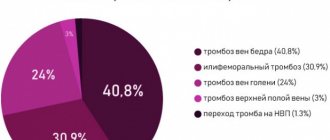
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
Phlebectomy is recommended in the following cases:
- pronounced varicose veins with a significant increase in the lumen of the veins;
- insufficiency of the valves of the affected vessel;
- the presence or risk of developing trophic ulcers;
- a large number of lateral tributaries near the main vein;
- transformation of the GSV (great saphenous vein);
- increasing clinical symptoms (swelling, feeling of heaviness in the legs, the appearance of a large number of spider veins, etc.).
Removal of varicose veins is not performed during pregnancy and lactation, in the presence of serious cardiovascular pathologies, acute vein thrombosis, exacerbation of chronic diseases, or infectious diseases.
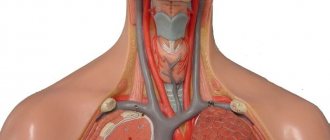
Modern technique of surgical crossectomy
Modern crossectomy includes the following stages:
Crossectomy technique
- A skin incision in the groin above the projection of the vascular bundle.
- Visualization of the great saphenous vein and its confluence with the femoral vein.
- Elimination of all venous tributaries in the area of the oval fossa.
- Disconnection by ligation of the great saphenous vein at its junction with the femoral vein.
- Layer-by-layer suturing of the surgical wound.
This technique is quite standard, and similar surgery is still performed today in public surgical hospitals. Often, in addition to crossectomy, phlebectomy of the trunk vein and its tributaries is performed. It is worth noting that crossectomy today is very rarely performed in modern urban medical centers. In good phlebology clinics, innovative technologies are already used to treat varicose veins. And believe me, it is always better to entrust the treatment of varicose veins to a good professional who specializes in modern endovascular methods for treating varicose veins.
Sometimes crossectomy is combined with phlebectomy or with other methods of treating varicose veins. It is also advisable to carry out a crossectomy during the day, when all the necessary highly qualified personnel are present at the state medical center or clinic, since the operation can suddenly develop from a simple one into a complex one.
Combined phlebectomy
This is the most effective method, which is successfully used in advanced stages of varicose veins of the lower extremities. In fact, during one surgical procedure, the doctor performs several minor operations using general or epidural anesthesia.
The combined intervention takes place in 3 stages:
- Crossectomy is the cutting off of the great saphenous vein from the venous system by ligating all tributaries. The intervention is performed through an incision in the groin or popliteal region.
- Stripping is the complete or partial removal of the affected vessel with a thin probe through punctures. There are various techniques for performing this operation: Babcock stripping, cryostripping, PIN stripping, etc.
- Miniphlebectomy – removal of small pathologically altered areas of blood vessels through punctures.
The operation can last from 1 to 5 hours. Its duration depends on the patient’s condition, stage of the disease, and anatomical features of the vascular system.
Surgical treatment of thrombosis
Surgical treatment is used in cases of complicated thrombosis. Indications for the operation are:
- ascending thrombosis of the superficial veins with a tendency to spread the process to the deep venous system;
- floating thrombosis with a high probability of migration;
- limited thrombosis of superficial veins, not amenable to conservative therapy.
The main types of interventions for thrombosis are thrombectomy and various options for phlebectomies - from minimally invasive techniques (crossectomy, Varadi miniphlebectomy) to radical ones. The choice of the type of surgical treatment in all cases depends on the form of thrombosis and the level of damage, the degree of circulatory impairment, and the general condition of the patient.
Medical phlebologists who are proficient in conservative and surgical methods for treating vascular pathology, including minimally invasive ones, will promptly provide qualified assistance for various types of superficial and deep vein thrombosis.
Phlebectomy at the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences
Phlebectomy for varicose veins helps restore impaired blood circulation, relieve the patient of unpleasant symptoms, and eliminate cosmetic defects. If you are looking for where to have this operation done in Moscow, contact the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Our clinic has created all the conditions for the safe treatment of varicose veins at all stages of the disease. Qualified specialists with extensive practical experience use the latest techniques with proven effectiveness.
To make an appointment and clarify the cost of services, you can call or use a special form on the website.
Rehabilitation gymnastics
A doctor may prescribe exercise therapy, but gymnastics should be dosed and not cause overwork. Walking will help avoid stagnation of blood and hardening of the veins. This is the optimal physical activity for operated legs. Before walking, you should wear compression stockings or secure an elastic bandage.
If the recovery is going well and the patient plans to return to strength training, you need to remember that you should not lift weights at all for a week after surgery, and lifting weights of more than 7 kg is contraindicated for six months.
Types of operations
Removal of a blood clot for external hemorrhoids
Removing a blood clot for external hemorrhoids is a simple operation that lasts only a few minutes. The doctor makes a small incision over the blood clot. Then the blood clot is removed with tweezers or a clamp; the wound is not sutured. The inflammatory edema subsides almost immediately, the pain subsides, and the patient’s general condition improves.
According to indications, a more complex operation can be performed - excision of an external hemorrhoid with blood clots , which is also performed under local anesthesia and does not require the patient to be hospitalized. During excision, the pathological element is removed, which reduces the risk of recurrent thrombosis.
Removal of a blood clot for internal hemorrhoids
Thrombosis of internal hemorrhoids is much less common and, as a rule, develops in the later stages of the development of the process (III-IV stages of hemorrhoids).
Treatment in this case is conservative. After stopping the acute process, treatment is carried out aimed at removing internal hemorrhoids (hemorrhoidectomy).
Prevention of relapse
Basic principles of prevention
Thrombosis of the hemorrhoidal node occurs as a complication of hemorrhoids, therefore, prevention of relapse consists in preventing the occurrence of enlarged hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoids are a disease with a hereditary predisposition. Therefore, if there has already been one attack, there is a high probability of relapse. However, the implementation of a negative scenario is possible in the presence of additional risk factors: ___• pregnancy, ___• taking hormonal drugs, ___• overweight, ___• constant diet violations: eating spicy and fatty foods, alcohol, ___• abuse of thermal procedures (bath and sauna) or regular hypothermia, ___• work involving prolonged sitting or heavy physical work.
Necessary precautions
Most often, acute thrombosis occurs as a consequence of prolonged bowel dysfunction (chronic constipation). Therefore, you need to achieve daily bowel movements with a diet rich in fiber.
It is advisable to refrain from physical and nervous overload, as well as from hypothermia and overheating of the lower half of the body. You should not abuse alcohol, as well as spicy, smoked and salty foods.
When working “sedentarily”, you need to take regular breaks, during which you should perform hemorrhoid-preventing exercises. Many chronic diseases can contribute to the development of hemorrhoids, so taking care of your health is a reliable prevention of thrombosis of hemorrhoids.
Dangerous for the development of hemorrhoids and obesity. With this pathology, intra-abdominal pressure increases, the rheological properties of the blood change, problems with stool arise, and hormonal levels are disrupted. Therefore, normal weight is not only beauty, but also health.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Thrombectomy is a low-traumatic method of treating acute thrombosis of hemorrhoids, which has both advantages and disadvantages. The method involves surgical intervention, so it is prescribed if conservative methods are contraindicated or ineffective.
Positive aspects of thrombectomy: ___• a short list of contraindications, ___• does not require hospitalization, ___• the shortest recovery period with a minimum number of restrictions, ___• minor side effects of the operation (pain, weakness, swelling), ___• complications are extremely rare.
Disadvantages of the method. Thrombectomy does not involve removal of the hemorrhoid, so recurrent thrombosis may develop. For this reason, in case of recurrent thrombosis, a more radical operation to remove thrombosed nodes (hemorrhoidectomy) is indicated.
Is it possible to do without surgery?
If doctors recommended thrombectomy of the hemorrhoid, this means that conservative therapy is not indicated in your case. You should not try to treat thrombosis with “traditional” methods.
If treatment is inadequate or absent, complications may develop: ___• bleeding, ___• gangrene of the node, ___• paraproctitis (purulent melting of peri-rectal fatty tissue).
In some cases, the affected node may open on its own and free itself from the blood clot. At the site of the “bump,” a fold of skin is formed – an anal fringe, which causes unpleasant sensations (itching, weeping) and is an unpleasant cosmetic defect.
Treatment of patients suffering from thrombophlebitis
Phlebologists at the Yusupov Hospital provide complex therapy for patients with thrombophlebitis. Treatment includes conservative and surgical methods. With the help of conservative therapy, doctors achieve the following goals:
- Improving microcirculation and physical and chemical characteristics of blood;
- Inhibition of platelet adhesive ability;
- Correction of venous blood flow;
- Elimination of inflammation in the vein wall;
- Prevention of continued thrombus formation, fixation of the blood clot to the walls of the vessel;
- Impact on microcirculation and tissue metabolism.
In order to ensure functional rest of the limb and prevent thromboembolic complications, patients in the early period of the disease are prescribed bed rest with an elevated position of the lower limb. Anticoagulant therapy is carried out under strict laboratory monitoring of hemostasis system parameters. At the onset of the disease, phlebologists use direct anticoagulants (heparin or low molecular weight heparin - fraxiparin). 2 days before stopping heparin therapy, doctors prescribe indirect anticoagulants to patients with thrombophlebitis, and the daily dose of heparin is reduced by 1.5–2 times by reducing the single dose. To improve microcirculation, patients suffering from thrombophlebitis are given intravenous drips of pentoxifylline (trental).
Reviews from patients and recommendations from doctors
We analyzed online reviews of patients who underwent removal of hemorrhoidal thrombosis. The vast majority of patients were satisfied with the procedure. The most common impression: “The procedure itself is not as unpleasant as waiting for it.”
No reviews of complications of the operation were found. The most common complaint is pain in the area of the postoperative suture, which disappears after a few hours, but may reappear during bowel movements.
A more serious drawback is the likelihood of relapse. In order to avoid recurrent thrombosis, you must follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
Surgery for deep vein thrombosis of the leg
Deep vein thrombosis is an acute vascular pathology, which is characterized by the formation of a blood clot in the veins of the lower extremities, which are located below the deep fascia. A fresh thrombus in a deep vein of the leg can break away from the vessel wall or fragment and cause pulmonary embolism. If thrombolysis therapy is ineffective, phlebologists install a temporary filter in the inferior vena cava to prevent complications.
In most patients, a thrombus is formed and blood flow through the vein is partially restored. Sometimes chronic venous insufficiency and trophic ulcers develop. Linton's operation is performed when there are trophic changes in the soft tissues of the leg over a long period. Complications often develop after this intervention. Currently, phlebologists for trophic ulcers prefer the operation of subfascial endoscopic dissection of perforating veins.
In order to undergo a course of treatment for thrombophlebitis and perform an operation at a reasonable price, make an appointment with a phlebologist by calling the contact center phone number. Doctors at the Yusupov Hospital take an individual approach to choosing a treatment method for each patient.
Briefly about the main thing
Thrombectomy is a minimally invasive (low-traumatic) operation that is performed to eliminate a blood clot formed in hemorrhoids.
This intervention is performed for acute hemorrhoids. Thrombectomy is performed under local anesthesia and takes no more than 10 minutes . The procedure has the shortest list of contraindications and does not require hospitalization of the patient. You can go home immediately after surgery .
The recovery period passes quickly and is not associated with serious restrictions. It will be necessary to follow basic hygiene rules: wash the anal area with warm water after each bowel movement. You should also follow all the doctor’s recommendations: ___• follow a diet, ___• limit physical and nervous stress, ___• avoid excluding thermal procedures, ___• take prescribed medications, ___• carry out local treatment of the postoperative wound.
Causes of thrombosis of hemorrhoidal veins
Thrombosis can develop as a consequence of an acute, first-time attack of hemorrhoids, as well as as a complication of chronic hemorrhoids. The likelihood of developing thrombosis in chronic pathology increases with increasing “length” of the disease and the size of the nodes.
An attack can be triggered by: ___• chronic stool disorders (constipation, diarrhea, constipation alternating with diarrhea), ___• increased physical activity, ___• labor, ___• consumption of spicy food and/or alcohol, ___• hypothermia, overheating.
The development of acute hemorrhoids is promoted by all conditions accompanied by an increase in intra-abdominal pressure - from pregnancy to chronic cough and obesity.
Another factor in the occurrence of hemorrhoids is stagnation of blood in the veins of the pelvis, which often occurs as a result of a sedentary lifestyle and “sedentary” work.
Mechanism of blood clot formation
Thrombosis of external hemorrhoids occurs more often. It is extremely rare that the process spreads from external to internal nodes. Even less commonly, it occurs isolated in internal nodes.
Thrombosis of the external hemorrhoid occurs in both acute and chronic processes. In both cases, the pathology develops as a result of a combination of three factors: ___• slowing blood flow in the node, ___• blood thickening, ___• damage to the vascular network of the hemorrhoid.
Signs of thrombosis
___• The main symptom of thrombosis is acute, excruciating pain that prevents normal bowel movements. The pain syndrome intensifies many times over with straining, movement, and also in a sitting position. In severe cases, the pain takes on a pulsating character and, depending on the location of the node, can radiate to the leg, inside the rectum or to the external genitalia. ___• Bleeding often occurs, which varies in intensity - from individual drops on the surface of the stool to a trickle of blood during bowel movements. ___• Thrombosis of the internal node causes the sensation of a foreign body inside the rectum. Since the bleeding injured node comes into contact with feces, a secondary infection may occur. In such cases, mucous or purulent discharge appears and body temperature rises.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of hemorrhoidal thrombosis is not difficult. The diagnosis is made by external examination of the anal area .
If the proctologist decides on surgical intervention, it will be necessary to take tests : ___• general blood test, ___• coagulogram, ___• blood glucose level.
It is necessary to tell the attending surgeon about all medications taken, since some medications (oral contraceptives, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.) affect blood clotting.
How the treatment method works
Removal of blood clots in modern clinics is controlled by CT angiography. With its help, you can very accurately determine the location of the blood clot and plan the course of the operation. Recently, percutaneous mechanical thrombectomy is more often used to remove blood clots from the arteries of the brain. A guide catheter is inserted into the femoral artery in the groin and then guided (visually controlled using a CT scan) to the site of the blockage. The catheter carries a special stent, which is folded. Passing through the thrombus, the stent straightens and captures it. The thrombus captured by the stent is removed through a micro-incision in the artery. If thrombectomy is not possible for any reason (for example, if the thrombus is located in an arterial branch), thrombolysis is performed. This method allows you to restore blood supply to brain tissue faster than with anticoagulant therapy.
When is vascular bypass used?
The operation “Bypass surgery of the vessels of the lower extremities” is used strictly for the following indications:
- Peripheral artery aneurysms (dilation of the vessel caused by damage to its walls);
- Atherosclerosis of veins (deposition of cholesterol plaques on the walls of the vessel);
- Chronic diseases with damage to the arteries of the lower extremities;
- Varicose veins;
- Thrombosis and thrombophlebitis;
- Primary manifestations of gangrene of the legs;
- Drug treatment is ineffective.
Bypass surgery of the vessels of the lower extremities is not performed when:
- It is possible to perform angioplasty;
- The patient is completely paralyzed;
- Poor test results;
- The work of individual organs is disrupted.