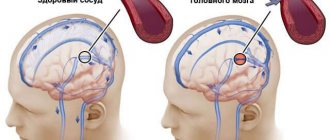
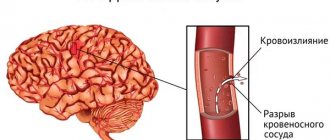
There is very little knowledge about the capabilities of the human brain. Only its structure, ability to coordinate the work of the whole organism and its effect on overall well-being are known. For example, as a result of a disorder of blood flow in the cerebral artery, speech, coordination of movements, and thinking are disrupted, and paralysis occurs. All these are symptoms of a stroke. Brain disorders, in particular brain tumors, epilepsy, and Alzheimer's disease, have a worse impact on the duration and quality of life.
Timely and innovative diagnosis makes it possible to effectively treat diseases of any part of the brain.
What does a brain MRI show?
Having received 3D images of the brain in different projections, the doctor has the opportunity to examine each area in detail. This allows us to draw conclusions about:
- processes occurring in brain tissue;
- condition of blood vessels;
- the presence, location, shape and size of neoplasms, hematomas or blood clots;
- the presence, stage and localization of other brain pathologies.
Thanks to MRI, it is possible to visualize the brain in different projections, which significantly increases the information content of the examination
If the results are not accurate enough or additional visualization of a specific area is required, an MRI of the brain with contrast may be ordered. The introduction of a contrast agent makes it possible to obtain a more accurate idea of the structure of brain tissue or pathological formation and to clarify its boundaries.
How the procedure works
This diagnostic method is absolutely painless and does not require general or local anesthesia. The patient is examined standing, lying or sitting, depending on which organ needs to be examined.
The surface of the skin is lubricated with a special gel, which facilitates signal transmission. The ultrasound technician then directs the probe to the desired area.
During duplex scanning of the brain, the sensor is placed in places called “ultrasonic windows” - parts of the skull where the bones are thinner or where there are physiological openings in them.
Through such zones, the ultrasound beam easily enters the cranial cavity.
During the procedure, the patient may be required to adopt a more comfortable position for the examination. The doctor may also ask you to hold your breath or do other similar actions. The manipulation lasts approximately half an hour and causes absolutely no discomfort.
How to do an MRI of the brain
Only the patient’s head enters the tomograph chamber, so the feeling of enclosed space is minimized
There is no need to prepare specially for the study. The only requirement is not to wear metal or jewelry, hairpins, or watches when going for an examination (or be prepared to remove them or take them out of your pockets before placing them in the tomograph). Also, during the procedure you cannot have magnetic media (flash drives, bank cards, etc.) with you, since the information stored on them will be destroyed.
The diagnosis will take 30–40 minutes. You cannot move your head during the process, but this restriction does not apply to the facial muscles. You can even talk to your doctor while he takes sequential pictures. From time to time, the doctor himself will contact the patient to inquire about his well-being.
If you suffer from claustrophobia, but an MRI of the brain is necessary, you need to say this in advance. Then the doctor will suggest taking a sedative before starting the procedure.
Highly specialized methods
- Doppler ultrasound provides detailed information about blood circulation in the large vessels of the brain and neck. This method allows you to identify pathologies of the vascular system at the initial stages, as well as evaluate the effectiveness of the therapy. The advantages of ultrasound scanning are that you do not need to prepare specially for it, the procedure is painless and has no contraindications.
On the eve of the ultrasound, the patient should stop smoking, drink tea, coffee and other caffeine-containing drinks, so as not to affect vascular tone.
- Electroencephalography is a study of the brain carried out to analyze its functional state, as well as its response to stimuli. With an EEG, the biocurrents of the brain are recorded, and even minor fluctuations are recorded. Data on bioelectrical activity are transferred to a special paper tape or recorded in a file and displayed on a computer monitor. EEG is used to diagnose and treat epilepsy, delayed mental and speech development, and identify the consequences of head injuries.
- Echoencephalography is an examination of the head using ultrasound. A device called an oscilloscope picks up the peculiar echo that is returned when ultrasonic waves are sent to the brain. Thus, an image appears on the display, from which one can judge the presence of tumors in the brain and disorders in its structure after skull injuries.
- Rheoencephalography is the recording of fluctuations in the electrical resistance of tissues in the process of passing a weak high-frequency electric current through them. REG provides accurate information about the condition of blood vessels, allowing one to examine their tone, elasticity, and blood filling. The method allows you to see separately the functioning of the venous and arterial systems of the brain and diagnose intracranial hypertension, atherosclerosis, vascular dystonia, and subdural hematomas. With its help, the effectiveness of treatment of the above pathologies is also assessed.
These rheoencephalograms are obtained by placing electrodes on the surface of the head, having previously lubricated them with a special paste to ensure better contact with the skin. When analyzing information received from the rheograph, organic changes depending on the age of the patients are taken into account.
- Electroneuromyography is a method of studying the brain, which is a recording of its biocurrents. ENMG allows you to identify neuromuscular diseases and dysfunction of the peripheral nervous system.
- Neurosonography – diagnostics of the brain of newborns and infants up to 9-12 months of age. The procedure is absolutely safe, because it is carried out using ultrasound. It is highly informative regarding the identification of pathologies at the earliest stages and can be carried out before the large fontanelle in the child’s skull heals.
- Craniography - in other words, this is a study of the head using X-rays. Allows you to make two projections of the skull (profile and full face) to record the presence of congenital or acquired bone anomalies.
Who needs to undergo an MRI of the brain?
Most often, a neurologist refers you to magnetic resonance imaging. Indications for research may include:
- regular dizziness and headaches of unspecified nature;
- decreased hearing or vision in the absence of an explanation from an ENT or ophthalmologist;
- frequent fainting;
- head injuries;
- infectious diseases of the brain;
- stenosis (narrowing of blood vessels);
- aneurysms (dilation of blood vessels);
- epilepsy;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- other neurological diseases.
Although brain tomography is a completely safe procedure, there are still contraindications. First of all, they are due to the presence of metal elements that cannot be removed during the procedure:
- braces;
- pacemakers;
- prostheses;
- staples on vessels;
- foreign objects;
- implants.
If there are fixed metal parts and devices, MRI cannot be performed.
Overweight patients may be limited by the diameter of the tomograph capsule.
It is not recommended to undergo an MRI during the first trimester of pregnancy, however, if there are medical indications, the diagnosis will be carried out. At a later date, the examination will not harm either the mother or the child. Breastfeeding women also do not have to worry: magnetic waves do not affect either lactation or the quality of milk.
Commonly Used Methods
CT scan
Diagnosis of brain diseases using CT is based on calculating the intensity of penetration of X-rays through brain tissue. Thus, it is possible to obtain their detailed cross-sectional image. Modern devices for computer diagnostics have a low level of radiation, which does not affect the accuracy of the results.
Such a brain examination may be prescribed if the patient has a history of:
- dizziness;
- headache;
- loss of consciousness;
- convulsions;
- strokes;
- speech and memory disorders;
- auditory and visual impairments.
This method of diagnosing brain pathologies is contraindicated for children and pregnant women. If intravenous administration of a contrast agent is necessary, the following are added to the list of contraindications: renal and liver failure, diabetes mellitus, heart disease, asthma, thyroid pathologies, allergic reaction to iodine.
If there are no contraindications, computed tomography is performed as many times as necessary to make a diagnosis and monitor the effectiveness of therapy.
CT scan does not require special preparation of the patient. Unless before the procedure with contrast, you should not consume food or liquid for 4 hours. The examination lasts from 15 minutes to half an hour. At this time, the person is on a movable table, which moves into the tomograph. The patient is not allowed to move, and sometimes will need to hold his breath at the command of the medical staff.
Magnetic resonance imaging
It’s not for nothing that in foreign films about the work of medical institutions, doctors constantly refer patients to MRI – today it is one of the leaders among brain research methods. Visualization of the state of the organ occurs thanks to the magnetic field constantly maintained in the tomograph. Electromagnetic waves are passed through it, the energy flow from which is repelled by hydrogen atoms, which are present in all cells of the human body. Computer equipment converts the data into images of brain tissue.
MRI is effective for diagnosing a wide range of diseases: from vascular pathologies to tumors.
Modern tomographs emit low-frequency electromagnetic fields and are equipped with a number of specialized computer programs, which allows one to obtain a detailed picture of the functioning of the brain.
Examination with a tomograph is contraindicated in the following cases:
- the patient is mentally unstable, has acute pain syndrome or is in a coma;
- The patient’s body contains metal and ferromagnetic implants, pins, clips on blood vessels, and permanent crowns on teeth.
- The patient's skin has tattoos made with paint containing metal particles.
Pregnant women are required to inform the doctor about the presence of pregnancy and its duration before an MRI.
As with a CT scan, for the examination a person must lie down on a movable table, where his body will be secured with special belts, and sensors that send and read a signal are attached to his head. Afterwards the table moves into the tomograph. Depending on the number of programs used for scanning, the duration of the procedure is 15-40 minutes. All this time the person must lie motionless.
The principle of using a low-frequency electromagnetic field makes MRI completely safe for children and adults.
Magnetic resonance angiography
This technique for studying the brain is based on the same principles as MRI, but its main task is to identify pathologies of the vascular bed. Modern equipment is designed to obtain a three-dimensional image of the entire network of brain vessels, as well as to isolate thin sections of individual vessels and nerve trunks.
Positron emission tomography
Using this method, you can examine the brain in order to record in a three-dimensional projection all the functional processes occurring in it. Analysis of the metabolism of brain structures occurs at the cellular level, therefore PET is the best way to distinguish benign from malignant neoplasms in the early stages. This type of tomography is also used to obtain information about the consequences of injuries, abnormalities in brain function, and to assess the condition of patients after strokes.
PET cannot be performed during pregnancy and breastfeeding, as well as diabetes.
You should not eat 4-6 hours before the procedure. It is recommended to have a protein-free dinner the night before. Part of the examination is the intravenous administration of a radiopharmaceutical. The scanning itself lasts 30-75 minutes.
What is the difference between CT and MRI of the brain?
Computed tomography is the only method that can compete with MRI. The principles of their operation differ, first of all, in the nature of the radiation: magnetic for MRI and x-ray for CT. For this reason, the first can be performed repeatedly without harm to the patient’s health, and the second can be performed no more often than a regular x-ray. At the same time, CT, unlike MRI, is not performed in a confined space, which makes it more preferable for claustrophobics.
In addition, MRI shows the chemical structure of the tissues being studied, and CT will tell us about their physical state.
Another important difference is that MRI is more effective for examining soft tissue, while CT is more effective for examining bones and joints.
The price of a brain MRI is not much different from the cost of a CT scan.
Sign up for diagnostics Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
When is magnetic resonance imaging needed?
For diseases in the head area, a computed tomography scan, which is more familiar to most patients, is often done. Unlike a conventional X-ray, a CT scan uses X-rays from different angles. The computer combines the complex picture obtained by the device into a common image and processes it to better show problem areas.
CT scan clearly shows hard tissues, foreign bodies, and fresh hemorrhages. Whereas tumors or long-standing organic lesions of the brain are not visible enough, sometimes they are completely invisible. To diagnose pathological changes in soft tissues, MRI is required.
There are purely technical differences between these methods, which are also taken into account in clinical practice. done quickly, in a matter of minutes. That is, a person admitted by ambulance can quickly undergo a vital examination. The patient lies on an open table, which is possible even in cases of severe obesity or claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces).
When an MRI is performed, the patient is inside the chamber, and more preparation time is required, as well as the examination itself. Instructions on what body position to take or to hold your breath are transmitted via loudspeaker. Just in case, the camera has a button to call personnel and provide emergency assistance.
To make it more specific in which cases MRI or CT is performed, we present the main clinical symptoms and indications.
To perform a CT scan:
- obvious traumatic brain injury;
- obvious bone changes;
- persistent or regular headache after a stroke;
- suspicion of internal hemorrhage;
- the likelihood of a foreign body inside the head.
To perform an MRI:
- suspicion of a tumor;
- strange fainting, dizziness;
- loss of hearing, vision for an unknown reason;
- long-term consequences of stroke;
- weakening of memory and attention.
Since magnetic resonance does not produce radiation to the brain, this method can be safely used repeatedly and repeatedly if changes in dynamics are needed to be monitored. For example, in preparation for surgery and after surgery. Repeated procedures are absolutely safe if the first one was tolerated satisfactorily.
Brain examinations are done even for young children with the following symptoms indicating a developmental disorder: physical or mental lag behind peers; convulsions, cases of loss of consciousness; stuttering and other problems with oral speech.
MRI of the brain performed at an early age clearly reveals organic lesions that arose in the prenatal period or somewhat later.