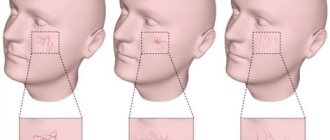
Capillary angiodysplasia (vascular birthmark, “port-wine stain”) is a disease known to people for many centuries. In this article we will talk about this pathology and how it is treated.
Vascular birthmark (“port wine stain”) is a malformation of small blood vessels in the skin. This disease appears as pink, bright red or purplish-purple spots that usually do not protrude above the skin. These spots are often quite large in size and occupy large areas of the face or body. The port-wine stain increases in size in proportion to the child's growth. These changes on the skin almost never disappear on their own; on the contrary, they often acquire a darker color and an uneven, nodular surface.
Until a certain point, there was no acceptable method for ridding a person of vascular spots. The main methods used to treat the disease were surgical excision, cryodestruction, and electrocoagulation. Such techniques relieved the patient of the disease itself, but left noticeable cosmetic defects. The advent of lasers in medicine has made it possible to effectively combat this kind of skin changes and obtain an excellent cosmetic effect.
It was thanks to the advent of laser equipment that it became possible to selectively coagulate blood vessels deep in the skin without damaging other tissues. In other words, after laser treatment there is no damage to the child’s skin.
Laser removal of wine stains
At the First Children's Medical Center, a medical device based on a copper vapor laser is used for children. Laser skin treatment allows the patient to get rid of the defect in several sessions without pain and without damaging surrounding tissues. Selective laser photothermolysis for angiodysplasia is a procedure that has the maximum cosmetic effect! Removing wine stains with a laser is the best method today. The procedure is performed painlessly, quickly, without cosmetic defects, on an outpatient basis. After exposure to the laser, the spot gradually begins to fade and disappears completely. In the vast majority of cases, anesthesia is not required.
How to suspect venous disease?
Venous disease itself involves a lack of blood flow. Depending on the affected area (brain and legs), dysplasia may be accompanied by:
- discomfort/pain/distension in the development zone (this may be due to thickening of the walls of blood vessels or venous duplication);
- skin pigmentation is often observed with venous dysplasia;
- due to compression of the venous system by strands of fibrous tissue, it is possible to stretch one leg relative to the other;
- Dysplasia often accompanies varicose veins.
Venous dysplasia occurs in approximately 2-3 babies out of 100. The exact reasons for its occurrence remain unknown. The disease can occur without symptoms (approximately 30% of cases). The most difficult cases of venous disease are associated with the concentration of affected vessels deep in the muscles.
The main threat is not, in fact, dysplasia, which is de facto a defect of the venous system (localized or generalized), but possible complications, the treatment of which should be addressed. These consequences of venous insufficiency include:
- various forms of vascular malformations (pathology of connections between veins and arteries, which can lead to insufficient blood supply to parts of the body);
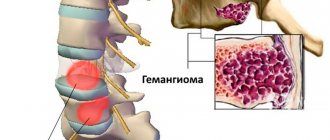
- cavernous hemangiomas (vascular formations visible on the skin);
- thrombosis;
- thrombophlebia;
- thrombotic ulcers;
- aneurysms.
How does laser treatment for port-wine stains work?
The procedure for laser removal of port-wine stains is quite simple and does not require the use of anesthesia. In some cases, the procedure is performed using a local anesthetic cream. During the procedure itself, the child may feel a slight tingling sensation. In general, the operation is very easy to tolerate for children of different ages and does not require long-term rehabilitation. In most cases, a series of several procedures is performed. As a result of each session, as a rule, the stain changes color (becomes less noticeable) and ultimately disappears completely.
Recognizing venous dysplasia
There are frequent cases of venous dysplasia developing into phleboangiotic dysplasia. In this case, disability cannot be avoided. In the case of sepsis or rupture of an aneurysm due to venous disease, death is also possible.
For this reason, diagnosis of dysplasia should be carried out as early as possible - at the first suspicion of venous insufficiency. In modern phlebology practice, various tactics for recognizing deep vein dysplasia are used. Since the external signs of the disease make it possible to accurately determine its location, the following is carried out in the problem area:
- CT/MRI/ultrasound;
- angiography and other phlebological manipulations.
Brain imaging (MRI) is often done to confirm.
Removal of capillary angiodysplasia (“port-wine stain”): advantages of laser treatment
The following advantages of using laser equipment in removing port-wine stains can be highlighted:
- laser radiation with certain parameters is able to penetrate the skin without damaging it.
- The wavelength used in the laser coincides with the absorption peak of hemoglobin, therefore it is maximally absorbed by hemoglobin and noticeably less by other tissues. Due to this, the deep layers of the skin are not damaged.
- Copper vapor laser radiation is almost not absorbed by water, which prevents overheating of surrounding tissues.
- Focusing the laser beam into a small spot allows you to limit the area of influence to the pathological area, avoiding irradiation of normal tissue.
- The pulsed nature of the radiation and the laser radiation dosage system allow you to control the absorbed energy and avoid overheating.
Thus, high-tech laser equipment allows procedures to be performed without damaging the surrounding tissue with maximum cosmetic effect, which is extremely important, since most operations are performed on cosmetically significant areas of the face or body.
For more detailed information regarding the treatment of skin pathologies or to schedule a consultation, please call 8 (8452) 244-000.
Children's health means parents' peace of mind!
Make an appointment with a surgeon
Choose a doctor
Capillary malformation - symptoms and treatment
Laser therapy is the main treatment method for capillary malformation. It is carried out only with selective lasers, since their waves act exclusively on blood hemoglobin [2][3][4][10].
Laser radiation affects the upper layer of capillaries, which causes sharp heating of red blood cells. As a result, the capillary either ruptures or sharply narrows.
Laser therapy can be started at any age, but optimally from the 1st month of life. If treatment is carried out under anesthesia, laser treatment is performed on average three times a year, but no more than four. It is believed that for successful socialization in society it is necessary to achieve the maximum result of treatment before starting school.
Laser treatment has its complications : temporary (reversible) and permanent (irreversible). All of them arise due to the thermal effect of laser radiation on tissue.
Swelling, redness and bruising are temporary complications. They indicate the effectiveness of the procedure and usually disappear 7-10 days after treatment.
Irreversible changes occur when the skin is overexposed to radiation. The resulting burn can lead to the appearance of a scar. These complications can be avoided by choosing a competent specialist and the right laser.
Another hardware treatment method is IPL - intensive pulselight, i.e. intense pulsed light . Unlike laser, IPL represents broadband light. Essentially, this is a powerful lamp, to cut off unnecessary ranges of which special filters are used. This technology is often used in cosmetology to treat skin diseases, including the treatment of capillary malformation.
Before the advent of laser technology, the main method of treating port-wine stains was surgical removal of the altered skin with plastic correction of the resulting defect. Hours of traumatic surgery were performed, often leaving disfiguring scars that caused more discomfort than the spot itself.
Sclerosation - administration of a drug (sclerosant) through an injection - is used in the treatment of combined malformations, for example capillary-venous. This method is not used in the treatment of simple port-wine stains due to the lack of a cavity into which the drug must be injected.
The use of beta-blockers in the form of systemic (propranolol, atenolol) or local therapy (timolol, arutimol) in the treatment of capillary malformation is ineffective, since they do not act on capillary angiodysplasia.
Among other things, experimental work is currently being carried out on the use of the drug sirolimus as systemic and local therapy, but this method has not yet received widespread use.
Laser removal procedure for hemagniomas
Intense pulsed light and a laser beam briefly increases the temperature in the treated area at a given depth - its spectrum corresponds to the absorption spectrum of hemoglobin. This causes the destruction of hemoglobin in dilated capillaries, as a result of which the walls of the vessels collapse.
Treatment of vascular formations of the skin is tolerated by most adult patients without anesthesia. Children are additionally given topical anesthesia with EMLA cream.
The blanching of hemangioma and angiodysplasia is visible after the first procedure, but until the vascular formation completely disappears, several sessions are required with an interval of 1 month.
Results before and after treatment:
Prices for hemangiomas removal. To make an appointment with a specialist, fill out the form.
Other laser correction procedures for cosmetic imperfections at the Baikal Center for Multidisciplinary Medicine (Irkutsk):
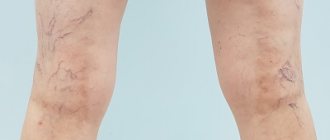
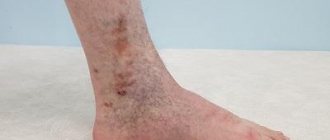
- Laser removal of unwanted blood vessels on the face, legs (rosacea, varicose veins);
- Laser removal of benign formations on the skin;
- Laser correction of scarred skin lesions;
- Laser removal of tattoos.
Top
Removal of hemangiomas, port-wine stains on the face with laser
Today, several types of lasers are used to treat and remove hemangiomas and angiodysplasias. However, not all of them are equally good. Numerous scientific studies have found that in most cases, the most effective for treating superficial forms of vascular formations of the skin (capillary hemangiomas and angiodysplasia) are lasers and IPL systems that emit light with a wavelength of 532 - 600 nm (green or yellow light). In the treatment of deep and invasive vascular formations such as cavernous hemangioma, Nd-Yag lasers with a length of 1064 nm provide excellent results. Therefore, it is important before treatment to correctly determine the type and depth of the vascular formation.
The capabilities of the Quantum installation allow the treatment of vascular formations of the skin at any depth, since it includes the full range of wavelengths of intense pulsed light from 515 nm to 1200 nm and a laser with a wavelength of 1064 nm.
For example: to remove capillary hemangiomas and angiodysplasias, an IPL attachment with replaceable 560 light filters is used, and to remove cavernous hemangiomas, it is better to use a contact laser attachment with a wavelength of 1064 nm.
Hemangiomas
Angiodysplasia (?) and hemangiomas (?) are vascular malformations. They occur in 2–12% and 0.3–1.0% of newborn children, respectively, and in 70% of cases they are located on the face and neck (in the area of innervation of the trigeminal nerve), which often creates a cosmetic defect and significantly affects the formation of a negative psychosocial status .
Cavernous hemangioma
It is the result of further development of capillary hemangiomas. In the process of growth and increase in size, as a result of capillaries overflowing with blood, some of them expand and rupture, followed by hemorrhage into the hemangioma tissue. The consequence of this process is the formation of small, blood-filled cavities (cavities), the inner surface of which is lined with endothelial tissue.
Capillary angiodysplasias (“port-wine stains”)
Refers to dysplastic vascular malformations. Unlike capillary hemangiomas, they do not grow, increasing only in proportion to the growth of the child’s body, and do not regress with age. In some cases, regardless of the duration of existence, severity and extent of the lesion, the course of vascular nevi can be complicated by ulceration, secondary infection, and bleeding. And extensive regressive hemangiomas can leave behind areas of residual retraction, atrophic skin changes and scars.
Capillary hemangiomas
They are among the most common benign vascular tumors and account for more than 50% of all childhood tumors. Having high mitotic activity in tumor cells, hemangiomas actively grow in the first year of a child’s life. And only 7–8% can regress on their own by 5–10 years. The other part may remain and even progress with age, creating significant cosmetic defects. Despite their benign nature, hemangiomas with progressive growth can destroy surrounding tissues and not only aggravate cosmetic problems, but also, when localized on the mucous membrane of the mouth, nose, eyelids or auricle, lead to dysfunction of organs and systems (breathing, vision, hearing) . Hemangioma in a mature person cannot manifest itself without the presence of a congenital lesion. Often the tumor is not visible because it is not on the skin.
Senile hemangioma
A smooth red nodule that forms on the skin. Most often, senile hemangiomas appear on the torso, but they can also occur on the skin of other parts of the body. The cause of the appearance of senile hemangiomas is unknown; most often such nodules appear on the skin of people who have reached the age of forty.