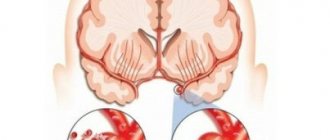
Dysphagia is diagnosed when there is a disruption in the functioning of the centers responsible for the swallowing process. As a result, 60% of post-stroke patients experience spasticity of the facial muscles, tongue, larynx or esophagus. And the question arises not only of adequate nutrition, but also of preventing complications such as aspiration pneumonia, which occurs when liquid or food particles enter the respiratory tract.
As a result, instead of active recovery after a stroke, the elderly person faces new problems: due to malnutrition and dehydration of the body, the rehabilitation potential is reduced, and there is a risk of airway obstruction, aspiration, etc.
How is diagnosis carried out and methods of working with swallowing problems after a stroke selected?
Dysphagia is diagnosed using several methods. Video fluoroscopy, fiberoptic endoscopy, ultrasound, manometry, and finger method are used. The main task of these methods is to determine at what phase of swallowing the patient has problems. Only by determining this can you solve the nutrition problem, take safety measures and work on the process of restoring the functions of all organs involved in the process. In a situation where the swallowing process is impaired after a stroke, a decision may be made to insert a probe for the first time.
This decision is made on the basis of certified screening tests that help determine whether this patient can be fed through a tube or not, since this may pose a risk of aspiration. The probe and tracheotomy tube are placed temporarily. No more than a month. Because the probe, no matter what “friendly” plastic it is made of for the human body, as a result of constant contact can form bedsores in the nasopharynx, esophagus, and cause damage to the mucous membrane. And constant irritation of the mucous membrane leads to the separation of protective secretions, which can interfere with the process of classes with a speech therapist.
The probe is placed for safety reasons and allows you to solve the power issue. If swallowing is restored, the probe is removed and the person begins to swallow on his own. Then the speech therapist, together with the nutritionist, determines exactly how to feed such a patient - use mixtures, specially crushed food, thickeners (since water is sometimes more difficult to swallow than, for example, puree).
But if swallowing has not been restored within a month, a gastrostomy tube is placed. It has a larger diameter than the probe, which allows, unlike a probe, to freely feed the patient not only with special mixtures, but also with coarser food. It is important that it is possible to clean it.
Sometimes a gastrostomy tube is placed to make swallowing exercises easier. Because doing this with a probe is much more difficult. Therefore, a gastrostomy tube can last a lifetime or as long as needed to restore the swallowing process.
Neurology Center in Moscow
Dysphagia is defined as difficulty in spontaneous swallowing. Swallowing is a rather complex process, consisting of 3 phases: oral, pharyngeal and esophageal. Many reasons can cause dysphagia, such as diseases of the thyroid gland, heart, lymph nodes, esophagus, oncology, and disorders of nervous functions.
Symptoms of dysphagia:
- Difficulty or inability to swallow
- Pain during swallowing
- Entry of liquid and food into the larynx, trachea and nose
Dysphagia may be associated with the following conditions:
- Inflammation in the mouth
- Inflammation of the esophagus, larynx, pharynx
- Presence of a foreign body
- Tumor or scar narrowing
- Diffuse spasm in the esophagus
Patients with impaired swallowing are often admitted to the neurology department. A speech therapist should work with them. When a patient enters the department, a speech therapist examines the quality of swallowing. For this purpose, a dysphagia rating scale, a three-sip test, and a protocol are used. Then the speech therapist describes in detail in his documents such parameters as the state of the patient’s facial expressions, the state of his articulatory apparatus, voice, breathing, and soft palate. The speech therapist gives recommendations to the patient and his family:
- How to properly feed a patient who has had a stroke
- Nutritional nature
- Independent exercises in facial gymnastics
For dysphagia, restorative training is provided to help relearn how to swallow. In the neurological department of the Yusupov Hospital there is a speech therapist who helps post-stroke patients with dysphagia normalize swallowing function.
Speech therapy classes are held every day at the hospital. One lesson lasts 20 minutes. The session ends with a speech therapy massage. If there is no dysphagia, the patient is shown a normal diet without restrictions. Mild dysphagia manifests itself as difficulty swallowing solid food, while liquid food passes without problems. The next degree is when the patient can only swallow liquid. Severe – there is difficulty swallowing liquids and saliva. The most severe degree is complete dysphagia.
How is exercise therapy performed for dysphagia?
First, the speech therapist must prepare equipment for the lesson. You will need the following equipment: pillows, table, chair (for patients who can sit), non-slip mat, mug, plate, knife, napkins. During the lesson, the atmosphere should be positive and calm. It is necessary to turn off the TV, if possible, to protect the patient from others with a curtain or screen. If necessary, isolate the patient.
Then you will need to prepare the patient for the lesson. You need to carefully clean his mouth. Food must be tasty and appetizing, and have a certain consistency. Food should be warm, but not hot. Patients with dysphagia take a long time to eat. If the patient is hypersensitive, you can feed him food at room temperature. Offer solid and liquid foods at different times. This will reduce the risk of aspiration.
What exercises can be used to restore swallowing?
- Cough
- Yawn with your mouth wide open
- Tighten your mouth and pretend to whistle without making a sound.
- Snore
- Gargle
- Swallow a spoonful of semolina porridge
- Say the sounds “a” and “e” 5 times
- Stick out your tongue and then pronounce the sound “g”
- Move your lower jaw forward and pronounce the sound “s”
- Swallow drops of water from a pipette
- Close your lips and make the sound “m”
- Pull the “i” sound high and low. This must be done on one exhalation.
Exercises to improve articulation:
- Pronouncing the sounds o, i, u
- Pronouncing the sounds p, f, v. Place the lower lip under the upper teeth
- Combination of sounds oh, fu, fi
- Pronouncing words syllable by syllable (window, raisin, ottoman, Fekla)
To register at the Yusupov Hospital:
- by phone: +7 925 191 50 55
- fill out the form: APPLICATION FOR TREATMENT
- Get advice by email [email protected]
- Clinic address: Moscow, Nagornaya st., 17 to 6
+7 (495) 506 61 01 –
REQUEST TO THE CLINIC
Dysphagia Treatment Methods
Treatment of dysphagia is often based on the use of compensatory and rehabilitative approaches. Compensatory techniques do not fundamentally solve the problem, but they can compensate for the weakness of the muscles that support the act of swallowing, and thereby reduce the symptoms of the disorder. This strategy involves changing the consistency of food to make it easier to swallow and performing positional treatment maneuvers (such as rolling or tilting the head) to help push food down the esophagus.
The rehabilitation method of treatment is aimed at changing the physiology of swallowing and restoring swallowing function, thereby achieving improvement in the long term. Treatments may include exercises to build strength in the muscles of the head, mouth, larynx and esophagus, as well as teaching swallowing techniques to block the airway. Currently, as part of rehabilitation treatment, various swallowing maneuvers are used - for example, “sip over the glottis”, when the patient inhales, holds his breath and then takes a swallow.
Rehabilitation program after coronavirus
Rehabilitation after Covid in the ICU is usually comprehensive: drug treatment is combined with rehabilitation procedures. The course of drug therapy is selected individually; the duration of taking the drugs is usually from 5 to 10 days. Simultaneously with taking medications, a personal course of rehabilitation procedures is drawn up and prescribed for a period of 2 to 4 weeks.
Course of drug therapy
With the help of medications, therapy is aimed at:
- Normalization of transport of nutrients and oxygen.
- Improving the metabolism of organs and tissues, reducing the level of free radicals.
- Reducing inflammatory and degenerative changes in nervous tissue.
- Improving the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
- Combating asthenic syndrome (fatigue, anxiety, memory impairment, decreased concentration).
- Improving the functioning of the autonomic nervous system (dizziness, sweating)
Course of rehabilitation procedures
- Intravenous laser therapy (ILBT) and magnetic laser therapy (MLT) - normalizes tissue respiration, activates blood circulation, thins the blood, eliminates lymph stagnation, restores the transport function of the blood, and stimulates the immune system.
- Reflexology (acupuncture, acupuncture) - improves microcirculation in organs and tissues, normalizes blood pressure, improves soft tissue tone, has a positive effect on the immune system, and has a calming effect.
- Manual and rehabilitation (restorative) medical massage (a combination of different techniques) - restores lost range of motion, improves muscle tone in problem areas, improves diaphragmatic breathing and the work of the respiratory muscles, improves blood circulation, and a general tonic effect.
- Classes in the physical therapy room (remedial physical therapy, kinesiotherapy, vector gymnastics) restore lost range of motion and normalize muscle tone, restore exercise tolerance, and activate the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Therapeutic and surgical treatment
Rehabilitation therapy is a fairly effective method of treating dysphagia. However, in cases where the disorder is caused by a chronic condition such as GERD, or is associated with a particular shape and size of the esophagus, medical treatment or even surgery may be required. Conservative treatment includes taking antacids or other medications to control the symptoms of GERD. If the cause of swallowing problems is a decrease in the level of salivation or thickening of saliva, the patient may be prescribed special medications.
If the difficulty in swallowing is caused by the diameter of the esophagus being too small or its muscle tissue being too dense, the defect is usually corrected surgically, for example, by performing laparoscopic cardiomyotomy. During the operation, the surgeon cuts the muscles of the lower esophageal sphincter to allow food to pass more freely from the esophagus into the stomach.
When to go to a rehabilitation doctor
You should make an appointment with us if, after recovering from COVID-19 and doing independent exercises at home:
- you continue to experience shortness of breath even with minimal physical activity,
- when exercising, you feel nausea, dizziness, chest tightness, and sweat a lot;
- your memory is not improving, your attention is still distracted, the feeling of fatigue does not go away;
- you are constantly in a bad mood and this condition does not go away for several weeks in a row.
All these signs may indicate that rehabilitation after coronavirus requires the participation of a doctor. We will help you adjust your health recovery plan and help you get back to your normal life faster.
Causes of swallowing disorders and signs of the condition
Tissue damage due to acute cerebrovascular accident (ACVA) may not affect a person’s ability to eat. In this case, immediately after regaining consciousness, the patient begins to eat in the usual way. The causes of problems with swallowing may be the result of a malfunction in the reflex processes or the result of paralysis of the facial muscles on one side of the face. Sometimes dysphagia occurs due to damage to the swallowing center in the brain stem. This is the most unfavorable scenario in which it is extremely difficult to eliminate the disorder.
Failure of swallowing function manifests itself in different ways:
- having difficulty chewing food;
- food does not move from the mouth to the throat and esophagus;
- when swallowing food, pain appears, saliva is released profusely;
- the contents of the mouth pass into the nasal passages, trachea and bronchi;
- eating food causes severe heartburn;
- due to pathological tension in the muscles of the esophagus, food does not pass through, but blocks its lumen.
Signs of impaired swallowing during stroke rarely appear as an isolated condition. Most often they are accompanied by defects or absence of speech, inability to control the flow of saliva, and a severe cough.
Consequences and dangers of dysphagia
Persistent impairment of the swallowing reflex reduces the patient’s quality of life and slows down the recovery process. The risks of disability for such patients are very high. The risk of developing severe complications increases the likelihood of death even after the patient recovers from critical condition.
Victims of stroke with impaired swallowing may develop:
Read also: Smoking leads to stroke
- bronchopneumonia - acute inflammation of the walls of bronchioles;
- dehydration of the body;
- persistent disturbance of energy metabolism;
- cachexia – weakness and extreme exhaustion due to weight loss.
The fact that the swallowing reflex is absent or impaired becomes obvious from the clinical picture.
To confirm the diagnosis, videofluoroscopy, pharyngeal monometry, fiberoptic assessment of swallowing using an endoscope, pulse oximetry and other research options are performed.
Swallowing phases
Choosing the most effective treatment plan for dysphagia depends largely on the cause of the problem and the stage at which swallowing difficulties occur. It is customary to distinguish three phases of swallowing:
- oral (oral) phase: entry of food into the oral cavity, chewing it, formation of a food bolus;
- pharyngeal (pharyngeal) phase: pushing the food bolus first into the middle and then into the lower part of the pharynx, which is accompanied by closure of the trachea, preventing aspiration of food into the respiratory tract;
- esophageal (esopharyngeal) phase: movement of the food bolus from the esophagus into the stomach.
Help from rehabilitation specialists during COVID-19
When discharged from the hospital, many people who have recovered from Covid receive a special reminder, which is designed to help them return to their normal lifestyle. However, not everyone is able to restore their health on their own. General recommendations are not suitable for every person, since everyone’s disease progressed differently and many developed complications as a result of the infection or discovered new pathologies.
To avoid deterioration of the condition, we recommend that you contact the rehabilitation specialists of our clinic . We work on individual programs, tailored to the indications of each individual patient and his medical history. This allows you to pay special attention to the most problematic areas.
Rules for eating with dysphagia
Improvement in the general condition of the patient after a stroke is an indication for the initiation of measures aimed at restoring swallowing. The sooner this is done, the better. Long-term use of the probe often causes laryngitis and psychological discomfort.
Read also: Is it possible to go back to work after a stroke?
When feeding against the background of problems with swallowing, you need to remember the following nuances:
- Food is divided into liquid and solid; both types of food are not given to the patient at one time. In this case, dense pieces of food will be difficult to pass through, so it is better to give preference to liquid products with a thick consistency.
- If reflex swallowing is impaired, liquids should also be chosen thick. Yogurt, jelly, fermented baked milk and similar textured products allow for a clear separation of sips. This reduces the likelihood that the patient will choke or choke. Water, fruit drinks, milk and juices flow in a continuous stream, which is why it is better to start giving them after the reflexes have been fully restored.
- During the recovery period, products that fall apart into crumbs (bread, cookies) or contain coarse dietary fiber (citrus fruits, cabbage) are prohibited.
- Before each new portion, you must make sure that there is nothing left in the patient’s mouth. The same should be done after finishing feeding.
- A person who has lost the ability to eat normally may need 30-40 minutes to consume one bowl of liquid soup. You can’t rush it, as this can increase the severity of nervous symptoms and disorders.
- Feeding is carried out in a sitting or half-sitting position; you cannot throw your head back.
The doctor decides what to do in cases where the patient’s consciousness is impaired and he aggressively reacts to the staff’s attempts to feed him. The process can be established with the help of loved ones; psychotherapy gives good results. Sometimes you have to return to installing a gastric tube or gastrostomy tube.
Nutritional Features
If the patient feels normal after installation, you can start eating immediately. All dishes served must have only a liquid consistency. They should be warm, that is, temperatures of 37-39 degrees. Hot foods may cause burns.
It is necessary to increase the volume of servings gradually; the first two or three times it should not be more than 100 ml. In the future it can be increased to 300 ml. The following products are best suited for enteral nutrition:
- Kefir;
- Fish, meat, vegetable broths;
- Thoroughly mashed puree;
- Rare porridges, especially semolina;
- Special mixtures.
Ready-made dry mixtures can be used as a basis for nutrition or in addition to the diet. They are rich in protein, which bedridden patients often lack.
The number of meals should be no more than 5, but not less than 3. A sterile syringe must be used for administration each time. The nursing service specialists strictly follow all the rules for feeding through zones and carefully monitor the hygiene of the entire process.
Organization of the feeding process in the first days after a stroke
There are many ways to quickly restore the swallowing reflex after a stroke, but they do not give results immediately. For the first 10-15 days in hospitals, such patients have to be fed using special devices. In severe cases and against the background of a change in the victim’s consciousness, the duration of such feeding increases to a month.
Gastric tube placement
If a person does not have sucking and pharyngeal reflexes, a gastric tube is installed. A hollow tube made of soft, hypoallergenic material is inserted through the nose through the upper digestive tract into the stomach. The manipulation is not very pleasant, but it lasts only 10-15 seconds and immediately after its completion you can start feeding. Through the device, the patient is administered special medicinal compositions based on nutrients. The device is changed every 2-3 weeks to prevent complications from developing.
The presence of a gastric tube does not eliminate the need for oral hygiene. The patient's teeth are treated with antibacterial agents three times a day. The oral mucosa should be regularly moistened. Excessive saliva should be removed with clean wipes or tampons.
Gastrostomy placement
If a person cannot swallow and even a month after the stroke he does not show positive dynamics, he is given a gastrostomy tube. An incision is made in the stomach area on the anterior abdominal wall. Through it, a soft hollow tube is inserted directly into the stomach, through which liquid and semi-liquid food is subsequently passed. If the paralyzed side of the body does not recover for a long time, installing a gastrostomy facilitates the patient’s feeding process and minimizes possible complications. If it is impossible to restore the swallowing reflex, the device can be used for life.