A condition in which the rhythm, frequency and depth of breathing is disrupted, and a feeling of air deficiency occurs, is called shortness of breath. The causes and treatment of this disorder can be very diverse. Shortness of breath can occur under various conditions. So, for example, there is shortness of breath when talking, shortness of breath when lying down, after sleep, shortness of breath at rest, etc. The breathing of a person with shortness of breath is frequent and noisy; it is these manifestations that give others reason to assume the presence of shortness of breath. Shortness of breath can be a consequence of quite serious diseases, therefore, when it appears, it is necessary to contact a specialist as quickly as possible, who will competently explain what shortness of breath is and how it manifests itself, and also prescribe a comprehensive diagnostic examination to identify the causes of its occurrence.
The Therapy Center of the Yusupov Hospital offers high-quality diagnostics and effective treatment of diseases accompanied by shortness of breath. If necessary, a pulmonologist can be called to your home.
What is shortness of breath and what causes it?
Shortness of breath refers to a whole range of symptoms. The main symptom of dyspnea is a feeling of ineffectiveness of the breathing movements performed. The person realizes that he doesn’t have enough air. He experiences chest tightness and general discomfort. Severe shortness of breath and palpitations are often combined . In this condition, your heart rate may increase.
Associated symptoms:
- respiratory rhythm disturbance - too frequent or rare breathing;
- suffocation;
- paleness of body skin;
- cyanosis (blueness) of the nasolabial triangle;
- dizziness;
- tinnitus.
The typical reaction of a person if shortness of breath appears is to stop any activity and find support. As a rule, if you sit or lie down, the condition will stabilize on its own after a few minutes. This technique works if the cause of shortness of breath and lack of air is excessive physical activity or severe emotional stress.
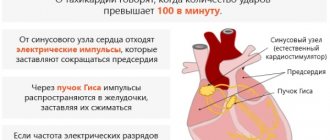
The mechanism of development of dyspnea is associated with the work of the body's reflex mechanisms. This is a kind of reaction to a change in the ratio of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood. As the concentration of carbon dioxide increases, the pH level decreases, which leads to stimulation of the receptors in the medulla oblongata. Next, the protective mechanism is triggered. A signal goes from the respiratory center to the periphery, stimulating increased breathing, the purpose of which is to increase the concentration of oxygen in the blood and increase its saturation. This mechanism most often causes severe shortness of breath and respiratory rhythm disturbances.
Types of dyspnea
Experts distinguish three groups of shortness of breath. The classification is based on provoking factors and the difficult breathing phase.
- Inspiratory. Difficulty breathing. Noisy breathing may occur. often occurs with pulmonary fibrosis, pathologies of the diaphragm, and heart failure.
- Expiratory. The patient experiences difficulty exhaling, which is typical for asthma, bronchitis, and emphysema.
- Mixed. Both phases of breathing are impaired. Most often it is a consequence of cardiac pathologies and diseases of the central nervous system.
Why does shortness of breath occur?
If a person suddenly develops severe shortness of breath, the reasons can be very diverse. Most often it is caused by the following conditions:
- cardiovascular diseases – due to these pathologies, blood circulation is impaired. Internal organs suffer from a lack of oxygen, and carbon dioxide accumulates in the blood. The body’s reaction to this condition is increased breathing: a larger volume of air is pumped through the lungs per unit of time. In the supine position and after physical activity, shortness of breath associated with heart pathology occurs or intensifies. Severe shortness of breath occurs with the patient sitting or half-sitting. This kind of shortness of breath is characterized by difficulty breathing;
- diseases of the respiratory system - the appearance of shortness of breath is associated with obstacles to the passage of air through the respiratory tract (for example, narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi). Therefore, shortness of breath is considered a typical symptom of bronchial asthma. With this disease, the patient experiences difficulty in exhaling. In addition, shortness of breath occurs in cases where the respiratory surface of the lung tissue is reduced. Such a decrease is accompanied by an increase in the intensity of lung function, i.e. frequent inhalation, which is necessary to maintain the required amount of oxygen entering the blood. The list of pathologies of the respiratory system accompanied by shortness of breath includes neoplasms, pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, etc.;
- anemia - even with normal activity of the lungs and heart, a deficiency of hemoglobin and red blood cells leads to insufficient provision of the organs with the necessary amount of oxygen. To compensate for this disorder, the body increases its breathing rate;
- neuroses and panic attacks - in these cases, clinical examinations do not reveal the presence of cardiovascular and pulmonary pathologies, but subjectively the patient suffers from lack of air, and the appearance of psycho-emotional changes provokes increased breathing, which causes shortness of breath;
- various tumors – shortness of breath occurs with a tumor of the thalamus, intestinal tumors, etc.;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract. For example, hoarseness, cough, shortness of breath with esophagitis are characteristic symptoms;
- obesity and diabetes are common causes of shortness of breath.
Causes of constant shortness of breath
Dyspnea can be provoked by a whole range of physiological and pathological reasons. The cause of shortness of breath without exertion can be chronic or acute diseases:
- pleurisy;
- respiratory tract tumors;
- asthmatic attack;
- pneumonia;
- false croup;
- tuberculosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- panic attacks;
- neuroses.
The cause of shortness of breath in a person at rest can also be long-term use of certain medications, in particular non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antipyretics based on acetylsalicylic acid.
Physiological reasons cannot be ruled out. For example, a feeling of lack of air often occurs in healthy people during prolonged exercise. Severe shortness of breath and palpitations when walking are considered normal . In both cases, the body actually experiences oxygen deficiency. After resting or changing activities to a calmer one, the state stabilizes.
4.Prevention of shortness of breath
Shortness of breath is often a harmless phenomenon and passes without special measures. However, you need to be attentive to this symptom if it repeats too often, and especially during those loads that previously passed without difficulty breathing. The occurrence of shortness of breath during movement in some cases can be a sign of serious disorders in the body. If you are sure that you are healthy, but your breathing is still impaired with increasing physical activity, there may be a number of reasons for this that you should try to eliminate on your own:
- reduce weight;
- lead a more active lifestyle;
- engage in feasible regular training (swimming, dancing, physical therapy, running);
- increase stress resistance, refuse excess information;
- take measures to increase immunity;
- quit smoking.
How to understand that you need a doctor's help
It is not always possible to independently determine the causes of shortness of breath during exercise or at rest. A pulmonologist will help with this; you should make an appointment with him if you experience shortness of breath and have trouble breathing . In case of an acute sudden attack with a significant deterioration in well-being, the patient needs emergency help. If you are concerned about shortness of breath and lack of air without exercise , then you need to visit a doctor as planned.
At your appointment, the pulmonologist will ask a number of questions, the answers to which will allow you to determine the exact cause of shortness of breath when walking , exercising, or at rest. List of main questions:
- how long has the symptom bothered you?
- severe shortness of breath occurs when walking and running or bothers you even when resting;
- which is more difficult - inhalation or exhalation;
- will the condition stabilize if you lie down;
- Are there any accompanying symptoms?
How does shortness of breath manifest in a child?
Shortness of breath is manifested by various symptoms that indicate that there is not enough oxygen in the body at the moment. In addition to difficulty breathing in and out, your child may also suffer from chest pain and nasal congestion. It is worth noting that for different types of shortness of breath there are different symptoms that lead to rapid breathing.
For shortness of breath, symptoms may include cough, sputum, wheezing, high body temperature, and intoxication. As a rule, the child seems scared, anxious, his face turns very red, and other parts of the body, on the contrary, turn pale. You can also focus on icy hands and feet.
When to see a doctor
In order not to worsen the child’s condition, it is necessary to urgently consult a specialist if at least two or three symptoms of the disease make themselves felt. If a child has difficulty breathing, then there is no need to engage in amateur activities.
Shortness of breath is a pathology that can be with a child for a long time and not particularly show its existence, but sooner or later the disease will worsen the situation and require complex treatment. The child’s recovery is carried out by a pediatrician or therapist who knows all the best treatment methods and will help the mother sleep peacefully.
Our medical center employs only the best specialists who use modern equipment and innovative methods for treating diseases, while offering reasonable prices. This will help every mommy seek help. Timely treatment of pathology will solve all problems.
Diagnosis and treatment of shortness of breath
Parents cannot diagnose a specific type of shortness of breath on their own. Even in the attending physician’s office, it is not enough for a specialist to simply visually examine the child and listen to his breathing in order to make a conclusion. As a rule, the doctor first evaluates the clinical symptoms of shortness of breath, after which he checks the test results and sends the child for an x-ray. It is the X-ray that makes it possible to draw conclusions about the baby’s condition and understand how affected the lungs are, what the severity of shortness of breath is, and whether there is a pathological process.
Based on the results, the specialist selects the best method of treatment and prevention. Treating shortness of breath at home is strictly prohibited, as this may worsen the condition. The best treatment option is to stay in a clinic under the supervision of a doctor, take a course of medication, and undergo therapy and procedures.
Features in newborns and infants
Absolutely anyone can understand that a newly born child has shortness of breath. All you need to do is count how many breaths your baby takes per minute. If the figure significantly exceeds 60 breaths per minute, then we can safely say that the newborn or infant is suffering from shortness of breath. As a rule, the ideal figure for infants is 30-35 breaths per minute.
Doctors say that shortness of breath in newborns can be a congenital pathology, which, after its full development, leads to health problems and disruption of the child’s immune system.
Quite often, shortness of breath begins to worry a newborn even after a normal runny nose, since it leads to the baby having a very hard time breathing, he constantly lacks oxygen, and in order to somehow normalize the condition, the child has to breathe twice as often. In order to correct the situation, you simply need to cure the child of a runny nose.
If signs of shortness of breath are detected in an infant or newborn, then it is imperative to visit a consultation with the attending physician as soon as possible, who will tell you about all the dangers, stereotypes, methods of treatment, recovery and prevention. Quite often, shortness of breath in a child is the first sign of diseases associated with lung problems or heart disease. If you do not pay attention to the baby's shortness of breath, it can lead to suffocation.
Diagnosis of dyspnea
After a conversation, to establish the exact causes of frequent shortness of breath, the doctor will prescribe a number of additional diagnostic procedures, as well as laboratory and functional tests. For complaints of dyspnea, the following are recommended:
- Spirometry. Allows you to quickly assess all key parameters of the respiratory system.
- Assessment of carbon monoxide (CO) content in exhaled air;
- Bronchodilation test. It is carried out to diagnose bronchial asthma or COPD, which can cause asthma attacks.
- X-ray examination. Recommended for suspected lung tumors or emphysema.
- MRI, CT. Allows you to clarify the diagnosis made after radiography. The size and location of the affected areas of the lungs are accurately determined.
- Laryngoscopy. Necessary to check the upper respiratory tract for the presence of foreign objects that impede breathing.
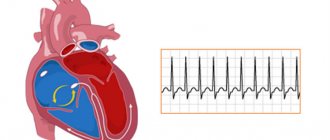
- ECG. Prescribed for suspected cardiac pathology. In case of significant rhythm disturbances and changes in the myocardium, ultrasound with Doppler is supplemented.
- Clinical blood test. Needed to determine the ESR, the number of leukocytes to identify the inflammatory process.
Treatment of shortness of breath depends on its cause , so the diagnostic stage is extremely important. Without instrumental and laboratory studies, it is impossible to establish the factors that provoke the symptom. Taking medications in this case will be unreasonable and ineffective.
Complications after difficulty breathing
People suffering from shortness of breath are limited in daily and social activities. This affects independence and reduces social significance. As it progresses, anxiety and worry arise. Sleep disturbance occurs and depression develops. Chronic heart failure is especially dangerous.
Metabolism and gas exchange disorders in the body can lead to dangerous complications:
- decrease in blood pressure;
- pulmonary edema;
- persistent breathing problems;
- attacks of suffocation against the background of cardiac cardiac asthma.
As the disease progresses, the following disorders are observed:
- blueness of the limbs and lips (cyanosis);
- suffocating cough at night;
- gurgling sensation in the heart area;
- the appearance of profuse cold sweat;
- development of pulmonary emphysema;
- discharge of sputum with traces of blood;
- decreased elasticity of lung tissue and blood vessels.
Pulmonary edema and heart failure are very serious and dangerous pathologies for human health. If shortness of breath occurs at rest, you should immediately seek medical help.
Shortness of breath and lack of air in an adult: emergency assistance
Choking, sudden deterioration in health, dizziness combined with lack of air is a reason for an emergency visit to a doctor, but assistance must be provided before doctors arrive. If the suspected cause of shortness of breath during or without physical activity is oxygen deficiency, you need to ensure rest - find support or put the patient to bed. You will also need:
- remove tight clothes, free your neck and chest;
- ventilate the room;
- reassure the patient.
Evaluation of patients with shortness of breath
At the first stage of examining an elderly patient with suspected chronic shortness of breath, doctors at the Yusupov Hospital determine which organ system is primarily affected: cardiac, pulmonary, both or neither. If the patient continues to suffer from shortness of breath despite intensive therapy, exclude the presence of a concomitant factor - an emotional reaction to the disease or a deterioration in general physical condition. Elderly patients with chronic cardiopulmonary disease may gradually limit physical activity because shortness of breath is associated with exertion, which leads to subsequent imbalance of the cardiovascular system and further worsens shortness of breath with walking or exercise. An analysis of anamnestic data, the results of a physical examination and plain radiography helps to establish an accurate diagnosis.
For chronic shortness of breath, which worsens in older people when walking, doctors perform first-level tests:
- Detailed general blood test;
- Metabolic indicators;
- Plain radiography of the chest organs;
- Electrocardiography;
- Spirometry;
- Pulse oximetry.
Second-level tests include echocardiography, determination of the level of brain natriuretic peptide, pulmonary function testing, Holter monitoring, and radioisotope research methods. If the diagnosis has not been established, after consultation with specialists, at a meeting of the Expert Council, a decision is made on the safety of performing third-level tests on elderly patients: examination of the cardiovascular system during exercise, bronchoscopy, and lung biopsy.
Drug treatment of dyspnea
If the symptom is caused by pathological processes, then treatment is prescribed depending on the cause of shortness of breath and lack of air . A doctor may prescribe one or more drugs from different pharmacological groups. According to the recommendations, for dyspnea the following are used:
- bronchodilators for quick relief of an attack;
- expectorants to clear the airways of mucus;
- antiviral or antibiotics to suppress the infectious process, depending on its nature;
- cardiotonics to reduce the load on the myocardium;
- corticosteroids to relieve swelling;
- cytostatics in the presence of malignant tumors.
If dyspnea is caused by physiological reasons - pregnancy, overwork, then there is no need to take medications. In this case, rest and adherence to preventive measures are important - reducing stress, regular walks, ventilating the premises.
Development mechanism
Shortness of breath is caused by a variety of complex reflex mechanisms involving higher nervous structures, so there are several theories of its development. Many doctors cite changes in oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood as the immediate cause of impaired breathing frequency and quality. An increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide, leading to a decrease in pH, has a significant stimulating effect on the bulbar centers, peripheral chemoreceptor zones of the arteries and central receptors located in the medulla oblongata.
At the same time, protective mechanisms are activated, the respiratory center of the brain stem sends activating impulses to the bronchopulmonary system, causing a pathological increase in breathing. The appearance of shortness of breath is associated with impulses from the fusiform nerve endings of the respiratory tract, which are activated as a result of various pathological processes. Sometimes increased work of the respiratory center is observed during descending cortical influences caused by hysterical or neurotic conditions.
The connection of the symptom with the temperature of the internal environment of the body has been proven. With hyperthermia, the sensitive areas of the respiratory center are washed with warmer blood, which causes their activation - so-called thermal shortness of breath occurs. A decrease in body temperature, on the contrary, leads to a decrease in respiratory movements. The development of dyspnea is influenced by the amount of muscle load and metabolic level. Most researchers believe that this mechanism is due to two types of reactions - slow humoral and fast neurogenic.
Subjective sensations in the form of lack of air and suffocation are primarily associated with the spread of excessive excitation from the centers of the medulla oblongata to the limbic structures and the cerebral cortex. This causes the appearance of negative emotional reactions of fear and anxiety in patients with shortness of breath. Sometimes unpleasant symptoms develop due to a discrepancy between the body's needs for ventilation and the functionality of the breathing apparatus to provide it.
Treatment and diagnosis of dyspnea in Kaliningrad
If you are concerned about shortness of breath and are looking for a qualified pulmonologist in Kaliningrad, make an appointment at our pulmonology center. For you:
- only competent, caring specialists;
- a full range of procedures for diagnosing lung diseases;
- comprehensive care for pathologies of the respiratory system: treatment of COPD, treatment of asthma;
- rehabilitation after coronavirus infection;
- comfortable living conditions.
You can make an appointment at our pulmonology center by calling 8 (4012) 971-961.
1.General information
Shortness of breath (dyspnea) is a deviation of the frequency, depth and/or rhythm of breathing from similar indicators of a healthy person of the same sex and age under the same conditions. Despite some cumbersomeness of this definition, it seems quite complete and accurate. The term “shortness of breath” seems intuitive, which often leads to misunderstandings between the doctor and the patient, who put different meanings into this word.
There are several classifications of shortness of breath:
- inspiratory (on inspiration), expiratory (on exhalation) and mixed (difficulties in both phases of the respiratory act);
- tachypnea (rapid shallow breathing) and bradypnea (slow breathing);
- physiological shortness of breath (transient, reversible intensification of breathing as an adequate adaptive response of the body to stress, injury or objectively low oxygen content in the inhaled air, which requires additional oxygenation) and pathological shortness of breath (caused by airway obstructions, bad habits, cardiovascular failure, obesity, diseases lungs, hematopoietic system, etc.).
This material is devoted to a type of dyspnea called dyspnea at rest (sometimes also called dyspnea at rest). In contrast to the antonymous “shortness of breath on exertion,” which is sometimes difficult to distinguish from the normal physiological response of the respiratory system, resting dyspnea is a much more unfavorable clinical and prognostic sign.
Sign up for a consultation
A must read! Help with hospitalization and treatment!