taking medications on your own, since without an accurate diagnosis it is impossible to predict the effect of the therapy used. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital Neurology Clinic conduct an examination and prescribe adequate treatment based on MRI diagnostics.
Procedures and operations
Treatment tactics depend on the degree of narrowing of the carotid arteries. Patients with severe (above 70%) stenosis of the carotid artery due to atherosclerosis are referred to a vascular surgeon for the purpose of stenting or carotid endarterectomy . Moreover, carotid endarterectomy should be performed within the first week after a microstroke. This tactic can reduce the risk of stroke and prevent disability and even death of the patient.
With a lesser degree of narrowing, surgery is used if the patient has already had transient disorders or strokes. Endarterectomy is the removal of cholesterol deposits from the wall of the carotid artery. This is a critical vascular operation in which the error is difficult to correct. During the operation, an incision is made in the neck area, the carotid artery is exposed and clamped. Endarterectomy begins with the common carotid artery, moving to the internal carotid artery. An incision in the artery is made along the outer surface 2.0 cm proximal to the plaque and ends behind the end of the plaque.
During the operation, the plaque with the intima and media is separated along the entire circumference of the artery and circularly intersected. To remove the plaque, use a flat, thin spatula. After removing the plaque, the patency of the artery is checked with a bougie and pieces of intima are removed. After endarterectomy from the external carotid artery, the same is done on the internal carotid artery. The arterial incision is closed with a patch. Auto-vein or synthetic material is used for the patch. At the end of the operation, test bleeding is performed from all arteries (external, common and internal carotid) before applying the final suture. Then the clamps are removed from the arteries in a certain order: first from the internal, from the external, and then from the common carotid. The subcutaneous muscle is sutured and sutures are placed on the skin.
Causes of female microstroke
The risk group includes people who have previously been diagnosed with:
- hypertension;
- arrhythmia;
- diabetes;
- thrombosis.
Most often, patients with abnormalities in the functioning of the cardiovascular system experience microstroke. In this case, you should not expose yourself to extreme physical activity. Additional risk factors are alcohol abuse, smoking and drug use. They provoke a pressure drop, followed by a spasm of cerebral vessels.
One of the risk factors for developing this disease is obesity. In combination with an addiction to fatty and spicy foods, excess weight negatively affects the condition of blood vessels.
Before taking hormonal contraceptives, it is important to obtain an appropriate prescription from a gynecologist. If you use oral contraception without regard to test results and other indicators, there is a possibility of causing circulatory problems.
Features and types of disease
A stroke often occurs suddenly, literally within a few minutes. Symptoms can persist for more than a day and can lead to death. According to statistics, the number of deaths from vascular pathologies of the brain is in second place among all cardiovascular diseases. And the percentage of disability is the highest.
In just one year, about 450,000 strokes occur in Russia - it affects one Russian every minute and a half.
Stroke is a broad concept that includes such types as:
- Cerebral infarction, or ischemic stroke. Common in older people who have had heart attacks. It develops when the blood vessels that supply brain cells become clogged. They die without receiving the elements important for life.
- Bleeding in the brain, or hemorrhagic stroke. Usually diagnosed at 45-60 years of age. Its appearance is promoted by hypertension, cerebral atherosclerosis, hypertension, emotional and physical stress. Hemorrhage occurs after loss of vessel integrity.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage. The age of the disease is 30-60 years. Those at risk include smokers, alcoholics, high blood pressure and excess weight. Hemorrhage occurs when a thinned artery ruptures.
Yes, strokes often target older people. But recently it has been diagnosed in young people as well. Although the stroke of a 30-year-old person differs from that of a 60-year-old, mainly in the course of the disease. Because the tissues of older men and women wear out significantly, the brain is affected more quickly in older age. Therefore, the likelihood of fully recovering from a stroke is much less than dying.
The difference between male and female strokes
Does stroke have a gender preference? Both men and women are at risk. Indeed, to a greater extent, the development of the disease is facilitated by an incorrect lifestyle, bad habits and stressful situations.
But statistics still indicate a difference in the number of sick men and women:
- between the ages of 18 and 40 years, pathology occurs less frequently in women;
- after 50 and 60 years - on the contrary, more often.
The fact is that until the age of 50, the female body is protected by the hormone estrogen. After menopause, women lose such protection, have a more difficult time surviving the disease and are more likely to die after a stroke.
First signs
It is important to know how a microstroke manifests itself in women so as not to miss its onset. Not everyone takes severe headaches seriously, but tries to cope with it on their own and uses painkillers. Analgesics do not help with painful sensations if their source lies in vascular pathology. In this situation, the pain appears and disappears throughout the day, as well as the feeling of nausea along with dizziness.
Migraines progress in a very similar way, and patients often reassure themselves that nothing terrible is happening to them. What an attack and a migraine have in common is that the victim reacts poorly to bright lights and loud sounds. However, signs of a microstroke in women also appear as follows:
- numbness of the limbs;
- speech difficulties;
- inability to control facial expressions;
- fainting.
Headache during a microstroke is often accompanied by poor coordination of movements, weakness, increased sweating and chills. Often, along with this, patients are bothered by discomfort in the heart area and high blood pressure.
The distinctive symptoms of a microstroke in older women are a serious decrease in cognitive abilities and sudden onset of vision problems. It should also be understood that in old age there is a high probability of relapse. In this regard, the most dangerous are the first three days after an attack: the overwhelming number of relapses occur during this period.
To understand how to recognize a micro-stroke in women, you should remember that the symptoms appear almost simultaneously, but last no longer than 24 hours. It is important to know that the signs of stroke and micro-stroke in women are similar. As a rule, after a sharp deterioration in health, everything seems to return to normal. But even if you feel that everything is fine, it is important to play it safe and see a doctor who can tell you for sure whether everything is fine.
Micro-stroke “on your feet”
Since the symptoms of a mini-stroke can last for a fairly limited time, some resilient men can suffer them without even stopping their daily activities. It seems to them that nothing terrible is happening - just a slight malaise, which goes away after an hour. Accordingly, neither a visit to a doctor nor adequate treatment occurs here.
This is very dangerous, because an ignored attack often becomes the reason for its rapid recurrence or, in general, the main factor in the development of cerebral ischemia. If this happens, the consequences will be very serious, including disability, and treatment will take several months or even years.
Symptoms of microstroke in women
A microstroke is periodically accompanied by nonspecific symptoms that indicate not only this disease. However, their appearance is a reason to immediately check your health.
Cerebral hypertensive crisis
During a crisis, blood pressure rises to high levels in an extremely short time. With such a significant difference, blood supply to parts of the brain is disrupted. A sharp jump is caused by various reasons, including excessive physical activity, abuse of bad habits, severe stress or overwork. In the event of a crisis, you should make an appointment for examination as soon as possible.
The main characteristic of a crisis is a sharp and significant increase in pressure in a very short time.
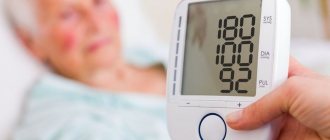
Suspicion of cerebral hypertensive crisis is diagnosed if the systolic (“upper”) pressure exceeds 180 mm Hg. Art., and diastolic (“lower”) overcomes the mark of 100-120 mm Hg. Art. Hypertensive patients easily ignore such a change, however, sudden changes in such a short period of time are not considered normal and are a good reason for going to a medical facility.
Transient ischemic attack
Transient ischemic attack (TIA) is a temporary acute disturbance of blood circulation in the brain. As a rule, it goes away within 24 hours. One of the most common symptoms of transient ischemic attack is visual disturbances. The patient temporarily suffers from the fact that he begins to see worse, stops seeing altogether, or loses this ability in one of the eyes. It is possible that vision loss is associated only with the upper or lower half of the visual field. Often, visual distortions last only a few seconds, but are repeated several times in one day.
Also, a transient ischemic attack affects the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. Some patients note unsteadiness of their own gait, dizziness, and instability.
Occasionally, TIA causes amnesia due to loss of short-term memory. In this case, memories of the past are retained, but the last few minutes or hours are completely lost from memory. As a rule, information about these events is returned within 24 hours.
Acute hypertensive encephalopathy
Hypertensive encephalopathy is a pathology that is a complication of hypertension. Its clinical picture develops in just a few hours.
First of all, a person is bothered by a bursting headache of varying severity. It is accompanied by nausea, vomiting and possible loss of consciousness. Some note visual disturbances: blurred vision and spots before the eyes.
In a particularly severe form, acute hypertensive encephalopathy turns into convulsions and leads to coma.
General information
Cerebrovascular diseases , which include stroke and transient ischemic attack (ministroke), are an important medical and social problem. What is a microstroke? This is a short-term episode of neurological dysfunction caused by temporary cerebral ischemia, which does not lead to changes in this part of the brain and the development of stroke .
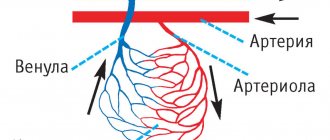
The arterial cerebral blood supply is formed from two vascular systems: vertebrobasilar and carotid. The carotid basin is formed by the external and internal carotid arteries, which arise from the common carotid artery, or rather from its carotid sinus. The internal carotid artery is a larger branch of the common carotid artery, which enters the skull, passing through the carotid canal and making several bends, which, in congenital pathology, can cause a deterioration in the blood supply to the brain. The internal carotid artery gives off five branches that supply blood to different parts of the brain and there are anastomoses (connections) between the branches.
The vertebrobasilar basin is formed by the basilar and two vertebral arteries, which enter the canal of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae (VI–II), and then make several bends along their course. Thus, even the anatomical bends and passage of the vertebral arteries in the bone canal of the cervical vertebrae are a predisposing factor to a decrease in blood supply to the brain under certain conditions, which will be discussed below.
The classic definition of transient ischemic attack indicates an interval of persistence of neurological symptoms of up to 24 hours. However, the 24-hour period is arbitrary, and the average duration of an episode can be 8-15 minutes, but most often the symptoms disappear within one 1 hour. Since 2002, the definition of this condition has been expanded and the main fact taken into account is the absence of pathological changes in brain tissue during the period of temporary ischemia .
A transient ischemic attack develops suddenly and has symptoms similar to those of a stroke , but they are reversible because transient ischemia does not cause changes in brain tissue. The highest incidence of micro-strokes is observed in people aged 65 to 80 years. However, cases are not uncommon in people of young working age from 29 to 45 years. In most cases, the causes of transient cerebrovascular accidents in young people are: increased blood pressure due to neurocirculatory dystonia or true uncontrolled arterial hypertension , as well as heart or blood diseases, which occurs even in children. Circulatory disorders can occur in any arterial area of the brain, but in the carotid area they occur 4-5 times more often than in the vertebrobasilar area.
Many patients do not attach importance to transient disorders and do not consult a doctor. In most cases, the diagnosis is established after the fact, when the doctor asks about other diseases. In the best case, the patient comes in, but the diagnosis is made from the patient’s words, since by the time of the examination the symptoms have already regressed. Nevertheless, TIA is an emergency condition that requires hospitalization of the patient, determination of the causes of cerebral ischemia and treatment according to the algorithm for acute cerebrovascular disorders. This is due to the fact that in some patients, attacks can be repeated during the day (2-3 attacks) and everyone after a TIA has a risk of developing stroke and myocardial infarction . Approximately one third of patients develop a stroke within a year after the first transient circulatory disorder.
Diagnostics
Considering that the symptoms of stroke and micro-stroke in women are often similar, it is extremely important to track the very first signs or carefully analyze the state of the body after an attack. Employees of the Yusupov Hospital conduct a comprehensive examination, thanks to which doctors make an accurate verdict and immediately begin developing a treatment plan.
Prehospital diagnostics
Prehospital diagnosis is one of the most significant stages in making a diagnosis. Due to the fact that the most striking symptoms disappear in less than 24 hours, many simply do not have time to seek help.
If the patient comes in at the first symptoms, the doctor makes the initial diagnosis by collecting an anamnesis and a neurological examination. This helps to refute or confirm the suspicion of a micro-stroke and pathological changes in the circulatory system.
Instrumental diagnostics
After the first appointment, you must undergo magnetic resonance and computed tomography. Thanks to these tools, the researcher determines which part of the brain has undergone necrosis. Based on the data obtained, a plan for further treatment measures is drawn up. Thanks to tomography, it is possible to identify those parts of the brain that are in danger of dying. Timely treatment will prevent further development of this process.
Angiography is a type of study that determines the patency of blood vessels in the head. This procedure determines whether there is a problem with clogged arteries.
Also, if an attack is suspected, an x-ray of the cervical spine is taken to determine the presence of cervical osteochondrosis. If the diagnosis is confirmed, then in parallel with eliminating the consequences of the attack, doctors deal with osteochondrosis and prevent compression and injury to the veins and arteries that lead to the head.
Differential diagnosis of various types of stroke
The essence of such diagnostics is to reliably determine the type of stroke and, in accordance with this, provide effective assistance. The differential diagnosis is made not only on the basis of the patient’s medical history, but also on the basis of the results of her tests.
In addition, each patient is required to be examined by related specialists: cardiologists, endocrinologists and ophthalmologists. Such a complete diagnosis makes it possible not to confuse a stroke with any other disease and to select effective and efficient therapy.
Treatment of microstroke in women
Treatment in this case is aimed at preventing the development of a full-fledged stroke with serious impairment of brain functions in the future.
To treat a microstroke, therapy is selected that restores blood circulation to the brain. In particular, doctors use vasodilators and medications that improve metabolic processes in blood vessels.
Also, during treatment, doctors adjust the treatment of related diseases. If the patient suffers from hypertension, then cardiologists are involved in the work and prescribe effective antihypertensive drugs. Together with them, a treatment plan is developed by a gynecologist and an endocrinologist, who render a verdict on the woman’s further use of hormonal contraceptives and, if necessary, select a remedy suitable for each specific patient.
Pathogenesis
The key point in the pathogenesis of this condition is reversible cerebral ischemia, which occurs when there is a mismatch between the needs of the brain and the currently existing blood supply. Local anemia of brain tissue develops when perfusion decreases below 18-22 ml of blood per 100 g/min.
A transient drop in blood flow, due to various reasons, causes the development of ischemia in the brain tissue and is accompanied by reversible focal symptoms. The main pathogenetic mechanisms for the development of transient disorders are: microembolism ; hypotonic and hypertensive crisis , pathological tortuosity of the main vessels of the brain, as well as disorders of the anticoagulation system of the blood.
The outcome of ischemic cerebral circulatory disorders is determined by the caliber of the artery, the rate of development of blockage, localization, and the development of collateral circulation. If cerebral perfusion is restored, regression of symptoms is observed and the episode of transient ischemic attack ends. In the event of a further drop in blood supply to 8-10 ml per 100 g/min, which causes irreversible changes in brain tissue, cerebral infarction ( ischemic stroke ) develops.
Recovery
To restore impaired brain functions after an attack, doctors select nootropic drugs. Their goal is to make the affected areas of the brain work and protect those parts that are in close proximity to the focus of necrosis. Taking nootropics has a positive effect on the condition of people who have suffered from certain neurological diseases.
Psychotherapists are involved in the recovery process of a woman after a mini-stroke. Working with them restores a deteriorated psychological state and strengthens the body's resistance to stress factors and nervous overload.
Consequences
If you pay attention to alarming symptoms in time, then timely and high-quality treatment will allow you to avoid noticeable consequences, even if the woman suffered the disease on her legs.
If a full examination is not completed, there is a risk of deterioration in cognitive function and general psychological well-being. People who did not receive help in time experience deterioration in their memory and ability to concentrate. In addition, patients experience mood problems. Often, even calm and balanced women face outbreaks of causeless sadness, aggression or even depression.
One of the most dangerous consequences is a recurrence or development of a full-fledged stroke, which can seriously impair the quality of life.
How to recover after a mini-stroke?
The following principles that patients adhere to contribute to rehabilitation and speedy recovery:
- A doctor is a specialist. And you need to trust specialists. If the patient is incompetent in matters of treatment and rehabilitation, it is worth following the doctor’s recommendations and taking the medications he prescribed;
- Don’t put it off until tomorrow... If a patient needs to do exercise therapy every day, this means that classes cannot be missed, otherwise the desired effect will not be achieved;
- The importance of support. After a ministroke or, worse, a stroke, the support of loved ones is very important for the patient. Sometimes they simply give up, patients become depressed, and only family and friends are able to influence and help a person they know well. You can accompany the patient to a massage or exercise therapy, help him prepare food so that it fits the diet, and just talk. Feelings of loneliness should not be present in rehabilitation.
- Systematicity. This means that if a patient is prescribed exercise therapy, he should not miss a single day; if he has a diet, then he needs to strictly follow it. In terms of timing, rehabilitation after a mini-stroke is an individual process, since everything depends on the degree of impairment and the patient’s condition.
- Gradualism. This means that the body does not recover immediately, it needs time. This means that it is better to leave the usual active workouts for later, and immediately after a micro-stroke go for a massage or exercise therapy.
Also, recovery and rehabilitation after a mini-stroke imply the following actions:
- Drug treatment
- Restoration of motor functions
- Vision restoration
- Restoration of speech function
- Normalization of psychological state
A ministroke usually affects the lower and upper extremities, and motor function is impaired. The grasping reflex may disappear, weakness in the arms and legs may appear (symptoms may intensify and then it will be impossible to move at all).
The following methods are used to restore motor functions:
- Exercise therapy. Therapeutic exercise is designed to normalize muscle tone and restore strength to the muscles.
- Massage. This procedure relaxes, stimulates blood circulation and normalizes muscle tone. In this case, a massage session can be carried out both by a specialist and by the patient himself, if he is ready to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations. You can also combine a procedure with a specialist and a home massage. This approach will speed up the recovery process.
- Physiotherapy. After a micro-stroke, the patient is usually prescribed warming, which allows the body to regain lost sensitivity.
Vision restoration
Frequent symptoms of a microstroke are double vision, darkening, spots, and even temporary blindness in one or two eyes at once. While the patient is undergoing treatment, the issue of vision restoration is dealt with by an ophthalmologist, and less often by a surgeon (if it is impossible to avoid surgical intervention).
During the rehabilitation period, the patient is usually prescribed pills that normalize vision function, and is also recommended to perform special exercises that stimulate the work of the oculomotor nerve. To record progress or regression, it is recommended to visit a doctor regularly.
Restoration of speech function
Confusion of speech is another symptom of a mini-stroke, which can be cured with proper treatment. But, if after treatment the speech function is not completely restored, special classes are conducted with the patient aimed at its restoration. They are usually carried out by a speech therapist or neuropsychologist. In case of complications and serious speech disorders, all basic speech skills are studied with the patient from scratch: listening (understanding what is heard), reading, writing, speaking.
The process of speech restoration will accelerate if the patient’s relatives continue to study with him at home. For the process to be effective, in addition to training with the victim, you just need to talk (ask him simple questions, patiently waiting for an answer; tell the news; share opinions, etc.), even if this seems useless at first glance. But we must remember that a person can only speak in a linguistic environment (that is, he must constantly hear speech in order to begin to produce it), which is the task of family and friends to create during the rehabilitation period.
Normalization of psychological state
Patients who have suffered a mini-stroke often experience depression (people with a fine mental organization and women are especially prone to it due to their physiology and psyche). Relatives need to try to understand this condition: the patient suddenly lost some abilities, is forced to take pills and regularly visit the doctor. His life has completely changed. To help him overcome this condition it is necessary:
- Interact and communicate with him more often;
- Go for walks, which will provide him with physical activity;
- Help you find a new hobby or return to an old one, if possible.
As soon as rehabilitation is over, it is better for a person to return to work: to the old one or, if this is not possible, to find a new one as soon as possible.
Any activity requires a certain amount of effort and time, therefore, by getting busy, the patient will think less about problems and, accordingly, will quickly overcome a depressive state.
Where and how to undergo rehabilitation and how long will it take to recover after a mini-stroke? These are the most frequently asked questions by patients. Of course, everyone wants to return to normal life as soon as possible, go to work or go on a trip.
Rehabilitation is possible both at home and in a hospital setting. In the first case, success will depend on those who surround the patient: on their willingness to communicate, care and support. Secondly, it depends on the literacy of specialists and the development of the rehabilitation program.
Expert opinion
Author: Tatyana Aleksandrovna Kosova
Head of the Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, neurologist, reflexologist
According to statistics, the number of cases of first-time transient cerebrovascular accident is increasing every year. A microstroke is provoked by various factors. It has been noted that the disease is most common among men of working age. According to clinical studies, in 10-15% of cases, myocardial infarction develops after a transient cerebrovascular accident. 30-40% of patients experience a major stroke over the next 5 years. Therefore, it is important to seek medical help on time and undergo preventive examinations.
Diagnosis of microstroke at the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using modern medical equipment. European CT and MRI installations make it possible to accurately determine the location of the lesion and its extent. An individual treatment and rehabilitation program is developed for each patient. The recovery period takes place under the supervision of experienced neurologists, massage therapists, exercise therapy instructors and physiotherapists. A personal approach can reduce the time of hospital stay and reduce the risk of recurrent microstroke.
Nutrition for microstroke of the brain
After an acute cerebrovascular accident, patients need a nutritious diet that ensures the body receives a balanced amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. A necessary component of a healthy diet is a sufficient amount of vitamins and minerals in the food consumed. After a mini-stroke, it is important to maintain a water regime.
When selecting products from which to prepare dishes, nutritionists recommend giving preference to whole grains or products made from them. After a micro-stroke, you should eat orange and dark green foods, peas and beans. The menu should include a sufficient amount of fresh, frozen or dried fruits and berries every day.
Diet after a stroke is aimed at reducing the risk of another attack. When selecting food products, you should pay attention to the following criteria:
- nutritional value (calorie content);
- presence of fat;
- the presence of saturated and trans fats;
- do you have cholesterol?
- content of table salt and fiber.
Limiting your intake of trans fats will reduce blood cholesterol, which is of great importance in cases of brain damage.
The diet after a microstroke should contain vitamins and minerals. Vitamin B6 is present in the following foods:
- carrot;
- sunflower seeds;
- walnuts;
- spinach;
- peas;
- herring;
- salmon.
Legumes and whole grains are rich in potassium, and α-pinoleic acid is found in sea fish. An important component of the menu after a microstroke are fruits and vegetables, seeds and nuts. The energy value of foods consumed per day should not exceed 2.5 thousand kilocalories.
Prevention
To prevent a micro-stroke, it is necessary to constantly monitor your health. If a woman suffers from arterial hypertension or other pathologies of the cardiovascular system, then she needs to measure her pulse and blood pressure twice a day. It wouldn’t hurt to get into the habit of keeping a diary with your morning and evening readings.
Those with diabetes are advised to regularly check their blood sugar levels. If this indicator is normal, it is enough to do a similar analysis a couple of times a year: it takes a little time, but warns of incipient health problems.
In addition, it is important to adhere to general recommendations for a healthy lifestyle: give up bad habits such as smoking and drinking alcohol, pay attention to physical education or gymnastics, and include walks in your life. It is better to reduce the amount of fatty foods on the menu and give preference to natural products.