Why does hypotension occur?
Hypotonicity can be both the result of adaptation of the nervous system to stress, and a sign of more severe (organic) disorders.
To identify the cause and prevent possible more severe disorders, parents need to visit a neurologist who will conduct all the necessary studies. Possible causes of hypotension:
- Complications during childbirth, fetal asphyxia;
- Severe pregnancy;
- Improperly organized nutrition of the baby;
- Genetic diseases and various developmental defects;
- Low birth weight, prematurity;
- Bad habits of the mother during pregnancy;
- Viral and/or infectious diseases of the newborn;
- Excess of vitamin D in the body.
An earlier visit to a neurologist will help solve the problem as quickly and effectively as possible, without waiting for possible complications.
Diagnosis of arterial hypotension
The main goal of diagnosis is to establish the presence of the disease itself and the conditions that caused it. To make a correct diagnosis, blood pressure is measured three times (an interval of three to five minutes). Daily monitoring of blood pressure is also carried out, aimed at determining fluctuations in value and circadian rhythm.
To exclude or confirm the presence of secondary arterial hypotension in a patient, a comprehensive examination of the nervous, endocrine and cardiovascular systems is necessary. The results used for this are:
- biochemical blood test (glucose, electrolytes, lipid fractions, cholesterol);
- electrocardiograms (with stress tests and at rest);
- echocardiography;
- electroencephalography;
- orthostatic test.
Patients with hypotension are advised to consult a neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist and ophthalmologist.
Symptoms
Parents can suspect hypotension simply by observing their child. Immediately after birth, the newborn exhibits physiological hypertonicity, so decreased muscle tone is immediately noticeable. At an older age, tone disturbances are also noticeable.
Possible signs:
- During the newborn period, the baby's arms and legs are not tucked towards the body; he lies in the “frog” pose with straightened arms and legs;
- Refusal of breastfeeding;
- Frequent regurgitation;
- Does not turn the head, does not hold the head at 3-4 months;
- Does not roll over at 5-6 months;
- Does not sit up independently at 6-7 months;
- Does not crawl on all fours at 7-9 months;
- Does not hold objects in hands (at 3-4 months);
- Lethargic, unemotional.
Additional diagnostics are carried out by the doctor during the examination. Looks for the presence or absence of neurological signs of hypotonicity, the presence of pathological reflexes, and, if necessary, prescribes additional research methods: ultrasound, neurosonography, EEG, MRI and others.
Causes of arterial hypotension
The causes of arterial hypotension can be different. The primary form of the disease in 80% of cases is caused by neurocirculatory dystonia. Its provocateurs are prolonged psychotraumatic situations and severe stress, depressive disorders, lack of sleep, and psychological trauma.
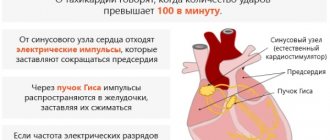
The cause of orthostatic hypotension is autonomic failure. When changing body posture, the amount of blood flowing to the heart through the veins decreases sharply. Accordingly, the heart begins to pump less blood, and the pressure in the systemic circulation drops.
Secondary arterial hypotension is always caused by other diseases, for example:
- stomach ulcer;
- anemia;
- hypothyroidism;
- myocarditis;
- arrhythmia;
- osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- diabetic neuropathy;
- tumor neoplasms;
- heart failure;
- infections.
Causes of acute hypotension:
- injuries;
- immediate blood loss;
- dehydration of the body;
- poisoning;
- cardiac dysfunction;
- anaphylactic shock.
The problem can also be caused by a lack of vitamins C, E, B, adherence to strict diets, and uncontrolled use of medications intended to treat arterial hypertension.
If we talk about the physiological form of the disease, it is observed during the period of adaptation to new climatic conditions, with increased physical activity, in people with a hereditary predisposition.
Mechanism of development of arterial hypotension
The pathogenesis of arterial hypotension, regardless of the causes of the disease, is always associated with one of the following factors:
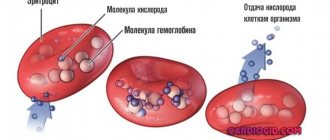
- Decrease in circulating blood volume. Occurs with internal/external bleeding.
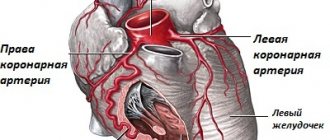
- Decrease in cardiac output and stroke. Diagnosed with diseases of the cardiovascular system, for example, with atherosclerotic and myocardial cardiosclerosis.
- Decreased venous blood flow to the heart. Develops with an overdose of ß-blockers, heart attack (myocardial dysfunction), severe forms of arrhythmia.
- Reduced resistance and tone of peripheral vessels. It is a consequence of collapse of an infectious or toxic nature, anaphylactic shock.
If left untreated
It is important to identify hypotension in time. Moms who have no experience with babies may not notice problems in their first child. It’s good when an experienced person is nearby or a doctor identifies the violation. If the decreased tone is not treated, it will affect the further development of the child. Much later he will begin to hold his head, crawl, and walk.
Violation of the appearance of these skills causes a delay in mental and speech development in the child. The development of his central nervous system occurs through the activation of motor functions. It is better to play it safe and consult a neurologist in vain than to miss alarming symptoms.
It is worth considering one more detail: hypotonia can manifest itself at different ages. It can be diagnosed almost immediately after birth - by checking reflexes. In this case, the cause of the disorder usually lies in birth trauma. Also, a violation of muscle tone can appear at any age, but its appearance is especially dangerous in the first 2 years of life, since this most often indicates a disturbance in the development of the central nervous system. At an older age, hypotension is usually a sign of complications after infectious or viral diseases.
Very often, in babies under the age of one year, an attentive mother determines that the muscles in the arms and legs are too tense, or, conversely, the muscles are too relaxed. When examined by a neurologist, a violation of muscle tone is determined.
Many questions immediately arise: what is it, how is it determined, for what reason does it arise, why it is dangerous for the baby and how it can be corrected.
Muscle tone (Latin tonus from the Greek tonos - tension, tension), a state of slight physiological contraction of a muscle at rest, ensuring its readiness for work. (G. G. Shanko). In other words, tone is muscle tension, which is necessary to maintain body posture and ensure its movements.
Before birth in utero, the baby is in the fetal position, when the arms and legs are bent and pressed to the body. physiological hypertonicity remains during the first three months of life . By 3 months, the tone of the flexor and extensor muscles is leveled out and a state occurs that we characterize as normotonia. At the same time, the baby’s arms and legs unbend much more easily, and the fingers of the hands are rarely clenched into a fist.
Changes in muscle tone may appear as
- muscular hypertension or muscle hypertonicity,
- muscular dystonia,
- muscle hypotonia or muscle hypotonia.
Do you have questions for your pediatric neurologist? Call: +375 (29) 333-88-77 from 9.00 to 18.00 seven days a week
If the baby’s arms and legs are tightly pressed to the body, it is difficult to straighten them, the baby cries, throws his head back - this is due to excessive muscle tension. The number of impulses that comes from the central nervous system to the muscles is significantly increased.
Muscular hypertension syndrome is characterized by an increase in resistance to passive movements, limitation of spontaneous and voluntary motor activity, increased tendon reflexes, expansion of their zone, and foot clonus.
The severity of muscle hypertonia syndrome can vary from a slight increase in resistance to passive movements to complete stiffness. If muscle hypertonicity is not pronounced and is not combined with pathological tonic reflexes and other neurological disorders, its effect on the child’s development can manifest itself in a slight delay in motor skills. It also happens that motor development progresses according to age and the child begins to sit, stand up and walk in time, but at the same time the child’s feet rest on the toes, which leads to gait disturbance. Walking on your toes for a long time can lead to shortening of the Achilles tendons, which can only be corrected by surgical treatment.
Muscle hypotonia syndrome is characterized by a decrease in resistance to passive movements and an increase in their volume. Spontaneous and voluntary motor activity is limited. Tendon reflexes may be normal, increased, decreased, or absent, depending on the level of damage to the nervous system. Hypotension can transform into normotension, dystonia, hypertension, or remain a leading symptom throughout the first year of life.
The syndrome of movement disorders in children of the first year of life can manifest itself as muscular dystonia - a condition when muscle hypotension alternates with hypertension, that is, muscle tone is constantly changing. Muscular dystonia is also said to occur when some muscles in a child are too relaxed, while others, on the contrary, are too tense.
Severe muscular dystonia syndrome can lead to delayed motor development or movement disorders (for example, gait disturbance). Transient muscular dystonia syndrome does not have a significant effect on the age-related motor development of the child.
Disorders of muscle tone are often caused by problems in the functioning of the central nervous system - the brain or spinal cord, and are most often a consequence of hypoxia and ischemia. Hypoxia is a condition in which the baby’s body and central nervous system lack oxygen. Ischemia is a disruption of the blood supply to tissues, leading to hypoxia.
Impaired muscle tone occurs in serious severe diseases of the nervous system, such as various forms of myopathies, spinal muscular atrophy, myasthenia gravis, and can also be a consequence of inflammatory, vascular and traumatic diseases of the nervous system, always observed in cerebral palsy.
Detection of muscle tone disorders requires observation by a pediatric neurologist .
Observation by a pediatric neurologist at home Call: +375 (29) 333-88-77 from 9.00 to 18.00 seven days a week
If necessary, the specialist will prescribe additional research methods :
- Neurosonography
- Doppler examination of cerebral blood flow
- Consultation with an ophthalmologist.
Treatment of muscle tone disorders
- Therapeutic massage and gymnastics.
- Physiotherapeutic, including thermal and electrical procedures.
- Water procedures, relaxing or tonic baths, swimming.
- Fitball exercises.
- Drug treatment: drugs from the group of nootropics, vascular, sedatives, neurometabolic, vitamin drugs.
In most cases, in children with mild disturbances of muscle tone, it is possible to restore the functioning of the central nervous system and achieve normotonia.
Ivanova M.I. neurologist of the first category.
Treatment of hypotension
First, the doctor conducts a thorough diagnosis to find out the cause of hypotension. If it is not a symptom of more severe disorders, then, depending on the severity of the condition, the following treatment measures may be prescribed:
- massage;
- physiotherapy;
- reflexology;
- osteopathic treatment;
- correctional classes with teachers (exercises are selected individually, taking into account the patient’s age, severity of disorders and other characteristics and are carried out regularly - this is the only way to get results);
- prescription of drug therapy and nutraceuticals.
Therapy for the disorder involves an integrated approach and the active assistance of parents - their participation in the development of the child.
Hypotension in children
There are non-drug and drug methods for treating hypotension in a child. For labile arterial hypotension, it is better to carry out therapy without the use of medications. If hypotension is persistent and prolonged, a combination of non-drug therapy and medications is used.
Non-drug treatment consists of:
- normalization of the child's regime
- good sleep at night
- spending about 2 hours outdoors every day
- exercise in the morning
- water procedures after exercise for vascular tone
- eating 4-6 times a day without limiting salt on an optimal water regime
Treatment without medications also includes massage:
- cervical-collar area
- general
- calf muscles
- hands
For hypotension, physiotherapeutic methods of treatment are used - Vermeule electrophoresis on the collar area with solutions of caffeine, magnesium sulfate, bromocaffeine, mesatone. For children and adolescents, water procedures are also relevant as treatment - fan and circular showers, underwater shower-massage. Doctors can recommend medicinal baths, psychotherapy, etc.
If non-drug therapy does not produce an effect, the following drugs are used:
- anticholinergic
- adaptogens
- cerebroprotectors
- nootropics
- antioxidants
- antidepressants
- tranquilizers
In most cases, treatment of hypotension in children with medications begins with adaptogens, most often herbal. These drugs are given to the child once every 24 hours in the morning. Course – up to 3 weeks. The use of nootropic drugs is necessary for children with arterial hypotension, since they often have cerebral insufficiency and immaturity of cortical-subcortical relationships. The following drugs are effective:
- piracetam
- glycine
- cortexin
- phenibut, etc.
If there is a need to improve cerebral hemodynamics and microcirculation, the child is given courses of cinnarizine and vinpocetine. Actovegin and Oxibral have an optimizing metabolic effect. Doctors can prescribe antioxidant therapy and correction of energy-deficiency diathesis for the child. Tranquilizers are prescribed to children with emotional stress, neurotic manifestations, hidden anxiety and phobias. Mainly used are activating tranquilizers, daytime anxiolytics (Grandaxin, trioxazine, etc.)
In any case, treatment requires an integrated approach. Therefore, independent choice of drugs and other methods may not have the desired effect. Be sure to consult an experienced doctor.
Diagnosis of arterial hypotension
The appearance of one or several symptoms of arterial hypotension is a reason to visit a general practitioner and cardiologist. To make a diagnosis, the doctor collects a complete medical history of the patient and conducts a series of studies. First of all, blood pressure is measured several times at short intervals. Low blood pressure readings (100/60 and below) indicate the presence of pathology. If necessary, the doctor measures blood pressure during a stress test that simulates high physical activity. Among the mandatory types of examination for hypotension is also an ECG. If necessary and if structural pathologies are suspected, vascular Dopplerography may be required. All this requires certain equipment of the clinic and appropriate skills among the staff.
In our medical center, all diagnostic procedures are performed by doctors who have extensive experience in eliminating vascular pathologies. Here you will always find a professional approach to the diagnosis and treatment of arterial hypotension of any etiology, occurring independently or against the background of other disorders.
Symptoms of arterial hypotension
Low blood pressure, as a rule, does not lead to a deterioration in a person’s well-being and often goes unnoticed. But in some cases, especially with sudden changes in blood pressure, patients experience the following symptoms:
- dizziness, especially when suddenly rising from a sitting or lying position;
- fainting or orthostatic collapse – with a sharp redistribution of blood from the head to the lower extremities;
- loss of consciousness due to oxygen starvation of the brain;
- headache – often occurs after physical activity and can last from several hours to several days;
- emotional destabilization and frequent stress, which can provoke symptoms of neuroses from the gastrointestinal tract: nausea, loss of appetite, bloating.