Noise in ears - These are auditory sensations observed in the absence of an external sound signal. In most cases, we are talking about subjective tinnitus (only the person himself can hear it), and only sometimes about objective noise (if, for example, the auditory sensation is caused by involuntary muscle vibration, then the doctor can also hear it - using a phonendoscope).
Data on the prevalence of tinnitus vary widely. This is explained precisely by the fact that tinnitus is not recorded objectively. The following experiment was conducted: people who had never complained of tinnitus before were placed in conditions of absolute silence. And 93% of those who took part in the experiment said they heard some kind of noise. On the one hand, we can simply not pay attention to the fact that we have tinnitus, since we live in a constant external sound background (for a city resident, this is a standard situation). On the other hand, in the absence of an external signal, hearing becomes sharper and begins to “read” the noises of the body itself, or the nervous system “makes up” for the missing sounds by generating a signal on its own (at the level of the nervous system this is no longer an acoustic vibration, but an electrochemical process).
How does tinnitus manifest?
Tinnitus may also be described as ringing, rustling, creaking, or buzzing in the ears.
In most cases, tinnitus does not interfere with normal life. At the same time, the symptom may intensify. Doctors distinguish four degrees of tinnitus (depending on the patient’s condition):
- first degree – tinnitus does not affect a person’s well-being;
- second degree – noise causes discomfort in quiet conditions and interferes with sleep;
- third degree - discomfort from tinnitus is constantly felt, the person does not get enough sleep, the quality of life deteriorates significantly;
- fourth degree - tinnitus creates unbearable discomfort.
An important point: noise is felt in one or both ears. Noise in one ear is caused by a local cause; if there is noise in both ears at once, then the problem is most likely systemic in nature.
It is also important what other symptoms are observed along with tinnitus. For example, is tinnitus accompanied by hearing loss (hearing loss). Sometimes tinnitus is accompanied by symptoms such as headache, dizziness, and nausea.
General treatment regimen
The effectiveness of the medicine for various diseases depends on the correctness of the therapy. The drug is not prescribed as a prophylaxis
When choosing a medication form and dose, it is important to consider such features as:
- patient's age;
- the presence of concomitant pathologies;
- severity of symptoms, etc.
For diseases diagnosed in adult patients, the following rules apply:
- Cerebrovascular diseases. In these cases, patients are prescribed a dose of 20-50 mg. It should be taken 2 or 3 times a day. The maximum amount of the drug should not exceed 150 mg. Treatment is carried out in courses of 1-2 months. The course is repeated six months later.
- Depressive conditions in older people. The most suitable dosage is 60-120 mg, divided into 2 or 3 doses. If necessary, it is reduced to 40 or increased to 200 mg. The duration of therapy can be up to 3 months.
- Asthenic conditions.
Patients are often recommended to take 40-80 mg of Picamilon per day. But in a severe situation, the dose can be increased several times (200-300 mg). Treatment lasts approximately one and a half months. Asthenia - A serious condition caused by alcoholism. It is treated by taking medication in an amount of 100-150 mg (in this case it is convenient to use Picamilon 50). A one-week course is enough to get results.
- Reduced performance. This problem requires the use of a dosage of 60-80 mg. Treatment is carried out for one and a half months.
If the patient has specific characteristics, the indicated doses of the medication can be changed, as well as the duration of use of the drug.
Intravenous or intramuscular administration of the drug is used in the presence of severe disorders. In this case, taking pills is ineffective. Most often, the injection form is indicated for the following disorders:
- Problems with cerebral circulation. To improve the patient's condition, it is necessary to administer 100-200 mg of solution 1 or 2 times a day. Both intravenous and intramuscular administration are allowed. These methods can be alternated: in the morning, give an injection into a vein, in the evening, use the intramuscular method.
- Alcohol poisoning. Picamilon is used together with other medications. The dose of the drug is calculated based on the patient’s weight. For 1 kg, 5 mg of the substance is required.
The principle of using the medicine is as follows. The tableted drug should be taken orally with water. It does not matter whether this is done before or after a meal. The injections must be carried out by a specialist.
Causes of tinnitus
Tinnitus can be caused by a wide range of causes, including some serious medical conditions. First of all, tinnitus is caused by pathologies of the hearing aid. They can be classified by area of localization.
Pathologies of the inner ear:
- presbycusis – atrophic and dystrophic changes in the inner ear of an age-related nature. In this case, tinnitus usually accompanies the development of hearing loss;
- noise damage to the inner ear. The reason may be, for example, listening to loud music on headphones for a long time;
- long-term use of certain medications that are characterized by ototoxicity (adverse effects on the hearing organs);
- otosclerosis (pathological growth of bone tissue of the inner ear). With otosclerosis, noise and hearing loss are observed first in one ear, and a few months later the pathology may develop in the second ear;
- Meniere's disease (fluid accumulation in the inner ear cavity). The main symptom of the disease is dizziness;
- labyrinthitis (inflammation of the inner ear). It also manifests itself primarily as dizziness. Tinnitus is a minor symptom.
Middle ear pathologies:
- Otitis media (inflammation of the middle ear). The main symptoms are ear pain, fever, and possible purulent discharge from the ear. Ear congestion and noise are caused by the presence of fluid (such as pus) in the tympanic cavity;
- exudative otitis (accumulation of fluid in the middle ear cavity). This type of otitis media is worth highlighting separately, since, as a rule, there are no other symptoms with it, except for hearing loss and tinnitus;
- damage to the eardrum (for example, as a result of sound trauma).
Pathologies of the external ear:
- sulfur plug;
- an insect or foreign body entering the ear canal.
Other possible causes of tinnitus
Tinnitus can also be caused by:
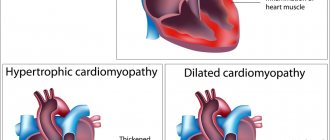
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system
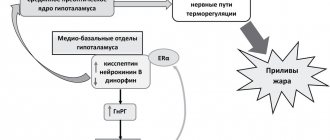
. In particular, with atherosclerosis, plaques on the walls of the arteries lead to disruption of blood flow, and turbulence (turbulence) occurs. This uneven movement of blood causes vibration, which is perceived by the hearing aid and is felt as tinnitus. The sensation of tinnitus intensifies with an increase in blood pressure, which can be persistent (hypertension), or can be caused by situational factors such as stress, alcohol or caffeine consumption;
- pathologies of the nervous system
. Noise in one ear, accompanied by hearing loss, dizziness and a sensation of “goosebumps” crawling across the face, is observed with a neuroma (tumor of the auditory nerve). Tinnitus can also be a symptom of multiple sclerosis or migraine.
Effective injections
Echocardiography of the heart: principle of operation, capabilities and indications for the study
If noise develops in the hearing organs, injections are also prescribed. The list of effective medications for injections includes:
- Cerebrolysin;
- Piracetam;
- Eufillin;
- Cavinton;
- Baclofen.
Cerebrolysin
The medication is relevant for pathologies caused by deterioration of metabolic processes in brain tissue. The medication is administered parenterally, in an individual dosage (from 5 to 50 ml per day). Therapy is carried out within 1-2 weeks.
Piracetam
This medicine is prescribed to patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD). The drug is administered intramuscularly or intravenously. The average dosage is 4 g per day, divided into several administrations. Treatment with Piracetam takes about 10 days.
Eufillin
The drug allows you to relieve sound disturbances associated with the post-stroke state of the body in older people. The product is injected into a muscle or vein, pre-mixed with a solution of sodium chloride.
Intravenous administration is performed slowly, about 5-6 minutes. Intramuscular injections are quite painful, which requires the parallel use of painkillers.
Eufillin is prescribed based on the patient’s body weight:
- single dosage – 7 mg per 1 kg of patient weight;
- daily dose – 13 mg/kg.
During the day, injections are performed at least 3 times. The total duration of therapy is 2 weeks.
Cavinton
Cavinton is often prescribed to patients suffering from noise phenomena after severe stress. This product can also be used during the recovery phase after a stroke.
The medicine increases cerebral blood flow and normalizes metabolic processes occurring in neurons. The drug is predominantly administered intravenously, 20-50 mg per day. After completing injection therapy, patients are often advised to take Cavinton Forte tablets (1 piece three times a day).
Baclofen
This remedy becomes effective if the disorder is caused by osteochondrosis. Injections are performed under sterile conditions, intratectally (into the cerebrospinal fluid).
When should you see a doctor if you have tinnitus?
If you begin to hear tinnitus, that is, if it appears and does not go away, you need to see a doctor and find out its cause in order to exclude the development of the most dangerous diseases.
You should definitely consult a doctor if you experience the following along with tinnitus:
- hearing loss;
- neurological symptoms (dizziness, loss of coordination, nausea, vomiting);
- severe headache or pain in the heart area.
You should also see a doctor if the intensity of the noise increases (if the tinnitus is causing a deterioration in your quality of life).
Capilar
It is worth clarifying that this is not a medicine, but a dietary supplement.
Mechanism of action
The active ingredient of this dietary supplement strengthens the walls of blood vessels, improves blood circulation in them, thins the blood and prevents the formation of blood clots.
REFERENCE! This is not just some kind of dietary supplement that can harm your overall health, but a supplement that has passed many tests in the country's leading scientific institutes (Institute of the Human Brain of the Russian Academy of Sciences, State Research Center for Preventive Medicine and the Central Military Clinical Aviation Hospital). Therefore, there is no doubt about the high effectiveness, as well as the complete safety of the drug.
Indications for use
Capilar is recommended to be taken in the following cases:
with increased stress on the body; with a constant feeling of fatigue; for problems with blood pressure; as a restorative drug after heart disease; with elevated blood sugar levels; for ailments related to the respiratory system; for diseases of the organs of vision; smokers (and it doesn’t matter whether he is active or passive); during physiotherapy to enhance its effect; to stimulate the immune system; to prevent premature aging of organs.
Treatment for tinnitus
Treatment for tinnitus involves identifying and treating the underlying condition. Unfortunately, some pathological changes that cause tinnitus are irreversible (such as age-related changes). In some cases, eliminating the cause of tinnitus is quite simple (for example, the doctor will remove the wax plug immediately). In other cases, serious examination and medication may be required.
The sooner you see a doctor, the greater the likelihood of restoring your hearing acuity and getting rid of tinnitus.