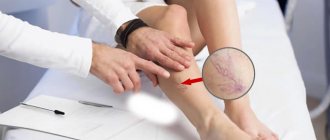
Causes of thrombosis
The main cause of arterial thrombosis is atherosclerosis, in which clots of fats or calcium compounds form on the walls of the arteries. They narrow the artery and can completely block blood flow or break off and block smaller vessels.
The development of arterial thrombosis in the vessels of the brain results in strokes, and in the coronary arteries - myocardial infarction.
There are many more reasons for the formation of venous blood clots:
- varicose veins of the lower extremities;
- loss of mobility, both complete and partial;
- bone fractures;
- hypercoagulability and other autoimmune disorders;
- heredity.
Thrombosis: causes, prevention
Thrombosis can occur in veins, arteries and microvessels. When the integrity of blood vessels is damaged, the formation of a primary blood clot is observed - this is a life-saving reaction that protects the body from bleeding. But absolute harm comes from uncontrolled continued thrombus formation, in which the resulting primary thrombus begins to grow without stopping, clogging the lumen of the vessels further and further - secondary thrombosis. The latter is a serious and dangerous disease. It is also dangerous because such blood clots can break off and, spreading with the blood, cause severe embolism in important organs, primarily the lungs.
The causes of thrombosis can be internal and external. The latter are most often associated with trauma (for example, one that causes bone fractures), leading, among other things, to damage to the integrity of the vein wall. The growth of a blood clot begins from this area. This situation is possible even with normal blood clotting, and even more so in cases where the body has a predisposition to increased clotting.
Internal causes in a number of people consist of altered blood proteins involved in the process of hemostasis. This condition is called thrombophilia. At the same time, both their quantity in the blood and their structure change. These changes can be congenital or acquired and are easily detected in the laboratory. In some cases, such changes are caused by gene disorders, which are revealed by molecular genetic research.
Developed concomitant diseases also contribute to thrombosis: varicose veins of the saphenous veins, capillary vessels, coronary heart disease, previous myocardial infarction, hypertension, obliterating atherosclerosis of the arteries, cancer, diabetes mellitus, previous sepsis, injuries, including bone fractures. Predisposing factors are also chemotherapy, hormone replacement therapy and use of contraceptives, unfavorable obstetric history: miscarriages, miscarriage, placental insufficiency, toxicosis, placental abruption.
Prevention of thrombosis should be carried out systemically and in several ways. First of all, it is important to find out the family predisposition and, in the presence of thrombosis of any location on the paternal or maternal side, conduct a biochemical and molecular genetic blood test for thrombophilia. The latter especially makes sense in the presence of so-called risk factors for thrombosis. These include: excess body weight, long-term smoking, diseases of the leg veins, impaired fat metabolism and high cholesterol, prolonged immobile sitting or standing and frequent hypothermia during production activities, etc.
When identifying a predisposition, one should strive to combat physical inactivity and limited walking as much as possible. It is necessary to modernize the working environment so as to achieve maximum activation and, above all, the work of the venous heart - the muscular-venous pump of the lower leg (therapeutic exercises, walking). In a sedentary profession (accountant, office manager, programmer), it is useful to take breaks every 30-45 minutes, walk a little or perform, as they said before, industrial gymnastics. It works if you train yourself to move your feet and fingers while working while sitting at a table. This can be done unnoticed by others. If possible, to relieve congestion in the legs, it is useful to periodically take a cowboy pose (leaning back in a chair, placing your feet on the edge of the table above heart level).
It is important to take advantage of every opportunity to walk and move your legs. The advice of the ancient Chinese is useful, they recommended taking 10 thousand steps daily. In this regard, a car, as a means of transportation, greatly robs one’s health. In some cases, forced immobilization occurs when traveling for many hours by transport: plane, bus, car. Drinking plenty of fluids, moving the ankle and knee joints, and changing body positions are in such cases an important means of preventing thrombosis.
Harmful circumstances leading to thrombosis are infections that also affect the inner lining of blood vessels. The most significant among them are viral infections of the upper respiratory tract. This is why such infections should not be carried on the legs, especially if there are signs of venous disease in the legs.
In the prevention of thrombosis, measures such as: giving up bad habits are also important; wearing compression hosiery (socks, stockings, tights); refusal to wear clothes that compress various parts of the body (belts, tight elastic bands on underwear, tight-fitting clothes, corsets, tight shoes); refusal to stay outside during heat or cold, taking hot baths and other thermal procedures, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight; following a diet that prevents blood clots. Also, you need to remember. That self-medication is dangerous, and medications should only be taken as prescribed by the attending physician.
Prevention of thrombosis includes a wide range of tasks, and it should be carried out in broad and narrow versions. An important place is occupied by the activation of the patient and the normalization of physical activity, the restoration of a healthy lifestyle, as well as the use of special medical devices in the most critical periods of life (travel, work overload, surgery, etc.) or for life.
Memo for the population
Prevention of thrombosis
Thrombosis is the intravital formation of a dense blood clot in the cavities of the heart or the lumens of blood vessels. It can develop in arteries, veins or capillaries.
The causes and triggers of this pathological condition can be various external and internal factors:
- age;
- blood clotting disorders;
- elevated cholesterol levels;
- smoking and alcohol;
- injuries;
- hereditary diseases;
- obesity;
- kidney diseases;
- sepsis;
- taking hormonal contraceptives or hormone therapy;
- chemotherapy;
- postoperative period;
- adynamia;
- prolonged forced poses;
- hypothermia;
- oncological diseases;
- pathologies of blood vessels.
The vessels of the heart and veins of the lower extremities are most often affected by thrombosis. First, a primary thrombus appears on the wall of the vessel, which begins to grow, increases in size and at a certain moment completely clogs the lumen of the artery, vein or capillary. This condition is already called secondary thrombosis, and it becomes a dangerous and serious disease. Under the influence of various reasons, blood clots can break away from the wall of a blood vessel and enter various vital organs (primarily the lungs) through the bloodstream, causing embolism. External causes of blood clots are most often associated with injuries that lead to disruption of the integrity of blood vessels. It is from this area that the formation of a blood clot begins. This development of events can occur against the background of normal blood clotting, and with a predisposition to an increased level of coagulation. Internal causes of thrombus formation are changes in blood proteins involved in blood clotting. This blood condition is called thrombophilia. With it, both the quantity of these proteins and their structure can change. Such pathologies can be acquired or congenital, and they are easily detected by laboratory tests. Another equally common internal cause of thrombus formation can be vascular pathologies. Varicose veins or atherosclerosis of the arteries leads to disruption of the structure of blood vessels and blood clots are most likely to settle on such vascular walls. Understanding the causes of blood clots can significantly help a person who does not have a medical education to prevent the development of thrombosis.
Preventive actions
Prevention of thrombosis should always be carried out in several ways and in a comprehensive manner. First, it is necessary to determine the possibility of a family predisposition, and in the presence of thrombosis of any location on the maternal or paternal side, conduct a molecular genetic and biochemical blood test to detect thrombophilia. Such measures are especially relevant for individuals who have at least one factor suggesting the development of thrombosis. An examination for thrombophilia is also indicated if the patient has a history of causeless and recurrent thrombosis, which appeared against the background of minor predisposing factors, such as minor injuries, taking oral contraceptives, pregnancy, travel, etc. This group of people includes people under 50 years of age . After identifying a tendency to thrombosis, their active and comprehensive prevention should begin. In most cases, it is indicated for men after 40 years of age, and for women after 50. Here are the main measures that need to be taken in order to avoid problems with blood clots: normalization of physical activity and the fight against physical inactivity, proper organization of working conditions, industrial and therapeutic exercises, walking in the fresh air, following the advice of the ancient Chinese about 10 thousand steps daily. Proper organization of long hours of travel by plane, car or bus: movements in the knee or ankle joints, drinking plenty of fluids, frequent changes of position, comfortable clothes. Prevention of infectious diseases: hardening the body, maintaining immunity, rational and fortified nutrition. Quitting bad habits: fighting smoking and drinking alcohol helps improve blood quality and prevents the development of vascular diseases. Wearing compression hosiery (socks, stockings, tights). Refusal to wear clothes that compress various parts of the body (belts, tight elastic bands on underwear, tight-fitting clothes, corsets, tight shoes). Refusal to stay outside during heat or cold, take hot baths and other thermal procedures, or stay in direct sunlight for a long time. Following a diet that prevents blood clots. Taking medications during critical periods of life and during excessive stress - anticoagulants, bioflavonoids, antiplatelet agents, nicotinic acid, folic acid, vitamins B6, B12 and E are prescribed (all drugs should be prescribed only by a doctor). How to deal with stretch marks during and after pregnancy? The well-being of the unborn baby largely depends on the well-being of the mother. Therefore, taking care of yourself on these important days is as important as taking care of your baby. Experts have developed a line of products to combat stretch marks and swelling of the legs. Prevention of thrombosis during surgical interventions can be classified as a separate category. It should be performed in all patients for whom surgical treatment is indicated, regardless of the likelihood of developing thrombosis. To implement it, physical and general methods of prevention are used: preference for minimally invasive operations, which are carried out in a shorter time and with minimal tissue trauma; the patient wearing special elastic compression hosiery; pneumomassage for the lower extremities; getting up and walking early after surgery; the patient's optimistic attitude towards treatment. For patients who require surgical treatment and who have serious risk factors for the development of thrombosis, drug protection before and after surgery with new generation anticoagulant drugs is indicated. General principles of diet for the prevention of thrombosis. The diet of people at risk of developing blood clots should include a variety of foods: cereals, fresh fruits, berries and vegetables, lean meats, dairy products and vegetable oils. The daily menu should include plant-based insoluble and soluble fibers that promote normal intestinal function and lower cholesterol levels. Eating foods high in Omega-3 is important. To do this, you can include fish (salmon, mullet, sardines, tuna, mackerel) and fish oil in your diet. These dietary changes will help reduce triglyceride levels and blood viscosity. It is recommended to season dishes with vegetable oils with the addition of garlic or ginger. This will help thin the blood and normalize blood circulation. Foods rich in flavonoids, the leader among which are red grapes, also help reduce the risk of blood clots. They can be: dry red wine (up to 100 ml per day), natural grape juice and fresh red grapes. The menu should include more foods high in vitamin E: wheat germ, flaxseed and olive oils, flax and sunflower seeds, wholemeal flour and avocado. This vitamin acts as an antioxidant and has a number of positive effects: strengthens blood vessels, has an anti-sclerotic effect, prevents the development of coronary heart disease and strengthens the immune system. It is recommended to exclude the following products from the diet: margarine; fatty meats; butter; chocolate; smoked meats; hard cheeses; cakes and other confectionery products with a high fat content. Avoid consumption of: sugar; refined flour; offal; egg yolks (no more than 3 pieces per week); carbonated drinks. The range of food products indicated for creating a diet for the prevention of thrombosis is extremely wide. From them you can easily create a varied menu for every day. Vascular thrombosis affects about 70% of the world's population. That is why knowing the reasons for its development and taking preventive measures to prevent it are so important for each of us.
Since thrombosis of arteries or veins is only a symptom of a disease, a doctor who treats this disease can talk about its prevention and treatment: a cardiologist, neurologist, vascular surgeon, phlebologist. A competent ultrasound diagnostic doctor provides invaluable assistance in diagnosing thrombosis. In case of recurrent thrombosis, consultation with a hematologist is necessary to exclude blood diseases.
Compliance with the above recommendations can significantly reduce the risk of thrombosis and improve a person’s quality of life.
About holding Health Day on the topic
“Reduce the risk of thrombosis!”
On December 24, 2021, the State Budgetary Institution “Center for Medical Prevention” of the Ministry of Health of the Krasnodar Territory will organize the next Health Day, which is held as part of Thrombosis Prevention Day under the motto “Reduce the risk of thrombosis!” Health Day is held according to a program of large-scale regional medical and social events with the aim of preventing atherosclerosis and diseases of the cardiovascular system, promoting the principles of a healthy lifestyle. An indicative Health Day with the participation of regional specialists will be held in the Timashevsky district. During the Health Day, organized jointly with the district administration and with the participation of the press, diagnostic tests, consultations, lectures, propaganda and festive events will be carried out.
The problem of frequent development of thrombosis has acquired social significance, and many doctors point to the need to popularize information about the prevention of blood clots among the population. Strokes, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, thrombosis of peripheral arteries and veins - all these pathological conditions and diseases can significantly harm health and shorten a person’s life. Many situations can provoke the formation of thrombosis: childbirth, any trauma, even brilliantly performed surgical operations, banal ARVI, etc. Such complications can not only turn a person into a disabled person, but also take his life. That is why it is important to pay attention to the prevention of thrombosis.
There are primary and secondary prevention. If the first option is used in the presence of a family predisposition, the presence of risk factors, and positive results of laboratory tests for thrombophilia, then secondary prevention is important in cases where a person has already suffered thrombosis. At the same time, the task is set to ensure that it does not repeat itself in the future. This problem is solved by a set of measures, including the multi-month prescription of medications (including anticoagulant) drugs.
Although some permanent factors cannot be eliminated (for example, unfavorable heredity, age), it is possible to eliminate and minimize transient risk factors: immobility, vascular diseases, fat metabolism disorders, smoking, etc. An important means of prevention is the use of compression hosiery. Depending on the condition of the legs and the ambient temperature, knee socks, stockings or tights may be used. Drug protection of people with an average degree of risk should be carried out during critical periods of life and during overloads, which increase the risk of blood clots, but which cannot be completely eliminated.
It is very important to timely assess the existing risks and, with the help of competent specialists, choose an adequate treatment program and a rational set of preventive measures.
GBUZ "Center for Medical Prevention" of the Ministry of Health of the Krasnodar Territory.
Mechanism of thrombus formation
The formation of a blood clot always follows one scenario: first, damage occurs (trauma to the vessel wall), platelets rush to the site of damage, which stick together into a strong clot and adhere to the wound. Next, fibrin threads are formed, and the vessel receives a “patch.” Over time, the tissues are restored, the blood clot dissolves as unnecessary.
A useful mechanism that saves people from blood loss due to injury can become dangerous when there is an excess of platelets - thrombophilia. An excess of these blood cells results in blood clots that are too large for minor injuries. The second important factor in thrombus formation is the very presence of damage. Thrombosis becomes a pathology if it begins in the absence of injury to the vascular wall.
Risk area
The risk of developing vein thrombosis increases with:
- hormonal therapy;
- presence of deep vein thrombosis in relatives;
- pregnancy;
- injury to veins during operations, fractures, cuts;
- physical inactivity;
- increased blood clotting;
- use of venous catheters;
- obesity;
- oncology;
- heart and lung diseases.
Arterial thrombosis is more likely to develop:
- for diabetes;
- high blood pressure;
- obesity;
- low activity;
- bad heredity;
- poor nutrition;
- high levels of bad cholesterol;
Older age increases the risk of both types of thrombosis.
Types of thrombosis
The two main types of disease are arterial and venous, but there are two large groups of patients that require more detailed consideration. Many doctors distinguish these variations into separate types of thrombosis.
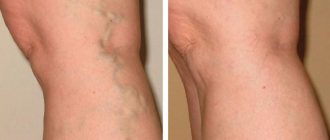
- Superficial vein thrombosis, or SVT, is when a blood clot blocks the superficial veins of the upper or lower extremities. Accompanied by a characteristic pattern of a darkened vein, its obvious relief. About 10% of cases of TPV, for which treatment was not started, result in serious complications, including tissue necrosis.
- Deep vein thrombosis, or DVT, occurs when a blood clot blocks the deep veins in the lower extremities or pelvis. Causes blood stagnation in the lower extremities, reduces the flow of oxygen-free venous blood to the heart, and significantly increases the risk of pulmonary embolism.
Blood clot prevention: an alternative to aspirin
Atherothrombosis is the main cause of myocardial infarction and one of the main factors in the development of stroke. The risk of atherothrombosis can be reduced with antiplatelet therapy. We talked about prevention with acetylsalicylic acid in the previous article “Blood clots and acetylsalicylic acid.” However, in addition to it, other antiplatelet agents are also used.
Handyman
Let's begin the description of the representatives of the group of antiplatelet agents with dipyridamole (Curantil), which has been used for many decades. The drug blocks the enzyme phosphodiesterase, which breaks down a compound called cyclic AMP (cAMP), thereby causing increased levels of this substance in the blood. At high concentrations, cAMP prevents platelets from sticking together and prevents blood clot formation.
The ability of the drug to reduce the risk of vascular accidents in patients who have suffered vascular ischemia is confirmed by Cochrane data1. Indications for the use of dipyridamole include the prevention of arterial and venous thrombosis, including after installation of stents and coronary artery bypass grafts.
However, today dipyridamole is not prescribed for the prevention of strokes as part of monotherapy, since it is significantly inferior in activity to modern antiplatelet agents. But it has found quite widespread use as a drug that normalizes blood flow in cases of cerebrovascular accidents, as well as placental insufficiency in pregnant women. In addition, it increases the body's resistance to viral infections - influenza and ARVI - and is used for the prevention and treatment of these diseases.
Modern and famous
Drugs of a potentially new class - P2Y12 receptor inhibitors - have become hope and support for many people who suffer from heart and vascular diseases or have already suffered a heart attack or stroke. These receptors located on the surface of platelets play a central role in platelet activation, their subsequent “clumping” and blood clot formation. Blocking the P2Y12 site can effectively resist thrombosis and thus reduce the risks of cardiovascular accidents.
One of the first drugs in this series of antiplatelet drugs was clopidogrel, which appeared on the market in the late 1990s under the trade name Plavix. Its antiplatelet effect appears just a few hours after taking the first 75-milligram dose (working dosage of the drug), and the drug has its maximum effect after 3-7 days of regular use. If you need to get immediate results, “loading” doses of 300–600 mg are prescribed. In such situations, clopidogrel has a powerful antithrombotic effect just a few hours after administration.
The original clopidogrel, Plavix, is registered in more than 100 countries around the world and is one of the drugs whose sales reach several billion dollars per year2. Until the patent expired, Plavix was the world's second-leading seller. Today, dozens of generic clopidogrel are available in pharmacies, which, of course, has greatly increased its availability.
In addition, other drugs from the group of P2Y12 inhibitors have already been registered in the Russian Federation. Prasugrel (trade name Effient), ticagrelor (Brilinta), ticlopidine (Ticlid) are widely used in clinical practice for the prevention of stroke, myocardial infarction and death from vascular disease in patients who have had a stroke or suffer from coronary heart disease or chronic diseases of the lower extremities ( intermittent claudication). The effectiveness of all drugs in this group, without exception, has been confirmed by many clinical studies and cannot be doubted.
It should be noted that the original prasugrel, ticagrelor and ticlopidine, like the original clopidogrel, are quite expensive. However, the vital indications for which they are prescribed and the results they provide make the investment worthwhile.
One drug is good, but two are better
Antiplatelet drugs definitely help reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, but sometimes resistance to the drugs develops and the likelihood of vascular events increases dramatically. Combination therapy, in which several drugs are prescribed at once, helps to overcome resistance.
Most often we are talking about two drugs, this is called double therapy. Increased effectiveness of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) compared to the use of a single drug is achieved due to the influence of drugs with different mechanisms of action on different stages of thrombus formation.
One of the essential components of DAT is always acetylsalicylic acid. Almost all people with coronary heart disease must take it constantly throughout their lives. The second component of the regimen is usually a P2Y12 inhibitor - clopidogrel, prasugrel or ticagrelor. The doctor decides which of the three drugs will be prescribed, based on the individual risk of blood clots and bleeding, the likelihood of which, alas, increases when taking antiplatelet agents.
The duration of dual antiplatelet therapy is also determined in each case. Patients who have had a myocardial infarction may be prescribed a combination of drugs for at least one year. If the risk of bleeding is low, DAPT may be extended. For patients after coronary artery stenting or those with a high risk of bleeding, DAPT is prescribed for at least a month.
Combination drugs that reduce the risk of thrombosis also include combinations of aspirin with dipyridamole (Agrenox) and aspirin with magnesium hydroxide (Cardiomagnyl). They have nothing in common with standard DAPT, which is based on a combination of acetylsalicylic acid + a P2Y12 inhibitor.
The first is approved for secondary prevention of stroke, but it is significantly inferior in activity to combinations with P2Y12 inhibitors. And the drug Cardiomagnyl is aimed at reducing the negative effect of acetylsalicylic acid on the gastric mucosa due to the absorption of hydrochloric acid by magnesium hydroxide. This improves aspirin tolerability, which is important during long-term treatment.
Marina Pozdeeva
Photo istockphoto.com
1 De Schryver EL, Algra A, van Gijn J (2007). Algra A, ed. Dipyridamole for preventing stroke and other vascular events in patients with vascular disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (2): CD001820.
2Top Ten Global Products – 2007″ (PDF). IMS Health. 2008-02-26.
Products by topic: (dipyridamole), (clopidogrel), (prasugrel), (ticagrelor), (Agrenox), [product strict="Cardiomagnyl"](Cardiomagnyl), (Thrombomag), (Trombital), (Fazostabil)
Deep vein thrombosis: causes, clinical picture, treatment
The mechanism of blood clot formation allows you to quickly cope with vascular damage, but sometimes the blood clotting process is disrupted, and blood clots occur without external influence, creating a risk to health and life. Deep vein thrombosis most often occurs:
- in older people;
- in patients after laparoscopy or surgery on large joints;
- with severe physical inactivity;
- after fractures and ruptures of internal organs (accidents, fights, etc.);
- during pregnancy and childbirth - in pregnant women, blood clotting is increased;
- with long-term use of oral contraceptives;
- in smokers.
The main symptom of DVT, which occurs when the blood clot is located above the lower leg, is swelling and pain in the affected limb.
General symptoms of thrombosis
The disease is quite difficult to identify in the early stages, but there are a number of signs that should alert the patient:
- swelling of the limbs in the evening;
- the appearance of a network of dilated vessels;
- fast fatiguability;
- sudden lameness after exercise;
- cold extremities;
- difficulty breathing;
- pain in the chest and back after stress and physical activity;
- dizziness and tinnitus;
- problems with coordination of movements;
- bloating, indigestion. abdominal pain without clear localization.
Since the primary signs of thrombosis can also be a consequence of other diseases, a complete diagnosis of the body is necessary. The localization of problematic sensations is not always directly related to the area of thrombus formation. For example, dizziness can also occur with damage to the coronary arteries - due to tissue hypoxia.
Specific signs of a blood clot
If treatment of the disease is not started in the early stages, more distinct signs appear that make it possible to recognize a blood clot:
| Type of thrombosis | Symptoms |
| Deep veins of the leg | cold hands or feet, fatigue, low exercise tolerance, intermittent claudication after a long walk |
| Pulmonary artery | Sudden onset of shortness of breath, bluish skin with a gray tint, drop in pressure, chest pain, heart rhythm disturbances, bulging neck veins, fainting, cough, wheezing, pinkish sputum, increased body temperature, pain in the right hypochondrium. |
| Coronary arteries of the heart | Pain behind the sternum, radiating to the back and neck, occurs during stress, physical activity, and is accompanied by shortness of breath and rapid heartbeat. |
| Arterial network of the legs | Chilliness, numbness of the feet, burning, pain when walking, which stops when you stop, the skin becomes pale, and then the fingers turn blue. |
| Cerebral arteries | Dizziness, unsteadiness, various visual disturbances, unclear speech, decreased muscle strength and sensitivity in the arm and leg, memory loss. |
In general, the main symptoms of extremity vein thrombosis are:
- swelling;
- heaviness in the arms or legs;
- fatigue;
- redness and swelling of the skin in the area of the blood clot;
- pain on palpation along the vein;
- local temperature increase.
Thrombosis of deep veins and internal vessels is much more difficult to determine; as a rule, the patient learns about them from the doctor, and the initial complaint may not have any connection with the formation of a blood clot.
When to see a doctor
The patient’s subjective sensations are extremely important for timely diagnosis of the disease. That is why you should not delay seeing a doctor if:
- there was a feeling of fullness in the legs when walking;
- the limbs are decorated with vascular mesh;
- often the heart hurts or the left side of the body goes numb - angina pectoris;
- there were sudden problems with vision, hearing, diction, swallowing, coordination;
- cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, weakness appeared;
- the kidneys or one kidney are sick. There was blood in the urine.
It is worth noting that a timely visit to a doctor with such signs can protect patients from heart attack, stroke, pulmonary embolism and other complications with high mortality.
UZ "Mogilev City Emergency Hospital"
Thrombophlebitis is a disease based on inflammation of the wall of a venous vessel and the formation of a blood clot in it. As a rule, thrombophlebitis develops against the background of varicose dilatation of blood vessels, mainly affecting the superficial veins of the legs. The danger of the process is that if the deep venous vessels of the lower extremities are damaged, it can lead to the development of complications such as pulmonary embolism, heart attack, and pneumonia.
Risk factors for thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities include:
- age over 40 years;
- sedentary lifestyle, work involving long periods of standing or sitting (drivers, surgeons, programmers, hairdressers);
- long bed rest;
- pregnancy, childbirth;
- diabetes mellitus, heart disease;
- varicose veins;
- taking hormones, chemotherapy;
- operations;
- obesity, excess weight more than 30%.
Causes of development of thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities.
A favorable condition for the development of thrombophlebitis is varicose veins of the lower extremities. In this case, there is stagnation of blood in the veins, weakness of the venous walls, venous insufficiency, increased venous pressure and deformation of the venous walls. All of these factors are enough for any infection to penetrate the vessel wall and cause inflammation. Reduced immunity, thickening of the blood caused by illness or medication also facilitate the establishment of infectious pathogens on the vascular wall. Thrombophlebitis can be triggered by injury to the venous wall, a medical procedure (intravenous injection, catheterization of a vein, vascular surgery, etc.), an infectious disease, for example, influenza, ARVI, pneumonia, tonsillitis, tuberculosis.
Classification of thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities
According to etiology, venous thrombosis is distinguished:
- congestive (with varicose veins of the lower extremities, due to extravenous compression of the veins and intravenous obstruction to blood flow);
- inflammatory (post-infectious, post-traumatic, post-injection, immuno-allergic);
- in case of disruption of the hemostasis system (for cancer, metabolic diseases, liver pathology).
By localization:
- thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins of the lower extremities (main trunk of the great, small saphenous veins, tributaries of the saphenous veins and their combinations);
- deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities (tibio-popliteal segment, femoral segment, iliac segment and their combinations).
Depending on the connection between the blood clot and the vein wall, the following options are possible:
- occlusive thrombosis,
- mural thrombosis,
- floating,
- mixed.
Symptoms of thrombophlebitis of the lower extremities
Acute thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins of the lower extremities often develops in the great rather than in the small saphenous vein and its tributaries and is, as a rule, a complication of varicose veins. It is characterized by the severity of local inflammatory changes in the area of the affected saphenous veins, so its diagnosis is simple and accessible. Spontaneous thrombophlebitis without varicose veins is often a consequence of gynecological pathology or the first symptom of a malignant neoplasm of the gastrointestinal tract, prostate, kidneys and lungs. The first manifestation of the disease is pain in the thrombosed area of the vein. Along the course of the compacted vein, skin hyperemia appears, infiltration of surrounding tissues occurs, and a picture of periphlebitis develops. Palpation of the thrombosed area of the vein is painful. There may be a deterioration in general health, manifested by symptoms of a general inflammatory reaction - weakness, malaise, chills, increased body temperature to subfebrile levels, and in severe cases to 38–39 ° C. Regional lymph nodes are usually not enlarged. The most characteristic clinical sign of acute deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities is sudden pain that intensifies with physical exertion (walking, standing). Then tissue swelling occurs, accompanied by a feeling of fullness and heaviness in the limb, and an increase in body temperature. The skin distal to the site of thrombosis is usually cyanotic and shiny. The temperature of the affected limb is 1.5–2°C higher than that of the healthy one. The pulsation of peripheral arteries is not impaired, weakened or absent. On the 2nd–3rd day from the onset of thrombosis, a network of dilated superficial veins appears.
Deep vein thrombosis, when only the veins of the calf muscles or 1-2 deep main veins are involved in the process, is accompanied by an erased clinical picture. The only sign of thrombosis in such cases is pain in the calf muscles and slight swelling in the ankle area. Clinical manifestations of thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins of the lower extremities and deep vein thrombosis are not always specific. In 30% of patients with superficial thrombophlebitis, the true prevalence of thrombosis is 15–20 cm higher than the clinically detectable signs of thrombophlebitis. The rate of thrombus growth depends on many factors and in some cases it can reach 20 cm per day. The moment of transition of thrombosis to deep veins occurs secretly and is not always determined clinically. Therefore, in addition to the data of a general clinical examination, the presence of thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities is confirmed on the basis of special diagnostic methods.
Methods for diagnosing deep thrombosis and thrombophlebitis of the superficial veins of the lower extremities
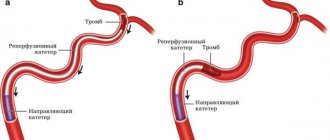
There are many methods for examining the venous system of the lower extremities: Doppler ultrasound, duplex scanning, phlebography, CT phlebography, photoplethysmography, phleboscintiography, phlebomanometry. However, among all instrumental diagnostic methods, ultrasound angioscanning with color mapping of blood flow has the maximum information content. Today, the method is the “golden” standard for diagnosing venous pathology. The method is non-invasive, allows you to adequately assess the condition of the vein and surrounding tissues, determine the localization of the thrombus, its extent and the nature of the thrombosis (floating, non-occlusive parietal, occlusive), which is extremely important for determining further treatment tactics.
Treatment
Treatment for the acute form of the disease is selected based on the condition of the blood vessels, the nature of the disease, and the location of the blood clot. Typically, conservative therapy is used for this, which includes local and general treatment. Patients are sent to the hospital.
Conservative therapy includes the following procedures:
- Applying one of the ointments: Vishnevsky or heparin.
- Semi-alcohol compresses or cold treatment, with mandatory elastic bandaging.
- For oral administration, drugs that help improve blood microcirculation, such as Trental, etc., are recommended.
- Chimes, aspirin, etc. are prescribed as inhibitors.
- Troxevasin, phlebodia, and detralex can be used to correct impaired blood flow in the veins.
- Drugs for pain relief, reduction of inflammation and reduction of temperature - analgin, ketarol, etc.
- For desensitization - suprastin, diphenhydramine, etc.
- Anticoagulant therapy – heparin, warfarin, etc.
After the acute inflammatory process has been relieved, physiotherapeutic treatment with diametric currents and UHF is recommended to increase the efficiency of blood clot resorption. Iontophoresis with heparin and proteolytic enzymes (chymotrypsin, trypsin, etc.) gives good results. Elastic compression should be continued for another two months after completion of the main treatment, while taking phlebodynamic drugs.
Surgical intervention is performed in emergency cases, for the following indications:
- Ascending thrombophlebitis of the large or small saphenous, superficial vein in an acute form, located on the upper or middle part of the thigh.
- Threat of pulmonary embolism.
- Melting of the thrombus with purulent exudate.
In the treatment of ascending thrombophlebitis, laser obliteration is also used, the essence of which is to heat the vein wall just above the thrombus. This allows you to remove pathological venous nodes from the main vessels, stopping the growth of a blood clot with an inflammatory process. An alternative technique for conducting a laser beam directed opposite to the movement of blood flow helps eliminate the likelihood of pushing a blood clot into the vessels. It is unique at this moment in time. In case of ascending thrombophlebitis, an effective method that does not allow a blood clot to develop and penetrate into deep vessels is an operation associated with ligation of the place where the superficial vein passes into the deep one. It's called a crossectomy. The manipulation is performed using local anesthesia.
Preventive measures for thrombophlebitis
Anyone who has two or more risk factors needs to take measures to prevent thrombophlebitis in the lower extremities. Timely prevention will help avoid inflammation and thrombosis in the veins, as well as complications of this disease such as pulmonary embolism.
Prevention of thrombophlebitis includes the following:
- physical activity;
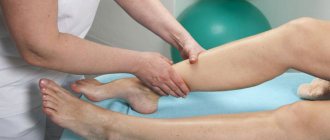
- massage;
- regular change of body position;
- wearing the correct shoes and clothing;
- adequate treatment of colds and infectious foci;
- avoid hypothermia, injuries, fractures, strong impacts;
- take care of the hygiene of the lower extremities;
- stop smoking;
- establish proper nutrition.
The fight against physical inactivity is to increase physical activity. Regular walking is necessary; cycling, swimming, and dancing have a beneficial effect. It is helpful to rest with your legs above the level of your heart. While lying down, place a rolled blanket or pillow under your feet. If you have to spend a long time in one position (riding a bus, flying on planes), you need to drink more fluid, try to change your body position if possible, and stretch your feet. Carry out hygiene procedures for the lower extremities daily. In the evening, take a contrast shower; ten-minute foot baths with sea salt and herbal infusions are useful. General hardening procedures will help strengthen the vascular walls. Pouring with cool water, rubbing, visiting the pool will reduce the symptoms of the disease. In the presence of varicose veins in the veins of the lower extremities, as well as during pregnancy, elastic bandaging or the use of compression hosiery is indicated. Excess body weight increases the risk of thrombophlebitic lesions of the veins of the lower extremities three times.
Preferred foods that reduce the activity of the coagulation system and strengthen the vascular walls:
- fish;
- seaweed;
- garlic, onion;
- dairy products;
- grapes, watermelon, melon;
- nuts, dried fruits, ginger, cinnamon. Prevention of exacerbation of thrombophlebitis
If the diagnosis of “thrombophlebitis” has already been made and there have been episodes of exacerbation, then the following measures are necessary to prevent new cases of the disease:
- use of compression garments or elastic bandaging of the lower extremities;
- constant intake of anticoagulants and vitamins under the supervision of a doctor;
- drink enough fluids throughout the day;
- avoid excessive physical activity and prolonged standing;
- Hot baths, steam baths, saunas are contraindicated.
Refusal to take preventive measures by patients usually results in exacerbation of thrombophlebitis. It is also necessary to follow a diet, maintain moderate physical activity and use massage techniques.
Prevention of thrombophlebitic complications in the postoperative period
Prevention of thrombophlebitis in patients during the postoperative period is necessary due to forced long-term bed rest and increased coagulation. Stagnation of venous blood after surgery can be avoided using medicinal and mechanical means:
- taking anticoagulants prescribed by a doctor;
- wearing compression stockings or using a specialized compressor;
- ensuring sufficient hydration of the body;
- use of gentle surgical techniques;
- Maximum reduction in bed rest.
The degree of effectiveness of preventive measures in the postoperative period varies from patient to patient, so doctors focus on the degree of risk.
What can a doctor do?
Depending on the severity of the condition, the doctor may:
- Order a test for thrombophilia.
- Prescribe Doppler examination of blood vessels.
- Prescribe an ultrasound of the veins.
- Refer to a more specialized specialist - with DVT to a phlebologist, with intestinal vein thrombosis - to a gastroenterologist, with a threat of coronary artery thrombosis - to a cardiologist.
- In severe cases, ensure urgent hospitalization.
- If you detect a blood clot that has not yet come off, completely covering large vessels, or if the blood clot breaks off, insist on surgical intervention.
- If a blood clot is diagnosed early, conservative treatment should be prescribed. For example, the drug Fazostabil has proven itself well as a means of promoting the resorption of blood clots and preventing their re-formation.
In addition, the specialist will be able to identify other diseases that can produce similar symptoms and prescribe appropriate treatment.
If the blood clot comes off
The thrombus is not always firmly attached to the wall of the vessel. When a clot is superficially attached, a simple surge in pressure, a blow, or a careless movement is enough for the clot to come off and travel through the circulatory system. Moving through the vessels, the detached thrombus sooner or later reaches the most important organs, and usually the pulmonary vein, if the thrombus was venous, or the left atrium, if arterial.
Pulmonary thrombus
In the most dangerous cases, blockage of the large vessels of the lung occurs, after which death occurs within a few minutes. A less severe option is infarction-pneumonia, when a blocked vessel bursts and the lungs begin to fill with venous blood, which is accompanied by acute pain and hemoptysis. In this case, the patient has every chance of survival.
The mildest case, when a blood clot enters the pulmonary veins, is accompanied by an increase in blood pressure in the lungs, pain, shortness of breath, and suffocation. If you call an ambulance right away, the patient is likely to survive.
Coronary thrombus
If a blood clot located in the left atrium or coronary arteries breaks off, the patient is at risk of: myocardial infarction, stroke if the blood clot enters the brain through the bloodstream, infarction of the intestines or kidneys if the arteries leading to them are blocked, as well as blood stagnation and gangrene with subsequent loss limbs if the blood clot gets into the large arteries of the arm or leg.
How to protect yourself from thrombosis?
14.10.2019
Thrombosis , along with the most dangerous diseases, claims a huge number of lives every year. In Europe alone, almost five hundred thousand people die every year. In poor countries this number can be several times higher. So why is this disease so dangerous and how to deal with it, we will tell you in this article.
To begin with, what is thrombosis ? Thrombosis is the occurrence of a blood in blood vessels , whether veins or arteries . Even if small in size, such a clot can be very dangerous. Because of it, blood stops flowing to important organs or muscles. When a blood clot adheres to the wall of a vessel , it begins to grow and eventually completely blocks the blood flow, which can lead to dire consequences. The blood clot also break loose, which can be even more dangerous. In any case, it is better to treat thrombosis before it occurs.
There are two types of thrombosis:
- arterial;
- venous.
Venous thrombosis is dangerous because a blood clot can form in the veins of the legs or pelvis, which can lead to it entering the main vessel of the pulmonary artery , and if this happens, it will be very difficult to save the person.
most often affected by venous thrombosis . The main causes are varicose veins , as well as pregnancy and childbirth . In these cases , the blood stagnates in one place, and blood clots form there, which later grow and become more dangerous.
Arterial thrombosis . It mainly occurs in people with heart and is often accompanied by atherosclerotic plaques. It can also occur with atrial fibrillation. Because of this, blood flow in the arteries . Arterial thrombosis is the main cause of arterial embolism, and this can lead to a heart attack .
Prevention of thrombosis
The main cause of thrombosis is a high level of low-density cholesterol in the blood . With heavy consumption of fatty, salty or fried foods, the amount of low-density cholesterol increases and atherosclerotic plaques begin to form. This leads to clogging of blood vessels and the formation of blood clots.
In order to avoid this, you need to monitor your diet, exclude fatty and salty foods from your diet, and also actively engage in sports. It is also necessary to regularly check the presence of cholesterol in the blood , thereby protecting yourself.
Excessive physical activity can also cause thrombosis . With high stress on the legs and back , blood clots can form the vessels Therefore, if you engage in strenuous sports or have hard physical work, then try to better monitor your diet and visit your doctor .
Women have an increased risk of thrombosis if they wear high heels. When a woman wears heels higher than three centimeters, the calf muscles stop pumping blood in the legs . If you often wear heels, blood will stagnate the veins , which will lead to the formation of blood clots. Therefore, it is better to refrain from wearing high-heeled shoes, and if you wear them, then you need to actively engage in sports and periodically go for a massage . This will reduce the risk of thrombosis .
In addition to all of the above, do not forget that a sedentary lifestyle also leads to the formation of blood clots. If you have an office job or often sit, then do not forget about exercise and massage . This will help you avoid consequences from your work.
By following all the points mentioned in the article, you will not only protect yourself from thrombosis , but also become much stronger and healthier. If you don't forget about physical activity and proper nutrition, many problems, including thrombosis , will bypass you.
Published in Phlebology Premium Clinic
Treatment of thrombosis
Treatment of thrombosis requires an integrated approach. There are modern techniques that allow you to dissolve a blood clot by introducing special drugs directly into the vessel. This method is justified in cases of immediate threat to life, since it prevents blood clotting for a long time and makes any injury dangerous.
More conservative methods involve the use of compression hosiery, installation of a vena cava filter to catch blood clots, as well as a number of drugs based on acetylsalicylic acid - they help restore normal blood clotting.
The duration of drug therapy is determined by the doctor.
Folk remedies in the treatment of thrombosis
In the treatment of thrombosis, folk remedies that provide thrombus resorption or thrombolysis can be used in parallel with medications. As a rule, doctors recommend:
- Turmeric, which contains curcumin, which helps dissolve blood clots.
- Garlic contains sulfur compounds that are effective in combating clots.
- Peppers: red, chili, hot - contain salicylates and protect against the formation of new blood clots.
- Flaxseed is a storehouse of Omega-3s that improve blood circulation. In combination with fatty red fish, they not only reduce the risk of thrombosis, but also increase the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels.
- Peppermint infusion helps lower blood pressure, reduce blood clotting, and dissolve newly formed clots.
The use of folk remedies must be coordinated with your doctor, since too much blood thinning can lead to internal bleeding and even death!
Prevention of thrombosis and re-formation of blood clots
A number of factors that provoke the formation of blood clots do not depend on the individual, however, even in the case of autoimmune disorders and hereditary predisposition, the risk of thrombosis can be reduced.
- Movement. Stagnation of blood due to a sedentary lifestyle contributes to damage to the veins, so you need to walk, walk, and play active games.
- Nutrition. The development of atherosclerosis and arterial thrombosis is facilitated by the abuse of trans fats, fast carbohydrates, bad cholesterol, alcohol, etc. Switching to a healthier diet will reduce your risk of developing many diseases.
- Wearing compression stockings. Recommended for pregnant women, people with varicose veins, as well as during and after operations. The degree of compression is determined by the doctor.
- When immobile for a long time, for example, on an airplane, it is necessary to wear loose clothing and take the most relaxed postures. Do not cross your legs to avoid blood stagnation.
- Older patients are recommended to take prophylactic medications that reduce the risk of blood clots.
To avoid re-formation of a blood clot, you should follow your doctor’s recommendations and respond as carefully as possible to all sensations in your body.
News
Prevention of blood clots in blood vessels
Platelets are one of the elements of our blood. Their natural purpose is to form a kind of “plug” when the integrity of the vessel is violated. If a wound appears, the platelets stick together, forming a small blood clot, and close the rupture site. This is how the mechanism for stopping bleeding is carried out. Sometimes this very mechanism fails, and thrombosis begins in the body.
Thrombosis is a chronic lifelong formation of platelet accumulations in blood vessels, parts of the heart, brain, and other organs.
The reasons for the formation of blood clots in blood vessels can be very diverse: heredity; improper diet; blood thickening; smoking and alcohol; sedentary lifestyle; problems with blood clotting; frequent stress, tension; phlebeurysm; atherosclerosis of arteries; oncological diseases and chemotherapy; postoperative rehabilitation period; congenital or acquired pathologies; infectious diseases; STI; taking hormonal and contraceptive medications;
pregnancy.
How to prevent blood clots? Basic tips for prevention are as follows:
-Normalize physical activity. Do exercises every day to tone blood vessels and restore blood circulation. If your job is sedentary, then try to do exercises or exercise in the morning and evening, do gymnastics or go to the gym.
-Spend time in the fresh air more often. This enriches the blood with oxygen, which has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the entire body.
-Complete cessation of bad habits. Alcohol and tobacco destroy the walls of blood vessels, making them thin and fragile.
-Do not wear tight, constricting clothing. In the compressed area, capillaries may be injured and platelets may accumulate.
-Change your usual diet, follow a special diet. Products must be specially selected, taking into account the individual characteristics of your body and your specific case of blood clot formation.
-Taking medications to thin the blood and improve the condition of blood vessels, strengthening them. As a rule, a complex of vitamins and anticoagulants are prescribed.
Drug prevention.
If there are already blood clots in the body, they need to be dealt with using medications. Substances that thin the blood are called anticoagulants. The specific drug and regimen for taking it will be prescribed to you by your attending physician, whom you will need to see regularly for consultation. If the thrombosis is caused by the use of medications, then the first step to recovery is not to take them anymore.
Drug prevention is aimed exclusively at improving the condition of the circulatory system: vitamins strengthen the walls of blood vessels from the inside and outside, anticoagulants thin the blood.
Remember that untimely treatment can lead to a heart attack or stroke. If a blood clot breaks off and travels through the body, it can stop and block a vessel leading to one of the vital organs. Pulmonary embolism is often fatal. The consequences are terrible, so when the first signs appear, do not hesitate to contact a doctor, he will tell you how to avoid complications.
Folk remedies for prevention
In order not to resort to medications, there are traditional methods to get rid of thrombosis. The main method of treatment is herbal teas and tinctures. There are many readily available plants that are natural anticoagulants. Drinking these drinks has a positive effect on eliminating clots.
For example, blueberries, viburnum, currants, sea buckthorn, raspberries - unravel blood clots.
Birch buds, linden leaves and flowers, hawthorn, dill, rose hips and others will help strengthen arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Diet to avoid blood clots
All platelets are composed of the protein fibrinogen. It is produced by the liver and then converted into fibrin. It is fibrin that plays the main role in blood clotting.
With the help of a properly structured diet, you can help your body thin and thicken the blood. For example, garlic, salmon, ginger are natural anticoagulants. There are products that regulate the level of fibrinogen in the blood: they lower or increase and, accordingly, slow down or accelerate the dissolution of platelet accumulations. Some affect the thickness and viscosity of the blood. That’s why the most important thing is to stick to your diet and watch what goes into your body.
The list of recommended products is extensive:
onion - oddly enough, this affordable product contains substances that prevent platelets from sticking together and help liquefy formed clots;
garlic - contains a powerful anticoagulant achoene, which is used to make medicines;
fish - Statistics show that people who eat at least a piece of fish every day are 2 times less likely to have heart attacks than those who do not eat fish at all. It is fatty fish or fish oil in its pure form that have the strongest antithrombotic effect. Fish oil acts on platelets so that they simply lose their ability to stick together;
olive oil - reduces the stickiness of colorless blood cells and prevents them from sticking together;
vegetables are the main enemies of blood clots. Fresh vegetables and fruits, high in vitamin C and fiber, help break down platelet clumps and prevent them from sticking back together.
You will have to give up many of your favorite foods, but the effect is worth it: sugar; all flour products;
Recommendations from experts
Doctors recommend that at the first sign of thrombosis, contact a specialist for qualified help. Since thrombosis is not an independent disease, but only a sign of another, more serious disease, you need to undergo additional examination, examinations and tests. Doctors certainly know how to identify thrombosis and prescribe the right course of treatment.
Take care of yourself and your health. Don’t self-medicate; it’s easy to make the situation worse, but getting rid of the consequences will take a long time and be difficult.
Exercise and proper nutrition are the key to a healthy body!
Prepared by:
Pikulskaya N.V.