Pathogenesis of renal edema
The mechanism of formation of renal edema is associated with the following phenomena in nephrological patients:
- massive loss of protein in urine;
- decrease in plasma albumin concentration;
- hyperlimidemia;
- increased movement of fluid from the intravascular space.
Patients have a high ratio of sodium and potassium in the urine, which indicates an imbalance of water and electrolyte balance.
The mechanism for the appearance of such a symptom is still not fully understood, but the characteristic picture indicates to the doctor pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis. Filtration and excretion of urine are also impaired with kidney cysts, benign or malignant neoplasms.
Features of therapy
Treatment for swelling in heart failure is to eliminate their causes. It is quite difficult to treat such a disease, but it is possible to overcome it. If you are able to stop the progression of heart failure, the patient's condition will return to normal. At the initial stage, it helps to reduce swelling through rest, weight massage and cold wraps. Then more radical therapeutic methods are used.
First of all, diuretics are used to remove excess fluid from the body. They can be synthetic drugs: furosemide, diacarb, Triampur, spironolactone, diuretics or natural Veroshpiron: a decoction of birch buds, cherry stems, flowers, cornflower, dandelion, parsley. The choice of treatment method depends on the stage of heart failure and the severity of clinical symptoms.
Swelling in the legs with heart failure, they can be controlled by cardiac glycosides: Celanid, digoxin, Corglicon. It improves myocardial contractility, stopping congestion and helping to remove excess water from the body.
RLO is also used: Valsacor, Mycardis, which lowers blood pressure, which reduces the release of fluid into the tissue and prevents pastozie. Effective potassium and magnesium preparations: Panangin, Asparkam, which restore heart rhythm, regulate vascular blood flow, restore the transmission of nerve impulses to the muscles.
Beta-adrenoblokery: Concor, Betaloc, nebilet, Corvitol are necessary for correcting heart rhythm, improving nutrition and oxygen supply to important internal organs.
Angioprotectors: Detralex, Troxevasin, diosmin, Escusan, Antistax strengthens the walls of blood vessels, normalizes regional blood flow, the cellular composition of the blood is stabilized, reduce pastowatość.
Characteristics of edema of renal origin
Diseases of the urinary system are accompanied by edema with the following features:
- rapid swelling - in less than a day;
- the greatest intensity is on the face, under the eyes, on the arms and legs, and on the abdominal wall;
- when changing posture and active movement, the fluid shifts;
- the surface of the edematous skin is soft and pale.
Swelling of renal origin first appears on the face in the morning, but in acute pathologies and advanced chronic stages the patient may suffer from swelling around the clock.
Additional events
Leg swelling due to heart failure can be alleviated
- reduce salt intake to 5 g/day;
- a balanced diet, drinking water up to 1.5 liters of liquid per day, including the first and third courses, medicinal tea, milk;
- as far as possible, protein foods should be included in the daily diet instead of carbohydrates and fats;
- in order to normalize your weight;
- Participation in physical activity should be limited, with the exception of heavy physical labor.
How to distinguish cardiac edema from renal edema
Swelling in diseases of the heart and blood vessels develops slowly - from several weeks to 2-3 months. Especially noticeable in the evening. First it appears on the legs and lower abdomen, the next stage is swelling of the abdominal cavity and enlargement of the liver, noticeable upon palpation of the abdomen.
Renal edema is typically localized on the face; as the disease progresses, it spreads to the extremities. The contour of the face sags and shifts, the skin becomes loose, and under the eyes it becomes bluish. The liver is not enlarged. Reliable differential diagnosis can only be carried out by a qualified doctor during an examination.
Content:
- Danger of leg swelling
- Factors leading to leg swelling
- Causes and treatment of leg swelling
Danger of leg swelling
This pathological condition is one of the symptoms of a large number of diseases. First of all, such symptoms are accompanied by diseases of the veins of the lower extremities, which lead to the development of chronic venous insufficiency. Chronic right ventricular heart failure also leads to peripheral edema. Nephrotic and nephritic syndromes due to kidney disease, hypothyroidism, lymphostasis due to congenital or acquired pathology of the lymphatic vessels and many other conditions can lead to increased swelling.
Factors leading to the development of edema include:
- a decrease in the oncotic pressure of the blood plasma or an increase in the oncotic pressure of the intercellular fluid, as a result of which the fluid passes from the vessels into the intercellular fluid along the oncotic pressure gradient
- increase in hydrostatic pressure in blood vessels
- pathological increased permeability of the microvasculature
- violation of the outflow of lymphatic fluid
- low mechanical pressure of adjacent soft tissues.
Causes and treatment of leg swelling
Edema of the extremities in chronic venous insufficiency develops due to impaired permeability of the vascular wall. In the initial stages, swelling of the legs and feet appears sporadically, usually in the evening, and completely disappears after rest. If it is impossible to compensate for the excess amount of fluid with the help of increased lymphatic drainage, edema increases. As a result, the elasticity of the skin decreases and permanent indurative swelling appears. There are also complaints of pain, numbness, discoloration of the skin, increased fatigue, dryness and increased pigmentation of the skin, and muscle spasms. Diagnosis of pathology of the veins of the lower extremities is possible through functional tests, instrumental examination - Doppler ultrasound or duplex angioscanning. A phlebologist diagnoses and treats vein diseases.
In chronic heart failure, as a result of a decrease in the contractility of the heart, hydrostatic pressure in the vessels increases and fluid penetrates into the intercellular space. In the initial stage, pastiness appears, and then actually symmetrical swelling of the lower extremities. They are dense, cold to the touch, worsen in the evening, but as the disease progresses they become permanent and generalized. For diagnosis, it is important to identify a history of a disease that could cause the development of heart failure, and identify other complaints (shortness of breath during exercise or night attacks, pain in the right hypochondrium, heaviness in the abdomen). An ultrasound examination of the heart will be decisive in making the correct diagnosis. To exclude concomitant pathology of the vessels of the lower extremities, Doppler ultrasound is performed. If you suspect CHF, you should consult a cardiologist.
Nephrotic edema occurs as a result of pathology of the glomerular apparatus of the kidneys, as a result of which a large amount of protein is lost in the urine and the oncotic pressure of the blood plasma decreases. This condition can be caused by various kidney diseases - glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, systemic vasculitis and many others. Such swelling usually spreads from top to bottom, it is warm and soft to the touch, and moves during palpation. Additionally, symptoms such as pain in the lumbar region, decreased urination, change in urine color, as well as various neurological disorders - headaches, increased fatigue, and sleep disturbances - may be observed. Diagnostics includes a urine test, determining the amount of daily protein excretion, a general blood test and biochemical study (increased lipids and decreased albumin in the blood, possibly increased creatinine as a marker of renal failure), ultrasound of the kidneys, Dopplerography of the renal vessels, contrast urography and other diagnostic methods renal pathology. The diagnosis and treatment of renal pathology is carried out by both a general practitioner and a nephrologist.
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease that is characterized by a decrease in the production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland and is manifested by the appearance of characteristic edema - myxedema (mucoedema). The outflow of lymph and blood decreases, vascular permeability increases, the composition of the intercellular fluid changes with the accumulation of hydrophilic substances. Myxedema differs in that due to the pronounced density, no trace remains when pressed. Most often it is localized in the face and lower extremities. Additionally, symptoms such as drowsiness, decreased blood pressure and decreased heart rate, hair loss, yellowish skin tint, and others are noted. Diagnosis consists of conducting a hormonal study with determination of TSH and thyroid hormones, performing an ultrasound of the thyroid gland and examining the pituitary gland if necessary. This pathology is treated by an endocrinologist.
Associated symptoms
Diagnosis of renal edema begins with an assessment of the clinical picture. For the urological profile of the disease, it includes the following complaints:
- difficulty urinating;
- lower back pain – shooting and pulling;
- decreased daily urine volume;
- weakness, lethargy.
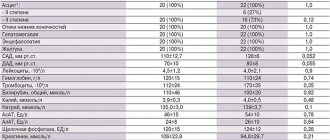
Laboratory diagnostic results indicate proteinuria, changes in sodium and potassium levels. Daily samples show a reduced volume of diuresis.
Read also
Alzheimer's disease
47,000,000 people suffer from dementia in the world.
Doctors call Alzheimer's disease the most common cause of dementia. Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disease accompanied by... Read more
Atherosclerosis
What is atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a narrowing of the arteries caused by the formation of plaque. As a person gets older, fat and cholesterol can accumulate in the arteries and form plaque. Accumulation…
More details
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
What it is? Why is this happening? Is this condition dangerous? What to do if doctors make such a diagnosis? These questions are always asked by patients who come to see a neurologist. According to classification...
More details
Hemorrhagic stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke is a type of acute cerebrovascular accident, which is characterized by the effusion of blood into the brain substance with the development of neurological deficit, often leading...
More details
Vegetative-vascular dystonia
Vegetative-vascular dystonia is a dysregulation of the autonomic nervous system, which manifests itself in the form of various clinical symptoms. This disease is diagnosed at different times...
More details
Diagnostics
It is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist; depending on the stage of the process, the examination can be carried out in an inpatient or outpatient setting. The issue is resolved at the discretion of specialists.
Approximate list of events:
- Oral questioning of the patient. Allows you to objectify symptoms and create a clear clinical picture. Used as part of routine initial examination.
- Anamnesis collection. Briefly. What illness did the person have when? How long. Lifestyle, family history, and other points are also clarified. Both methods are basic. They are necessary to determine the vector of further actions.
- Auscultation, listening to heart sounds. If insufficiency, and, as a consequence, swelling of the legs occurs against the background of a defect in the cardiac structures, dull irregular tones and splitting are detected.
- Measurement of blood pressure and heart rate. The first indicator is consistently below the norm, because the symptoms of burning contractile function are increasing. Heart rate is first of the tachycardia type, that is, acceleration, then the reverse process.
- Daily monitoring. Usually prescribed as part of a comprehensive diagnosis. Records vital signs for 24 hours. Dynamic observation.
- Electrocardiography. Brings to the surface arrhythmias and possible defects. But decoding requires high-quality training of specialists.
- Echocardiography. Shows deviations of the anatomical plan.
Consequences
After a certain amount of time, the heart weakens until it can no longer contract strongly enough. This causes the volume of blood released into the systemic circulation to decrease.
The heart muscle tissue slowly dies and is replaced by scar tissue. Decreased blood output in the long term can lead to several consequences. Initially, patients notice swelling in their legs and experience shortness of breath. The supply of nutrients and oxygen to the body decreases, and then this is observed at rest.