Focal changes in the brain substance of a dyscirculatory nature are dangerous diseases that worsen the health status and change the lifestyle of patients. Sometimes people have problems with their physiology due to dead neurons.
Features of the development of the disease
Before considering therapeutic techniques suitable for eliminating this disease, it is necessary to determine the causes of its occurrence. Otherwise, recovery will be difficult. Focal changes in the brain substance of a discirculatory nature are a disorder that causes damage to the brain in different places.
The disease can be classified as chronic because it develops slowly with complex consequences. The disease is considered chronic because it develops slowly with complex consequences.
Causes and signs of pathology
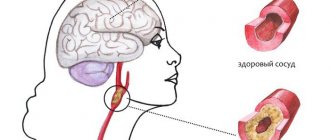
Nervous tissue is provided with intensive blood supply; a feature of perfusion in the brain is the bridges between the vessels. In case of emergency oxygen starvation, blood circulation is restored by another vessel.
Neurons are vulnerable even to a short-term lack of nutrition; cell death leads to irreversible processes in the brain - motor abilities and intelligence are impaired.
With age, blood vessels become less elastic and fragile. A common cause of damage to the cerebral cortex is concomitant diseases of the vascular system.
Reasons leading to defeat:
- Arterial hypertension;
- Vascular atherosclerosis;
- Hyperhomocysteinemia (high levels of homocysteine in the blood);
- Metabolic disorders;
- Inflammatory diseases of the meninges (leptomeningitis, pachymeningitis, arachnoiditis);
- Amloid angiopathy (amloid is deposited in the arteries);
- Multiple sclerosis;
- Damage to the cerebral cortex (trauma);
- HIV infection;
- Circulatory disorders (stroke, heart attack, dystrophic changes);
- Dyscirculatory changes (impaired blood circulation in the vessels of the skull, as well as in the spinal cord);
- Consequences of ischemia.
Brain tissue receives nutrition from the carotid and vertebrobasilar basins, interconnected in the velisian circle. In case of abnormalities or anatomically undeveloped vessels, there is no way to compensate for hypoxia by restoring blood flow through an anastomosis (connection with another vessel), which leads to focal damage to the brain of a vascular nature.
Symptoms of lesions of brain cells in the initial stage do not have a clear clinical picture, which leads to further destruction of axon bundles (white matter).
Clinical signs:
- Muscle spasms;
- Increased blood pressure;
- Dizziness;
- Mental disorders;
- Epileptic seizures;
- Migraine;
- Speech impairment;
- Decreased memory;
- Paralysis.
Stages of development
In comparison with other types of pathologies, focal transformations of the discircular type spread in several stages. Each has its own distinctive features. Therefore, specialists must first understand at what stage this disorder is in order to determine the optimal therapeutic technique.
In the initial stages, it is difficult to determine the presence of the disease, since the process of circulatory disorders in the head is poorly developed. In such a situation, the specific signs of the disorder are still not expressed, so diagnosis will be difficult . Patients also do not describe specific complaints.
The second stage is characterized by deterioration of the tissue in the brain, which gradually dies. Such processes are caused by problems with cerebral circulation. At the last stage, half of the brain matter dies, the functioning of the organ is disrupted, and recovery cannot be expected. In each patient, symptoms manifest themselves depending on the individual characteristics of the body.
Discirculatory encephalopathy - what is it?
Dyscirculatory encephalopathy (DEP) is a common disease that affects many patients with arterial hypertension. Due to impaired blood supply to the brain, changes begin to occur in the tissues, which ultimately lead to disruption of brain functions.
Unfortunately, the manifestations of DEP in the early stages (headache, tinnitus, nausea) are such that patients may not consult a doctor about them, considering them to be the result of fatigue or stress. As DEP develops, decreased visual and hearing acuity, impaired coordination, and autonomic disorders may appear. With severe brain damage and significant microcirculation disorders, patients may experience mental disorders. In the Department of Neurology of the Yauza Clinical Hospital, doctors conduct a comprehensive diagnosis of DEP and prescribe comprehensive treatment that takes into account the causes of the development of the disease in a particular patient.
Causes of the disease
There are many reasons why single focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature are observed. The disease develops due to impaired blood supply. Often such processes are observed because the cervical spine is injured, or the likelihood of developing osteochondrosis increases.
The disorder can manifest itself against the background of heart disease or after a head injury. Patients who are overweight or lead an unhealthy lifestyle are often susceptible to the disease. Periodically, the disorder occurs in diabetics, cancer patients, and in patients who are regularly in stressful situations.
Focal transformations often occur in old people, but in recent years young people have been visiting neurologists much more often.
Causes of vascular problems
The genesis of vascular damage is inseparable from the mechanism of development of the underlying disease and provoking factors. The “impetus” for the onset of damage to the arteries of the brain can be:
- arterial hypertension and hypotension;
- diabetes mellitus with metabolic disorders;
- smoking and alcoholism, drugs;
- stressful situations;
- lipid and lipoprotein metabolism disorders, obesity;
- dystonia of the autonomic nervous system;
- tendency to weather dependence;
- traumatic brain injury;
- motor passivity.
Focal circulatory disorders are found in the brain when:
- systemic vasculitis;
- blood diseases;
- congenital and acquired heart diseases;
- aneurysmal vasodilation;
- cervical osteochondrosis.
Blood from a ruptured aneurysm squeezes the brain matter
Symptoms
Dyscirculatory changes can manifest themselves in the form of the following symptoms: high blood pressure, epileptic seizures, problems with mental activity, dizziness, stagnation of the vascular bed in the head, constant migraines, sudden contractions of muscle tissue, and possible paralysis.
Preventive measures
To prevent dyscirculatory encephalopathy, a healthy lifestyle and a balanced diet mean a lot. Increased physical activity also provides good preventive results. It is necessary to control the level of blood pressure, the content of cholesterol and its fractions in the blood.
Diseases of the cerebral vessels are considered the most common pathology in the practice of a neurologist. Dyscirculatory encephalopathy is one of the leading causes of cognitive impairment, dementia, and disability in old age. A comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition, the impact on the underlying cause of the disease and symptoms helps to improve the quality of life and prevent serious complications.
Examination methods
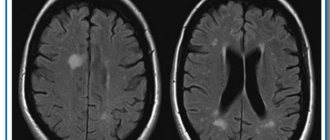
The main method for diagnosing the disease is MRI of the head, which reveals hyperintense inflammation, small heart attacks, post-ischemic degeneration, and enlargement of the ventricular system. The number of heart attacks can range from one to many. Fine-focal transformations indicate serious brain damage, which can result in disability. Blood circulation suffers in problem areas.
Ultrasound or duplex scanning is used as diagnostic techniques, which can determine blood flow disturbances, such as asymmetric distribution of fluid throughout the vessels. CT makes it possible to recognize traces of heart attacks in the images in the form of lacunae filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Often the cerebral cortex atrophies, the ventricles increase in size, and dropsy appears .
MRI can detect the following disorders. Transformations of the cerebral hemispheres. Such lesions appear due to blockage or compression of an artery located in the spine. This is often due to congenital pathologies or atherosclerosis. In rare situations, a vertebral hernia appears.
Focal changes. Their presence often indicates a pre-stroke condition of the patient. Sometimes they are used to determine dementia, epilepsy, and other disorders caused by atrophy of arteries and veins. If such changes are detected, immediate treatment is required.
Microfocal transformations appear in all people after 50 years . It will be possible to examine them using contrast media only in a situation where they arise in the form of a disease. Fine-focal transformations are not clearly detected and eventually lead to a stroke.
Transformations of white matter in different areas of the brain are subcortical and periventricular in nature. This type of damage is provoked by continuously high blood pressure, especially with regard to hypertensive crisis. Often, single lesions are congenital in nature; the danger arises due to the proliferation of damage in the brain. In such a situation, symptoms develop regularly.
When there is a high probability of the disease in a patient, examinations should be carried out every year. For preventive purposes, CT or MRI is performed once every 2-3 years.
Diagnostics
Since dyscirculatory focal changes for a long time are similar to chronic fatigue syndrome, the disease requires accurate diagnosis. The diagnosis is established after a thorough examination, as well as six-month observation by a neurologist. The basis for a medical opinion about the nature of the pathology is the constant presence of the main symptoms.
When contacting the doctor, he prescribes a comprehensive examination, which consists of the following methods:
- Laboratory research. They check the composition of the blood, determining the presence of negative factors. This requires general and biochemical blood tests and a coagulogram. Cholesterol and sugar levels are also determined.
- Continuous blood pressure monitoring.
- ECG and EchoCG.
- Echogram and electroencephalography of the brain.
- MRI.
- Fundus examination.
Advantages of MRI diagnostics
As a result of pathological dyscirculatory changes in the structural tissues of the brain, characteristic morphological signs appear. They are diagnosed using magnetic resonance examination methods: nuclear MRI, magnetic resonance imaging and angiography.
An MRI examination allows you to identify foci of dyscirculatory encephalopathy, localize their exact location and determine the cause of pathological changes in the brain.
- Diffuse transformations of the cerebral cortex. The provoking factor is congenital or acquired pathology of the cerebral or spinal arteries (intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine, arterial thrombosis or narrowing of the lumen).
- Multiple focal tissue damage. This pathology precedes the development of stroke. This condition is characteristic of senile or pathogenetic vascular atrophy accompanying dementia, epilepsy, and ataxia.
- Age-related microfocal changes. Their appearance is typical for brain tissue after 55 years, since with age structural tissues are increasingly susceptible to endogenous changes. MRI diagnoses only those microdamages that arise as a result of negative external influences.
- Discirculatory foci in the white structural matter of the parietal or frontal lobes. The cause of such changes is hypertension from the acute stage, or this tissue structure is due to its formation during the period of prenatal development (congenital).
The presence of focal changes in the brain is the basis for periodic preventive examinations at least once every three months.
Modern methods of therapy
Therapeutic measures are necessary to eliminate the main symptoms of the disease that provokes brain disorder. You will have to use medications that inhibit the development of pathology.
Vascular medications such as pentoxifylline, vinpocetine, cinnarizine, and dihydroergocriptine are required . They have a beneficial effect on the blood supply to brain tissue, stabilize the functioning of capillaries, increase the plasticity of red blood cells, and make the blood liquid. The drugs help eliminate vascular spasm and increase the resistance of arteries and veins to hypoxia.
Cytoflavin and piracetam are used as antioxidant and antihypoxic drugs. Treatment with vestibulotropic drugs stops dizziness, eliminates unsteadiness during movement, and improves the quality of life of patients. At high blood pressure levels, constant monitoring of pressure numbers and contraction frequency is required, stabilizing them according to indications.
Today, doctors pay a lot of attention to substances that block calcium channels, stabilize blood pressure, and act as neuroprotectors. Cerebrolysin helps restore cognitive functions.
Treatment of DEP in the clinical hospital on Yauza
Comprehensive diagnostics allows specialists to prescribe adequate drug treatment. It should be aimed primarily at normalizing blood supply to the brain and blood pressure, correcting symptoms and preventing further damage to blood vessels and brain tissue. It is also important to use drugs that normalize the metabolism of brain cells and increase vascular tone.
In addition, neurologists at the Yauza Clinical Hospital offer each patient an individual complex of non-drug therapy, which includes reducing alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and regular dynamic physical activity. It is also important to follow nutritional recommendations: limiting the consumption of table salt, saturated fats, sufficient consumption of potassium, magnesium and calcium salts, eating foods that improve the functioning of the circulatory system.
You can see prices for services in the price list or check by calling the phone number listed on the website.
Impact on key risk factors
Due to the high importance of recurrent strokes for the progression of motor and cognitive disorders in patients with DEP, a higher priority is the prevention of vascular complications. Correction of existing symptoms is secondary. In such patients, “aggressive” prophylaxis is necessary.
Antihypertensive therapy
Maintaining normal blood pressure levels can help prevent or slow the progression of DEP. Most often, in the presence of chronic cerebral circulatory failure, doctors recommend the use of drugs belonging to the groups of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers. These medications are believed to have protective properties against the brain, blood vessels, heart and kidneys.
If these drugs are not enough to control blood pressure, they are combined with other drugs - diuretics, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers. Only a doctor can prescribe medications suitable for patients with DEP.
Correction of carbohydrate metabolism
There are no doubts about the cause-and-effect relationship between dysfunction of carbohydrate metabolism and the development of circulatory disorders in the brain. To correct the pathological process, an appropriate diet and medications that lower blood sugar levels are prescribed.
Lipid-lowering therapy - statins
Since the other main cause of DEP is cerebral atherosclerosis, patients with this disease are often prescribed drugs that lower blood cholesterol levels. The most commonly used drugs are statins, which in addition to lowering cholesterol levels also improve the condition of the inner layer of blood vessels (endothelium), reduce blood viscosity, stop or slow down the progression of atherosclerosis and have an antioxidant effect.
Antithrombotic therapy
One of the mandatory components of the treatment plan for patients with DEP. Antiplatelet agents affect platelets, preventing them from sticking together (aggregation), which improves cerebral circulation. Low-dose aspirin is most often prescribed.
Reduced homocysteine levels
Elevated levels of homocysteine (a sulfur-containing amino acid) are a risk factor for the development of vascular disease and dementia. To correct indicators, folic acid and B vitamins (B12, B2 and B6) are prescribed.
Healthy lifestyle and exercises for memory development
Bad habits, lack of physical activity and poor nutrition have an impact on the deterioration of cognitive functions over the years. This confirms the benefits of a healthy lifestyle in preventing the development of mixed and vascular dementia.
Thanks to the conducted research, it was possible to confirm the relevance of the concept of “cognitive reserve”. According to this concept, a healthy lifestyle significantly reduces the likelihood of developing dementia. Receiving higher education does not have any effect on the prognosis of the disease.
Dementia drugs
To reduce the severity of clinical symptoms in dementia, drugs are prescribed whose action is aimed at improving the transmission of signals between neurons through synapses. Active substances prevent neuron death: glutamate NMDA receptor antagonists and acetylcholinesterase inhibitors.
Antidementia drugs reduce the severity of behavioral (aggression, agitation) and cognitive (problems of attention, speech and memory) disorders. Medicines do not improve the general condition of the patient, but significantly slow down the rate of deterioration of symptoms.
Nootropic and vasoactive drugs
The use of vascular drugs to combat vascular lesions is unjustified. The effectiveness of the use of Ginkgo Biloba, ergot alkaloids and methylxanthines is controversial.
Physiotherapy
Complex therapy, which combines drug and non-drug methods of combating the disease, is more effective. Among the effective physiotherapeutic methods for treating DEP, the following should be highlighted:
- Exercise therapy (a set of exercises is prescribed individually by a doctor);
- transcranial magnetic stimulation;
- acupuncture;
- massage of the collar area;
- vortex fields;
- electromyostimulation.
Surgery
The need for surgery arises if the pathological process develops against the background of rapid progression of narrowing of the lumen. Surgery is also necessary if serious complications develop.
The following types of operations are widespread:
- Stenting. It involves inserting a special dilator into the vessel to improve blood flow in the part of the artery that has been narrowed.
- Carotid endarterectomy. It is carried out for atherosclerosis in order to cleanse the internal walls of the carotid artery.
Surgical intervention does not completely eliminate the disease, but it makes it possible to improve the patient’s condition and slow down the progression of the disease.
Spa treatment
With progressive organic changes in brain tissue that occur as a result of chronic vascular insufficiency, sanatorium treatment is recommended. This approach to therapy is possible only in the absence of pronounced changes in the psyche and deterioration of cerebral circulation. Such patients are sent to balneotherapeutic and climatic resorts with hydrogen sulfide and radon waters.
Treatment of cognitive pathologies
Donepezil is used to improve memory, concentration, and performance. The medicine stimulates the production of neurotransmitters, improves the quality of the passage of impulses as intended. The activity of patients during the daytime improves, apathy disappears, hallucinations and meaningless mechanical repetitions of the same actions are eliminated.
Rivastigmine should not be used by people with ulcers, problems with the intestines, cardiovascular system, or respiratory disorders.
For typical emotional disorders, doctors advise using antidepressants. Selective inhibitors perform remarkably well during treatment. These products are available only with a doctor's prescription.
At-risk groups
If there are no signs of the disease, it is preferable to find out about risk groups. According to statistics, focal disease more often manifests itself in the following disorders: atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, VSD, diabetes, heart muscle disease, regular stressful situations, work without movement, abuse of alcohol, tobacco, drugs, obesity.
As a result of age-related changes, brain damage occurs. After reaching 60 years of age, minor lesions of the disorder appear.
Dystrophic damage
In addition to damage caused by vascular origin, other types of the disease are distinguished. These are focal changes in the brain substance of a dystrophic nature. This type of disease occurs due to a lack of nutrients. Let's consider the main causes of the disease: too low blood pressure, osteochondrosis, oncology, skull injuries.
Dystrophic brain damage is detected due to the lack of useful substances. Patients exhibit the following symptoms: brain activity deteriorates, dementia, migraines appear, muscle tissue is weakened, some muscle groups are paralyzed, and dizziness.
Classification of the disease
In modern medicine, it is customary to distinguish the following types of insufficient blood supply to the brain:
- Binswanger's disease. This type of vascular circulation disorder leads to insufficient blood supply to the white matter of the brain. With this disease, the destruction of neurons occurs, which will soon lead to senile dementia - dementia. The first alarming symptom is severe pressure drops within one day. Then memory begins to deteriorate greatly.
- Pathological processes in the great vessels. Such disorders include narrowing of the lumens, strong bends, and thrombosis of blood vessels, which lead to a lack of circulating blood.
- Consequences of micro-strokes. When small vessels are blocked, there is a clear deterioration in the nutrition of the gray or white matter of the brain. This process cannot happen for a person without consequences. The patient may experience both general signs of the disease and disruptions only in certain body functions.
Doctors' recommendations
Quit tobacco products or get rid of addiction. Do not drink alcohol or drugs. Move more, do exercises. The permissible intensity of physical activity is determined only by a doctor. Sleep 7-8 hours a day. Doctors advise increasing sleep duration when diagnosing such disorders.
You need to eat a balanced diet; it is preferable to develop a diet together with your doctor in order to take into account all the nutritional components that help with destructive processes in the brain. Neurons need to be nourished with useful substances.
Review other bad habits. It is better to get rid of regular stressful situations. It is better to change your job if it is a little stressful. Relax more often, choose the most suitable ways for this. Visit the doctor for examinations at the specified frequency in order to timely record changes in pathological processes and timely apply therapeutic techniques.
Nervous tissues are characterized by increased vulnerability. Neurons die when there is a lack of oxygen, so you need to treat your body with special attention.
Vascular changes in the brain on MRI
MRI: ischemic zone during stroke (highlighted with a red oval)
If cerebrovascular pathology is suspected, special attention is paid to the condition of the arteries during MRI of the brain. The study always involves the introduction of contrast, and it is called magnetic resonance angiography. In urgent situations in case of vascular accidents, CT is performed, since X-ray diagnostics takes less time and clearly demonstrates the area of damage during hemorrhages, but after stabilization of health, magnetic resonance angiography is quite justified. The study shows atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots and aneurysms (protrusions), their localization, and wall deformation.
With an ischemic stroke, darkened and blurred areas of irregular shape are visible almost immediately on magnetic tomograms, appearing on a computer scan only at the end of the first day. The lesion is often unilateral. The outpouring of blood from a ruptured vessel gives an intense light color, but only in the first hour and a half from the moment of the disaster, and then becomes invisible on MRI, although it is clearly visualized using CT. As a consequence of a stroke, a fluid-filled pseudocyst is formed, and deformation of the nerve tissue appears. MRA is indispensable in the diagnosis of tumor angiogenesis. Increased vascularization of a pathological focus is always suspicious of a malignant neoplasm, which grows and feeds due to increased blood flow. If the vessels do not keep up with the growth of the tumor, areas of ischemia and necrosis appear.