In this article we will try to figure out whether it is possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke and what the consequences are.
No one is immune from diseases in this world; some of them can seriously threaten human life. For example, stroke has the second position on the list of deadly diseases. What kind of pathology is this and how is it dangerous for the patient?
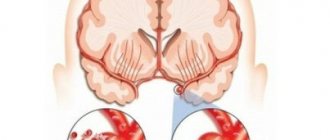
A stroke is a circulatory disorder that causes cells in the brain to die, resulting in either death or varying degrees of disability.
Stroke: main causes
Is it possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke? We’ll figure it out below. In the meantime, let’s find out what causes the disease.
The main reason for this dangerous pathology is that one of the brain vessels is blocked by blood clots or foreign objects. Blood cannot get through this barrier; as a result, acute oxygen starvation occurs, and some of the cells die. This phenomenon is called “ischemic stroke”. It is better to find out in advance whether it is possible to fly after such a pathology.
A hemorrhagic stroke is when an artery ruptures and blood spills into the outer tissue of the brain, causing swelling that causes the death of cells and nerve fibers.
The main thing is timely help
This disease is very dangerous for human health; half of the cases are fatal. But if you provide the patient with medical care in time, his life can be saved. After a stroke has occurred, the patient must be placed in the intensive care unit within 3-4 hours, in some cases an operation by a neurosurgeon will be required. The less time it takes to get to the hospital, the higher the chances that the person will remain alive and will not become disabled. However, the area of the affected area of the brain is important: serious complications cannot be avoided if it is large.
Recommendations for patients after surgery
Inpatient rehabilitation phase During the first hours after surgery,
you will wake up in the intensive care unit.
The anesthesiologist and nurse will monitor your body temperature, pulse, blood pressure and other indicators. During surgery, you may have a catheter inserted into your bladder to monitor the amount of urine you produce. You will also have a chest tube connected to a drainage device. During the first hours/days after surgery, your voice may be slightly different from normal, this is normal. You may remain in the recovery room for one or several days, depending on your condition after surgery. Then you will be transferred to the ward in the surgical department where you were originally located. Frequently Asked Questions Will I experience pain after surgery?
You will experience pain after surgery, this is normal.
Your doctor and nurse will ask you frequently about your pain and give you pain medications as needed. If the pain does not go away, tell your doctor or nurse. Pain relief is essential so that you can clear your throat, breathe deeply, and get out of bed and walk. Remember that taking painkillers can lead to constipation (retention of stool for more than 2-3 days). If constipation occurs, consult your doctor. Upon discharge, your doctor will give you recommendations on taking pain medications. What is pleural drainage and why do I need it?
A chest tube is a flexible tube that drains blood, fluid, and air that accumulates in the chest cavity after surgery. This tube is placed between the ribs in the space between the chest and lungs (see Figure 1).
Picture 1
Chest drainage and pleural banking.
The timing of drainage of the pleural cavity is individual for each patient.
Removal of pleural drainage is carried out by the attending physician if 2 conditions are met: 1) the amount of fluid released does not exceed 200 ml/day 2) there is no air flow through the drainage . Why is it important to walk after surgery?
Walking helps prevent blood clots from forming in the legs.
It also reduces the risk of other complications, such as pneumonia. During your postoperative hospital stay, try to set yourself a goal of walking 1.5-2 km daily. Will I be able to eat after surgery?
You will gradually return to your normal diet when you are ready.
Your healthcare provider will provide you with more information. Can I shower?
You can shower 48 hours after your chest tube is removed.
A warm shower is relaxing and helps reduce muscle pain. Try to avoid contact of the wound with water until it is completely healed. If you do get the bandage wet, contact your doctor to change the bandage. When can visitors come to me?
Visitors can visit you as soon as you are transferred from the intensive care unit to the surgical unit.
You can find out the hours during which visits are allowed from your attending physician at the department. When will I be discharged from the hospital?
The length of your hospital stay depends on many factors, such as the type of surgery you had and how well your recovery was. You will remain in the hospital until your doctor thinks you are ready to go home. Your doctor will tell you what day and time you can expect to be discharged. Your doctor will tell you if you need to stay in the hospital longer than planned. The following are examples of reasons why you may need to stay in the hospital for a longer time:
- prolonged release of air through pleural drainage;
- problems with healing of postoperative wounds;
- breathing problems;
- increase in temperature in the postoperative period (38.0 °C) and higher.
Recovery after returning home Will I feel pain when I return home?
The duration of the presence of pain and discomfort in the area of surgical access is different for each person and depends on a large number of factors.
Thus, pain after open operations will be stronger and longer lasting than after video-assisted thoracoscopic and robotic operations. For some people, pain in the area of the surgical wound or a feeling of tightness or aching muscles may continue for 6 months or longer. This doesn't mean there's anything wrong with you. Follow the guidelines below. Take pain medications as directed by your doctor and as needed. Call your doctor if the prescribed medicine does not relieve your pain. Do not drive or drink alcohol if you are taking prescription pain medication. As your surgical wounds heal, the pain will become less painful and you will need less pain medication. To relieve pain and discomfort, mild painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are suitable: ketanov, ibuprofen (Nurofen-express), Nise (imisulide), xefocam (lornaxicam), diclofenac, as well as other drugs in this group. Pain medications should help you as you return to your normal routine. Take enough medication so that you can exercise comfortably. Remember that it is normal for a slight increase in pain as your activity level increases. Keep track of when you take pain medications. Pain medications are most effective 30 to 45 minutes after you take them. It is better to take the medicine at the first appearance of pain and not wait for it to intensify. How should I care for surgical wounds?
After surgery, you will have several incisions. The location of the incisions will depend on the type of surgery performed. They will be performed at the site of the operation and at the site of the chest tube. You may experience some numbness below and above the incision, as well as along the intercostal space where the incision was made. You may also experience tingling and tenderness in the area around your incisions as they heal. By the time you leave the hospital, your surgical wounds will begin to heal.
Change the wound dressing daily and clean the wound with skin antiseptic/diamond green/betadine (check with your healthcare provider for instructions on how to care for surgical wounds).
Upon discharge, your attending physician will give recommendations on when to remove sutures from post-operative wounds. To do this, you will need to contact a surgeon at the clinic at your place of residence.
If, after discharge from the hospital, discharge appears in your postoperative wounds, contact your doctor.
What should I eat at home?
Eating a balanced, high-protein diet will help you recover faster after surgery.
Your diet should include a source of healthy protein at every meal, as well as fruits, vegetables and whole grains. How can I prevent constipation?
After surgery, your bowel movements will change.
There may be problems with bowel movements (stool excretion). If you can, drink 8 glasses (250-300 ml each, 2 liters total) of fluid daily. Drink water, juices, soups, milkshakes and other caffeine-free drinks. Caffeinated drinks, such as coffee and soda, remove fluid from the body. Both prescription and over-the-counter medications are used to treat constipation. If constipation occurs, start with 1 of the following over-the-counter medications: Docusate sodium (Norgalax) 100 mg. Take 3 capsules once daily. This remedy softens the stool and causes only minor side effects. Senna 2 tablets before bed. It is a stimulant laxative that may cause cramping. How can I speed up the recovery process?
Exercise for at least 30 minutes a day. This will make you stronger, improve your well-being and promote recovery. Incorporate a daily walk into your daily schedule. Just walking down the street or walking on a gym will do. If the weather is not very suitable for walking, you can spend time in the shopping center. Climbing stairs is also suitable as a workout. When you return home, continue to do deep breathing exercises and exercises that stimulate coughing. Drink fluids so that the mucus is not thick and can be easily coughed up. Ask your doctor how much fluid you should drink daily. For most people, this will be at least 8-10 glasses (250-300 ml) of water or other liquids (such as juices) per day. During the winter months, run a humidifier in your bedroom. Follow the instructions for cleaning this device. Change the water in it frequently. Avoid contact with people who have a sore throat or cold or flu symptoms. All this can cause an infection to develop.
Do not drink alcohol, especially if you are taking pain medication.
Do not smoke.
Smoking cigarettes will always be harmful to your health. It is especially dangerous during the recovery period after surgery. Smoking causes blood vessels to narrow. This reduces the amount of oxygen supplied to wounds during their healing process, which significantly slows down the regeneration process. Remember, if you are not able to quit smoking on your own, you can contact the “Smoking Quit Assistance Center” located on the territory of the St. Petersburg NIIF by contacting them on the hotline (+7). Can I return to normal activities?
It is very important that you return to your normal activities after surgery. Distribute their implementation throughout the day. Walking and climbing stairs are excellent exercise. Gradually increase the distance you walk. Climb the stairs slowly, resting and stopping as needed. Do light housework. To the best of your ability, try to dust, wash dishes, cook simple meals, and do other tasks. When going about your business, use the arm and shoulder on which the operation was performed. For example, wash yourself, comb your hair, take things out of the closet shelf with this hand. This will help restore full function of the arm and shoulder.
You can return to your normal sex life as soon as the post-operative wounds have healed, without experiencing any pain or weakness.
Your body will tell you when you are overtired.
As you increase the intensity of your exercise, monitor your body’s reaction. You may notice that you have more energy in the morning or afternoon. Schedule your activities for the time of day when you feel more energetic. Is it normal to feel tired after surgery?
Typically, a person has less strength than usual after surgery.
Recovery time is different for everyone. Increase your activity every day to the best of your ability. Always maintain a balance between periods of activity and periods of rest. Rest is an important factor in your recovery. It may take some time for you to return to your normal sleep pattern. Try not to sleep during the day. Showering before bed and taking prescribed pain medications will also help. When will I be able to drive?
You will be able to drive again after: the range of motion of the arm and shoulder on which the operation was performed is restored to full extent;
you will not take narcotic pain medications (which make you drowsy) for 24 hours. Can I travel by plane?
Do not fly by plane until your doctor allows it; in the first months after surgery, try to use other means of transport or completely avoid long-distance travel.
When can I return to work?
The time frame for returning to work depends on what type of job you have, what type of surgery you had, and how quickly your body recovers.
If you need a certificate to return to work, contact your doctor. When can I lift weights?
Check with your doctor before lifting weights.
It is generally not recommended to lift anything heavier than a normal grocery bag (5kg) for at least 1 month after surgery. Ask your doctor how long you should avoid lifting heavy objects. This depends on the type of surgery you had. Which doctors should I see after surgery?
Upon discharge from the hospital, your attending physician will give you a discharge summary with further recommendations.
If it is necessary to consult any specialists, this will be indicated in the epicrisis. What questions should you contact your doctor about?
Sometimes in the postoperative period the patient may be bothered by the following conditions:
- shortness of breath appeared or worsened;
- swelling of the chest, neck, or face;
- the voice changed dramatically;
- temperature increased (38.0 °C) or higher;
- the pain has sharply increased and does not go away after taking painkillers;
- redness or swelling appears around the postoperative wound;
- there is discharge from the postoperative wound that has an unpleasant odor, thick consistency or yellow color (similar to pus);
- no bowel movements for 3 days or longer;
- new symptoms or physical changes appear;
And if you have any questions or concerns regarding your health, please contact your healthcare provider.
Full version
© Website of a medical organization
The information posted on the site is not a public offer
- Cabinet
- Personal data
- Coupons
- My services
- Test results
- My requests
- Exit
Long rehabilitation
Even with a successful operation, the patient will undergo rehabilitation for a long time. Most people after a stroke learn to live again and deal with the negative consequences of the disease. On average, a patient’s normal life can begin only after 2 months. It takes much longer to return to work; Driving a car or business trips to other cities and countries are unavailable to many for a very long time.
Patients who have suffered a stroke in the recent past, whose life was completely or partially associated with travel, ask doctors the question: “Is it possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke?”
Will flights be allowed?
As a rule, the doctor's answer will be positive. You can use air transport, but there are certain conditions and restrictions. This is important to remember. The problem is that, in fact, flying is a tiring and difficult process even for a healthy person.
Due to severe changes in pressure, stress and panic, and an unfavorable atmosphere in the aircraft cabin, repeated cerebral hemorrhage may occur, which will be fatal for most patients. What is especially scary is that qualified assistance will not be provided, because it is impossible to do this at altitude.
What points should be taken into account?
So, what is the opinion of doctors about whether it is possible to fly after a stroke? Typically, attending physicians allow such travel if the following points are taken into account:
- How much time has passed. If more than six months have passed since the operation, but not less than 2 months. It is a big plus if no health-threatening complications arise during this period. That is, after complete recovery from a stroke, you can fly.
- Quality of rehabilitation. The recovery period for the patient was completed successfully, massage and physical exercises were used.
- At what level is your blood pressure? It should be normal, without a sharp rise and fall, the threshold of 140/90 should not be exceeded. Regular intake of prescribed medications is important.
- Is the patient susceptible to aerophobia? Is it possible to fly after a brain stroke if you have a fear of flying? It is extremely important that a person does not suffer from aerophobia, as it provokes severe anxiety and stress.
If all conditions are met and the patient has confidence in his abilities, then he is allowed to fly and is prescribed certain recommendations.
Insurance programs for stroke and heart attack
Not all insurance companies offer special insurance programs for critical illnesses, which include strokes and heart attacks. For example, Raiffeisen Life has a program that includes the listed diseases in the list of insured events - the “Health Standard Plus” program. In addition, it will provide protection in case of diagnosis of cancer. When choosing an insurance program, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- Does the insurance cover only Russia or is it possible to travel abroad for treatment? There are programs that provide free flights for the sick person and accompanying person abroad, and payment for treatment in foreign clinics. In this case, you need to clarify which countries are covered by the insurance (for example, “Health Standard Plus” includes treatment in clinics with a premium level of service in Europe and Russia, in addition, the client can independently choose a country and clinic for treatment from the list proposed Insurer);
- the amount of payments is 100% of the insured amount or a lesser amount. What amount will the company pay directly upon diagnosis of stroke and heart attack, will the stay in the clinic and surgical intervention be paid for;
- availability of treatment limits (the “Health Standard Plus” program provides for an exceptionally high treatment limit - €2,113,000);
- maximum age of the insured and other requirements;
- the ability to connect family members to the program.
We state: everyone can protect themselves from strokes and heart attacks by leading a healthy lifestyle and undergoing timely diagnosis. There are insurance programs that allow you to receive support in the form of cash payments when diagnosing strokes and heart attacks. At a time when a person urgently needs money for treatment, recovery, rehabilitation, representatives of the insurance company will be nearby. The opportunity to receive help in qualified clinics is often a decisive factor in the process of full recovery of health after a stroke and heart attack.
The preparation must be correct
We continue to figure out whether it is possible to fly after a stroke. In advance, the patient must prepare himself and his blood vessels for high load.
The preparation process includes:
- Taking certain medications. Most often, doctors prescribe special blood-thinning medications (aspirin is considered the most popular) that prevent blood clots in blood vessels and relapse of the pathology.
- Passing examinations. Before the flight, an electrocardiogram and ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head are required. This is required to eliminate the possibility of aneurysm formation. During the flight, pressure changes are possible, and an aneurysm may rupture, leading to a fatal brain hemorrhage on an airplane after a stroke.
- Own first aid kit. The patient must plan in advance what medications he will take with him on the plane. The first aid kit should consist of medications that stabilize blood pressure and sedatives; medications against motion sickness are also useful.
If the preparation is carried out correctly by the patient, then it is possible to fly after a stroke.
Also, the trip will be comfortable if you purchase special pillows for the head, in this way the unnecessary load on the cervical spine and blood vessels will be reduced. Excessively fatty foods are contraindicated before a flight; it is better to prefer light foods.
Symptoms worsen at altitude
At altitude, the typical symptoms of hypertension worsen:
- The occurrence of migraine is a cerebrovascular disease due to prolonged spasm of blood vessels in the head. A dangerous complication is the cerebral form of hypertension (stroke). To prevent arterial hypertension from developing into a malignant form, it is worth defeating migraine at the initial stage.
- The appearance of pressing chest pain. The heart works overtime, so discomfort in the chest may turn out to be angina. If there is a history of myocardial ischemia in hypertensive patients, they should fly with great caution.
- Having severe shortness of breath. Limited space and elevation lead to a feeling of lack of oxygen; reflex shortness of breath may occur in response to stress. To avoid real suffocation, the patient’s breathing must be deep and even; oxygen cocktails can come to the rescue.
- Development of tachycardia. The intense work of blood vessels leads to a rapid heartbeat, because they quickly pump large amounts of blood. This leads to spasm of blood vessels and tension in their walls.
Let's find out whether it is possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke: doctors' opinions, all the pros and cons
In this article we will try to figure out whether it is possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke and what the consequences are.
No one is immune from diseases in this world; some of them can seriously threaten human life. For example, stroke has the second position on the list of deadly diseases. What kind of pathology is this and how is it dangerous for the patient?
A stroke is a circulatory disorder that causes cells in the brain to die, resulting in either death or varying degrees of disability.
Stroke: main causes
Is it possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke? We’ll figure it out below. In the meantime, let’s find out what causes the disease.
The reason for this dangerous pathology is that one of the brain vessels is blocked by blood clots or foreign objects. Blood cannot get through this barrier; as a result, acute oxygen starvation occurs, and some of the cells die. This phenomenon is called “ischemic stroke”. It is better to find out in advance whether it is possible to fly after such a pathology.
A hemorrhagic stroke is when an artery ruptures and blood spills into the outer tissue of the brain, causing swelling that causes the death of cells and nerve fibers.
The main thing is timely help
This disease is very dangerous for human health; half of the cases are fatal. But if you provide the patient with medical care in time, his life can be saved.
After a stroke has occurred, the patient must be placed in the intensive care unit within 3-4 hours, in some cases an operation by a neurosurgeon will be required. The less time it takes to get to the hospital, the higher the chances that the person will remain alive and will not become disabled.
However, the area of the affected area of the brain is important: serious complications cannot be avoided if it is large.
Long rehabilitation
Even with a successful operation, the patient will undergo rehabilitation for a long time. Most people after a stroke learn to live again and deal with the negative consequences of the disease.
On average, a patient’s normal life can begin only after 2 months.
It takes much longer to return to work; Driving a car or business trips to other cities and countries are unavailable to many for a very long time.
Patients who have suffered a stroke in the recent past, whose life was completely or partially associated with travel, ask doctors the question: “Is it possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke?”
Will flights be allowed?
As a rule, the doctor's answer will be positive. You can use air transport, but there are certain conditions and restrictions. This is important to remember. The problem is that, in fact, flying is a tiring and difficult process even for a healthy person.
Due to severe changes in pressure, stress and panic, and an unfavorable atmosphere in the aircraft cabin, repeated cerebral hemorrhage may occur, which will be fatal for most patients. What is especially scary is that qualified assistance will not be provided, because it is impossible to do this at altitude.
What points should be taken into account?
So, what is the opinion of doctors about whether it is possible to fly after a stroke? Typically, attending physicians allow such travel if the following points are taken into account:
- How much time has passed. If more than six months have passed since the operation, but not less than 2 months. It is a big plus if no health-threatening complications arise during this period. That is, after complete recovery from a stroke, you can fly.
- Quality of rehabilitation. The recovery period for the patient was completed successfully, massage and physical exercises were used.
- At what level is your blood pressure? It should be normal, without a sharp rise and fall, the threshold of 140/90 should not be exceeded. Regular intake of prescribed medications is important.
- Is the patient susceptible to aerophobia? Is it possible to fly after a brain stroke if you have a fear of flying? It is extremely important that a person does not suffer from aerophobia, as it provokes severe anxiety and stress.
If all conditions are met and the patient has confidence in his abilities, then he is allowed to fly and is prescribed certain recommendations.
The preparation must be correct
We continue to figure out whether it is possible to fly after a stroke. In advance, the patient must prepare himself and his blood vessels for high load.
The preparation process includes:
- Taking certain medications. Most often, doctors prescribe special blood-thinning medications (aspirin is considered the most popular) that prevent blood clots in blood vessels and relapse of the pathology.
- Passing examinations. Before the flight, an electrocardiogram and ultrasound examination of the vessels of the head are required. This is required to eliminate the possibility of aneurysm formation. During the flight, pressure changes are possible, and an aneurysm may rupture, leading to a fatal brain hemorrhage on an airplane after a stroke.
- Own first aid kit. The patient must plan in advance what medications he will take with him on the plane. The first aid kit should consist of medications that stabilize blood pressure and sedatives; medications against motion sickness are also useful.
If the preparation is carried out correctly by the patient, then it is possible to fly after a stroke.
Also, the trip will be comfortable if you purchase special pillows for the head, in this way the unnecessary load on the cervical spine and blood vessels will be reduced. Excessively fatty foods are contraindicated before a flight; it is better to prefer light foods.
Symptoms worsen at altitude
At altitude, the typical symptoms of hypertension worsen:
- The occurrence of migraine is a cerebrovascular disease due to prolonged spasm of blood vessels in the head. A dangerous complication is the cerebral form of hypertension (stroke). To prevent arterial hypertension from developing into a malignant form, it is worth defeating migraine at the initial stage.
- The appearance of pressing chest pain. The heart works overtime, so discomfort in the chest may turn out to be angina. If there is a history of myocardial ischemia in hypertensive patients, they should fly with great caution.
- Having severe shortness of breath. Limited space and elevation lead to a feeling of lack of oxygen; reflex shortness of breath may occur in response to stress. To avoid real suffocation, the patient’s breathing must be deep and even; oxygen cocktails can come to the rescue.
- Development of tachycardia. The intense work of blood vessels leads to a rapid heartbeat, because they quickly pump large amounts of blood. This leads to spasm of blood vessels and tension in their walls.
Maybe you should choose another transport?
A person must take responsibility for his own condition while traveling. After a mini-stroke, you can fly on an airplane. However, if you have a choice of mode of transport, it is better to choose a bus or train. It may take longer to get there, but many unpleasant health issues will be avoided.
What are the dangers of flying after a stroke?
However, during the flight, the patient may in any case encounter various kinds of problems that cannot be foreseen in advance.
So, the problems could be the following:
- Dry air. The skin dries quickly due to air conditioning on airplanes, and the unpleasant thing is that the body quickly becomes dehydrated. But this provokes thickening of blood in the vessels, which can turn into a mortal danger for a person after a stroke.
Therefore, you need to drink more fluids, but not tea and coffee, but pure water, and still. Alcoholic drinks are strictly prohibited; their influence is detrimental to the cardiovascular system, and as a result, a heart attack can occur.
Long sitting position
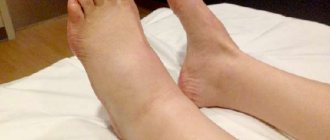
Passengers on the plane remain motionless for a long time. Physical inactivity can cause blood clots, resulting in a recurrent stroke. This possibility will be higher the longer the flight lasts. Flights typically last more than five hours, so passengers often experience swollen feet.
Wearing compression garments under regular clothing will help prevent this. Women can buy special compression tights. They will disperse the blood where it stagnates.
Sometimes it is acceptable to get up from your seat at least once and walk around the salon, of course, when this is not prohibited. To disperse blood throughout the body, it is good to rotate your hands, feet and neck.
In general, simple health-improving exercises will help.
Discomfort
Sitting for a long time is uncomfortable due to the small distance between the chairs. To improve your position, you can take off your shoes and put on slippers, thereby allowing blood to flow better to your feet. It would be a good idea to use a special pillow under your neck; its benefits have already been discussed above.
Stress, anxiety, fear
It is better to try to avoid this. It's normal to feel anxious during a flight. Both women and men suffer from this equally. To reduce stress levels, drink a sedative: the drug Novo-Passit or valerian tincture is safe.
The most dangerous moments of a flight for a patient will be takeoff and landing, as well as turbulence.
Landing and takeoff
Their main danger is that at this time the atmospheric pressure changes. This negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
There is less oxygen in the cabin, which leads to dizziness, shortness of breath and problems with the heart. This all has an adverse effect on the patient after a stroke and can cause re-hemorrhage.
What else is dangerous about flying on an airplane after a stroke?
Turbulence
An unpleasant vibration appears when the plane hits air pockets. Under its influence, the heart rhythm may be disrupted, as well as blood circulation and blood supply to the brain. A new blood clot forms, and subsequently another stroke.
The only advice in this case would be the following. You need to calm down and try to sleep.
If you follow all the doctors’ recommendations, nothing bad should happen, especially if throughout the flight the patient kept his blood pressure under control, consumed enough fluids and stretched his legs. The trip will be comfortable and without serious consequences. How to fly by plane after a stroke?
How to transport a sick person by plane?
Many problems during a flight can be avoided if the special state of the body is discussed in advance with the air carrier at the stage of booking a ticket.
It is important to understand that if transportation involves a transfer, then the conditions must be agreed upon along the entire route.
Are there any age restrictions for old people? If an elderly person does not have any special health problems, then a medical certificate and support will not be required. A person needs help only when getting on and off.
At the stage of booking a ticket, you should notify about limited mobility and possible additional assistance (about a special diet, special services - for example, receiving a stroller or gurney at the airport), etc.
Passengers requiring special assistance in the aircraft cabin must be issued a medical certificate by a doctor.
If it is necessary to have an accompanying person, a second seat in the cabin is provided next to the stretcher.
Patients are boarded before the rest of the passengers board, and disembarked after everyone else.
Disabled persons must travel with accompanying persons. If transportation is carried out under the supervision of the carrier, then consent must be obtained in advance from the company itself, and it must be in writing.
People who are blind or hearing impaired must also be accompanied. If this is not possible, a guide dog may be present on board. Typically, such a dog can be kept in a cabin without a crate if:
- man depends on the animal;
- there is a certificate of training for such needs;
- it has a muzzle, the animal is located at the human’s feet.
Before any flight, persons with special medical conditions should consult their attending physician.
In order for a sick, disabled or elderly person to fly on a regular aircraft, and these categories of citizens need care, a certain number of seats are purchased for accompanying persons - medical staff, loved ones.
We looked at the question of whether it is possible to fly on an airplane after a stroke.
Source: https://autogear.ru/article/470/135/mojno-li-letat-na-samolete-posle-insulta-mneniya-vrachey-vse-za-i-protiv/
What are the dangers of flying after a stroke?
However, during the flight, the patient may in any case encounter various kinds of problems that cannot be foreseen in advance.
So, the problems could be the following:
- Dry air. The skin dries quickly due to air conditioning on airplanes, and the unpleasant thing is that the body quickly becomes dehydrated. But this provokes thickening of blood in the vessels, which can turn into a mortal danger for a person after a stroke.
Therefore, you need to drink more fluids, but not tea and coffee, but pure water, and still. Alcoholic drinks are strictly prohibited; their influence is detrimental to the cardiovascular system, and as a result, a heart attack can occur.
What effects does our body experience at altitude?
- The ability to think clearly decreases. This is explained simply: the brain needs a sufficient amount of oxygen to function normally.
- Ringing in the ears, stuffiness. The reason is sudden pressure changes, especially noticeable during takeoff and landing.
- Taste buds become dulled. Why is this happening? The combination of low atmospheric pressure and dehydration reduces the sensitivity of taste buds by approximately 30%. Don't forget to drink water on the road! By the way, dehydration explains why tomato juice tastes so good on an airplane.
- Night vision deteriorates. Photoreceptor cells in the retina are in dire need of oxygen, so when the oxygen content is low, their efficiency decreases.
- Dry skin. Conditioned, very dry air is supplied to the cabin. Thermal water in an aerosol or hydrogel masks will help your skin out of stress.
- Motion sickness. An unpleasant disease (and this is exactly a disease, and it has an official name - kinetosis) affects 30% of the world's population. Kinetosis occurs due to a discrepancy between the information from the sensory organs and the vestibular apparatus. Simply put, the nervous system becomes confused when it receives opposing signals from different body systems at the same time.
- Circadian rhythms are disrupted. These cyclical processes in the body, associated with the alternation of day and night, are responsible for the alternation of sleep and wakefulness, and help the body regulate all body activities. With a sudden change in time zones, the body needs time to adjust to the new regime. We may experience jet lag, which is expressed by absent-mindedness, decreased performance, a general feeling of malaise, and gastrointestinal disorders.
- The risk of thrombosis increases. During long flights, you have to sit in one position for a long time, which causes blood stagnation. To minimize risks, we recommend doing simple exercises that speed up the blood in the extremities.
People who have a hereditary predisposition to thrombosis, or are at risk of thrombosis, are recommended to regularly take tests for five laboratory indicators of the risk of thrombosis and monitor their dynamics:
1. Prothrombin
- a complex protein, one of the most important indicators of a coagulogram, characterizing the state of the blood coagulation system.
2. Activated partial thromboplastin time
- reflects the work of the so-called internal pathway and the general cascade of the human blood coagulation system and is the most sensitive indicator of blood clotting.
3. Fibrinogen
- under the influence of thrombin, two subunits of peptide A and peptide B are split off from fibrinogen, and it turns into insoluble fibrin, which becomes the basis for the formation of a blood clot.
4. D-dimer
- a fibrin breakdown product, a small protein fragment present in the blood after the destruction of a blood clot.
5. Cholesterol
- one of the most important indicators of lipid metabolism, used as a screening test to assess the risk of atherosclerotic changes and vascular disorders in the future.
Long sitting position
Passengers on the plane remain motionless for a long time. Physical inactivity can cause blood clots, resulting in a recurrent stroke. This possibility will be higher the longer the flight lasts. Flights typically last more than five hours, so passengers often experience swollen feet.
Wearing compression garments under regular clothing will help prevent this. Women can buy special compression tights. They will disperse the blood where it stagnates. Sometimes it is acceptable to get up from your seat at least once and walk around the salon, of course, when this is not prohibited. To disperse blood throughout the body, it is good to rotate your hands, feet and neck. In general, simple health-improving exercises will help.
Turbulence
An unpleasant vibration appears when the plane hits air pockets. Under its influence, the heart rhythm may be disrupted, as well as blood circulation and blood supply to the brain. A new blood clot forms, and subsequently another stroke.
The only advice in this case would be the following. You need to calm down and try to sleep. If you follow all the doctors' recommendations, nothing bad should happen, especially if throughout the flight the patient kept his blood pressure under control, consumed enough fluids and stretched his legs. The trip will be comfortable and without serious consequences. How to fly by plane after a stroke?
What is the algorithm for preventing stroke?
Let's try to imagine a stroke prevention scheme for a middle-aged person.
- A prerequisite is a healthy diet, giving up bad habits, maintaining normal body weight and daily physical activity.
- Examination for susceptibility to atherosclerosis: taking into account heredity, blood test for lipid profile, ultrasound of brachiocephalic arteries with assessment of the thickness of the “intima-media complex” (an expert method for early diagnosis of atherosclerosis). If elevated levels of “bad” cholesterol and signs of atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries are detected, discuss with your doctor the issue of prescribing drugs that lower cholesterol levels.
- Daily (Holter) monitoring of ECG and blood pressure to identify “hidden” hypertension and possible heart rhythm disturbances that threaten cardioembolic complications. It is recommended not to allow periodic increases in blood pressure above 130/80 mmHg. Art. If rhythm disturbances are detected, additionally perform cardiac ultrasound (EchoCG).
- MRI of the brain with X-ray contrast agent to identify possible aneurysms of the cerebral arteries. If they are detected, it is possible to perform low-traumatic endovascular clipping of aneurysms or open surgery.
If you still have questions, you can contact a cardiologist or neurologist online in the Doctis application.