Electrocardiography is included in the list of recommended studies for most patients, both adults and children. Therefore, its competent removal is an important skill for a medical specialist. The procedure involves sequentially performing the necessary steps and taking into account some features and nuances, which we will look into today.
Stages of the ECG procedure
Electrocardiography is a research method in which the electrical fields of the heart are recorded, provoked by contractions of the heart muscle. As a result, the specialist receives a cardiogram - an image of curve graphs. They can be displayed on a monitor or recorded on a special paper tape. To carry out this type of diagnosis, you need professional medical equipment - a cardiograph. This device consists of three required elements.
- An input device including electrodes, lead cables and their switches.
- Signal amplifier - allows you to amplify them to the value necessary for analysis.
- Recording unit for direct recording of a cardiogram.
When conducting an ECG, a specialist works sequentially with all these blocks, following a clear algorithm. It, in turn, is divided into several stages:
- preparing the room, equipment and patient for ECG;
- application of electrodes and connection of leads according to a specific scheme;
- adjusting the gain to correctly display the signal on the cardiogram;
- direct recording of the electrocardiogram.
For informative and reliable research results, it is necessary to avoid errors at each of these stages. Therefore, let’s take a closer look at their algorithms and features.
Methodology
To correctly take an ECG, you must follow the following algorithm of actions.
1. The manipulation begins with the subject being placed on a trestle bed or couch. It is necessary to expose the wrists, ankles and chest. It is important to monitor the patient’s emotional state, because any anxiety will be reflected in the cardiogram.
2. Electrodes are applied. A pad, usually made of gauze, soaked in isotonic saline solution is first placed between the skin and the electrode. You can use electrode paste, which improves conductivity. Electrodes should be applied and secured on the inner surface of the forearm and, accordingly, the lower leg.
Rules for applying electrodes on the upper extremities: red – right, yellow – left, on the lower extremities: green – left, black – right.
The last electrode does not record readings; it is used to ground the system to avoid electric shock from a faulty device.
3. Chest electrodes usually have suction cups because they must be removed and moved during the recording of the electrocardiogram. The places of their attachment are degreased and moistened with a tampon soaked in saline solution.
Layout of lead points on the chest
Additional chest leads V7, V8, V9 are usually removed when there is a need to clarify the picture of the posterobasal part of the left ventricular wall. This ECG technique is called Slopak. In total, two electrodes are applied - yellow (indifferent) - on the hand and red (active) on points in the intercostal space, midclavicular, anterior and axiolar regions.
Neb leads are also considered additional, they are bipolar, they allow one to evaluate focal changes in the myocardium of the posterior, anterolateral and upper part of the anterior wall of the left ventricle. The value of the technique is that the potential is measured directly above the heart region, and the limbs (from which standard electrodes were removed) fall out of the electrical circuit. This makes the signal very strong and allows transmission over long distances.
For leads along the Sky, standard electrodes are used, but they are placed according to a certain pattern. Point A – anterolateral, D – posterior, I – upper region of the anterior wall of the myocardium
4. After removing any lead, the nurse stops recording and only then switches the device to recording the next lead. Standard leads are recorded during quiet breathing, and then lead III is additionally written during inhalation. The next stage is recording the enhanced leads. To diagnose non-respiratory arrhythmia, registration is made after inhalation with breath-holding. At the end of the recording, the lead switch is placed in the “O” position. Remove the electrodes from the subject, wipe the attachment points dry.
Installation of electrodes
Both reusable and disposable electrodes can be used to take an ECG. The first option is used more often in medical institutions, because is more economical. Kit includes:
- electrodes for limbs: 4 pieces;
- electrodes placed on the chest (one or 6);
- pears with suction cups.
Each electrode must be connected to a cable that matches its color. The designations must be memorized, because Most often there is confusion with them.
- A red cable is connected to the electrode on the right hand.
- On the left is yellow.
- The green wire is connected to the electrode on the left leg.
- On the right there will be a black, grounding cable that does not take readings.
Home visit
Modern devices for taking ECGs are compact enough to call a cardiologist to conduct an examination at home. Portable devices have the same accuracy class as stationary devices in diagnostic and treatment institutions. As a rule, disposable electrodes are used with the device. In addition, usually a doctor who arrives to a patient’s call can decipher the cardiogram on the spot, which is very convenient and sometimes vital for seriously ill patients with acute chest pain and children.
The portable electrocardiograph can be six or twelve-channel, which fully meets diagnostic needs
The electrocardiography method allows you to evaluate the activity and condition of each part of the heart. Determine the areas of ischemia and the threat of infarction, the area and localization of the lesion, atrial and ventricular rhythm disturbances. This is a painless and fairly simple method that has high informative value and high patient adherence.
Fixation of electrodes on the limbs
On the legs, a pair of electrodes are fixed on the inside of the lower leg at the very bottom. It must be remembered that a grounding sensor is attached to the right leg. On the hands, electrodes are attached to the forearms.
With standard leads, indicators are taken as follows:
- left and right hands - first position;
- right arm and left leg - second position;
- left leg and arm - third position.
Thus, an Einthoven triangle is obtained, each side of which corresponds to one and possible leads.
Enhanced leads involve collecting a signal using one electrode, which records the potential difference between the area where it is applied and the conventional electrical zero. They have the following designations:
- right hand - aVR;
- left hand - aVL;
- left leg - aVF.
Cardiograph device
Most devices have a similar structural principle.
Schematic representation of the electrocardiogram recording chain
- Electrodes that need to be applied to the body and attachments to them (suction cups, belts, etc.).
- A switch that activates a pair of electrodes at the input to the amplifier.
- An amplifier that increases the signals from the electrodes so that they can be recorded, but ignores background noise, for example, from the movement of the subject.
- Recorder with the function of recording a cardiogram curve on film/paper.
- Filters that suppress network interference.
Before recording a cardiogram, it is necessary to calibrate the device - record millivolts
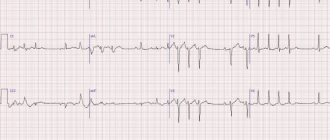
The technique of taking an ECG before starting recording involves calibrating the device - recording the calibration millivolt. This is the direct responsibility of nurses conducting functional diagnostics. Before recording data from the patient, a voltage of 1 millivolt is applied, and the device should display a deviation of 10 mm on the tape. If there is no calibration on the tape, then the correct reading of a given cardiogram can be questioned.
Fixation of electrodes in chest leads
If a single-channel study is carried out, then only one electrode is used. But in modern ECGs, for more accurate diagnosis, in most cases, 6 are used. They are designated by the Latin letter V and are superimposed at the following points:
- V1 - at the right edge of the sternum in the 4th intercostal space, the red wire is connected;
- V2 - also in the 4th intercostal space, but on the left edge of the sternum, wire color - yellow;
- V3 - in the middle between the 4th and 5th intercostal spaces along the left line, connect the green cable;
- V4 - along the midclavicular line in the 5th intercostal space, wire color - brown;
- V5 - along the anterior axillary line in the 5th intercostal space, connected to a black cable;
- V6 - in the middle of the axillary line at the same level with V450m, the wire color is blue (possibly purple).
Indications for the procedure
ECG is a fairly popular procedure that is prescribed to everyone, from the youngest patients to adults. The reasons for the study can be either a routine examination or complaints of ailments. The procedure is required:
- for admission to first grade;
- passing the driver's license exam;
- teenagers who are undergoing changes in their body;
- admission to secondary and higher educational institutions after school.
ECG is also indicated for patients who have the following health problems:
Read also: What to do if you forgot your email from Faceit
- shortness of breath while walking or other activities, as well as at rest;
- high blood pressure;
- pain in the chest, neck, back and abdomen;
- fainting;
- swelling of the limbs;
- general weakness;
- heart murmurs and so on.
An ECG is also done before surgery, when registering for a sanatorium, and for issuing medical documents. A cardiogram should be done every year for people over 40 years of age.
Electrocardiography technique
ECG is a basic examination that helps identify serious pathologies
The procedure for performing an ECG is very simple and does not take longer than 10 minutes.
The study is carried out in a specially equipped room, which ensures that no stranger will see the patient, since the top will need to be removed before the ECG.
The patient is positioned on a couch, allowing him to relax and bring his heart rate back to normal. The air temperature in the office is also always maintained at normal levels so that the heart rate does not increase or decrease due to temperature changes.
This is done for the reason that it is possible to find out accurate and correct results only if the heart beats in a familiar, calm rhythm.
The procedure for performing the ECG procedure:
- All preparatory work is being carried out. Electrodes are placed on the ankles, arms and torso, so these areas need to be exposed. It is also necessary to remove all iron jewelry from yourself. Afterwards, the patient sits on the couch and relaxes on it to normalize the heartbeat while the doctor enters the data into the documents.
- Next, electrodes are attached to all the necessary points.
- After this, the doctor connects all the electrode wires to a special device. They must be connected in a certain order and each to its own place, otherwise the result produced by the device will not be correct. But an experienced doctor can easily cope with this task.
- The completion of the procedure is obtaining a cardiogram. In most cases, the final result is not announced immediately, but after a few days. This is necessary in order to study in detail the state of the heart.
How is an ECG done for children?
Giving an ECG to a child can be challenging. It is difficult, and sometimes impossible, to make a very young patient lie quietly for several minutes. Children's crying, hysteria and panicky fear of doctors will certainly affect the results of the cardiogram, distorting the picture.
The main role in preparing the child is played by parents, who should, if possible, explain to the child what needs to be done without frightening or exciting him.
Taking any sedatives (for example, valerian) before an ECG is unacceptable!
Contraindications
It cannot be said that an ECG has any contraindications, since this is a vital procedure and it is simply impossible to do without it.
But difficulties may arise when conducting electrocardiography; they are due to the fact that the electrodes connected to the body cannot always be attached to it or fully convey information. This may happen due to:
- Damage to the skin or injury to the chest and other areas of the body where the electrodes should be attached;
- Obesity;
- The hair is very thick, which simply does not allow the electrode to attach to the skin, so it must be shaved off before going to the hospital.
How is a cardiac cardiogram taken?
The algorithm for taking an ECG is as follows:
- To obtain data, the patient undresses to the waist, freeing his chest from clothing. It is also necessary to expose the skin on the wrists and ankles.
- The patient lies down or sits on the couch.
- The nurse places the suction cups. The application of electrodes during ECG occurs only after treating the surface of the skin with a conductive solution or water to improve the quality of the received signals.
- The device turns on and the specialist takes a cardiogram. How long does the manipulation last? On average about 5 minutes.
It is important that the functional diagnostic room is warm, since physiological tremors can distort the examination results.