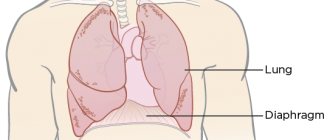
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) is a painful feeling of lack of air, in extreme terms taking the form of suffocation.
If shortness of breath occurs in a healthy person against the background of physical activity or severe psycho-emotional stress, it is considered physiological. Its cause is the body's increased need for oxygen. In other cases, shortness of breath is caused by some disease and is called pathological.
According to the difficulty of the inhalation or exhalation phase, shortness of breath is distinguished as inspiratory and expiratory, respectively. A variant of mixed shortness of breath with limitation of both phases is also possible.
There are several types of shortness of breath. Dyspnea is considered subjective if the patient feels difficulty breathing, dissatisfaction with inhalation, but this cannot be measured and there are no factors for its occurrence. Most often it is a symptom of hysteria, neurosis, and thoracic radiculitis. Objective shortness of breath is characterized by a violation of the frequency, depth of breathing, duration of inhalation or exhalation, as well as increased work of the respiratory muscles.
Diseases associated with shortness of breath
In diseases of the respiratory system, shortness of breath may be the result of an obstruction in the airways or a decrease in the respiratory surface area of the lungs.
An obstruction in the upper respiratory tract (foreign body, tumor, accumulation of sputum) makes it difficult to inhale and pass air to the lungs, thereby causing inspiratory dyspnea. Reducing the lumen of the final sections of the bronchial tree - bronchioles, small bronchi due to inflammatory edema or spasm of their smooth muscles prevents exhalation, causing expiratory shortness of breath. In the case of narrowing of the trachea or large bronchus, shortness of breath takes on a mixed character, which is associated with the limitation of both phases of the respiratory act.
Mixed shortness of breath will also be due to inflammation of the lung parenchyma (pneumonia), atelectasis, tuberculosis, actinomycosis (fungal infection), silicosis, pulmonary infarction or compression from the outside by air, fluid in the pleural cavity (with hydrothorax, pneumothorax). Severe mixed shortness of breath up to suffocation is observed with pulmonary embolism. The patient takes a forced sitting position with support on his hands. Choking in the form of a sudden attack is a symptom of asthma, bronchial or cardiac.
With pleurisy, breathing becomes shallow and painful; a similar picture is observed with chest injuries and inflammation of the intercostal nerves, damage to the respiratory muscles (with poliomyelitis, paralysis, myasthenia gravis).
Shortness of breath in heart disease is a fairly common and diagnostically significant symptom. The cause of shortness of breath here is a weakening of the pumping function of the left ventricle and stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation.
The severity of heart failure can be judged by the degree of shortness of breath. At the initial stage, shortness of breath appears during physical activity: climbing stairs more than 2-3 floors, walking uphill, against the wind, moving at a fast pace. As the disease progresses, it becomes difficult to breathe even with slight exertion, when talking, eating, walking at a calm pace, or lying horizontally. In the severe stage of the disease, shortness of breath occurs even with minimal exertion and any actions, such as getting out of bed, moving around the apartment, bending the body, entail a feeling of lack of air. In the final stage, shortness of breath is present even at rest.
Attacks of severe shortness of breath, suffocation that occur after physical, psycho-emotional stress or suddenly, often at night, during sleep are called cardiac asthma. The patient is in a forced sitting position. Breathing becomes noisy, bubbling, audible at a distance. The release of foamy sputum may be observed, which indicates the onset of pulmonary edema; the participation of auxiliary muscles in the act of breathing and retraction of the intercostal spaces are noticeable to the naked eye.
In addition, shortness of breath in combination with chest pain, palpitations, and interruptions in cardiac function can be a sign of acute myocardial infarction, rhythm disturbances (paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation) and is caused by a sharp decrease in heart function, a decrease in perfusion and oxygen supply to organs and tissues.
A group of blood diseases, one of the symptoms of which is shortness of breath, includes anemia and leukemia (tumor diseases). Both are characterized by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and red blood cells, the main role of which is oxygen transport. Accordingly, oxygenation of organs and tissues deteriorates. A compensatory reaction occurs, the frequency and depth of breathing increases - thereby the body begins to consume more oxygen from the environment per unit of time.
The simplest and most reliable method for diagnosing these conditions is a general blood test.
Another group is endocrine (thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus) and hormonally active diseases (obesity).
With thyrotoxicosis, the thyroid gland produces an excess amount of hormones, under the influence of which all metabolic processes are accelerated, metabolism and oxygen consumption increase. Here, shortness of breath, as with anemia, is compensatory in nature. In addition, high levels of T3 and T4 increase the work of the heart, contributing to rhythm disturbances such as paroxysmal tachycardia, atrial fibrillation with the consequences mentioned above.
Shortness of breath in diabetes mellitus can be considered a consequence of diabetic microangiopathy, leading to impaired trophism and oxygen starvation of cells and tissues. The second link is kidney damage - diabetic nephropathy. The kidneys produce the hematopoietic factor erythropoietin, and its deficiency causes anemia.
With obesity, as a result of the deposition of adipose tissue in the internal organs, the work of the heart and lungs is hampered, and the excursion of the diaphragm is limited. In addition, obesity is often accompanied by atherosclerosis and hypertension, which also entails disruption of their function and the occurrence of shortness of breath.
Shortness of breath to the point of suffocation can be observed with various types of systemic poisoning. The mechanism of its development includes an increase in the permeability of the vascular wall at the microcirculatory level and toxic pulmonary edema, as well as direct damage to the heart with disruption of its function and stagnation of blood in the pulmonary circulation.
Deep breathing
The technique is performed to ventilate all respiratory tracts, helps relieve symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections, and restores and straightens the lungs after infections. Doctors in Rostov speak positively about the benefits of daily practice as a preventive measure.
The exercise has contraindications:
- pregnancy,
- dry non-productive cough.
To perform this, you need to take 3-4 deep breaths only through your nose so that the air is warmed and moistened in the nasopharynx. It is worth taking a break between breaths to prevent hyperventilation.
Causes of shortness of breath
There can be quite a few reasons for shortness of breath. Among them:
- strong physical activity (sports, work);
- myocardial infarction, irregular heart rhythms, heart defects, myxomas, other heart problems;
- allergies, bronchial asthma, tuberculosis, emphysema, pneumothorax, pneumonia, pulmonary obstruction, cancer;
- vasculitis, primary type hypertension, aneurysm;
- myasthenia gravis, lateral sclerosis;
- ascites;
- uremia;
- anemia;
- pericardium;
- hyperventilation syndrome.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of shortness of breath comes down primarily to assessing the general condition of the patient and collecting an anamnesis. Based on the current clinical picture, additional studies are prescribed:
- chest x-ray;
- MRI;
- urine and blood tests;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- ECG;
- spirometry;
- Ultrasound of the neck.
The exact list of necessary diagnostic measures is prescribed by the doctor after consultation with the patient.
Types of shortness of breath
In medicine, this problem has its own name - dyspnea. According to the international classification, the following types of shortness of breath are distinguished:
- bradypnea;
- tachypnea.
Bradypnea is a decrease in breathing with a slowdown in respiratory rate to 12 or less movements per minute. Tachypnea is an increase in shallow breathing with a frequency of more than 20 movements per minute.
Based on intensity and time interval, dyspnea is divided into types:
- chronic – observed for several years;
- acute – lasts from 2 minutes to several hours;
- subacute – from several hours to 2 days.
Most often, shortness of breath is observed in diseases of the respiratory (bronchopulmonary) and cardiovascular systems. These diseases are extremely life-threatening. Therefore, if you suspect shortness of breath, you should immediately consult a doctor to undergo examination and receive timely treatment.
Treatment of shortness of breath
Treatment for shortness of breath is selected depending on what root of the problem is discovered after diagnosis.
- If a foreign body is detected in the respiratory organs, surgical intervention is performed.
- For bronchial asthma, selective beta-agonists are used.
- For heart failure, diuretics, narcotic analgesics, and vasodilators are prescribed.
- If the cause is neurology, then the emphasis is on special breathing exercises.
- For obstructions, anxiolytics, respiratory support, oxygen administration and other measures are prescribed.
One of the symptoms of osteochondrosis is shortness of breath
Depending on where osteochondrosis is localized, certain symptoms may occur. If the affected area is located in the chest area, the patient cannot breathe deeply. The intercostal muscles are tense, causing breaths to be frequent and shallow. This is shortness of breath.
To provide competent assistance to the spine,
It is not enough to eliminate this symptom. After all, in addition to it, other pathologies appear. The functioning of the esophagus is disrupted, the person constantly feels a lump in the throat. If the symptom does not disappear for a long time, and this occurs with continuous irritation of the nerve roots, an ulcer develops.
When the disease is localized in the cervical region, shortness of breath appears due to problems with the diaphragm. The vagus nerve is irritated. Oxygen starvation leads to the fact that a person begins to lack air. Symptoms of hypoxia appear.
Causes of shortness of breath
Breathing becomes heavy for 3 reasons:
- Problems with the diaphragm. Pinches the phrenic nerve. Incessant hiccups, pain in the liver and heart are the consequences of compression of the nerve roots. In addition to discomfort, a person lacks oxygen.
- Pain when exhaling/inhaling. The roots of the sensory nerve in the thoracic region are compressed. This is the main cause of suffocation. If the patient breathes deeply or exhales sharply, the pain syndrome intensifies. There is less carbon dioxide in the blood. Dizziness becomes more frequent. Possible fainting.
- Impaired blood flow in the neck area. It carries nutrients to the brain. Their deficiency leads to the malfunction of individual cents, including the respiratory system. Nerve tissues are deprived of oxygen, which leads to serious consequences.
- Lung diseases. There is no direct connection with osteochondrosis. However, the disease can modify lung tissue. Patients often suffer from bronchitis and pneumonia.
There are also external factors that provoke shortness of breath:
- Staying in an unnatural position for a long time;
- rachiocampsis;
- Anatomical changes in the chest;
- Rupture of ligaments, muscle fibers in the chest area;
- Physical fatigue.
By the way, shortness of breath does not always indicate osteochondrosis. Sometimes it is a symptom of another disease. To find out which one, consult your doctor. He will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis.
Medical therapy
To eliminate pain, specialists prescribe non-steroidal analgesics. They are effective from the first day of admission. The person does not experience much difficulty breathing. The pain syndrome is less pronounced than before. Neuromuscular blockades are also used. The drug can be administered intravenously. These methods are advisable only if the patient’s condition is serious.
Medicines are the basis of treatment. Additional methods in the form of physiotherapy, acupuncture, exercise therapy, and manual therapy are also used. As a rule, they are used in combination.
If you have been diagnosed with osteochondrosis and have shortness of breath, it’s time to sound the alarm. This symptom indicates that internal organs are beginning to fail. Their normal functioning is disrupted, and irreversible degenerative changes begin.
Preventing shortness of breath
To restore your health and prevent shortness of breath, take measures to prevent this disease. Follow simple recommendations, and the effect will not take long to appear. Do therapeutic exercises every day. Spend at least 20 minutes on the lesson. Pay attention to every part of the body, especially the affected area. If you sleep in a soft and cozy bed, you will have to sacrifice comfort. Buy a semi-firm mattress. The pillow should be low.
Aromatherapy will help improve your breathing and relax.
Give preference to plant essential oils. Hypoxia worsens in enclosed spaces, so ventilate the room more often and walk outside more. Strengthen your immune system. To do this, create a balanced diet. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr