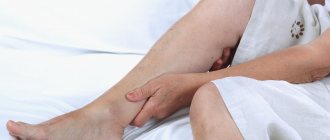
Feel itchy on your feet? Is your skin red and flaky? Such symptoms are characteristic of a specific disease called varicose dermatitis. This is not the simple dermatitis that many of us imagine.
Varicose dermatitis is a skin lesion that occurs in places where the veins have ceased to fulfill their functional purposes. It is not an independent disease. Occurs as a result of vascular damage by varicose veins and thrombosis.
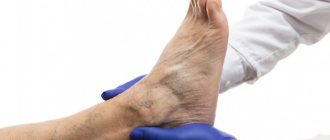
In case of damage to the extremities by varicose dermatitis, it is necessary to contact a phlebologist, since first of all it is necessary to treat the cause of the disease, and not the affected area.
Trophic venous eczema - what is it?
Trophic venous eczema is a pathological condition that occurs in the form of autoimmune dermatitis, that is, serous non-infectious inflammation of the skin (mostly the papillary layer of the dermis and epidermis), accompanied by symptoms of swelling, redness, itching and pain.
Trophic venous eczema
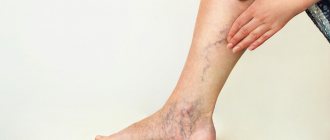
Venous eczema is a type and common form of eczema, which is caused by congestion in the skin due to impaired venous outflow. Venous eczema is also called varicose, congestive or gravitational. It most often has a chronic (recurrent) course. The pathology affects one or both lower extremities in combination with venous insufficiency. In the modern European, and most popular among leading experts, classification of chronic venous diseases - CEAP, this pathology is designated as C4a. This means quite severe tissue damage due to chronic venous edema.
Table of contents
- Etiology and pathogenesis
- Clinical manifestations
- Principles of treatment
Hemosiderosis of the skin (post-traumatic hemosiderosis, pigmentary capillaritis, hemorrhagic pigmentary dermatoses, pigmentary purpuric dermatoses) is a condition that occurs after an injury with blood entering the soft tissues (the appearance of a hematoma), or as a result of diseases, the common manifestation of which is the deposition of hemosiderin in the skin.
In our company you can purchase the following equipment for the treatment of skin hemosiderosis:
- M22 (Lumenis)
- IPL Quantum (Lumenis)
Hemosiderin is a dark yellow pigment composed of iron oxide. It is formed during the breakdown of two proteins - hemoglobin and ferritin, for example after blood enters the body's tissues. This can occur after an injury (bruise, injection), when a hematoma forms under the skin. Macrophages do not always have time to utilize the “subcutaneous” blood, as a result of which hemosiderin begins to accumulate in the area of damage. It forms rather persistent local discolorations, which can cause aesthetic discomfort in patients.
The following diseases are also hemosiderosis:
- Pigmented progressive dermatosis of Schamberg
- Annular telangiectatic purpura of Majocchi
- Lichenoid purpuric pigmentary dermatitis Gougerot-Blum
- Favre-Shay ocher dermatitis
- Touraine's arcuate telangiectatic purpura
- Eczematid-like purpura of Doukas-Kapetanakis
- Itchy Leventhal's purpura
- Pigmented purpuric and telangiectatic dermatitis (Purpura senilis)
- Orthostatic purpura
Below we will focus on the most common conditions and pathologies.
Why does trophic venous eczema occur?
Venous eczema is most often observed in middle-aged and elderly patients - according to leading European dermatologists, it affects up to 20% of patients over 70 years of age. This is due to the following reasons:
- Phlebeurysm.
- Previous deep vein thrombosis of the affected limb.
- The presence of venous trophic ulcers.
- Previous cellulitis on the affected limb.
- Chronic swelling of the lower leg, aggravated by hot weather and prolonged static position (standing).
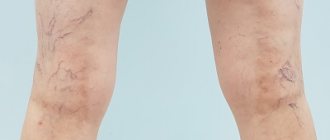
The main cause of the pathology is varicose veins, which is why you can sometimes come across the term “Varicose eczema”.
Venous eczema of atypical localization
Quite often, signs of eczema can be found in young patients with a long history of varicose veins. There is no doctor, both in public and private clinics, who would not observe venous eczema in patients under 40 years of age.
Causes and types of dermatitis
The disease occurs when the protective function of the skin is weakened due to prolonged exposure to aggressive substances or decreased immunity. The cause of the pathology can be the following factors:
- mechanical irritation, friction, compression of the skin;
- thermal burn or frostbite, ionizing, UV and other radiation, electric current;
- contact with chemicals contained in skin care products, household chemicals, decorative cosmetics, as well as salts of heavy metals, acids or alkalis, medications for external use;
- allergic reaction to plant pollen, animal hair, food, medications;
- infection with viruses, bacteria or fungi;
- taking antibiotics, sulfonamides, novocaine-containing drugs;
- systemic diseases, hormonal disorders, hypovitaminosis, pathology of the digestive organs, liver, disorders of carbohydrate and fat metabolism, helminthic infestation, influenza and ARVI.
According to etiological factors, there are:
- Perioral dermatitis. It occurs due to the abuse of cosmetics, improper local use of hormonal drugs, the use of medicated fluoride-containing toothpastes, hypovitaminosis A and E. In childhood, it appears with increased salivation and during teething.
- Atopic dermatitis. Occurs mainly in children prone to allergic reactions and has a hereditary predisposition. Irritants may include foods, allergens of plant or animal origin, dust mites, Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxins, and mold fungi. Rashes in a child of the first years of life are localized mainly on the face and extensor surfaces of the limbs, and at an older age and in adults, dermatitis appears on the elbows and popliteal folds.
- Contact allergic dermatitis. Appears when the skin comes into contact with substances to which the immune system is sensitized. May develop at lightning speed and be accompanied by anaphylactic shock.
- Actinic dermatitis. An allergic reaction to ultraviolet radiation, also known as sun allergy.
- Drug dermatitis. Occurs as a reaction to the use of medications (iodine, brilliant green).
- Seborrheic dermatitis. The cause of the disease is fungi of the genus Malassezia. Exacerbation occurs in hot and humid weather, with stress, hormonal, immune and neuroendocrine disorders, when the activity of the sebaceous glands increases. In places where they accumulate, the symptoms are more pronounced. Most often, seborrheic dermatitis affects the scalp, face, and upper third of the body.
- Infectious dermatitis. It develops when the skin is damaged by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
- Dry dermatitis. Occurs in people with sensitive skin during the cold season.
- Lichen planus. It is characterized by the appearance of red or pink plaques and intense itching. May affect nail plates.
- Toxidermy. A disease of an allergic nature, in which an irritant enters the body through the blood, respiratory system or oral cavity. There are medicinal, food and professional forms.
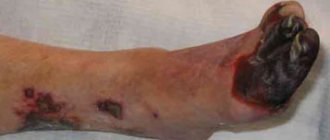
Trophic venous eczema is very bad
Varicose eczema has a chronic, relapsing course and a tendency to progress. Quite often you can encounter a situation, especially in public hospitals, when only dermatologists treat venous eczema. Considering the main etiological component of the pathology, impaired venous outflow, treatment of such patients takes years.
Chronic recurrent eczema on the right lower limb
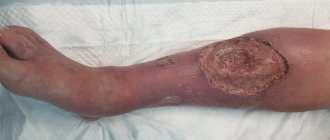
The disease slowly recedes, but invariably appears again. Moreover, trophic changes in the lower extremities progress, lipodermatosclerosis occurs, and then an ulcer appears.
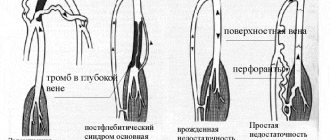
Why does trophic venous eczema almost always appear on the lower extremities?
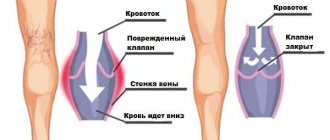
The answer to this question lies in the pathogenesis of varicose veins, the dominant cause of venous eczema. Varicose veins affect exclusively the lower extremities, where, according to the gravity gradient, it is in their distal parts that trophic disorders occur. One of which is venous eczema.
Trophic eczema of the lower extremities
Pathological eczematous changes in the skin of the lower extremities are most often caused by varicose veins, since they are the cause of impaired venous outflow (up to 90% according to leading experts in the region).
Trophic venous eczema - diagnosis
Diagnosis of venous eczema in public and private urban medical institutions often begins in a dermatologist’s office, where a specialist evaluates local changes in the skin. It is very important here that the patient is referred to a good phlebologist in a timely manner. If eczematous changes are associated with venous pathology, then treatment of skin manifestations only is likely to be ineffective. Even a visual examination by a phlebologist using all kinds of functional tests often does not reveal the true cause of the pathology. At this stage, the best solution would be a good ultrasound examination of the veins of the lower extremities.
Ultrasound diagnosis of trophic venous eczema
Only competent modern diagnostics of the venous system will help determine the correct treatment tactics.
Symptoms
Varicose dermatitis on the legs develops in 3 main stages:
- The skin in the vein area is slightly changed. The skin becomes purple-reddish and periodically itches. During palpation, small compactions can be felt. The skin peels and becomes colder to the touch. Sometimes you can see transparent bubbles.
- Swelling and associated soreness are observed in the affected areas. Peeling of the skin is noticeable. The itching becomes intense. Transparent bubbles are very noticeable and burst from time to time. In place of the burst bubbles, a wound surface appears. Palpation of the affected areas reveals lumps resembling wen.
- The number of transparent bubbles increases significantly. The skin becomes brownish. There are so many burst bubbles that the area where they were located becomes wet. The patient suffers from severe itching. The skin becomes covered with ulcers that are prone to suppuration.
Trophic eczema, treatment in Moscow
Good treatment of venous eczema in Moscow can be divided into local (topical effect on skin inflammation) and treatment of the venous system. In the first, a dermatologist is often actively involved. Local treatment includes:
- Ointments and creams, steroid drugs, both as part of the latter and as part of systemic treatment.
- The use of antibiotics and antiseptics when an infection occurs.
Often, in the conditions of public medicine, patient care ends at the stage of the above topical treatment. This is not the best solution, since the disease is based on completely different reasons and a relapse of the disease will not take long to occur. Namely, venous stasis, which requires a slightly different approach. It is very important that a patient in Moscow has a timely appointment and diagnosis with a good phlebologist who can determine the correct tactics for managing the patient. The treatment of venous eczema is based on eliminating stasis and improving venous blood flow. Correction of the latter most often involves removing pathologically altered varicose veins. The presence of innovative technologies in modern Moscow centers makes it possible to effectively treat even complicated forms of varicose veins, moreover, on an outpatient basis.
Treatment of trophic eczema in our phlebology center
Leading medical centers in Moscow for the treatment of venous pathology use thermoobliteration techniques for these purposes. In a good city medical phlebology center you can count on safe, effective treatment. Modern vein removal procedures are performed under local anesthesia through skin punctures with minimal surgical trauma.
Complications of dermatitis
Any form of dermatitis accompanied by skin damage can be complicated by infection.
In the chronic course of the disease, thinning of the skin and the appearance of small dilated vessels - telangiectasia - are possible. With prolonged atopic dermatitis, a child may develop asthma and allergic rhinitis. Among the adverse consequences of the seborrheic form of the disease are acne with the formation of visible skin defects, abscess, and baldness. The most serious are considered generalized complications such as Quincke's edema, Lyell's syndrome or Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Trophic varicose eczema - treatment without surgery
The main factor in the development of congestive eczema is the pathology of the venous system. Therefore, there is no need to talk about any effective treatment without radical intervention. The best solution would be to stop the inflammation and carry out a procedure to remove varicose veins. But is surgery really that scary?
Trophic eczema - laser treatment in our center
Modern European technologies for vein removal are not inferior to advanced manipulations in dentistry in terms of minimal surgical trauma and possible side effects. But today it would not even occur to anyone to refuse caries treatment due to fear of intervention.
Trophic venous eczema - laser treatment (EVLO, EVLT), radiofrequency treatment (RFA, RFO)
Considering that radical treatment of varicose eczema is the treatment of venous pathology, it is modern methods of removing varicose veins that will be the main way to combat eczema itself. Today, the undisputed leaders at the forefront of innovative treatment of varicose veins are thermal obliteration techniques, laser and radiofrequency. If we compare both technologies, there are simply no fundamental differences for the patient.
Treatment of trophic eczema with radiofrequency
What are the advantages of thermoobliteration technologies:
- Radicality and effectiveness (when used by experienced specialists, the result is practically 100%).
- Low invasiveness, the procedure is carried out through skin punctures.
- Highest cosmetic value.
- Full outpatient, no need for anesthesia or hospitalization.
- Safety and comfort of the procedure for the patient.
The result of laser treatment of trophic eczema after 1 month
After endovascular treatment, the symptoms of eczema quickly resolve on their own.
Prevention
Prevention of varicose dermatitis involves an active lifestyle, walking, a varied diet, most of which is healthy food, as well as adherence to a diet developed by a doctor, treatment of chronic somatic diseases, which can be completed at the EUROMEDPERSTIZH clinic. Among other things, wearing comfortable shoes, foot massage and contrast douches are of great importance.
"EUROMEDPERSTIZH" treatment of varicose dermatitis in our clinic is the choice of a person who wants to be healthy!
Results of treatment of trophic venous eczema. Photos before and after treatment
The result of treatment of trophic eczema using endovenous laser coagulation (EVLC) using German Biolitec technology in our center
Photos before and after treatment of trophic eczema on the left lower limb
The result of treatment of trophic venous eczema using radiofrequency ablation (RFA) in our patient
Photos before and after treatment of trophic venous eczema on the left lower limb
Frequently asked questions from patients on the Internet about trophic venous eczema
How to treat venous eczema of the legs in Moscow?
For good treatment of venous eczema of the lower extremities in Moscow, you need to contact a competent specialist, a phlebologist. The doctor will conduct a detailed diagnosis, including an ultrasound examination. Only after this can we talk about modern treatment. The best solution would be to find a good city phlebological center, where the ultrasound will be performed by the phlebologist himself.
What is the modern treatment for venous eczema of the legs in Moscow?
In Moscow, good modern treatment of venous eczema that meets European standards includes innovative technologies for both diagnosis and treatment. Leading city phlebological centers, including our Moscow Innovative Phlebological Center, successfully treat venous eczema. First, a detailed duplex angioscanning of the venous system of the lower extremities is performed. Only then is treatment prescribed, including the fight against local inflammation and modern treatment of the true cause of eczema, varicose veins.
How to treat venous eczema with folk remedies?
Specialists of the Moscow City Phlebological Center have good experience in working with various trophic disorders in venous diseases, including venous eczema. Leading phlebologists at our center do not recommend treating venous eczema with folk remedies. The disease responds well to treatment using modern technologies, but we often encountered serious complications after treatment with folk remedies.
My mother has venous eczema on her legs, which doctor is best to see?
If you suspect that your mother has venous eczema, it is better to first contact a good phlebologist, a doctor specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of venous pathology. First you need to understand the cause of inflammation in the lower extremities. You may need the help of a dermatologist. If eczema is of venous origin, then now there are modern European technologies with the help of which curing your mother will not present any special problems.

![Rice. 1. Functioning of the glymphatic system of the brain (according to [11]) 1. Glymphatic system functioning (according to [11])](https://expert35.ru/wp-content/uploads/ris-1-funkcionirovanie-glimfaticheskoj-sistemy-mozga-po-11-fig-1-330x140.jpg)