How the heart works
To make the description of atrial fibrillation as clear as possible, it is worth understanding how our heart works and works.
The heart is a hollow muscular organ consisting of four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The principle of operation is probably known to everyone: like a pump, it moves blood throughout the body, saturating the organs with oxygen.
The sinus node, an electrical system located in the wall of the atrium, is responsible for the beating of the heart. It generates an impulse that is evenly distributed over the area of the heart, causing rhythmic contraction and relaxation - the pulse.
What is atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a heart disorder in which the electrical impulse is distributed unevenly throughout the heart. Because of this, the heart chambers work uncoordinatedly: instead of contractions, twitching or “flickering” occurs in the atrium, and the ventricles also contract in the wrong rhythm.
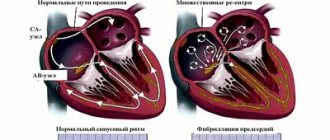
The picture on the left shows a normal heart rhythm, sinus. The electrical signal is generated in the sinus node and spreads evenly through the conduction system of the heart. The right shows how electrical impulses are generated randomly in different places and cause atrial fibrillation.
There are 3 forms of atrial fibrillation:
Paroxysmal or paroxysmal - manifests itself in short attacks that go away on their own within a few minutes or hours. Some people may have only one attack in their entire life, while others may have them several times a day. In this case, you need to consult a doctor to rule out pathology and other forms of the disease.
Persistent or temporarily stable - attacks can last several days, weeks or months. Characterized by the inability to restore heart rhythm without drug treatment and therapy.
Chronic or permanent - occurs, as a rule, with prolonged atrial fibrillation. In this case, the heart rhythm is not restored with the help of treatment, but learning to maintain normal well-being of the body is a feasible and important task.
If an attack lasts longer than 48 hours, blood begins to stagnate in the upper parts of the heart: clots form and the risk of complications increases - blood clots and, subsequently, stroke. Therefore, seeking cardiac care for any manifestation of arrhythmia is a vital necessity.
How to relieve an attack yourself?
If signs of a sharp deterioration in the condition appear, it is important to act quickly. The algorithm for providing first aid is as follows :
- Call an emergency medical immediately
- Avoid any physical activity. Take a lying position .
- Try to calm down . During an attack of atrial fibrillation, you should not be nervous or think about bad consequences. It is important to try to normalize the breathing process - you need to breathe evenly, inhale through your nose, exit through your mouth.
- Provide fresh air flow (open a window). You need to remove all uncomfortable clothing - outerwear, tight T-shirt or sweater, scarf. It is necessary that nothing is squeezing your neck; to do this, you should unbutton the collar of your shirt. Remove all belts from the belt and unfasten the top button on trousers, jeans, skirt, etc.
- Wipe your face with a damp, cool towel. This will help the person calm down and normalize the functioning of the sweat glands.
- Drink a glass of cool water . Often the cause of atrial fibrillation is dehydration. Fluid intake ensures normalization of heart rate.
- Taking sedatives (infusion of motherwort or valerian, Corvalol) will help stop the attack.
Important! If emergency methods do not bring relief, then you must wait for an ambulance to arrive. Before the arrival of specialists, the patient is not recommended to remain alone; it is important that a loved one be with him.
Causes and symptoms
Most often, heart rhythm disturbances are diagnosed in patients with risk factors such as:
- coronary heart disease - myocardial infarction, hypertension, angina pectoris;
- congenital pathology, trauma, heart surgery;
- diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction, obesity;
- old age - over 65 years old.
Causes of heart problems, regardless of age, also include: smoking, taking drugs and certain medications, frequent consumption of alcohol and caffeinated drinks - coffee, strong tea, energy drinks.
How you feel with atrial fibrillation largely depends on the heart rate per minute:
- pulse exceeds 90 beats - anxiety, increased sweating, tremors of the limbs appear;
- pulse is less than 60 beats - the brain does not have enough oxygen, so pre-syncope and fainting, cloudiness of consciousness, and increased fatigue occur.
- The pulse is normal - disorders can be asymptomatic, detected by chance or during a routine examination. The danger lies in the absence of warning factors - a person cannot control the consequences, such as blood clots or stroke, because he does not know about the disease.
Common signs of the disease include dizziness, shortness of breath, pain in the chest or shoulder blades, and a feeling of heartbeat. But it cannot be said that these symptoms only signal arrhythmia or heart disease. To make an accurate diagnosis, diagnostics is needed.
Arrhythmia attack: when the heart asks for help
The human heart is a unique organ that itself creates impulses that contribute to its beating. In the absence of problems with the myocardium, these shocks are not felt. If a person hears them, it means that the heart’s function is impaired. This condition of the heart muscle is called arrhythmia.
Types and symptoms of pathology
Arrhythmia is a pathological process due to which there are disturbances in the frequency, rhythm, and contraction of the heart. In a person with normal functioning of the sinus node, the speed of tremors fluctuates between 60-90 beats/minute. During an attack of arrhythmia, their number may decrease or increase, depending on the type of pathology.
Arrhythmia occurs in the presence of predisposing factors:
- neurocirculatory dystonia is a mental disorder characterized by the spontaneous occurrence of panic attacks;
- thyroid diseases (thyrotoxicosis, hyperthyroidism and others);
- cardiomyopathy, myocarditis;
- cardiac ischemia;
- previous heart attack;
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- heart defects;
- pregnancy.
More than 10 types of arrhythmias occur in medicine. They differ in origin, symptoms, and course of the disease.
8
24/7
Sinus bradycardia
An attack of arrhythmia in which the pulse rate is below 55 beats per minute is called bradycardia. It can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- blood pressure surges;
- severe weakness;
- dizziness;
- feeling of discomfort in the heart area.
Bradycardia can even occur in people who exercise while they are resting or sleeping. Typically, the pathology is accompanied by low blood pressure and decreased thyroid function.
Paroxysmal tachycardia
A condition in which the heart rate reaches 240 beats per minute is called tachycardia. There are 2 forms of it: pathological (with existing heart disease) and physiological.
It is dangerous because it reduces the level of blood filling of the ventricles, which negatively affects the general condition of the internal organs.
You can recognize it by the following signs:
- cardiopalmus;
- blurred or darkened vision;
- chest pain;
- dizziness, fainting;
- profuse sweating.
Sinus arrhythmia
With such an arrhythmia, the heart rate decreases during inspiration and increases during exhalation. This condition often occurs in teenagers and pregnant women. An attack of this type of arrhythmia does not have a negative impact on the person’s condition and does not require treatment.
Atrial fibrillation
The pathology of the heart rhythm is caused by incomplete contraction of the atria, and the ventricles, on the contrary, often contract, reaching 240 beats/minute; in dangerous conditions, the heart rate reaches 600 beats. A prolonged (more than 2 days) attack of atrial fibrillation provokes the formation of blood clots, ischemic stroke, and death. There are 2 types of it: chronic (lasts more than a week) and transient (manifested by relapses).
Atrial fibrillation is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- trembling in the chest;
- weak pulse compared to heart rate;
- anxiety, fear;
- lack of air;
- dizziness, sometimes loss of consciousness.
This type of arrhythmia affects men much more often than women.
Extrasystole
Heart disease is considered the most common form among arrhythmias. It is expressed by untimely contractions of the atria.
Among the patient complaints, the following symptoms were noted:
- strong heartbeats or sensations of heart stopping;
- lack of oxygen;
- excessive sweating;
- fear of dying;
- pallor of the skin.
Medications are used to help with an attack of arrhythmia.
It is noted that extrasystole is more associated with vegetative or psycho-emotional disorders.
8
24/7
Ventricular or atrial flutter and heart block are the worst types of arrhythmia. Signs of pathologies are:
- loss of consciousness (fainting);
- hoarse, confused breathing;
- no pulsation;
- cardiac arrest;
- signs of clinical death.
In this case, it is necessary to try to stop the arrhythmia attack on your own by resorting to emergency measures, otherwise the patient may not wait for the cardiac team to arrive.
Causes
The causes of arrhythmia attacks lie in the conduction system of the heart muscle. If there is a failure in it, a person develops one of the types of pathology. The direct provocateurs of arrhythmia attacks are diseases of the heart itself (ischemic heart disease, heart attack, defects, cardiac dystrophy, cor pulmonale, pathologies of the conduction system). However, there are other reasons, which include:
- kidney and stomach diseases;
- tumors;
- hormonal imbalance;
- stressful situations, psychological disorders;
- diseases of the central and autonomic nervous system;
- head injuries, disturbances in the blood supply to the brain;
- drug intolerance or overdose;
- violations of water-salt metabolism;
- changes in the level of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood;
- atherosclerosis (narrowing, blockage of blood vessels);
- anesthesia of cardiac tissue;
- electric shock;
- heart surgery.
Based on all of the above, it is clear that there are a huge number of reasons for the development of arrhythmia.
Diagnosis of arrhythmia
At an appointment with a cardiologist, you should tell all the existing signs of the disease. The clinical picture will help the doctor make an approximate diagnosis. However, the patient will need to undergo additional examination to determine the exact cause of the disorders.
One of the first diagnostic methods is listening to heart sounds (auscultation), as well as electrocardiography. In some cases, Holter monitoring is performed. To do this, use a special device that is not removed throughout the day. The purpose of this type of diagnosis is to monitor the heart rate within 24 hours. With its help, any deviations in heart rhythm are recorded.
If, however, deviations are not recorded, an arrhythmia attack is artificially induced.
- Electrophysiological research method. To do this, a catheter is placed in a vein that leads to the heart, and electrical stimulation of the heart muscle is performed. The method allows you to accurately determine the presence and stage of arrhythmia.
- Stimulation through the esophagus.
- Tilt test.
Treatment at different stages
If an arrhythmia attack occurs for the first time, you need to call an ambulance and carry out first aid measures. You should follow the instructions for emergency resuscitation step by step:
- put the patient into bed or sit the patient in a chair;
- calm down and open the window to let fresh air in;
- in severe cases, it is necessary to provoke a gag reflex;
- perform a breathing exercise in which, closing your eyes and taking a deep breath, hold the exhalation for a couple of seconds;
- give the patient sedatives (Corvalol, Valocordin, motherwort tincture).
Qualified specialists know how to relieve an attack of arrhythmia with the help of medications. In medical practice, medications are used to relieve attacks:
- sodium channel blockers (Quinidine, Novocainomide, Propafenone, Lidocaine);
- beta-blockers (Egilok, Bisoprolol, Atenolol, Metoprolol);
- potassium channel blockers (Amidarone, Sotohexal, Cordarone, Nimotol);
- calcium channel blockers (Amlodipine, Dilteazem, Nimotol, Verapamil).
Cardiac glycosides, magnesium and potassium preparations (Asparkam, Panangin) are also used.
In the absence of effect from drug treatment, deterioration of the patient's condition and serious heart disease, surgical intervention is performed.
Forecast
If there is an arrhythmia that does not pose a threat to human life, there is no need to worry about treatment. However, you can live a normal life even with serious forms of arrhythmia.
The prognosis for the disease mainly depends on the patient himself. To normalize the condition, you need to follow simple rules:
- strictly follow all recommendations of the attending physician;
- tell the doctor about the side effects of the prescribed medications, do not replace them yourself and report any worsening of the condition;
- monitor blood tests.
Prevention
To prevent arrhythmia attacks, doctors will tell the patient what to do:
- promptly treat existing diseases of any body system, including infectious diseases;
- adhere to proper nutrition (exclude fatty, fried, sweet foods, or at least reduce their consumption to a minimum);
- engage in simple physical exercise (do exercises in the morning, walk in the park or other places with low levels of air pollution);
- monitor your daily routine (healthy sleep for at least 8 hours, naps for 20-60 minutes during the day);
- get rid of bad habits (alcohol, smoking, drugs, drinking energy drinks and large amounts of coffee);
- maintain normal weight;
- control blood sugar levels in diabetes and blood pressure in hypertension;
- experience more positive emotions, avoid stressful situations.
An attack of cardiac arrhythmia is a difficult condition. However, it is treatable. The main thing is not to neglect timely diagnosis and consult a doctor in case of any violations. By undergoing an annual examination, you can reduce the likelihood of developing severe pathologies to a minimum and significantly improve your quality of life. Visiting a doctor today is the key to good health and longevity in the future.
8
24/7
Diagnostic methods
To determine atrial fibrillation, a comprehensive examination of the heart and related organs is performed, and the patient’s physical condition is also analyzed.
The examination includes:
- electro- and echocardiography,
- daily or multi-day ECG monitoring,
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland and hormone analysis,
- clinical and biochemical blood test,
- determination of potassium and magnesium levels,
- lipid profile,
- physical stress testing.
It is convenient to undergo complex diagnostics in a specialized cardiac center: you don’t have to waste energy, time and additional money on visiting doctors in different clinics in your city. The result of the diagnosis should be a detailed plan for further treatment.
Ready-made recipes
Dill seeds help with symptoms of atrial fibrillation. To do this, pour boiling water over the seeds and let them stand for 30 minutes. You will need boiling water - 1 cup, seeds - a third of a cup. The resulting finished decoction can be drunk three times a day, 1/3 cup. It is recommended to do this before eating.
Lovage and its roots are used as medicine. You need to grind them, wash them, and leave them in a liter of warm water for about 12 hours. You can take the tincture throughout the day.
Another recipe includes mint, St. John's wort and rosemary, as well as valerian roots. You need to pour boiling water into this mixture and then simmer over steam for about half an hour. The broth cannot be brought to a boil. The resulting tincture must be filtered and allowed to cool. It is taken up to four times a day (1/3 cup).
You can take rose hips - 20 g, hawthorn fruits - 20 g. Add 3 tablespoons of motherwort to them. The whole thing is poured with boiling water and infused for 12 hours in a dark place. The decoction is taken 100 ml in the morning and evening.
A good remedy is obtained if you take yarrow, valerian roots, hops (cones), and lemon balm. Herbs are taken in two parts, and lemon balm needs three parts. Mix the collection thoroughly. Then pour 1 tablespoon of herbs with boiling water (a glass) and leave for about 40 minutes. Drink up to 5 times a day.
Another collection consists of mint and calendula. You need to take 50g of the mixture and pour boiling water (0.5l). Let cool, strain, add a couple of tablespoons of honey. You need to drink up to 4 glasses a day.
Treatment options
There are two treatment tactics: monitoring the rhythm or frequency of the heart. The cardiologist determines how to treat arrhythmia and what to take individually, depending on the case.
Control of the rhythm of contractions - restoration of sinus, that is, normal, heart rhythm. It is achieved by taking antiarrhythmic drugs or electrical stimulation of the heart - cardioversion. Antiarrhythmic drugs have a positive effect on the electrical conductivity of the heart, thereby reducing the likelihood of repeated failures.
They may also prescribe ablation - the impact of radiofrequency pulses on the arrhythmic area of the heart.
Ablation treatment can be successful in 70% of cases or more: it depends on the severity and nature of the lesion, the duration of the arrhythmia, and the size of the heart cavities. Risks associated with the procedure are rare.
Monitoring your ventricular rate helps eliminate heart palpitations and the risk of heart failure. This method is used in cases where it has not been possible to restore a normal heart rhythm, or the patient does not show symptoms.
Frequency control is carried out in several ways:
- reduce the spread of electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles with the help of drugs,
- ablation is performed to eliminate the delay in pulse propagation,
- a pacemaker is installed to simulate an electrical impulse.
General rules for first aid
The rules for providing first aid for the treatment of paroxysm of atrial fibrillation are carried out differently depending on several characteristics of the attack:
- blood pressure level;
- shortness of breath at rest;
- duration of the attack;
- heart rate;
- primary or repeated paroxysm.
Depending on this, emergency doctors either try to restore sinus rhythm or reduce the heart rate, while simultaneously preventing the formation of blood clots. For this purpose, medications are used, and, if necessary and conditions exist, electropulse therapy is used.
What you can and cannot do at home during an attack
If an attack of irregular heartbeat develops, you must immediately call an ambulance.
Before the medical team arrives, you can:
- give the patient a semi-sitting position;
- unbutton tight clothes;
- provide fresh air access to the room;
- invite the patient to breathe with his stomach, wipe his face with a handkerchief dipped in cold water;
- give 20 - 30 drops of Corvalol in half a glass of water;
- prepare for the arrival of the team: organize its meeting, prepare medical documents, previous ECGs, think about transporting the patient to the ambulance (such a need may arise, but the duties of the ambulance personnel do not include carrying the patient);
- reassure the patient, tell him to call the doctors.
When detecting an attack of MA before the arrival of the ambulance, you cannot:
- give the patient medications before the ambulance arrives, including nitroglycerin;
- massage the eyeballs or the area of the carotid arteries;
- waste time measuring blood pressure without preparing for the arrival of medical personnel;
- collect things for hospitalization (this will be the time while the doctor examines the patient, relieves the attack, etc.; hospitalization is not always required);
- worry and panic.
How to stop an attack of MA on your own (a pill in your pocket)
Some patients whose diagnosis of “paroxysmal atrial fibrillation” has been established for a long time, and attacks occur less than once a month, can learn to independently stop such paroxysms. This tactic is called “pill in the pocket.”
It is used in intellectually intact patients who can adequately assess their condition. The “pill in your pocket” strategy should not be used if the next attack of arrhythmia caused any new symptoms:
- chest pain;
- dizziness;
- weakness in the limbs;
- facial asymmetry and so on.
In such cases, you should not stop the paroxysm on your own, since these symptoms may be a sign of the development of a heart attack or stroke.
If paroxysmal fibrillation proceeds as usual, the patient can take the drug propanorm at a dosage of 450–600 mg.
The patient should consult his cardiologist in advance about in what cases and in what dose to take this medicine. It is better if the first dose of propanorm is taken in a hospital, under the supervision of medical professionals.
Ways of control in everyday life
Irregular heart rhythm is not a death sentence. An active and harmonious life is possible both during the treatment period and after it. It’s enough to learn to live by new rules that embody a healthy lifestyle:
- follow a balanced diet - do not indulge in fatty, fried and too salty foods;
- reduce bad habits to a minimum - reduce alcohol consumption and stop smoking;
- engage in physical activity - walk regularly or add an hour of cardio training per day;
- maintain normal weight and blood pressure;
- monitor your blood sugar levels.
At the Chernaya Rechka Heart Medicine Center, we not only treat arrhythmia and other heart diseases, but also help them adapt to life after them: we teach them a healthy lifestyle and make it a habit.