What does BP mean?
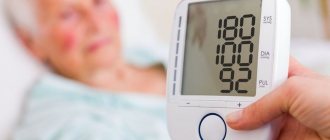
A pressure of 160 over 70 is called second-degree systolic hypertension. This is a fairly serious disease that significantly increases the risk of cardiovascular disease over the next 10 years of life. The normal blood pressure for a person of any age is 120/80 mm Hg. Art. If the level of the lower indicator is close to ideal, then a deviation of 40 mm for the upper indicator means overstrain of the heart muscle at the time of pumping blood.
Depending on age, systolic hypertension carries the following dangers:
- increased blood flow in an elderly person leads to serious complications in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, since in elderly people the vessels are worn out due to age-related changes;
- for an adult the pressure is 160 to 70 mm Hg. Art. is also a reason to consult a doctor. Women suffer from hypertension less often than men, since they monitor their lifestyle more carefully and as long as the menstrual cycle is not disrupted, pressure changes are quite rare for them;
- A child's developing body also finds it difficult to tolerate sudden changes in pressure, and this condition can pose a significant threat to the health of children.
A reading of 160/70 is dangerous regardless of age.
Are such indicators dangerous?
Arterial hypertension of the second degree is a very serious disease that requires constant medical consultation. The fact is that increased blood flow significantly increases the risk of developing pathologies of the cardiovascular and other systems by up to 20%. The list of disorders that hypertension leads to includes:
- stroke;
- heart attack;
- heart failure;
- renal failure.
Each of these diseases can lead to death. However, this is not a verdict. Arterial hypertension of the second degree is easy to treat - you just need to consult a doctor in time.
The norm for everyone
For young people, lower - diastolic - pressure in the range of 90-70 is normal. Moreover, with a pressure of 100 to 70 they can feel normal. With age, they reach 120 to 90 – the generally accepted “norm”.
Also, any difference between the upper and lower pressure, which does not exceed 60 units, fits into the usual indicators.
Increased blood pressure can be caused by many reasons. Serious illnesses often provoke pressure surges. If you have the following diseases or are at risk, visit your doctor for examination and treatment:
- Predisposition to hypertension;
- Kidney diseases;
- Diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- Heredity;
- Diabetes.
In cases where the pressure constantly rises and stays at the marks, it is considered that the pressure is increased, since the blood presses with more force than necessary on the walls of the vessels, moving throughout the body.
In this case, indicators of 160 to 100 are considered borderline. Any deviation is already considered a dangerous condition. This is especially true for lower pressure. Every hypertensive person knows that the upper blood pressure is “knocked down” if it is elevated. But at low values of the lower threshold, people get lost, and sometimes do not pay attention to the alarming symptom at all.
Reasons
The main cause of isolated hypertension is the unhealthy lifestyle typical of residents of large cities. Possible trigger factors include:
- excess weight;
- lack of sleep;
- an abundance of fatty, salty or sweet foods in the diet;
- stress;
- lack of physical activity;
- physical inactivity.
All of the above reasons are indeed more typical for residents of modern cities.
Symptoms
The symptoms of hypertension seriously affect a person’s performance and morale. The following ailments may indicate increased blood pressure:
- nausea;
- dizziness;
- trembling fingers;
- facial redness;
- chest pain;
- blurred vision.
And also read on our website: What do pressure readings of 140 over 60 mean, is this normal, why is it dangerous and what should the elderly and pregnant women do?
It is also worth noting headache as a separate, natural symptom of hypertension. If you have a headache, feel free to take aspirin, it will alleviate or eliminate this ailment.
Blood pressure norms
Blood pressure has its own norm for each age. For example, the norm characteristic of a teenager will be a sign of hypotension for an elderly person.
To determine your normal pressure, a special formula has been developed.
So, for children from 7 years of age until young people reach the age of 20 years, the normal pressure is calculated using the following formula: systolic pressure is equal to a factor of 1.7 multiplied by age, plus 83. Diastolic pressure is equal to a factor of 1.6 multiplied by age, plus 42.
Thus, if you suspect that a child has a jump in pressure in one direction or another, using this formula you can independently determine the norm and proceed from the result obtained.
For an adult, a different coefficient is applied: systolic pressure is equal to 0.4 times age, plus 109. Diastolic pressure in this case is equal to 0.3 times age, plus 67.
Below is an example of blood pressure norms for different age categories:
- From 1 year to 10 years: normal blood pressure is 95 per 60 mm Hg. Art.;
- From 10 to 15 years: the norm will rise and is a limit of indicators from 95 to 60 mm Hg. Art. up to 110 at 70mm Hg. Art.;
- From 16 to 20 years: the norm is considered to be blood pressure readings from 110 to 70 mm Hg. Art. up to 120 at 80mm Hg. Art.;
- From 21 to 40 years: for this category of people, generally accepted indicators are between 120 and 70 mm Hg. Art. up to 130 at 80 mm Hg. Art.;
- From 41 to 60 years - the normal blood pressure readings are even higher than 140 per 90 mm Hg. Art.;
- From 61 to 70 years – the indicators rise to the level of 140-147 by 85 mm Hg. Art.;
- Over 71 years of age: during this period of life, indicators such as 147 per 85 mm Hg are typical. Art.
These standards are generally accepted throughout the world, but in practical medicine there is also such a thing as “working pressure”.
This is the name for increased or decreased blood pressure, according to the age norm, at which a person feels good and does not have any problems with disruption of his rhythm of life.
Pulse
The pulse of a healthy person varies from 60 to 80 beats per minute. With hypertension, an increased pulse indicates possible pathologies in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. A decrease is observed in hypertensive patients who have taken antihypertensive drugs. Therefore, if your blood pressure rises to 160/70 and your heart rate increases, consult a doctor immediately.
Also, tachycardia can occur with excessive physical exertion, but in this case the heart rate will return to normal on its own after a few minutes.
General information
Blood pressure (BP) characterizes the state of the cardiovascular system at the time blood passes through it. It represents a mechanical effect on the walls of blood vessels of moving volumes of blood.
Blood pressure is determined by two indicators: upper and lower. The upper, also known as systolic, pressure determines the vascular tone at the moment of heart contraction. The lower one, that is, diastolic, on the contrary, determines the state of the vessels at the moment of relaxation of the heart muscle.
What to do with such blood pressure?
First aid for hypertension does not depend on the patient’s age group. Providing it at home will not be difficult if you know the algorithm for the necessary actions:
- Assist the patient into a semi-recumbent position.
- Provide a flow of fresh air into the room.
- Take an extra dose of antihypertensive drugs if they were previously prescribed by your doctor.
- Measure your blood pressure every 20 minutes. If after taking the actions your condition does not return to normal, call an ambulance immediately!
For headaches, take analgin, and for chest pain, nitroglycerin. Do not exceed the dose of antihypertensive medications under any circumstances - a sudden drop in pressure can lead to serious complications.
The tonometer shows pressure 160 to 60: is this dangerous?
Blood pressure 160 over 60 - what does this mean?
Let's look at the numbers a little. The first number reflects the force with which blood is ejected into the vessels during heart contraction (systolic pressure). The second number indicates the force with which blood flows through the vessels (diastolic pressure).
Increased upper pressure and decreased lower pressure, which you have been experiencing for several days or weeks, should be the reason for examination by a doctor.
In the case of tonometer readings of 160/60, we have:
- The upper pressure is 160. This indicates increased blood ejection/heart contraction. It is systolic pressure that experts pay increased attention to, since its increase can provoke a heart attack or stroke. A periodic or constant increase in systolic pressure may indicate mechanical wear of blood vessels and heart muscle, blockage of veins, insufficient blood circulation and various heart diseases.
- The lower pressure is 60. With normal upper pressure values (up to 130 units), such a diastolic pressure figure is not dangerous to human life and health. But if the top number exceeds 140 units, the likelihood of having serious diseases increases. In this situation, it is recommended to examine the kidneys (renal veins), thyroid gland and spine (for possible vascular entrapment).
- And another important indicator is pulse pressure (the difference between the upper and lower). 160-60=100 units. This is quite a high figure. Pulse pressure reflects the speed of blood movement through the capillaries. Let's imagine how this happens. Blood enriched with oxygen and nutrients passes through the capillaries, transferring nutrition to the cells. If its speed is too low (pulse pressure below 50), then the cells are fed unevenly, but if it is too high (above 75 units), then the cells do not have time to receive the necessary nutrition. We conclude: both high and low pulse pressure leads to oxygen starvation and insufficient nutrition of organs and tissues.
The reasons for pressure 160 to 60 may be:
- Pathologies of the heart muscle;
- Circulatory disorders, increased blood viscosity;
- Blockage and (or) narrowing of blood vessels, their age-related wear;
- Kidney problems, endocrine disorders, or pinched blood vessels in the spine.
What to do? Your actions could be as follows:
What medications to take
There are several groups of drugs to lower blood pressure. The doctor will choose a medicine that is suitable specifically for you and will correspond to the characteristics of your body.
Sedative medications
The effect of sedatives is to stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system. They will help you isolate yourself from sources of stress and relax.
However, it is worth knowing that they do not have any direct effect on blood circulation, although the treatment of hypertension consists of both relieving psychological stress and lowering blood pressure with medications. Examples of sedatives for hypertensive patients are:
- Afobazole;
- Glycised;
- Valerian;
- Motherwort.
And also read on our website: What do blood pressure readings of 150 to 100 mean, how to reduce them, what pills to take, causes and treatment
Despite the lack of a direct antihypertensive effect, these drugs can reduce the likelihood of an increase by affecting the nervous system.
Analgesics and antispasmodics
If you suffer from hypertension, you should be careful in choosing analgesics. A side effect of many of them is an increase in blood pressure, so before taking any drug, read the instructions for its use or consult your doctor.
Also, analgesics can have a detrimental effect on the functioning of the kidneys and liver, as they can be toxic. The following analgesics may increase blood pressure:
- Citramon;
- Rrigand-d;
- Kaffetin.
If there are no special means to lower blood pressure at hand, it is permissible to use the following antispasmodics:
- No-shpa;
- Papazol;
- Spazmolgon.
Decoctions of cumin or fennel will also help get rid of cramps.
Diuretics
Diuretics are the first-line drugs for lowering blood pressure, since its increase is often caused by excess fluid in the body. The following diuretics may be prescribed by your doctor:
- Furosemide;
- Spironolactone;
- Veroshpiron.
Diuretics are also actively used for liver and kidney diseases to remove accumulated fluid and toxins.
To what degree of danger does this pressure belong?
In medicine, there is the following classifier of stages of arterial hypertension:
- Normal blood pressure: it corresponds to 130 to 85 mmHg. Art.
- High normal: this form of hypertension is in the range of 130-139 at 85-89 mmHg. Art.
- First degree: soft, determined by indicators of 140-159 at 90-99 mmHg. Art.
- Second degree: moderate, its indicators are 160-179 per 100-109 mmHg. Art.
- Third degree: severe, the pressure in this case is higher than 180 to 110 mm Hg. Art.
Thus, the pressure we are considering is within the range of 160 to 70 mmHg. Art. refers to the second degree of arterial hypertension, but has a lower systolic index.