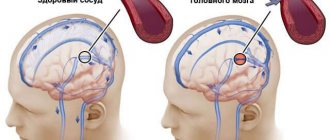
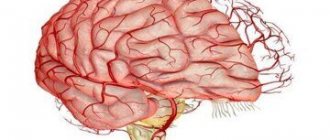
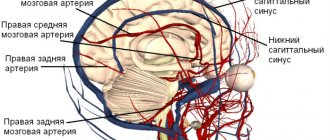
Hypertensive encephalopathy is a chronic progressive change in the brain associated with arterial hypertension that is difficult to correct.
Widespread. It is detected mainly in old age. offers professional assistance for hypertensive encephalopathy. To make an appointment please call...
Causes
Encephalopathy develops against the background of high blood pressure. Found in individuals diagnosed with hypertension. It is provoked by symptomatic hypertension due to glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, hydronephrosis, aortic atherosclerosis, hyperaldosteronism, hypercortisolism, pheochromocytoma. The risk increases if the following factors are present:
- Lack of blood pressure control. It develops more quickly in those patients who do not monitor their blood pressure, do not take antihypertensive drugs in a timely manner, or use insufficient doses of medication.
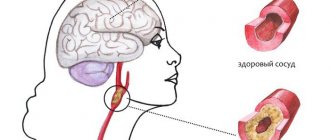
- Hypertensive crises. Each jump in blood pressure affects the walls of blood vessels, which become thinner and more permeable. Adjacent areas of brain tissue are saturated with blood.
- Pressure fluctuations. Due to changes in blood pressure, blood vessels quickly wear out, and the lumen of the arteries narrows. Temporary hypotension after taking the medicine causes a sharp dilation of blood vessels and insufficient blood supply.
- Nocturnal hypertension. Crises during sleep often go unnoticed. The pressure remains elevated for a long time, which leads to spasm of the arteries and ischemia of cerebral tissue.
Stages of development of the disorder
In its pathogenesis, angioencephalopathy goes through three stages. Each of them is characterized by certain manifestations.
- At the initial stage, the lumen of the vessels narrows, and the lack of blood supply is not yet clearly expressed. Typically, patients attribute all symptoms to banal overwork. They are worried about weakness, fatigue, and sleep disturbances. Headaches and the appearance of spots before the eyes are possible.
- At the second stage, the signs of cerebral angioencephalopathy remain the same, but now they are more pronounced. This period is accompanied by massive destruction of cells and the connections between them. The gait becomes shaky and unstable. Sometimes there is trembling in the limbs. The emotional sphere also suffers. There is increased irritability and resentment increases.
- The third stage is characterized by severe disturbances of the psyche and mental functions against the background of irreversible damage to brain tissue. It becomes difficult for a person to navigate in space. He loses the ability to independently carry out work activities. Symptoms may vary depending on which part of the brain is involved in the pathological process. Impaired vision, hearing, and sensitivity are not excluded.
The last stage of angioencephalopathy is the most difficult. In this case, the pathology can cause dementia (dementia).
Pathogenesis
When blood pressure rises, the arterioles narrow compensatoryly. The walls of the vessels gradually thicken due to hypertrophy of smooth muscle fibers, and the lumen, on the contrary, decreases. The brain is less well supplied with blood, and chronic ischemia develops. Lack of nutrients and oxygen provokes degeneration of cerebral structures. The changes are aggravated against the background of crises and acute stroke.
Classification
The disease is characterized by a gradual worsening of degenerative processes and progression of manifestations. Severity matters when determining optimal treatment methods, therefore in clinical practice there are 3 stages of pathology:
- First. It is characterized by a predominance of nonspecific subjective complaints of cephalgia, inattention, increased fatigue, and memory impairment. During a special examination, a slight decrease in cognitive functions is determined.
- Second. Subcortical, dysmnestic, ataxic, pyramidal and vestibular symptoms are revealed. As a rule, there is a predominance of one, or less often, two syndromes. Cognitive abilities are moderately impaired. Problems arise in social adaptation and professional activity.
- Third. Neurological symptoms increase and become more diverse. Sometimes secondary parkinsonism, symptomatic epilepsy, and pseudobulbar syndrome are detected. Cognitive disorders worsen, reaching the level of dementia. The ability to work is lost, the ability to self-care is limited.
Symptoms
In the initial phase, headaches, absent-mindedness, fatigue, and problems when trying to concentrate are prevalent. Subsequently, the picture is determined by the predominance of one or another neurological syndrome. Vestibular ataxia is manifested by coordination disorders and unsteadiness when walking. Subcortical lesions are characterized by hyperkinesis, tremors of the limbs, and parkinsonian phenomena; pyramidal syndrome is characterized by muscle weakness; and dysmnestic syndrome is characterized by amnesia.
Problems in the field of higher nervous activity are represented by a deterioration in productivity and speed of thinking, loss of motivation, difficulties in self-organization, a narrowing of the range of interests, and a decrease in criticism. Characterized by emotional instability. Behavioral and affective disorders are possible. The condition either improves or worsens.
When moving to stage 3, the medical history is supplemented by gross cognitive and organic disorders. The clinical picture includes amnesia, agnosia, apraxia, severe intellectual decline, and loss of professional skills. Progression of dementia and neurological disorders is noted. Due to ataxia, parkinsonian and pyramidal symptoms, patients experience difficulty moving and self-care.
The course can be complicated by strokes, often leading to severe disability. A dangerous negative consequence of pseudobulbar syndrome is the entry of liquid and food particles into the respiratory tract, followed by aspiration pneumonia.
Clinical manifestations of toxic encephalopathy
The signs of the disease and the course of the disease largely depend on the neurotoxin that caused this condition. Depending on the severity and duration of symptoms, the disease can be acute or chronic. But even the acute form rarely goes away without any consequences. Residual effects persist for a long time (and in some cases throughout life). Typically this is:
- regular headaches with dizziness;
- general weakness, increased fatigue;
- irritability;
- sleep disturbances (difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings, nightmares);
- autonomic dysfunction syndrome, which is manifested by increased sweating, tremor of the fingers of outstretched arms, and decreased muscle tone;
- cognitive disorders: deterioration of memory and attention; often the patient experiences difficulties even with reading fiction and watching TV shows and films.
After acute toxic encephalopathy, hypothalamic crises may periodically occur, accompanied by:
- increased headache;
- rise in blood pressure;
- pain syndrome in the chest area;
- chills with trembling;
- attacks of anger and irritability.
Symptoms of the acute form of the disease
This type of illness is typical for poisoning with heavy metals and volatile solvents; it is relatively rare in alcoholism and drug addiction, usually against the background of an already existing deficiency or disturbances in thiamine metabolism.
Clinical manifestations of the pathology include:
- oculomotor disorders (eye paralysis, strabismus, decreased response to light stimuli);
- astasia and abasia (loss of the ability to move without support and assistance);
- generalized convulsive syndrome;
- amnesia, and often the patient replaces events that he does not remember with fictitious ones;
- oral automatisms;
- repeated vomiting;
- severe headache;
- increase or decrease in body temperature;
- tachycardia;
- acute psychosis.
Without timely medical care, there is a high risk of death due to cerebral edema, stroke, and acute respiratory failure.
Symptoms of chronic toxic encephalopathy
With a prolonged course, there are 5 stages of the disease:
- Prodromal. Signs of the disease can only be visible to the patient’s loved ones. Pay attention to lack of concentration, absent-mindedness and forgetfulness.
- First. Apathy develops, coordination of movements decreases, mild tremors are possible, sleep disturbances, loss of appetite, and weight loss are typical. Various emotional disorders are noted: feelings of internal tension and anxiety, fear.
- Second. Personality and behavioral disorders come to the fore, which many take to be the initial symptoms of dementia.
- Third. Speech disorders, severe disorientation, and a decrease in almost all reflexes are characteristic.
- Fourth. Toxic encephalopathy of the most severe degree: coma develops with loss of all neurological functions.
Very often the disease is complicated by concomitant acute and chronic somatic pathologies. Thus, in addition to neurological symptoms, manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system are often noted. As a rule, the immune system suffers greatly, which leads to a decrease in resistance to various bacterial, viral and fungal infections. And in such cases, the negative influence of waste products of pathogenic microflora “joins” the action of the neurotropic poison - infectious-toxic encephalopathy develops.
Diagnostics
The development of hypertensive encephalopathy of the brain is indicated by typical symptoms against the background of elevated blood pressure. The examination plan includes the following procedures:
- Neurological examination. Initially, there are no changes, then the picture is determined by the prevailing neurological syndromes.
Consultation with a cardiologist. The doctor confirms primary hypertension and, if indicated, refers to other specialists to clarify the cause of secondary hypertension. Daily blood pressure monitoring, ECG, and echocardiography are prescribed.- Mental status assessment. Requires the participation of a neuropsychologist and psychiatrist. Indicated for psychopathological manifestations.
- Neuroimaging. Using MRI data, the severity of degeneration is assessed, the presence of lacunar infarctions in the anamnesis is confirmed, and other cerebral pathologies are excluded.
- Cerebral circulation studies. MRA, transcranial Dopplerography, duplex scanning are informative. The narrowing of arterioles is visualized, and the extent and severity of damage is assessed.
In case of epileptic seizures, an EEG is additionally performed. Patients with signs of renal dysfunction are prescribed a consultation with a nephrologist and ultrasonography. Hypertensive encephalopathy is differentiated from encephalitis, neoplasms, Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease, slow infections of the central nervous system, and demyelinating processes.
Risk factors
Doctors have been actively studying angioencephalopathy of the brain for several decades, what it is, and the features of its course. Thanks to numerous studies, they were able to identify the so-called risk group, being in which increases the likelihood of developing pathology. It includes people:
- those suffering from addictions (smoking, alcohol abuse);
- experiencing chronic fatigue;
- exposed to daily stress;
- not watching their diet.
In addition, the presence of hypertension among close relatives significantly increases the risk of angioencephalopathy.
Treatment
Efficacy largely depends on successful normalization of blood pressure. As part of symptomatic treatment, measures are taken to improve intracerebral circulation, stimulate local metabolism, and restore brain functions. Pharmacological support includes:
- Vasodilators. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors and calcium channel blockers eliminate arteriolar spasm.
- Means for improving microcirculation. Pentoxifylline and long courses of anticoagulants are recommended.
- Neuroprotectors. Glycine, gamma-aminobutyric acid and antioxidants increase cell resistance to hypoxia and lack of nutritional compounds.
- Other medicines. They are selected taking into account current symptoms and laboratory test data. It may be necessary to prescribe statins, nootropics, tranquilizers, antidepressants, and anticonvulsants.
Taking medications
It is not possible to completely restore brain function with angioencephalopathy. Therefore, the therapeutic methods used for treatment should be aimed at slowing down destructive changes in cerebral circulation and eliminating the microsomatic processes that provoked them.
The chronic form of the pathology does not require hospitalization. The patient can be admitted to the hospital only if there is a somatic defect and a high probability of stroke.
Depending on the stage of cerebral angioencephalopathy, treatment is carried out using the following drugs:
- Nootropics (“Nootropil”, “Actovegin”). Helps improve metabolic processes between cells.
- Antihypertensive drugs (“Lisinopril”, “Nimodipine”). Stabilizes blood pressure and improves its performance.
- Anticoagulants (“Curantil”). With their help, they achieve a decrease in blood viscosity.
- Statins (“Lovastatin”, “Simvastatin”). Drugs from this group are recommended for atherosclerosis, since in this case it is necessary to reduce cholesterol levels.
- Chondroprotectors. Used in the presence of severe problems with the spinal column.
If a patient suffers from diabetes, he is given a special diet and appropriate medications.
Cost of services
| CONSULTATIONS OF SPECIALISTS | |
| Initial consultation with a psychiatrist (60 min.) | 6,000 rub. |
| Repeated consultation | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychiatrist-narcologist (60 min.) | 5,000 rub. |
| Consultation with a psychologist | 3,500 rub. |
| Consultation with Gromova E.V. (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| PSYCHOTHERAPY | |
| Psychotherapy (session) | 7,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (5 sessions) | 30,000 rub. |
| Psychotherapy (10 sessions) | 60,000 rub. |
| Group psychotherapy (3-7 people) | 3,500 rub. |
| Psychotherapy session with E.V. Gromova (50 minutes) | 12,000 rub. |
| TREATMENT IN A HOSPITAL | |
| Ward for 4 persons | 10,000 rub./day |
| Ward for 3 persons | 13,000 rub./day |
| Ward 1 bed VIP | 23,000 rub./day |
| Individual post | 5,000 rub. |
| PETE | 15,000 rub./day |
This list does not contain all prices for services provided by our clinic. The full price list can be found on the “Prices” , or by calling: 8(969)060-93-93. Initial consultation is FREE!
Prognosis for recovery
The sooner treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of a favorable outcome. Doctors find it difficult to give any prognosis for cerebral angioencephalopathy, since its course depends on several factors:
- location of the lesion;
- timeliness of diagnosis and therapy;
- general state of human health;
- severity of the primary disease.
According to medical statistics, vascular encephalopathy is the cause of dementia in older people in 15% of cases.
Forecast
The prognosis is determined by the stage, the effectiveness of antihypertensive therapy, the nature and characteristics of the course of the underlying pathology, and the presence of concomitant diseases. Early initiation of treatment allows you to stabilize the condition and maintain performance and intellectual functions for a long time. In later stages, complete recovery is not possible; the main goals are to slow progression and minimize neurological symptoms.
Neurologists know well what kind of disease hypertensive encephalopathy is, and they know how to correctly diagnose and treat this pathology. To make an appointment, call tel. 8(969)060-93-93.
Prevention
Encephalopathy is a complex disease. There is no clear method to prevent its occurrence and eliminate all risk factors. Doctors recommend adhering to the following rules:
- provide yourself with a full daily routine with alternating work and rest, a full night’s sleep;
- minimize stress;
- eat properly and balanced, avoid overeating and excess body weight;
- ensure sufficient supply of vitamins and microelements;
- quit smoking, drugs, alcohol;
- exercise in moderation (not professionally);
- promptly identify and treat chronic diseases: hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerosis;
- consult a doctor at the first signs of trouble.