The problem of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities (DVT) and subsequent pulmonary embolism (PE) in the postoperative period has been and remains one of the most pressing in modern surgery.
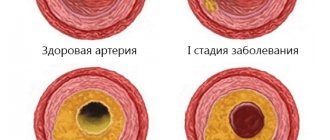
According to domestic and foreign authors, depending on the type of surgical interventions and risk factors in patients, the incidence of DVT reaches 10 - 60%, and fatal pulmonary embolism occurs in 1 - 5% of cases.
In this regard, the prevention of venous thromboembolic complications in the pre- and postoperative period becomes extremely important.
Prevention of thrombosis and thromboembolism in various groups of patients
All patients, regardless of risk group, require elastic bandaging of the limbs with long-stretch bandages. The bandage is applied from the fingers to the upper third of the thigh. Compression should be carried out before the operation, during it and then continuously, day and night, until the patient is adequately activated (that is, when he begins to walk fully). It is permissible not to use compression in patients undergoing minor surgical interventions on an outpatient basis (ingrown toenails, small lipomas, etc.).
Let's define the terms
But to answer the main question of this article, we suggest understanding the terminology.
After all, there are two diseases: thrombophlebitis and thrombosis. Prevention of both is important, but it is achieved in different ways. The main differences between the two diseases are presented in the table below.
So, the table presents the main characteristics of both diseases, their similarities and differences. The main difference between thrombophlebitis and thrombosis is the localization (superficial or deep veins), as well as the mechanism of disease development. However, both of them pose a real threat to life, so it is very important to prevent blood clots.
| Thrombophlebitis | Thrombosis | ||
| The essence of the problem | Formation of thrombi (blood clots) | ||
| Localization | Superficial veins | Deep veins | |
| Features of the affected vessels | Usually develops in altered veins (for example, with varicose veins), including those with damaged walls | Can develop in healthy vessels, resulting from a violation of blood properties | |
| Phlebitis | Present | May occur without inflammation of the vein, which explains the mild severity of symptoms | |
| Factors contributing to the development of the disease | Varicose veins, other vascular pathologies, vein injuries, pathological changes in the composition of the blood, imbalance in the functioning of the coagulation and anticoagulation systems of the blood, a decrease in the speed of blood flow in the venous bed (or in some part of it), infections, etc. | ||
| Symptoms | Redness and thickening in the area of the vein, sharp pain, especially when walking and exertion, noticeable swelling | Swelling of the leg, pain that occurs in response to stress | |
| General poor health | Maybe | Maybe | |
Thrombosis: prevention
To avoid deep vein thrombosis, it is also necessary to maintain a certain level of physical activity, prevent excessive weight gain, and pay attention to the nature of your diet. But since deep vein thrombosis is caused by a disorder in the composition of the blood, to prevent the disease it is recommended to undergo an appropriate examination and do a coagulogram.
Provoking factors for the development of thrombosis can be increased physical activity, smoking, and alcohol intake. Thus, a healthy lifestyle and reasonable exercise also prevent the development of thrombosis.
Thrombophlebitis: prevention
Since thrombophlebitis is the most common complication of varicose veins, all measures that prevent varicose veins and stagnation of blood in the veins will be effective in preventing this disease. Moderate but regular physical activity, weight control, absence of prolonged static tension, a balanced diet, as well as wearing properly selected compression hosiery will help you prevent the onset or progression of varicose veins. They will also serve as a good prevention of thrombophlebitis.
If you already have a diagnosis of varicose veins, try to prevent the disease from progressing. Here, wearing compression hosiery plays an important role, which normalizes blood circulation in the veins. Don't forget to wear knitwear if you have a long plane flight or train journey. A forced sitting position during a move or flight, often uncomfortable, provokes thrombophlebitis. You should also avoid lifting heavy objects and allowing sudden temperature changes - thrombophlebitis can be caused by overheating in a sauna or too much sunbathing.
Uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives
Due to the high content of estrogen, some contraceptives activate the blood coagulation system, which results in the formation of blood clots.
How to warn. Avoid long-term uncontrolled use of hormonal contraceptives, which are contraindicated in case of varicose veins, thrombophlebitis, acute liver diseases, diabetes mellitus, and malignant diseases. Therefore, before prescribing them, it is necessary to undergo an examination: look at the condition of the liver, mammary glands, hemostasis, and do an ultrasound of the female genital organs. And repeat these studies annually.
By the way
In addition to the reasons listed above, the following are also at risk of developing venous thromboembolism: patients with atrial fibrillation, heart failure; pregnant women; obese people; patients with diabetes mellitus; heavy smokers.
Varicose veins
According to official statistics, every fourth Russian suffers from chronic venous insufficiency of the leg veins. However, the real incidence of venous vessels significantly exceeds the official indicators, because those suffering from this disease, as a rule, turn to a doctor already at those stages when swollen varicose veins not only clearly spoil the beauty of the legs, but also significantly worsen the quality of life.
Article on the topic
In spite of varicose veins. How to help your blood vessels
How to warn. The best way is not to start the disease by contacting a phlebologist at the first symptoms. They are famous. Among the subjective ones (those that the patient feels) are pain, heaviness, and fatigue of the legs. There may also be cramps, itching and burning. Objective (visual) – varicose veins, intradermal reticular varicose veins (spider veins), swelling of the legs.
Symptoms associated with spinal pathology (this is exactly what Dmitry Maryanov ), flat feet, and joint disease are often mistaken for venous disease. Only a phlebologist can correctly assess the patient’s complaints, who will prescribe ultrasound Dopplerography of the vessels of the legs, and, if necessary, prescribe anticoagulants (blood thinners) and elastic compression products (stockings, knee socks, tights). Modern surgical techniques make it possible to avoid removing veins and making skin incisions.
Our information
At different times, the following died from pulmonary embolism: Wilhelm II (Emperor of Germany), Frida Kahlo, Francoise Sagan, Lyudmila Gurchenko, Leonid Gaidai. Other recent victims of a detached blood clot are football player Alexey Arifullin and Zenit sports director Konstantin Sarsania.
Vein thrombosis (phlebothrombosis) - symptoms and treatment
Treatment tactics for superficial and deep vein thrombosis differ from each other.
Superficial thrombophlebitis is most often treated on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a surgeon or cardiovascular surgeon. Antiplatelet therapy that prevents thrombus formation (acetylsalicylic acid preparations, etc.) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (for severe pain) are usually prescribed.
Local treatment is of particular importance. The most popular are heparin-based ointments and gels; semi-alcohol compresses are also used. Heparin has a local anticoagulant anti-inflammatory effect and also improves microcirculation. The mechanism of action of semi-alcohol compresses is based on the decongestant effect of alcohol and its antiseptic properties. Compression hosiery plays an important role in the favorable outcome of treatment of superficial thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities. Thanks to moderate elastic compression, a frame is created around the limb, which stabilizes the venous walls, preventing increased stretching. In addition, the risk of a blood clot breaking off and migrating to the heart and lungs is reduced, since it becomes fixed to the vessel wall.
If it is impossible to provide outpatient medical observation, the patient should be hospitalized in a hospital [15].
Deep vein thrombosis requires more serious approaches to treatment. Anticoagulant therapy is mandatory, which significantly reduces the risk of pulmonary embolism. It must be remembered that timely and adequate prescription of anticoagulants can minimize the consequences of thrombosis and significantly reduce the severity of postthrombophlebitis syndrome [1][2].
Modern anticoagulants are divided into two groups: direct and indirect. Direct drugs include heparin and its low molecular weight analogues. Direct anticoagulants are prescribed in the acute period of deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities. The duration of use is about two weeks, depending on the specific clinical situation and the general condition of the patient.
Indirect anticoagulants act indirectly and are used for a long period of time (4 months or more). The mechanism of action of indirect anticoagulants is to block the synthesis of blood coagulation factors in the liver, as well as a number of biochemical reactions. This group of drugs is completely safe. A number of patients with cardiovascular pathology take them for life. However, taking some drugs is necessarily accompanied by laboratory monitoring of blood coagulation parameters (international normalized ratio - INR, prothrombin index - PTI, fibrinogen, etc.).
Modern medicine and pharmacology have in their arsenal such drugs that do not require laboratory control. Their dosage is calculated per kilogram of the patient’s body weight. Important! Anticoagulants are taken under the mandatory supervision of the attending physician.
The main risk of anticoagulant therapy is gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients should monitor the condition of the gastrointestinal tract: carry out timely drug therapy for gastric ulcers and chronic gastritis, and also, if necessary, undergo fibrogastroscopy (only as prescribed by a doctor).
If signs of gastrointestinal bleeding appear (black stools, vomiting “coffee grounds”), you should immediately seek medical help in a surgical hospital.
Despite the fact that a number of deep vein thromboses, depending on the location of the clots, can be treated on an outpatient basis, groups of patients who have:
- signs of pulmonary embolism (shortness of breath, chest pain, cough, sometimes with hemoptysis, drop in blood pressure, rapid pulse, cyanosis of the skin);
- iliofemoral (iliofemoral) and more extensive thrombosis;
- thrombosis of the superior and inferior vena cava;
- primary localization of thrombophlebitis on the thigh with damage to the great saphenous vein;
- primary localization of thrombophlebitis in the upper third of the leg with damage to the small saphenous vein;
- ascending thrombophlebitis - superficial thrombophlebitis, spreading to the above segments, despite adequate therapy;
- a floating thrombus in the superficial or deep vein system, identified by duplex ultrasound scanning at the prehospital stage.
Surgical treatment for venous thrombosis depends on the location of the clot.
In case of thrombophlebitis of the superficial saphenous veins above the knee joint, it is necessary to raise the question of performing a Troyanov operation - ligation of the great saphenous vein to prevent the spread of a blood clot into the deep vein system.
For deep vein thrombosis, surgical approaches may be as follows:
- deep vein thrombectomy - surgical removal of a blood clot;
- thrombolysis - the introduction of special drugs into the vascular bed that dissolve blood clots;
- placement of vena cava filters (clot traps);
- a combination of these methods.
Rehabilitation of patients who have suffered venous thrombosis is always complex. It is aimed at preventing relapse of the disease and includes:
- preventing the action of provoking factors;
- active motor mode;
- body weight control;
- taking pharmaceutical drugs;
- wearing elastic knitwear;
- pneumomassage of the limbs;
- physiotherapeutic and sanatorium-resort treatment.
Prolonged stay on bed rest
More than a quarter of all cases of deep vein thrombosis and fatal thromboembolism occur after surgery. Due to prolonged stay in bed, the speed of blood flow in the veins decreases. As a result, dangerous blood clots form in large vessels (in the veins of the leg, iliac, femoral, popliteal). Patients in oncology, trauma and orthopedic departments are especially at risk of developing deep vein thrombosis.
Article on the topic
Seconds count. What causes and how does thromboembolism develop?
How to warn. To prevent this complication, all patients without exception are prescribed to wear compression stockings for a month after surgery. Elastic bandages are less preferable because when bandaging your legs with them, it is difficult to achieve the desired degree of compression.
And of course, to maintain normal muscle tone in the legs, it is necessary to activate the postoperative patient as early as possible.