- Diagnosis
- Causes
- What to do
Dizziness (vertigo) is a condition in which a person feels as if his body or objects around him are moving, although in fact they are motionless. This is a common reason for visiting a doctor. Unpleasant sensations cause discomfort to a person and serve as a symptom of pathology occurring in the body, especially if they appear constantly and have a long-lasting effect. Therefore, it is very important to find out the causes of frequent dizziness.
Mechanism of development of vertigo
If we consider dizziness from an anatomical point of view, the causes of this condition are quite simple. The vestibular apparatus, responsible for human balance and coordination in space, is located in the inner ear. Vision and muscle reflexes help a person navigate the environment. All received information enters the brain. And it is he who controls the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
Sometimes the connection between the inner ear and the brain can become disrupted. A person loses the ability to navigate in space. Dizziness appears. To restore the lost connection, the brain immediately launches several reactions at once. Some of them may affect neighboring centers (for example, emetic). This leads to the appearance of unpleasant accompanying symptoms.
Sudden dizziness: 5 simple reasons
Typically, loss of communication between the brain and the vestibular system is rare and does not last long.
Dizziness that occurs is not considered a pathology in the following cases:
- Ride the carousel. Such entertainment creates a serious load on the vestibular apparatus. And if it is naturally weak and untrained, then it may well fail. Such dizziness usually occurs in women, since they also have psycho-emotional experiences added to the load.
- Stress, anxiety. If dizziness occurs during a speech in front of a large audience or after a reprimand from a boss, then the cause of vertigo is the production of a large amount of adrenaline. This hormone causes vasospasm. And this leads to a temporary deterioration in blood flow in the brain.
- Climbing to heights. In this case, the unpleasant phenomenon is also considered a physiological norm. When rising to a height, a person’s eyes cannot quickly focus on distant and close objects. Abrupt switching between objects causes dizziness.
- Hunger. Similar problems are common to all fans of strict diets. If a person does not receive enough nutrition, then a glucose deficiency occurs in his body. The absence of the main “fuel” leads to deterioration of brain function and the appearance of dizziness.
- Active exercises. Exercise enthusiasts should remember moderation. Excessive exercise can cause low blood pressure. This leads to dizziness and sometimes fainting. The unpleasant condition may be caused by unsuccessful sudden movements of the head, as a result of which the blood supply to the brain is disrupted.
An attack of dizziness may occur in response to taking certain medications. The most common sources of unpleasant symptoms are NSAIDs, antidepressants, antibiotics, and cancer medications. If your head is “turned” by medications, be sure to consult a doctor to change the drug.
Treatment and first aid
If dizziness occurs, place the patient on his back so that his head, neck and shoulders lie on a pillow, because in this position, kinking of the vertebral arteries is eliminated. You should avoid turning your head to the side, you need to open the windows, ventilate the room, put a cold bandage on your forehead, you can slightly moisten it with vinegar. Having measured the pressure and temperature, take measures to normalize them; if the heart rate is more than 100 beats per minute or an irregular heartbeat appears, and if dizziness is accompanied by nausea and repeated (more than 3 times) vomiting, you must call an ambulance. The prognosis depends on the nature of the dizziness.
Severe dizziness: 6 pathological causes
The causes of dizziness are not always harmless. Sometimes illnesses become sources of unpleasant conditions. In this case, dizziness occurs quite often and can last longer than a few seconds. To cope with this phenomenon, you need to consult a doctor. The severity of a symptom can be reduced (and sometimes completely eliminated) only through proper treatment of the underlying disease.
So, the causes of dizziness may include the following pathologies:
- Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD). A complex disorder in which a person experiences multiple impairments. All these symptoms are associated with malfunctions of the autonomic system. One of the common signs of VSD is dizziness. Such attacks are usually caused by sudden movements and rapid changes in posture. Dizziness does not last long. They go away on their own, without any intervention.
- Disorders in the cervical spine. Various injuries, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias can periodically remind you of themselves with sudden attacks of dizziness. They usually appear after active neck movements. The attack is accompanied by pain in the affected area, sometimes a crunching or crackling sound is heard.
- Anemia. Dizziness may occur due to iron deficiency. Most often this pathology is observed in children and women. With anemia, attacks are accompanied by high fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and pre-fainting conditions.
- Psychogenic dizziness. The reason for this pathology lies in the patient’s increased anxiety (people with an unstable psyche) or in the stress they have endured. Such people usually complain of poor sleep, fear of losing consciousness, a periodic feeling of shortness of breath, and increased heart rate.
- Vertebrobasilar insufficiency. This is a pathology in which blood flow in the vertebral or basilar arteries is weakened. Such problems lead to disruption of brain function. The pathology is characterized by regular attacks of dizziness, which can last up to an hour. In addition, patients complain of nausea, vomiting, and visual disturbances may occur. I often have a headache.
- Hypotension. A decrease in blood pressure is often accompanied by attacks of dizziness. Sometimes lightheadedness may occur.
Severe dizziness: 6 dangerous reasons
In some cases, vertigo signals the development of severe conditions that require immediate medical attention. Causes of severe dizziness may include:
- Labyrinthitis (internal otitis). A viral infection in the inner ear may be asymptomatic at first. The only sign of otitis media is dizziness, which lasts for several minutes. Such attacks are repeated quite often. In the future, the viral process can affect the nervous system or brain.
- Concussion. Sometimes after a head injury, only dizziness appears. This symptom should not be ignored. It serves as direct evidence of a concussion. To eliminate the risk of swelling or serious brain damage, you should immediately seek medical help.
- Stroke. If dizziness is accompanied by sudden weakness, complaints of numbness of a body part, visual impairment, speech disturbances, then the risk of stroke is high. This is a severe pathology in which blood circulation in the brain is disrupted.
- Migraine. Dizziness accompanied by a severe headache may indicate a migraine. Many people believe that this condition is harmless. But doctors say that migraine, especially in an advanced state, can lead to severe damage (sometimes even to a heart attack or stroke).
- Cardiovascular diseases. Such pathologies are characterized by the appearance of dizziness every time a person gets up. It is caused by a sharp decrease in pressure. Symptoms like these may indicate dehydration, which is causing your blood to thicken. But if the problem is not fluid deficiency, then it may be the development of arrhythmia or heart failure.
- Tumors. Regular attacks of vertigo combined with headaches, usually in one side of the head, can signal the development of a tumor in the brain.
Symptoms of dizziness
Dizziness (the medical term is “vertigo”) is disorientation in space. It seems to a person that he is rotating and moving, although in fact he is motionless. It also happens the other way around - you get the feeling that everything around you is spinning and moving - objects, trees, the ground under your feet.
The sensations can be different - from rotational movements to the impression of instability, when everything around (or you yourself) trembles, staggers, moves. The body or parts of it may appear to be moving. Describing their condition, many say that they feel like they are in a strong sea motion or riding on a swing.
Additional symptoms when feeling dizzy:
- My head is spinning.
- An illusion of mobility of your body or surrounding objects is created.
- Nausea, weakness, and even fainting appear.
- Cold sweat appears.
- Heart rate increases.
- Fear and panic appear.
- Legs or arms go numb.
- Hearing deteriorates or ringing in the ears bothers you.
You may feel suddenly dizzy for a few seconds or longer - up to half an hour, an hour or a constant feeling. The frequency of attacks also varies - some experience them regularly under certain conditions, while others experience them only a couple of times in their lives. Some patients notice frequent patterns when dizziness appears. These could be trips in transport, experiences.
What to do?
It is almost impossible to independently determine the causes of frequent attacks of dizziness. Therefore, those who regularly experience vertigo are advised to go to an appointment with a therapist, or a neurologist. The specialist will carefully examine the patient’s complaints and prescribe diagnostic tests. If necessary, the doctor will refer the patient for consultations with an ENT specialist, an ophthalmologist, a cardiologist, or an endocrinologist.
To identify the causes of vertigo, the patient may be prescribed the following tests:
- Neurological tests. They allow you to assess the functionality of the vestibular apparatus.
- MRI or CT. Such brain studies reveal various disorders (hemorrhages, tumors, vascular pathologies).
- Ultrasound Doppler. Using Doppler ultrasound, the condition of the vessels of the head and neck is studied.
- Audiometry. Diagnostics allows us to assess hearing function.
- EEG. To study the activity of the cerebral cortex, the doctor will prescribe electroencephalography.
To quickly cope with dizziness (of course, if it is not caused by dangerous reasons), you can sit on any surface, relax a little and take 5-6 deep breaths. Be sure to open the window (if you are indoors) to provide fresh air. If the causes of vertigo are harmless, then such actions are quite enough for the dizziness to disappear without a trace.
Diagnostic methods
To understand why the patient feels sick, sick, and dizzy, a full examination should be performed. Various techniques are aimed at identifying hidden pathologies that require specific treatment. During the initial examination, the doctor collects medical history data. It is important to describe in as much detail as possible under what conditions the headache begins, how often attacks occur and how long they last. To confirm the diagnosis, the following techniques may be needed:
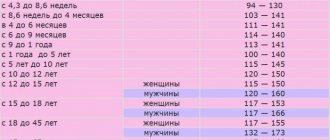
- first of all, measuring blood pressure; the patient is also recommended to monitor it at home;
- tests to check balance, including the Romberg test (deterioration in coordination of movements is manifested by staggering in a standing position, with eyes closed, feet shifted and straight arms extended forward);
- a general blood test will indicate inflammatory processes, as well as various types of anemia;
- blood test for glucose levels;
- heart examination, which includes ultrasound diagnostics and electrocardiogram;
- tests to assess hearing and visual acuity;
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- study of blood flow in the vessels of the neck and head - a contrast agent is used for this;
- electroencephalography - analysis of the bioelectrical activity of brain cells;
- computer or magnetic resonance imaging is the most accurate, informative way to examine the brain, including soft tissues and blood vessels, which allows you to obtain a complete image of the affected area.
At the Clinical Institute of the Brain, you can undergo a complete diagnosis and determine the causes of nausea, dizziness, and headaches. The regimen is selected individually, based on the results of the initial examination of the patient. An experienced doctor will prescribe only those studies and tests that will determine the nature of the pathology. This is the most important stage in solving the problem, since the diagnostic results allow you to select the most effective treatment regimen.