The entire hematopoietic system of a child is characterized by extreme functional instability (lability), easy vulnerability to the most insignificant exogenous factors.
A decrease in the amount of hemoglobin, red blood cells, the appearance of immature elements of red blood, leukocytosis with the formation of young cells are observed in children much more often and develop faster than in adults. The formation of foci of extramedullary hematopoiesis, and sometimes a complete return to the embryonic type, can be caused in children not only by severe anemia and leukemia, as in an adult, but often occur under the influence of various infections, intoxications and other harmful factors (bronchopneumonia, pyelonephritis, otitis media and etc.). Blood for infections, analysis - children's clinic "Markushka"
Peripheral blood of a healthy child
Erythrocyte system : erythropoiesis begins with a bone marrow stem cell that is sensitive to erythropoietin (a glycoprotein produced in response to tissue hypoxia in the fetal liver and the child’s kidney), and proceeds through its differentiation into an erythroblast, then into a pronormocyte, basophilic normocyte, polychromatophilic normocyte, oxyphilic normocyte, reticulocyte.
Of the estimated 18 divisions that occur during the transformation of a stem cell into a mature red blood cell, erythropoietin significantly stimulates the final 8-10 divisions. The preceding cell divisions that give rise to erythropoietin-sensitive erythroid progenitor cells are largely erythropoietin-independent.
The lifespan of red blood cells is 100-120 days. With the help of phagocytic macrophages of the spleen, liver, lungs, and lymph nodes, an average of 1.4% of red blood cells are destroyed per day.
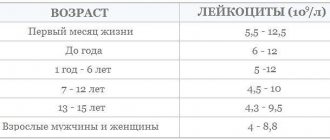
Composition of peripheral blood in a child
The composition of a child's peripheral blood undergoes significant changes in the first days of life after birth. Immediately after birth, red blood is characterized by an increased hemoglobin content and a large number of red blood cells. From the end of the 1st to the beginning of the 2nd day of life, a decrease in the content of hemoglobin and red blood cells occurs.
The blood of a newborn by a distinct anisocytosis, observed within 5-7 days, and macrocytosis (the diameter of erythrocytes is somewhat larger in the first days of life - up to 8.5-9 µm, the norm is 7.5 µm). The blood of a newborn contains many young red blood cells, which indicates the active processes of erythropoiesis. During the first few days of life, it is possible to detect nucleated forms of erythrocytes in the blood, most often normocytes and erythroblasts. The number of reticulocytes in the first hours of life ranges from 8 to 42%. The high content of erythrocytes and hemoglobin, as well as immature forms of erythrocytes in the peripheral blood in the first days of life indicates intensive erythropoiesis as a reaction to the lack of oxygen supply to the fetus during intrauterine development and during childbirth.
After birth, due to the establishment of external respiration, hypoxia is replaced by hyperoxia
After birth, due to the establishment of external respiration, hypoxia is replaced by hyperoxia . This causes a decrease in erythropoiesis and a drop in the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin levels. Red blood cells produced in utero have a shortened lifespan compared to that of older children and are more prone to hemolysis. The lifespan of red blood cells in children in the first days of life is 12 days, which is 10 times less than in adults and older children.
The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) depends on many chemical and physical properties of the blood. In a newborn, ESR is 2 mm/h, in young and older children - 4-8 mm/h, in adults - 5-8 mm/h. Slower erythrocyte sedimentation in newborns is explained by low levels of fibrinogen and cholesterol in the blood, as well as blood thickening, which is especially pronounced in the first hours after birth.
Tasks of neutrophils
Neutrophils, together with lymphocytes, are the main “attacking” link of the immune system. They can move freely not only along the bloodstream, but also pass through the vascular wall into the tissue. This ability to move is provided by false “legs” in the form of a protrusion of the wall.
When approaching a bacterium, the cells surround it with their protoplasm, draw it inside and dissolve it. In this case, the neutrophils themselves die. They are replaced in the bone marrow of children by millions of new ones, to whom information about the affected “enemy” is transmitted. Segmented cells can destroy bacteria and fungal infections, but are powerless to fight viruses.
An increase in the number of segmented leukocytes in a child’s blood test during an infectious disease indicates a good protective reaction of the baby, the ability to resist pathological organisms.
A decrease in cells relative to the norm causes concern for the doctor and indicates low immunity.
Leukocyte system
Leukocyte system : leukopoiesis begins with a bone marrow stem cell and proceeds through its differentiation into a myeloblast, then into basophilic, neutrophilic and eosinophilic segmented cells through the phases: promyelocyte - myelocyte - band cells.
Neutrophils are continuously supplied to the skin, mucous membranes and other peripheral tissues. Their daily turnover is about 100 billion cells. The lifespan of granulocytes is from 14 to 23 days. Neutrophils spend most of their lives in the bone marrow. On their way to peripheral tissues, neutrophils spend about 10 hours in the intravascular space, and at any moment only half of the intravascular cells are in motion, while the other reversibly adheres to the endothelial surface of the vessels (mural cells). The latter are a reserve pool of mature cells that can be called upon in case of infection or inflammation.
Features of the number of leukocytes
There are features and numbers of leukocytes . In the peripheral blood in the first days after birth, the number of leukocytes is 18-20 -109/l, with neutrophils predominating (60-70%). The leukocyte formula is shifted to the left due to a large number of band forms and, to a lesser extent, metamyelocytes (young).
With age, the leukocyte formula undergoes significant changes
This is reflected in a decrease in the number of neutrophils and an increase in the number of lymphocytes . On the 5th day of life, their number is comparable (the so-called first crossover), amounting to about 40-44% in the white blood formula with a ratio of neutrophils and lymphocytes of 1:1. Then there is a further increase in the number of lymphocytes (by the 10th day to 55-60%) against the background of a decrease in the number of neutrophils (approximately 30%). The ratio between neutrophils and lymphocytes will be 1:2.
Gradually, by the end of the 1st month of life, the shift of the formula to the left disappears, myelocytes completely disappear from the blood, the content of band forms decreases to 4-5%.
By the beginning of the 2nd year of life, the number of lymphocytes begins to decrease, and the number of neutrophils increases, respectively, by 3-4% of cells per year, and at 5 years a “second crossover” is observed, in which the number of neutrophils and lymphocytes is again compared (1:1 ratio) . After 5 years, the percentage of neutrophils gradually increases by 2-3% per year and by 10-12 years reaches values like those of an adult - about 60%. The neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is again 2:1.
This parallelism of changes in neutrophils and lymphocytes can be explained by the commonality of their functional properties, which play a role in immunity. The lifespan of lymphocytes is 100-300 days.
Absolute and relative neutrophilia in the first days after birth is explained by the entry of maternal hormones into the child’s body through the placenta, thickening of the blood in the first hours of extrauterine life, resorption of interstitial hemorrhages, and adaptation of the body to external conditions.
The content of eosinophils, basophils, and monocytes practically does not undergo significant changes during the growth of the child. The number of leukocytes further decreases to (7.6-7.9)x10(9)/l.
Decreased neutrophils
A decrease in the number of cells in a row is called neutropenia. The level of segmented neutrophils decreases in three cases of the pathology mechanism:
- if too many cells die in a protective reaction;
- if their production in the bone marrow is blocked;
- when cells are destroyed during diseases of the hematopoietic organs.
Similar conditions in children are possible:
- with severe anaphylactic reaction;
- for viral infectious diseases (measles, influenza, rubella, respiratory diseases, mumps, viral hepatitis) that suppress general immunity;
- for various anemias;
- after radiation therapy;
- when painkillers and anticonvulsants are used in treatment.
A decrease in the indicator is observed in cases of poisoning with household chemicals.
Particular diagnostic importance is attached to the condition when neutrophils are low and lymphocytes are high. Lymphocyte cells respond to viral infection. A similar combination is found in the child’s blood:
- during a viral disease;
- for tuberculosis;
- if there is hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- in HIV-infected children;
- for malignant blood diseases (lymphocytic leukemia, sarcoma).
If such deviations do not last long and return to normal on their own as you recover, you can think about completely restoring the immune system. Long-term changes require repeated tests and additional examination of the child.
We are trying to recover as quickly as possible
There is a rare genetic blood disease that is detected in childhood - Kostman neutropenia. There are no neutrophils in the body. A child deprived of protection is susceptible to frequent infections and pustular diseases. The first year of a baby’s life is especially dangerous. Subsequently, the protective function is carried out by compensatory growth of monocytes and eosinophils.
Platelets
Platelets , like all other blood cells, originate from a bone marrow stem cell with subsequent differentiation: thrombopoietin-sensitive cell - megakaryoblast - promegakaryoblast - megakaryocyte - platelet. About 35-40% of circulating platelets are destroyed daily due to aging and the body's ongoing clotting process.
Platelets are directly involved in the process of hemostasis. The activity of platelet coagulation factors in newborns and infants is reduced. The duration of bleeding is not changed, the clotting time may be prolonged, especially in children with severe jaundice (over 6-10 minutes).
Hematocrit number , which gives an idea of the percentage ratio between formed elements and blood plasma, varies depending on age. The hematocrit value increases in cyanotic congenital heart defects, in a state of dehydration, etc. A decrease in hematocrit is observed in anemia and diseases accompanied by hydremia.
Materials and methods
The study included 165 patients (92 men - 55.8%, and 73 women - 44.2%) who were treated at the Moscow State University Research Center from April to June 2021 with a diagnosis of COVID-19. The diagnosis of COVID-19 was confirmed by taking a swab from the oropharynx followed by PCR analysis for SARS-CoV-2. The age of the patients ranged from 24 to 96 years, with an average of 59.9 years (IR = 46.9 – 66.9 years).
The study of the level of biochemical blood parameters was performed on an automatic biochemical analyzer AU480 Beckman Coulter, Germany. A complete blood count was performed on a hematology analyzer XN 2000 Sysmex Corporation, Japan. The study of hemostasis parameters was carried out using an automatic hemostasis analyzer STA-Compact Diagnostica Stago SAS, France.
CT of the lungs and chest organs was performed on a 32-row Somatom Scope computed tomograph manufactured by Siemens (Germany). The studies were carried out with a slice thickness of 1 mm.
During the first study, a standard CT protocol was used with a tube voltage of 120 kV and automatic modulation of the tube current in the range of 200–400 mA; for repeated CT scans, a low-dose CT protocol was used with reduced tube voltage parameters (100 or 110 kV) and automatic modulation of the current on the tube in the range of 40–120 mA. With the standard protocol, the average radiation exposure was 3.9±0.4 mSv, with the low-dose protocol - 0.9±0.2 mSv. CT studies were performed upon admission and discharge of the patient; during hospitalization they were repeated as clinically necessary, but not less than once every 5 days.
All obtained images in DICOM format were stored in the radiological information network (PACS/RIS) of the Moscow State University. Syngo.via workstations (Siemens) were used for CT processing and analysis. When processing and describing CT data, we used a semi-quantitative scale for assessing the volume of zones of infiltration and consolidation of the lungs, recommended by the Temporary Guidelines for the Prevention, Diagnosis and Treatment of the New Coronavirus Infection COVID-19 of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation, versions 6–9 (CT1–CT4), as well as programs quantitative analysis of infiltrative changes in the lungs during COVID-19 pneumonia "Multivox" (developer - , Moscow) and "Botkin.AI (developer - , Moscow).
To objectify the severity of the clinical condition and adequately assess the effects of the therapy, we used two scales. Firstly, the original scale for assessing the clinical condition of patients with coronavirus infection (SHOX-COVID), published previously [1]. This scale includes a clinical assessment of the severity of the disease, the degree of inflammation, the risk of thrombosis (D-dimer) and the severity of lung damage, according to CT data (Table 1).
Table 1
Scale for Assessing the Clinical State of Patients with COVID-19 (SHOKS-COVID) (modified by Mareeva V.Yu., 2020)
Secondly, the NEWS-2 distress syndrome severity scale (Reproduced from: Royal College of Physicians. National Early Warning Score (NEWS) 2: Standardizing the assessment of cute-illness severity in the NHS. Updated report of a working party. London : RCP, 2017), modernized for patients with COVID-19 (Fig. 1) [2].
Figure 1. NEWS-2 distress syndrome severity scale (Reproduced from: Royal College of Physicians. National Early Warning Score (NEWS) 2: Standardizing the assessment of cute-illness severity in the NHS. Updated report of a working party. London: RCP , 2017), modernized for patients with COVID-19.
As an additional measure of the severity of the disease, the length of hospitalization was also determined.
Statistical analysis was carried out using the statistical software package GraphPad Prism (GraphPad Software, USA). To determine the normality of distribution, the generalized D'Agostino Pearson test was used. Since the distribution of the studied indicators was considered to be different from normal, the data were presented as median (50%) and interquartile range (25%; 75%). The Mann-Whitney test was used to compare two unrelated populations, and the Wilcoxon test was used to compare data in two related populations. When conducting correlation analysis, the Spearman test was used. Differences were considered statistically significant when the p value was less than 0.05.
Peripheral blood in premature infants
The red blood of a healthy premature baby at birth is characterized by erythroblastosis, reticulocytosis, increased red blood cell and hemoglobin counts, as well as anisocytosis and poikilocytosis. Soon after birth, there is a gradual drop in the content of red blood cells and hemoglobin, and by the 2-3rd month of life, most preterm infants develop anemia, known as “early anemia of prematurity.” Its pathogenesis is based on increased hemolysis and functional immaturity of bone marrow hematopoiesis. The cause of intense hemolysis is the predominance of unstable red blood cells containing fetal hemoglobin in the blood of premature babies.
Thus, in healthy premature infants, anemia in the 2-3rd month of life can be considered as a manifestation of adaptation when replacing extramedullary hematopoiesis with bone marrow. In sick children, early anemia is often accompanied by more pronounced changes in the content of red blood cells and hemoglobin and has a long course.
By the beginning of the 4th month, there is a spontaneous increase in the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin, but a month later there is a repeated decrease in levels and late anemia of prematurity develops, caused by a lack of iron in the body. Unlike early, late iron deficiency anemia can be prevented and effectively treated with iron supplements.
What are neutrophils?
Neutrophils in the blood are one of the types of white blood cells - leukocytes and granulocytes. Being in the blood, they occupy about 75% of the total number of white blood cells.
Neutrophil granulocytes are a very significant component of leukocytes. Their number will necessarily be recorded in the leukocyte formula of the blood, and is designated as neut .
A neutrophil count that does not fall outside the established range indicates that the child’s immune system is functioning correctly. It quite effectively protects the child’s body from bacteria and viruses entering it.
Blood in children after one year of age
Blood in children over the age of one year also has its own characteristics. The amount of hemoglobin in children over 1 year of age clearly increases, gradually approaching the figures of an adult, although at this age there are significant individual fluctuations. The number of red blood cells also increases in parallel; their absolute quantities and growth rates in children of different ages are subject to fairly wide individual fluctuations. The number of erythrocytes with supravital granularity gradually decreases, reaching by school age the figures characteristic of adults, that is, about 2%. The color index ranges from 0.85 to 0.95.
It should be noted that recently, in both children and adults, some changes : a trend towards a decrease in the number of leukocytes is definitely emerging (in children aged 2 to 15 years).