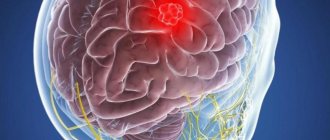
Brain glioma is the most common type of tumor that grows from glial tissue, which makes up the supporting cells of the nervous system. Gliomas account for about 60% of all tumors localized in the brain. The name of the types of gliomas - astrocytomas, ependymomas and others - comes from the name of the cells that form the tumor.
Services for the diagnosis and treatment of brain glioma are offered by the leading multidisciplinary medical center in Moscow - Yusupov Hospital. Positive treatment results are achieved thanks to the high professionalism of the oncology center’s doctors and advanced technologies used to combat brain tumors.
Classification
- Astrocytomas are the most common type of glioma, localized in the white matter of the brain. Depending on the type, astrocytic glioma of the brain can be fibrillary (protoplasmic, gemistocytic), anaplastic, glioblastoma (giant cell, gliosarcoma), pilocytic astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, and subependymal giant cell astrocytoma.
- Ependymomas - can occur in 5-7% of cases of brain tumors, are characterized by typical localization in the ventricular system of the brain.
- Oligodendrogliomas account for 8 to 10% of all brain tumors and develop from oligodendrocytes.
- Chiasmal glioma - spreads along the optic nerve into the orbital cavity, can grow into the hypothalamus, and affect the third ventricle of the brain. This tumor causes endocrine imbalance, metabolic disorders, decreased vision, and is characterized by intracranial hypertension, depending on the location and size of the tumor.
- Mixed gliomas – oligoastrocytomas, anaplastic oligoastrocytomas.
- Neuromas make up 8 to 10% of tumors.
- Choroid plexus tumor is a rare type of glioma, occurring in 1-2% of cases.
- Neuroepithelial tumor of unknown origin - this group includes astroblastoma and polar spongioblastoma.
- Diffuse glioma of the brain stem is a tumor with a high degree of malignancy, cancer of the central nervous system. People of any age are affected, but the tumor is rare in adolescents and children. The survival prognosis for this type of tumor is poor. Diffuse glioma develops in the area of the brain in which all the important nerve connections are located, providing communication between the analyzing nerve centers of the brain and the impulses of the musculoskeletal system of the extremities. The tumor very quickly causes paralysis.
- Neuronal and mixed neuronal-glial tumor - occurs in extremely rare cases (up to 0.5%). This group includes gangliocytoma, ganglioglioma, neurocytoma, neuroblastoma, neuroepithelioma).
- Gliomatosis cerebri.
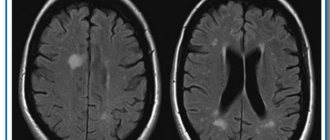
Normal magnetic resonance imaging of the brain
MRI of the brain, normal
The normal MRI of the brain is a relative concept, depending on the age, gender of the patient, changes in tomograms are necessarily compared with symptoms. The doctor evaluates the symmetry of the lobes, the size of the ventricles, blood vessels, the uniformity of their filling with a contrast agent, the absence of neoplasms, malformations, and much more. A computer program builds layer-by-layer images, after examination they are printed onto films and examined by placing them on a X-ray viewer. Next, fill out a conclusion form indicating the preliminary diagnosis. It is hardly possible to decipher an MRI of the brain on your own without special training: an inexperienced person, even if he sees a lesion, will not figure out what caused its appearance. All questions can be asked to the doctor who conducted the study. In unclear situations with ambiguous results, obtaining a second opinion is justified. Often patients, having read the words “neoplasm, tumor, NEO” in the conclusion, try to immediately find out the prospects of the disease from the radiologist, which fails. These questions can be answered by a neurosurgeon after receiving the biopsy results. Sometimes, to complete the picture, it is necessary to additionally do an MRI of the cervical spine.
Degrees
There is a WHO classification, according to which gliomas are divided into four grades:
- Grade I – slow-growing benign glioma, which is associated with a long life expectancy;
- Grade II – slowly growing “borderline” brain glioma, which tends to progress to grades III and IV;
- III degree – malignant glioma;
- IV degree – fast-growing glioma of the brain: the life expectancy of patients with this diagnosis is significantly reduced.
Causes of GM damage
Focal lesions can be caused by a variety of reasons.
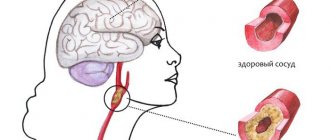
- How to check the blood vessels of the brain, what methods are used
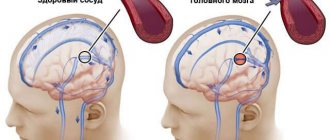
In case of focal lesions of the brain of a dyscirculatory nature, the cause may be a lack of nutrients caused by circulatory disorders (with ischemic heart disease, stroke and other pathologies). Often the cause of the disease is a neoplasm. It has a negative effect on neighboring areas of the brain, causing various changes in them, including the death of brain cells.
Symptoms
The symptoms of brain glioma depend on the location of the tumor, its size, and it consists of general cerebral and focal symptoms.
Most often, brain glioma manifests itself as persistent and constant headaches, in which patients experience nausea and vomiting, after which there is no relief, as well as convulsions.
In addition, depending on which part of the brain is affected by glioma, patients have speech impairment, weakened muscles, and may experience paresis and paralysis of the arms or legs, face and other parts of the body. Visual or tactile function, coordination of gait and movements may be impaired.
The psyche may change, and the development of behavioral disorders is often noted. In addition, memory and thinking are impaired in patients with brain gliomas. Due to impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, intracranial hypertension and hydrocephalus develop.
Who is at risk
Any disease has its own risk groups. People belonging to such groups should closely monitor their health and immediately consult a doctor at the first suspicious symptoms. With focal pathologies, this group includes patients:
- Hypertension, hypotension.
- Diabetes.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Rheumatism.
- Obesity.
- Sensitive, emotional people living in constant stress.
- Leading a sedentary life.
- Elderly people, regardless of gender (starting from 55-60 years).
They also provoke the development of vascular pathologies:
- Meteor dependence.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Osteochondrosis.
- Addiction.
- Arrhythmia.
- Aneurysms of cerebral vessels.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of brain glioma is based on the results of a thorough neurological examination and other special diagnostic tests.
First of all, the doctor at the Yusupov Hospital Oncology Center assesses the condition of reflexes and skin sensitivity, and motor function of the limbs. If the patient complains of deterioration in visual function, he is prescribed a consultation with an ophthalmologist.
The neuromuscular system is assessed using instrumental diagnostic methods - electromyography and electroneurography. In addition, a lumbar puncture is performed to identify atypical cells in the cerebrospinal fluid. This study is also used for ventriculography and pneumomyelography.
Modern imaging methods that provide layer-by-layer images of brain tissue are of great importance in the diagnosis of brain tumors. These include computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These studies are considered quite safe and very informative; they help determine the location, size, shape and structure of the tumor.
To determine the displacement of the midline structures of the brain, an ultrasound examination of the brain (M-echo) is performed.
Additionally, cerebral contrast angiography (x-ray examination of cerebral vessels), electroencephalography, scintigraphy and PET may be prescribed.
Make an appointment
Clinical manifestations
In case of intracerebral tumors, general cerebral symptoms come first. They are associated with the appearance of hydrocephalus, provoked by increased intracranial pressure. Headaches are dull and bursting in nature. An additional symptom is dizziness. It occurs when rotating the head, often accompanied by nausea and tinnitus. First of all, dizziness occurs with tumors of the cerebral hemispheres.
One of the symptoms of the disease is vomiting, which is not associated with food intake and occurs mainly in the morning on an empty stomach and at the peak of the pain syndrome. With the growth of a tumor in the area of the ventricle of the brain, it is possible to identify mental disorders that manifest themselves with irritability, aggressiveness, or periods of severe apathy.
Patients' attention is impaired, memory deteriorates, and delusional states and hallucinations may occur. The tumor begins to affect surrounding tissues, causing displacement and infringement of brain structures, signs of ischemia, and insufficient blood flow.
Treatment
Like any malignant tumor, brain glioma is treated with three main methods that are used in modern oncology - surgery, radiation therapy (including radiosurgery) and chemotherapy.
The gold standard treatment for brain glioma is surgery. If the tumor is operable, surgery is performed to remove the tumor.
Radiation therapy is performed before and after surgery. For inoperable tumors (if the glioma is localized in a hard-to-reach place), this method is used as a separate method. Today, traditional radiation therapy has been replaced by stereotactic radiosurgery.
Chemotherapy treatment of glioma can be used both preoperatively and postoperatively.
Surgery
The operation to remove malignant glioma is open, involving craniotomy, during which the skull is opened. The main goal of surgery is to remove as much of the tumor as possible while leaving healthy brain tissue intact, thereby preventing neurological damage. A certain localization of gliomas allows the effect of surgical treatment to be achieved up to 98%.
No operation to remove a tumor guarantees a 100% result, since there is always a possibility that cancer cells remain in the brain tissue. However, surgical intervention eliminates compression of surrounding brain tissue and the symptoms of glioma, as well as restores cerebrospinal fluid circulation if intracranial hypertension is present.
The effectiveness of surgical treatment of brain glioma largely depends on the skill and experience of the operating specialists. Treatment of brain tumors at the Oncology Center of the Yusupov Hospital is carried out using high-precision tomographs and neuronavigators, thereby minimizing the likelihood of a relapse of the disease.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy may be given before surgery to shrink the tumor before excision, or after surgery to kill any remaining tumor cells.
In addition, this method can be used as an independent method when the tumor is localized in a hard-to-reach place, which prevents its surgical removal. In this case, radiation therapy does not completely destroy the tumor, but can significantly stop its growth.
Traditional radiation therapy is accompanied by a number of undesirable effects: patients experience nausea, decreased appetite, and increased fatigue. At the site of radiation exposure there is a high probability of hair loss and the development of radiation dermatitis. As a rule, side effects of radiation therapy appear 10-14 days after irradiation.
In addition, late complications of radiation exposure are known: patients experience memory impairment to varying degrees, and radiation necrosis may develop (scar tissue forms around the dead tumor tissue).
Radiosurgery
Due to the fact that surgical treatment of brain tumors does not guarantee a complete cure, a relapse of the disease may occur after surgery. Therefore, it is advisable to use additional treatment methods - radiation therapy and chemotherapy. As a rule, relapses are localized at the borders of healthy tissue with the area where the tumor was removed. In such cases, it is recommended to use radiosurgery: cyber knife, gamma knife, Novalis.
Radiosurgery is an innovative method of radiation therapy, the essence of which is to irradiate a glioma with a beam of radiation from different angles, which ensures that radiation reaches the tumor and minimal irradiation of soft tissues.
During the procedure, the position of the patient's head and the location of the tumor are constantly monitored using computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, so that the radiation beam is directed exclusively to the malignant neoplasm.
This method is non-invasive, as no incisions are required to perform it. Thanks to this, there is no risk of intraoperative complications and side effects associated with traditional radiation therapy.
In addition, radiosurgery is an absolutely painless method that does not require anesthesia or preparatory measures, and there is no recovery period. The only limitation to radiosurgery is the size of the tumor.
It is important to understand that the effect of radiation therapy occurs gradually, unlike surgery. However, radiosurgery is often the only alternative treatment for inoperable brain gliomas.
Examination methods
The main method for diagnosing the disease is MRI of the head, which reveals hyperintense inflammation, small heart attacks, post-ischemic degeneration, and enlargement of the ventricular system. The number of heart attacks can range from one to many. Fine-focal transformations indicate serious brain damage, which can result in disability. Blood circulation suffers in problem areas.
Ultrasound or duplex scanning is used as diagnostic techniques, which can determine blood flow disturbances, such as asymmetric distribution of fluid throughout the vessels. CT makes it possible to recognize traces of heart attacks in the images in the form of lacunae filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Often the cerebral cortex atrophies, the ventricles increase in size, and dropsy appears.
MRI can detect the following disorders. Transformations of the cerebral hemispheres. Such lesions appear due to blockage or compression of an artery located in the spine. This is often due to congenital pathologies or atherosclerosis. In rare situations, a vertebral hernia appears.
Focal changes. Their presence often indicates a pre-stroke condition of the patient. Sometimes they are used to determine dementia, epilepsy, and other disorders caused by atrophy of arteries and veins. If such changes are detected, immediate treatment is required.
Microfocal transformations appear in all people after 50 years. It will be possible to examine them using contrast media only in a situation where they arise in the form of a disease. Fine-focal transformations are not clearly detected and eventually lead to a stroke.
Transformations of white matter in different areas of the brain are subcortical and periventricular in nature. This type of damage is provoked by continuously high blood pressure, especially with regard to hypertensive crisis. Often, single lesions are congenital in nature; the danger arises due to the proliferation of damage in the brain. In such a situation, symptoms develop regularly.
When there is a high probability of the disease in a patient, examinations should be carried out every year. For preventive purposes, CT or MRI is performed once every 2-3 years.
Treatment of glioma at Yusupov Hospital
Oncologists at the Yusupov Hospital have enormous experience and effective methods of treating cancer. An individual treatment program is drawn up for each patient, based on the results of a thorough diagnostic examination. The Oncology Center of the Yusupov Hospital is equipped with innovative equipment for high-quality diagnosis and treatment of gliomas and other brain tumors.
An appointment with an oncologist can be made by calling the Yusupov Hospital or online on the website using the feedback form. The coordinating doctor will answer all your questions and tell you about the cost of medical services and the conditions for hospitalization of the patient.
Make an appointment