Indications for biochemical blood tests
The study is carried out at the first stage of diagnosing any somatic diseases of any profile. It is mandatory to refer a patient for blood biochemistry in case of the following complaints and symptoms:
- Regular disruptions in digestion (nausea, vomiting, heaviness in the abdomen, bloating, flatulence, diarrhea or constipation, heartburn, discomfort in the hypochondrium);
- Sustained pain of any localization (headache, muscle, joint, in the area of internal organs);
- Respiratory disorders (persistent cough, shortness of breath, spasms);
- Signals from the nervous system (tremor of the limbs, chronic fatigue, insomnia, dizziness and fainting);
- Malfunctions of the genitourinary system (changes in the smell and color of urine, changes in the frequency of urination, discomfort during the process);
- Signals from the cardiovascular system (rapid or rare heartbeat, high or low blood pressure);
- Weakness of the immune system, which is expressed in frequent and long-lasting respiratory diseases;
- Pathological changes in the skin and the presence of visible tumors on the body;
- Signs of endocrine disorders (persistent thirst or hunger, sudden changes in weight, constant feeling of heat or cold).
Important Notes
Material for research
Children under 7 years of age: venous blood/capillary blood (for special indications). Children over 7 years of age and adults: venous blood.
Capillary blood collection for research is carried out only for children under 7 years of age and adults whose veins are difficult to access (for special indications)!
According to GOST R 53079.4-2008, indications for taking capillary blood are possible in newborns, in patients with very small or hard-to-reach veins, with large-area burns, and in severely obese patients.
How to prepare for donating blood for “biochemistry”?
In order for the results to be as accurate as possible, you must follow the rules for preparing for a blood test for a biochemical study:
- Within two days, switch to a gentle diet - eliminate fatty, sweet, spicy, salty, smoked foods, and also give up alcohol, coffee and strong tea;
- The day before, refrain from any stressful procedures and activities for the body - baths and saunas, contrast showers, heavy physical activity;
- If you are taking medications, discuss with your doctor whether they will affect the test results;
- 6-12 hours before the BAC, you should not eat any food or smoke. You are only allowed to drink plain water.
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
AST also increases in acute hepatitis and other severe lesions of hepatocytes. A moderate increase is observed in obstructive jaundice, in patients with liver metastases and cirrhosis. De Ritis coefficient, i.e. the ALT/AST ratio, normally equal to 1.33, is lower than this value in liver diseases, and higher in heart diseases.
If the activity of ALT and AST increases, we recommend that you sign up for a consultation with a hepatologist and undergo a liver examination using the Fibroscan apparatus -
Elastometry / elastography of the liver
Decoding and data of normal indicators
The result of the analysis is a conclusion, which is usually a table about the content of chemicals and biological agents in the blood. The first column indicates the indicator, the second - the identified value, and the third - the normal range. Only a specialist, assessing the indicators, can determine the presence of disturbances in water-salt metabolism, identify inflammatory processes and infections, and also assess the performance status of all the patient’s organs.
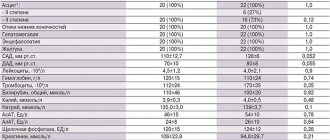
As for normal indicators, the data for adults looks like this:
| Analysis | Men | Women |
| Total protein | 64-84 g/l. | 64-84 g/l. |
| Hemoglobin | 130-160 g/l | 120-150 g/l. |
| Haptoglobin | 150-2000 mg/l | 150-2000 mg/l |
| Glucose | 3.30-5.50 mmol/l. | 3.30-5.50 mmol/l. |
| Urea | 2.5-8.3 mmol/l. | 2.5-8.3 mmol/l. |
| Creatinine | 62-115 µmol/l | 53-97 µmol/l. |
| Cholesterol | 3.5-6.5 mmol/l. | 3.5-6.5 mmol/l. |
| Bilirubin | 5-20 µmol/l. | 5-20 µmol/l. |
| AlAT (ALT) | up to 45 units/l. | up to 31 units/l. |
| ASAT (AST) | up to 45 units/l. | up to 31 units/l. |
| Lipase | 0-190 units/l. | 0-190 units/l. |
| Alpha amylase | 28-100 units/l. | 28-100 units/l. |
| Pancreatic amylase | 0-50 units/l. | 0-50 units/l. |
Decoding the main indicators of the LHC
Total protein.
A biochemical blood test determines the total concentration of various proteins, which consist of amino acids. Protein takes an active part in the processes of coagulation, processing and transport of nutrients to organs and tissues.
Hemoglobin.
This specific protein from the red blood cell system is responsible for transporting oxygen in the body
Haptoglobin.
A blood plasma protein that binds hemoglobin and is responsible for preserving iron in the body. Also involved in the control of local inflammatory processes.
Glucose.
An important component responsible for carbohydrate metabolism. Its content in arterial blood is higher than in venous blood.
Urea.
This is the main product of protein breakdown, in which nitrogen unnecessary by the body is removed in the urine.
Creatinine.
This, like urea, is the end product of protein metabolism. The content of creatinine in the blood depends on gender, age, and muscle mass.
Cholesterol
. A component of fat metabolism, which is also involved in the construction of cell membranes and the synthesis of vitamin D and sex hormones. Another name is cholesterol. There are: total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol.
Bilirubin
. The breakdown product of hemoglobin, a toxic substance of two types: direct and indirect. They form a “general” one and the norm when deciphering a biochemical blood test is indicated specifically for it.
AlAT (ALT).
Alanine aminotransferase is an enzyme contained in the cells of the liver, kidneys and heart, so its presence in the blood indicates the destruction of the cells of these organs.
AST (AST).
Aspartate aminotransferase is a cellular enzyme that is involved in the metabolism of amino acids and is found in the liver cells of the heart and kidneys.
Lipase.
An enzyme that promotes the breakdown of fats.
Amylase.
It breaks down carbohydrates from food and ensures their digestion. There are alpha-amylase (diastase) and pancreatic amylase.
It is important to remember that only a specialist can evaluate the results of a blood test, decipher a biochemical analysis, make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment!
Description
AST catalyzes the transamination reaction, which results in the conversion of oxaloacetate (oxaloacetic acid, OA) to aspartic acid (aspartate) by transferring an amino group to the OA molecule. The second product of the reaction is α-ketoglutaric acid (α-ketoglutarate), one of the intermediate products of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. The reaction plays an important role in the process of releasing ammonia from amino acids. The ammonia is then processed in the urea cycle, since the aspartate obtained during the reaction is needed to form argininosuccinate. In addition, in the process of reverse reaction, aspartate is converted into oxaloacetate. Thus, this reaction is of great importance in the processes of gluconeogenesis. For diagnostic purposes, determination of AST activity is usually carried out in conjunction with determination of the activity of another aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase (ALT, ALT). Both enzymes are present in cells of various tissues, but ALT is present in significant quantities only in liver tissue. In myocardial tissue and skeletal muscles, the amount of AST is 20 times higher than the level of ALT. Sometimes very high AST activity is observed, which can exceed the normal limit by 100 times. This occurs in diseases associated with severe tissue damage - acute hepatitis, compartment syndrome, tissue hypoxia. In case of hepatitis, AST readings exceed the norm by 10–20 times and this occurs during the prodromal stage (at the time of the appearance of jaundice or shortly before that). During myocardial infarction, AST activity increases after 12 hours. The peak of activity occurs 24–36 hours after a heart attack and is 10 times higher than normal. Then the indicators decrease within two to three days, which is evidence of the absence of damage to the heart muscle.
In most diseases associated with an increase in AST concentration, there is a simultaneous, although less high, increase in ALT concentration. However, with hepatitis, the activity of ALT in the blood plasma may exceed the activity of AST. AST concentration is often measured as part of a “biochemical profile.” AST concentrations exceeding the upper limit of normal by more than 20 times are most often observed in the prodromal stage of viral hepatitis. A doubling of concentrations is sometimes observed in the absence of clinical symptoms of tissue damage. The cause in this case is most often alcohol abuse. This enzyme does not have tissue-specific isoforms, and if no other biochemical abnormalities are found and no obvious reasons for such an increase, then the analysis should be repeated after 2-3 weeks.
What to look for first?
According to therapists, the main parameters are the level of hemoglobin, platelets, leukocytes and ESR, also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. And also the leukocyte formula - the percentage of leukocytes of different types.
Hemoglobin, an iron-containing protein in red blood cells that is responsible for gas exchange and metabolism, is the first thing therapists look at. Hemoglobin levels in women are lower than in men due to differences in muscle mass. Elevated levels are much less common than low levels and may hint at pathologies of the heart, kidneys or bone marrow. He is referred to a hematologist, unless the patient is a donor. After a transfusion, their red blood cells are restored sharply, so their number increases greatly and they have to continue donating blood to maintain balance. But the decrease is most often caused by an unbalanced diet, physical overload and liver disease. A greatly reduced reading is a sign of more serious problems.
“If a man has very low hemoglobin, I suspect bleeding,” Shcherbina shares her experience. “Perhaps tiny drops of blood are released in the stomach or intestines, perhaps it’s hemorrhoids, or the ureter is bleeding due to urolithiasis. In women, this, coupled with pallor, indicates serious anemia.”
Platelets are responsible for blood clotting. If their level is low, the patient will not be taken for surgery - it will not be easy to stop the bleeding. At elevated levels, there is a high risk of thrombus formation—blood clots that block a vessel and cause a heart attack or stroke. The level of platelets indicates the condition of blood vessels, and in combination with others helps to understand the nature of many diseases.
Leukocytes protect the body from infections, viruses and allergens. Before the healthcare reform in Russia, the norm was considered to be (6−8)*109/l, now (4−11)*109/l. A deficiency of white blood cells may indicate problems with the immune system, a lack of B vitamins, or a malfunction of the bone marrow. An elevated level indicates inflammation in the body, and the degree of its intensity helps to understand the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
“If leukocytes are less than 4*109/l, ESR is more than 30 mm/h, and in the leukocyte formula neutrophils are increased to 70−80%, I am looking for a source of inflammation,” says Victor Shcherbina. — At a temperature below 40 °C it can be pneumonia or acute prostatitis. If the situation is the opposite - an excess of leukocytes and a lack of neutrophils, I suspect lymphocytic leukemia and refer to a hematologist.”
Thus, the leukocyte formula helps to understand the source of problems based on the immune reaction: as a rule, only cells, for example, lymphocytes, react to viruses, and neutrophils react to bacteria. According to Andrey Besedin, for example, inflammation can be caused by both viruses and bacteria, and leukocyte counts are needed to determine treatment tactics and monitor the patient.
Amino acids and proteins
Protein often decreases during fasting or when following diets, but it can indicate a number of pathologies: chronic bleeding, problems with metabolic processes, anemia. Underestimated data is the norm during breastfeeding, during pregnancy (late pregnancy), for bedridden patients or in case of significant physical exertion.
The interpretation of the tests taken during blood biochemistry is considered carefully and normal values should not be exceeded. The protein is present in excessive amounts in individuals with autoimmune diseases, during infections, in cases of significant kidney pathologies or in the presence of malignant tumors.
Reduced levels of amino acids are a bad indicator, observed when there are problems in metabolic processes, often resulting in kidney or liver problems.
Data on microelements and vitamins
Often, normal blood biochemistry levels are checked when clarifying vitamin levels in men or women. Attention should be paid to sodium and potassium. If there is too much sodium, you may experience muscle cramps, irritability and excessive thirst. A minimal amount of the element leads to headaches, the desire to constantly sleep, vomiting, and coma.
If potassium is elevated, arrhythmia, underestimation of blood pressure, and confusion are possible. Vomiting and nausea are signs of low potassium, and sometimes the condition leads to involuntary bowel movements or urination.
Norm of AST in the blood
In order to correctly evaluate the obtained indicators of plasma enzymatic activity in relation to AST, you need to know its normal values. Most laboratories usually indicate the norm next to the result obtained. This is due to the fact that different reagents and methods can be used to determine the AST indicator. The types and standards given in the table are considered generally accepted.
| Determination method | Norm for men | Norm for women | Norm for children |
| Optical (in ME) | Up to 40-41 IU | Up to 34-35 IU | Up to 50 IU |
| Reitman-Frenkel reactions (in mcomol/(h/ml)) | 0,1-0,45 | 0,1-0,35 | 0,2-0,5 |
If a biochemical blood test yields AST values that do not exceed standard values, this indicates the normal functioning of the enzyme systems of the heart and liver and the preserved integrity of the cellular composition of these organs. If there are clinical symptoms of their damage, other specific markers (ALT, troponins, creatine phosphokinase, etc.) must be examined!
If medications are the cause of the increase
Often in women over the age of 50, an increase in enzyme levels occurs from prolonged drug treatment. These may be hormones, antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs. If you notice that the enzyme increases after taking medications, you need to contact your doctor to adjust your therapy. You can replace toxic drugs with gentle ones that will not be harmful to your body.
With the development of high technology, medicine can use blood tests to identify more and more problems in the body. Today, despite the fact that enzyme analysis began to be carried out quite recently, it is already used everywhere. Today, not a single operation is performed without this study; it is prescribed to patients with various ailments. Thanks to this, doctors can now quickly and painlessly identify many diseases at an early stage, which means timely treatment and prevention of dangerous conditions.