30.11.2018
A.A.
(Last update: 07/10/2019)
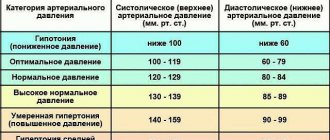
It is worth paying close attention to such a parameter as pulse pressure. It represents the difference between systolic and diastolic readings. The normal pulse pressure is considered to be 30-50 mm Hg. Art. Therefore, a pressure of 150 to 60 is in most cases considered a pathology.
With a high pulse pressure, the heart muscle can work under increased load, which accelerates the aging process. As a result, a person’s well-being deteriorates significantly. If there is a large difference between systolic and diastolic pressure, the likelihood of a heart attack increases.
What does it mean
What does an increase in blood pressure (blood pressure) up to 150/80 mm mean? rt. Art. According to accepted standards, this pressure indicator is a symptom of mild hypertension. The upper pressure indicator is 150 mm. rt. Art. exceeds the lower one by 70 mm. rt. Art.
This is quite a big difference, since the maximum permissible difference is 50 mm. rt. Art. This condition is considered in medicine as isolated hypertension, which is much more dangerous than classic hypertension.
Symptoms of isolated systolic arterial hypertension
Most often, ISAH is asymptomatic, especially at the first stage of the disease. This happens to people who have crossed the 45-year mark, for example. And this is the main danger of pressure 150/70 (150/60) and higher, belonging to this category. The latent course leads to sudden heart attacks and strokes, so it is very important to pay attention to the characteristic symptoms of the disease that gradually arise:
- increased anxiety, nervous tension for no apparent reason;
- constant nausea;
- retrosternal discomfort;
- migraine;
- spots before the eyes;
- feeling of hot flashes, heat in the chest;
- increased sweating;
- pastiness;
- dyspnea.
The symptoms are nonspecific individually, but a combination of several at once is a reason to contact a cardiologist.
In the elderly
A SBP reading of 150 units, combined with a heart rate of 60 to 90/minute, is the norm for an elderly person.
| Age | Maximum permissible blood pressure norm | |
| men | Women | |
| 60 years | 142/85 | 144/85 |
| 70 years old | 145/82 | 159/85 |
| 80 years old | 147/82 | 157/83 |
| 90 years old | 145/78 | 150/79 |
In this case, the pulse difference is very important: if it does not go beyond the normal range - 30-50 mm Hg. Art., everything is fine. Deviation in any direction is a pathology that requires correction.
In pregnant women
Pregnancy is a period of hormonal changes throughout the body, which affects vascular tone, stress on the heart and blood pressure. Typically, the expectant mother is characterized by hypotension: in the first trimester, progesterone increases, which increases heart rate and reduces blood pressure. Therefore, SBP readings are 150 units with a normal DBP level of 70 or 60 mm Hg. Art. - a pathology for a pregnant woman that requires establishing the cause of such growth.
In the second half of pregnancy, a systolic marker equal to 150 units may be the physiological norm due to a decrease in progesterone synthesis and an increase in blood pressure in combination with tachycardia (the total volume of circulating blood increases by 50%).
Blood pressure 150 over 80 – normal or abnormal?
Diagnosis of such blood pressure values must be considered individually. In the vast majority of clinical cases, blood pressure 150 over 80 - alternatively, 155 over 80 - is a deviation from the norm. It is considered as mild hypertension.
Important! If blood pressure readings of 150 over 80 are recorded in the morning after waking up, then the risk of a heart attack or stroke is high.
But an assessment of this level of blood pressure must be given taking into account the following characteristics of the patient:
- age group;
- gender;
- endocrine status;
- person's profession.
In young age
Blood pressure of 150/80 in children and adolescents may well be acceptable. But this statement applies only to the period of puberty, which lasts from 12 to 19 years.
If a child exhibits pathological symptoms, this means that the condition requires medication adjustment: the teenager is prescribed medications with an antihypertensive effect. After the teenager turns 19, blood pressure levels normalize and become stable.
In old age
An increase in blood pressure to the level of 150/80 in an elderly person is not considered normal by doctors, but is quite acceptable. As a rule, people over 50 years of age have several chronic diseases, so blood pressure is almost always elevated.
The development of isolated hypertension poses a serious threat to the health of an elderly person, therefore, in some cases, hospitalization in a hospital is recommended for adequate treatment. Increased blood pressure is much more common in women than in men.
This is due to the active restructuring of hormonal levels against the background of the onset of menopause. It is worth noting that representatives of the stronger sex also experience serious changes in hormonal levels: a change in the balance of androgens occurs. But the male body adapts to the new state much faster and more efficiently.
During the period of bearing a child
During pregnancy, large-scale hormonal changes occur in a woman's body. And although during this period a decrease in blood pressure is typical, in some cases, on the contrary, it increases. But blood pressure levels during pregnancy should not significantly exceed the usual “working” values. The difference should be 10 mmHg. in both directions, i.e. both increase and decrease.
Isolated hypertension is especially dangerous during pregnancy
If the values are very different from the usual ones, then we are talking about the development of pathology. The cause of high blood pressure should be determined by a doctor. Treatment in this case is mandatory, since high blood pressure can cause harm to the child.
For different body types
Blood pressure levels may also depend on a person's body type. Larger, heavier people are slightly more likely to have high blood pressure. This is due to the peculiarities of the course of metabolic processes, as well as the need for the heart to work in a more active mode, pumping blood throughout the body.
Features of the profession
Some types of professions can be provoking factors for hypertension. These include professional sports and work involving increased physical activity.
Gender
In women, physiological increases in blood pressure are much more common. The reason for this is weaker blood flow. But, again, everything is individual.
Hormonal status
In addition to the period of puberty, the time of bearing a child and menopause, an increase in blood pressure is also possible during menstruation.
Reasons for dissonance of meanings
As a rule, a pressure of 150 over 70 is diagnosed in older people, which is associated with age-related changes that determine an increase in systolic indicator:
Blood pressure 140 over 50 - what does this mean?
- Destruction and thinning of the muscle layer in the vessels lead to a decrease in their elasticity, an increase in diameter, resulting in a disorder in blood pressure regulation.
- The atherosclerotic process contributes to disruption of the contractile activity of arteries due to cholesterol deposits on the internal vascular membranes.
- Deterioration of kidney function affects the mechanisms of blood pressure regulation.
- Destruction of special receptors located in the myocardium, which are responsible for the response of the arteries to changes in systolic pressure. Normally, receptors should detect an increase in values and instruct the vessels to balance them.
- Deterioration of blood supply to the brain, due to which the pressure regulation centers located in it are disrupted.
These features are typical for older people and are the causes of dissonance between the upper and lower indicators.
Important! An increase in the pulse difference can be observed with excessive myocardial activity, when blood is actively pushed into the vessels, which leads to an increase in systolic pressure.
A decrease in diastolic indicator indicates a decrease in the elasticity of the arteries. Its value depends on the functioning of the kidneys, since they produce renin, a hormone that regulates the contractile activity of blood vessels. With low production of the hormone, arterial tone decreases, as a result of which the vessels cannot contract normally.
Factors contributing to an increase in PD:
- stressful situations;
- emotional and mental stress;
- iron deficiency;
- disorder of the thyroid gland.
An increase in PP is also observed during excessive physical activity, sudden changes in ambient temperature, and also during periods of viral diseases.
No ads 2
Causes
The development of persistent arterial hypertension is most often caused by several provoking factors. In most cases, the reasons are:
Normal blood pressure during pregnancy
- predisposition at the gene level;
- errors in nutrition - abuse of fatty and sweet foods;
- overweight, obesity;
- kidney diseases complicated by generalized edema;
- diabetes;
- pathologies of the heart and vascular system;
- severe pregnancy;
- the use of oral contraceptives, drugs with a hypertensive effect;
- salt abuse;
- smoking, alcohol abuse;
- frequent stress, chronic fatigue.
In the overwhelming majority of diagnosed clinical cases, an increase in blood pressure to 150/80 is due to age-related changes occurring in the body. Why does this happen, what is the provoking factor? Against the background of the natural process of wear and tear of blood vessels, damage to their walls, a decrease in elasticity, and an increase in peripheral vascular resistance are noted.
The reason for the increase in blood pressure is also a change in the functioning of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. It is she who is responsible for maintaining the physiological level of blood pressure. Kidney disease, accompanied by fluid retention in the body, can provoke a persistent increase in blood pressure.
The next harmful factor is the formation of cholesterol plaques on the walls of vascular beds. In some cases, an increase in blood pressure to 150 to 80 occurs due to excess dosages of drugs with a hypertensive effect.
Features of treatment
A persistent increase in blood pressure to 150 to 70 (150/60) is the first degree of hypertension, ISAH, which needs correction. Competent treatment tactics are as follows:
- determination of target pressure (those blood pressure numbers at which the patient feels comfortable);
- selection of individual medications;
- development of a diet (weight loss, salt restriction);
- exercise therapy;
- reasonable alternation of sleep, rest, work.
Such activities can be carried out both at home and in a hospital setting.
How to normalize blood pressure at home
Blood pressure of 150 to 70 (150/60) or higher can be reduced at home; the person needs to be kept at rest. In addition, they recommend:
- put mustard plasters on calves;
- give a cup of weakly brewed (slept) tea with a spoon of honey and the juice of half a lemon or a glass of cranberry juice;
- you can wipe your whiskey with 6% vinegar, and also stand on a napkin soaked in it with your bare feet for about 20 minutes, no more
If there is no result, calling an ambulance is mandatory; before its arrival, constant tonometry is required.
Medicines for ISAH
There is a standard set of medications for the relief of ISAH or first-degree hypertension:
- diuretics: Furosemide, Hypothiazide, Triampur (for diabetics - Indapamide);
- adrenergic blockers: Atenolol, Bisoprolol, Metoprolol succinate, Nebivolol, Carvedilol;
- calcium antagonists: Norvasc, Verapamil, Anipamil, Amlodipine, Nifedipine
At the discretion of the doctor, the list of drugs can be expanded.
Consultation with a psychologist
A feature of the treatment of ISAH is the consultation of a psychotherapist or psychologist to stabilize the psycho-emotional state of a person who is encountering a similar diagnosis for the first time. Recent scientific data indicate that hypertension is of a psychosomatic nature, and it most often affects people:
- ambitious, vain;
- vulnerable, unsure of themselves;
- those who do not know how to forgive;
- unable to control themselves;
- living in discord with themselves.
The explanation is simple: people prone to self-examination, self-flagellation, and uncertainty constantly need hormonal doping, but such activity of the body has its limit.
Once an already well-functioning mechanism that helps to behave in a certain way due to stress hormones in the blood breaks down, self-healing after stress becomes impossible, and hypertension develops. The systolic indicator is the most sensitive to psychosomatics, so it is the one that begins to increase first.
A psychologist will teach you how to control yourself, breathe correctly, and find the right reaction to a stressful situation. Motivation and psychological acceptance are powerful treatment tools to help cope with the disease.
Symptoms
Blood pressure 150/80 mmHg. not always accompanied by severe symptoms. Sometimes the patient is not even aware of the existing health problem. The absence of clinical manifestations indicates the presence of hypertension, which is characterized by a persistent and prolonged increase in blood pressure and progressive myocardial hypertrophy.
At the beginning of the development of pathology, the heart begins to work in an increased mode. This is a necessary necessity, since only in this way can the body compensate for the increase in blood pressure.
But after a certain period of time - it is individual for each patient - the myocardium is depleted, which causes heart failure. The latter condition often provokes myocardial infarction and ischemia.
When blood pressure rises, the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- headache;
- dizziness;
- attacks of nausea;
- dyspnea;
- noise in ears;
- causeless anxiety;
- darkening of the eyes;
- chest pain;
- facial redness;
- numbness of fingers and toes;
- swelling.
Since the lower indicator remains within the physiological norm - 80 mmHg. – then the person has a significantly increased pulse difference, so he may experience the following unpleasant conditions: fainting, increased fatigue, changes in body temperature. As a rule, when blood pressure increases to 150/80, a person experiences an increase in heart rate to 100 or more beats per minute.
Pulse
Many factors influence heart rate:
- Breath.
- Arterial pressure.
- Stress hormone levels.
- State of the cardiac conduction system.
In a healthy person over 20 years old, the pulse is in the range of 60-80 beats per minute. With high blood pressure, an increase in the number of heart contractions is usually observed. However, due to the large number of factors affecting the pulse, it can not only become faster, but also slow down. In this case, do not hesitate and call a doctor.
And also read on our website: What do blood pressure readings of 170 over 100 mean - the reasons, what to do and how to lower it at home?
Heart rate 60 at this blood pressure
Modern electronic blood pressure monitors show heart rate in addition to blood pressure numbers. This is no accident. Pay attention to this indicator and report it to your doctor if it falls outside the range of 60-80 beats per minute or the tonometer detects an arrhythmia.
A pulse of 60 is not pathological. However, it is at the lower limit of normal. This may indicate incipient disturbances in the conduction system of the heart, which requires additional medical examination and a clinical minimum of examinations.
Be aware that such heart rate values can occur while taking beta blockers. In this case, this is a therapeutic effect that does not require correction.
Is there any danger?
A short-term increase in blood pressure to 150/80 mmHg. does not pose a threat to life, but with long-term isolated hypertension, the patient may experience various kinds of complications.
Important! The pathology is particularly dangerous during pregnancy, as it can provoke the development of intrauterine complications in the fetus.
Isolated hypertension can cause the development of the following pathological conditions:
- atherosclerosis;
- disturbances in myocardial function;
- heart failure;
- stroke;
- long-term cerebrovascular accident;
- deterioration in the functioning of the visual apparatus;
- complications of diabetes;
- metabolic syndrome.
Treatment of the disease is carried out using different groups of drugs
Treatment
Treatment of pathology is carried out according to a standard scheme. The patient will be prescribed medication, a review of the usual lifestyle and diet, and feasible physical activity. If desired, the patient can supplement the basic recommendations with traditional medicine recipes.
Medicines
Drugs from different groups may be prescribed. This:
- Diuretics. Having a strong diuretic effect, they promote the rapid removal of fluid and reduce the volume of circulating blood. As a result, this leads to normalization of blood pressure indicators.
- Calcium antagonists. Drugs in this group block calcium channels, which leads to relaxation of the myocardium and a decrease in arterial tone.
- Beta blockers. Medicines help reduce the activity of the main functions of the myocardium - excitability, conductivity, automaticity and contractility.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Drugs in this group block the transition of angiotensin I to angiotensin II.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and physical activity
A person with isolated hypertension must stop smoking and drinking alcohol. A prerequisite for stabilizing the condition is physical activity. The following will be beneficial for the patient’s health:
- swimming;
- race walking;
- cycling, skiing, skating;
- morning work-out;
- dancing;
- yoga classes.
Important! In the presence of myocardial ischemia and other pathologies, accompanied by oxygen starvation and an increase in blood pressure to 150, climbing high into the mountains is prohibited.
Proper nutrition
It is necessary to completely exclude or minimize the consumption of certain food groups from the menu. These are highly salty and fatty dishes/products, baked goods. The basis of the diet should be dietary meat - chicken, turkey, beef, veal - and fish, cereals, vegetables and fruits.
Benefits come from drinking cranberry juice and beet juice. In the cooking process, you can only use boiling, steaming and baking in the oven without oil.
Folk remedies
What else can you do to normalize your blood pressure? If desired, drug therapy can be supplemented with folk recipes. Good results are obtained by using decoctions and infusions based on the following plants:
- peony root;
- motherwort;
- valerian;
- hawthorn, rose hips (berries);
- chokeberry;
- viburnum, lingonberry (berries);
- swamp grass;
- mistletoe.
You can add a little honey to the finished products. This will enhance the healing properties and improve the taste.
Non-drug way to normalize blood pressure
If a person does not tolerate an increase in blood pressure to 150/80 mmHg, then you need to know how you can quickly alleviate the condition. The recommendations will be especially useful if you do not have an antihypertensive drug on hand.
- Cold compress. A soft cloth should be moistened in water, wrung out and applied to the area of the solar plexus and thyroid gland.
- Taking a contrast shower. The procedure involves alternating comfortably hot and cool water.
- Vinegar compress. A cloth soaked in an aqueous solution of vinegar is applied to the back of the head and the area of the calf muscles. The duration of the procedure is 10 minutes.
Disease prognosis
If the patient strictly follows all the recommendations of the attending physician, the prognosis of the disease is positive. Recovery occurs in a short time. Difficulties in treatment can be caused by primary hypertension, i.e. a pathology that has developed independently and is not a complication of another disease. In this case, the outcome depends on the effectiveness of the pathology that provoked its appearance.
Prevention
Prevention of high blood pressure:
- adherence to sleep and wakefulness;
- healthy eating;
- quitting smoking, alcohol;
- daily walks in the fresh air, feasible physical activity.
Do not forget that it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it later. A persistent increase in blood pressure up to 150/80 mmHg is in most cases a dangerous condition that requires adequate therapy. This is why a person is advised to seek medical advice as early as possible.