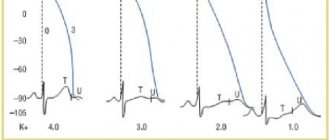
During pregnancy, the female body needs more nutrients than usual. Expectant mothers often suffer from a lack of magnesium and potassium. These microelements regulate myocardial metabolism, improving heart function and preventing dangerous complications.
Panangin is a combination medicine based on easily digestible potassium and magnesium, which nourishes and strengthens the heart muscle. The drug corrects the deficiency of the minerals described above, and is also used to prevent hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. During pregnancy, Panangin is used only after a doctor’s prescription, since the medication has contraindications.
Nuances of dental treatment for pregnant women
The period of gestation in itself is not a contraindication to dental treatment. But when visiting a doctor, he must be warned about pregnancy, and also tell the due date. In this case, the following features arise during dental treatment:
- Bleaching is not allowed.
- Local anesthesia is required.
- It is possible to treat caries, pulpitis, periodontitis and gum inflammation.
- Under no circumstances should general anesthesia be used.
- Chemical and photo-curing materials can be used for filling. Polymer lamps do not harm the child.
Advice to expectant mothers - try to treat your teeth and gums before pregnancy or between the 3rd and 6th months of pregnancy, and also review your diet. If you have carious cavities, you will pass on a bouquet of microbes to your unborn child, and the destruction of your own teeth will accelerate several times.
Medvedeva Tatyana Dmitrievna, Pediatric dentist, dental therapist, work experience 19 years
Use during pregnancy
According to the instructions, medications containing calcium interfere with the absorption of magnesium, and elements of group B (namely pyridoxine), on the contrary, accelerate its absorption. However, you should consult your doctor on this issue. In addition, the doctor must be warned about what medications the expectant mother is taking. This is necessary to adjust the regimen for taking Panangin for pregnant women in order to avoid side effects.
A pregnant woman must follow the dosage of the drug
Often, expectant mothers in the 2nd and 3rd trimester complain of shortness of breath and a feeling of heart fluttering. Such symptoms are not a reason to take Panangin on your own! In this case, you should consult a doctor who will conduct an examination and establish a diagnosis. If we are talking about potassium and magnesium deficiency, then the doctor will prescribe Panangin. Otherwise, the drug should not be taken, since an overdose of the microelements described above is dangerous for expectant mothers.
Regardless of the period (second or third trimester), a pregnant woman must follow the dosage, frequency, and duration of use of the drug, as determined by the doctor. This is necessary since the dose of the medication is different for each patient. And if one woman can take 1 tablet in 24 hours, then the dose of medicine for another can be 3 pills three times. The medication is usually taken after eating food, since digestive juice reduces the effectiveness of the drug by destroying some of the ions.
Features of dental treatment at different stages
0-12 weeks. The 1st trimester of pregnancy is very important for the fetus. It is during this period that the baby’s vital organs and placenta are formed. Therefore, the fetus is essentially not protected yet. Serious treatment cannot be carried out at this stage. But the doctor may prescribe topical medications to relieve the inflammatory process. These may be Cholisal, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin.
13-24 weeks. At this time, the placenta has already formed and protects the baby. Therefore, dental treatment and other procedures can be performed.
From the 25th week until birth. At this time, the female body is weakened, and the uterus is very sensitive to the effects of drugs. In addition, a visit to the dentist is often stressful for an expectant mother. Therefore, it is better to wait for treatment procedures until the feeding period. However, this does not apply to cases of acute toothache.
Arterial hypertension and pregnancy
Pregnancy with arterial hypertension (AH) is considered a risk group for miscarriage, increased perinatal and maternal morbidity and mortality. Therefore, women with hypertension need to plan pregnancy in advance, in consultation with a general practitioner and obstetrician-gynecologist.
An important feature of the classification of blood pressure during pregnancy is the differentiation of chronic and gestational hypertension. Chronic hypertension usually precedes pregnancy or can be diagnosed before the 20th week of pregnancy. In most cases, this type of hypertension persists after 42 days after birth. Chronic arterial hypertension includes:
- Primary (hypertension, essential hypertension).
- Secondary (symptomatic), when arterial hypertension is a manifestation of diseases of the kidneys, adrenal glands, thyroid gland, cardiovascular system, etc.
Gestational hypertension
, as a rule, develops after the 20th week of pregnancy and in most cases disappears within the next 42 days after birth. The following types of gestational hypertension are distinguished:
1. Without proteinuria
(transient, transient hypertension), in which the daily loss of protein in urine is less than 0.3 g/l.
I degree
(moderate) – without complicated course.
II degree
(severe) - with a complicated course: high diastolic blood pressure (more than 110 mmHg), hypoalbuminemia (less than 18 g/l), thrombocytopenia (less than 100x10*9/l), oliguria, intrauterine growth retardation, pulmonary edema , neurological symptoms
2. With proteinuria
(preeclampsia, preeclampsia). Urinary protein excretion is more than 0.3 g/l per day.
I degree
- without complicated course.
II degree
- with a complicated course and daily proteinuria more than 3.5 g/l
3. Preeclampsia.
4. Eclampsia:
convulsive and non-convulsive forms.
Arterial hypertension, which cannot be classified in the antenatal period, is also distinguished.
A correctly collected anamnesis, blood and urine tests, an objective examination, including measurement of blood pressure in both arms, ABPM, ultrasound of the kidneys, auscultation of the heart and lungs, ECG, and fundus examination help in diagnosing hypertension. A hyposodium diet, work and rest schedule for a pregnant woman are important components of good health. Properly selected antihypertensive therapy, according to FDA recommendations, avoids the development of the most common complication of hypertension - the development of preeclampsia, which can develop from 28-32 weeks; as well as feto-palecentral insufficiency, fetal hypoxia, the occurrence of FGR; abruption of a normally located placenta; premature birth, intrauterine fetal death.
Treatment of mild arterial hypertension can be carried out on an outpatient basis, while pregnant women with moderate to severe hypertension, newly diagnosed, should be sent to the hospital to monitor hemodynamic parameters and select therapy. European recommendations and the FDA (USA) for the treatment of hypertension during gestation include methyldopa, calcium antagonists, Labetolol, and b-blockers as the drugs of choice. Complex therapy necessarily includes magnesium preparations (MagneB6, MagnelisB6, Magnerot, Panangin). The use of diuretics (furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide) occurs more often in a hospital, in combination with other drugs, when there is fluid retention in the body, in the absence of contraindications (FGR).
The sequence of antihypertensive therapy depends on the trimester of pregnancy and the expected effect, and is regulated by a general practitioner and an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Obstetric care is recommended in a specialized cardiology maternity hospital or a maternity hospital at a multidisciplinary hospital.
Author of the publication: Vasilisa Mikhailovna Petushinova, general practitioner (pregnancy care), gastroenterologist. Conducts receptions in the clinic building on Novoslobodskaya.
Dental diagnostics during pregnancy
If there is a need to remove a tooth or the patient has been diagnosed with pulpitis, an image cannot be avoided. However, traditional X-rays are contraindicated for pregnant women. After all, the fetus is sensitive to radiation. If an x-ray is necessary, it is best to postpone such a diagnosis to the 2nd trimester. In this case, it is necessary to cover the patient’s abdomen and pelvic area with a lead belt. It minimizes exposure to radiation.
The safest method of dental diagnosis for pregnant women is digital radiovisiography. This technique allows you to reduce the radiation load by 90% compared to conventional x-rays.
Features of anesthesia for pregnant women
During pregnancy, drugs that have minimal effects on blood vessels are used for pain relief. They also cannot cross the placenta and affect the baby.
Lidocaine is contraindicated during pregnancy. It can cause a sharp decrease in blood pressure, cramps and weakness.
Today, the best anesthesia option for pregnant women remains drugs based on anticain:
- Ultracaine.
- Altrifryn.
- Ubistezin.
- Alfacaine.
The listed drugs do not constrict blood vessels, which would be harmful for the expectant mother. They also have a local effect, so they do not affect the baby.
Panangin - basic information
A synthetic complex preparation based on potassium and magnesium in the form of aspirants is easily absorbed and stimulates natural metabolic processes. The active substances are non-toxic and therefore not dangerous to the fetus. The drug is often used as part of complex therapy.
Panangin is produced in the form of tablets and solution
Panangin is produced in the form of tablets and solution, which have the following composition.
Tablet form:
- potassium, magnesium aspirantate;
- corn starch, potato starch;
- talc;
- magnesium stearate;
- povidone;
- pyrogenic silica, etc.
Liquid for intravenous use:
- potassium, magnesium aspirantate;
- purified water.
Panangin during pregnancy is prescribed in the following cases:
- Arrhythmia.
- Reduction or complete cessation of coronary blood flow.
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Taking cardiac glycosides.
- Potassium and magnesium deficiency due to poor nutrition.
Thus, Panangin supports the activity of the heart and blood vessels and is used as part of the complex treatment of cardiac pathologies.
The drug is often prescribed in the 2nd trimester to replenish the deficiency of potassium, magnesium and improve myocardial function. In such cases, the medication is used to prevent and treat cardiovascular diseases. This is necessary, since during pregnancy the load on the myocardium increases due to an increase in the volume of pumped blood. This often leads to exacerbation of chronic diseases in the expectant mother.
The beginning of the second trimester is often complicated by heart rhythm disturbances, shortness of breath, swelling, and convulsions. To eliminate such symptoms, Panangin is prescribed. The drug improves heart function, has a sedative effect, has a beneficial effect on the nervous system, and increases resistance to stress.
If a pregnant woman takes glycosides and diuretics to treat heart disease, then Panangin reduces the negative effects of these drugs. For this reason, the combination remedy is often combined with other medications (Ginipral, Riboxin, Magne B6, etc.). However, Panangin cannot be combined with all medications.
Tooth extraction during pregnancy
Tooth extraction is a good reason for stress. During pregnancy it is strictly contraindicated. Therefore, the decision to remove a tooth is made only in extreme cases:
- The presence of a cyst more than 1 centimeter in diameter.
- Fracture of the root or crown.
- Acute pain that cannot be relieved in any other way.
- A deep focus of caries, which is a source of suppuration.
Wisdom teeth should never be removed in pregnant women. After all, after such an operation the socket often becomes inflamed. Stopping this process requires taking antibiotics. This, in turn, is extremely undesirable for the mother and fetus.
Magnesium deficiency
Magnesium is also extremely important in metabolic processes. In addition, magnesium transports potassium across the plasma membrane. Therefore, it is impossible to eliminate potassium deficiency without compensating for magnesium deficiency. Combination preparations that contain potassium and magnesium are used precisely for this purpose.
Magnesium deficiency causes muscle spasms, tremors, and dizziness.
Causes of hypomagnesemia:
- Functional kidney failure.
- Diarrhea with pancreatitis.
- Diabetes mellitus, thyroid diseases, etc.
Potassium deficiency is manifested by tremor (muscle tremors), muscle spasms, nervousness, dizziness, and lack of coordination of movements.
Thus, potassium and magnesium are vital, and their deficiency can lead to serious illnesses.