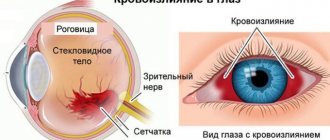
Thrombosis of the popliteal vein: symptoms
Standard symptoms of popliteal vein thrombosis appear only in half of the cases, so sometimes the disease is difficult to diagnose. The main symptoms of the pathology include acute, prolonged pain in the lower leg area, which can intensify in the evening and at night.
.
Statistics on the localization of thrombotic lesions
Also, popliteal thrombosis may be accompanied by the following changes:
- when playing sports and physical activity, the leg begins to hurt sharply;
- if you try to bend your foot towards you, you feel pain in your lower leg;
- the limb swells, turns blue, the skin begins to shine;
- there is a feeling of heaviness and distension in the limb.
The person may feel weak and have trouble moving.
Images
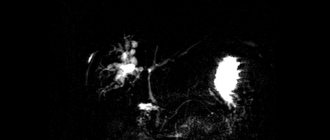
Dilated occlusive-thrombosed medial sural vein
The saphenous vein, sclerosed as a result of foam scleroobliteration, is located suprafascially at the level of the upper third of the leg.
Scleroobliterated saphenous veins and sural vein thrombosis
- Views: 4057
- Comments:
Did you like the post? Do you find it useful or interesting? Support the author!
Thrombosis of the popliteal vein: causes
The exact cause of blood clots in the vessels has not yet been identified. But several factors are known that provoke thrombosis of the femoral-popliteal segment. These include:
- Age. Most often, the disease affects women after 40 years of age. Older people are more likely to get sick than younger people. After age 50, the risk doubles every ten years.
- Surgical operations. During operations, tissues are injured, blood circulation in them is disrupted, and as a result of anesthesia, blood clotting may increase.
- Limb fractures. The disease manifests itself in more than half of cases after a broken leg. Such injuries disrupt blood flow, and as a result of prolonged immobility of the limbs, the muscles weaken and the blood stagnates in them. As a result, a blood clot appears in the lumen of the vein.
- Phlebeurysm.
- Oncological diseases also often lead to the appearance of blood clots. In many cases, the disease manifests itself in patients who have had tumors surgically removed.
- Sedentary lifestyle, long forced bed rest or sedentary work.
- Thrombosis of the popliteal vein occurs during pregnancy and childbirth due to the high pressure of the uterus with the fetus on the pelvic organs and lower limbs.
- Prolonged static load, injury or compression of a vein, which impairs blood circulation.
- Using hormonal medications (such as birth control) that contain estrogen. Such drugs increase blood clotting, which leads to the formation of blood clots.
- Insufficient fluid intake.
- Heart disease, inflammation, infectious diseases.
- Hypothermia of the limb.
- Long journeys during which a person is forced to sit for a long time.
- Systematic overeating, unhealthy diet and obesity.
- Smoking and alcohol.
Risk group
This disease affects middle-aged and older men who have:
- injuries with vascular damage;
- addiction to smoking;
- problems with excessive body weight;
- slow blood flow;
- blood clotting dysfunction;
- undergone operations on any organs and parts of the body.
The risk group also includes pregnant women, women in labor and women who frequently take oral contraceptives. This also includes people who lead a sedentary lifestyle and those who like to sit with their legs crossed.
Popliteal vein thrombosis: diagnosis
To determine the exact signs of thrombosis, duplex ultrasound scanning (USDS) is used. The method helps to find a blood clot, measure it, determine its exact location, and recognize whether it is floating in the vessel. The method also helps to examine the condition of the veins. In addition, during the examination, doctors receive information at what speed the blood moves.
Diagnosis of popliteal vein thrombosis
Doppler ultrasound is also used in diagnosis. This method is used to determine the patency of the veins and find the place where the thrombus is located.
results
A 42-year-old woman consulted a vascular surgeon with complaints of swelling of the right leg and heaviness in the limb. It is known from the anamnesis that two weeks before the visit, the patient underwent foam sclerotherapy of the saphenous veins of the right popliteal region and the upper third of the leg under ultrasound control in a planned manner at one of the private clinics in the Saratov region.
Upon examination, attention is drawn to mild swelling of the right shin at the level of the middle and lower third, noticeable only when measuring the circumference with a centimeter tape (difference 3 cm). Moses and Homans symptoms are negative on both sides. The pulsation is clear at all levels, symmetrical on both sides. The temperature of the skin is the same to the touch.
When performing ultrasound angioscanning of the veins of the lower extremities, sclerotic saphenous veins are clearly located in the right popliteal region, as well as at the level of the upper third of the leg (the phenomenon of so-called sclerophlebitis).
Also noteworthy are two medial sural veins occlusively thrombosed by masses of unspecified date (the level of the upper third of the leg is 35.0 mm from the anastomosis with the popliteal vein). The apex of the thrombus is clearly visible, without signs of flotation. The total length of the thrombus is 6 cm and 4.5 cm in the two visualized sural veins.
Ultrasound examination did not reveal any perforating veins connecting the sclerotic saphenous veins with the thrombosed deep medial sural veins of the right leg. When examining the veins of the left lower limb, no ultrasound signs of pathology were detected.
The patient was given recommendations from an angiosurgeon (class 2 elastic compression on the right lower limb, tablet Warfarin 5 mg once a day in the morning under the control of INR every two weeks in the range of 2.0-3.0, as well as tablet Detralex 500 mg, 1 tablet . 2 times a day for 2 months).
A routine examination three months later revealed a satisfactory degree of recanalization of the sural veins on the right (patency of at least 70%). A control scan two months later did not reveal any ultrasound signs of thrombosis in the sural veins, but ectasia of previously thrombosed veins up to 6.0 mm (on the colateral side no more than 2.0 mm) is noteworthy.
The patient notes a significant improvement in her condition; swelling is a concern only in the warm season towards the end of the day. Anticoagulant therapy was discontinued with recommendations to monitor coagulation levels and take tablets. Cardiomagnyl 75 mg per day after lunch, followed by dynamic monitoring of ultrasound scanning once every 6 months.
Popliteal vein thrombosis: treatment
If we talk about the dangers of popliteal vein thrombosis, then first of all it is worth mentioning its complications. More than 10% of patients die from them. If the disease is not treated, blood clots can break off and travel through the vessels. When they enter the lungs, they completely block the lumen of the pulmonary artery. This leads to death in most cases.
It is the danger of complications that is taken into account when choosing a treatment method. Most patients are recommended to be treated in a hospital. If their risk of thromboembolism is high, treatment will take longer. In the first days of treatment (from 3 to 10 days), the patient must remain in bed. In this case, the affected limb should be elevated at all times. This is especially important if doctors are unable to conduct a complete examination.
The ratio of venous and arterial thrombosis
If conservative treatment of thrombosis does not have an effect, doctors recommend that the patient undergo surgery.
Many patients are given medication to treat thrombosis in combination with the use of elastic compression bandages, which help protect the valves and increase blood flow. To increase the effectiveness of treatment, local topical preparations are used. Such products (creams, ointments, venotonic tonics) are recommended to be used regularly after exacerbations, as a preventive measure.
Treatment is also accompanied by internal medication. The patient is prescribed anticoagulants to slow blood clotting and protect against blood clots. For severe pain, analgesics are also prescribed. To increase blood flow from the legs, phlebotonics are used.
Expert opinion
Angioprotectors are widely used in the treatment of this disease. These are special preparations with complex action. They suppress the inflammatory process, restore vascular walls, improve blood composition and accelerate microcirculation. Also, such products help fight swelling. .
Vascular surgeon, phlebologist
Osipova Ekaterina Yakovlevna
In some cases, antibiotics are also used in treatment. The doctor develops suitable therapy in each case individually.
To reduce the manifestations of popliteal vein thrombosis, the use of Normaven® products is recommended as an additional measure. Testing of the Foot Cream proves that its use for 3 months can reduce the feeling of heaviness and fatigue in the lower extremities, minimize cramps and swelling, and also reduce the severity of the vascular pattern. The product was developed by specialists from the pharmaceutical company VERTEX and has the necessary documents and certificates.
Treatment of thrombosis with folk remedies
Treatment methods
In this case, treatment is:
- conservative;
- operational.
Conservative treatment involves adherence to a strict regimen to prevent blood clot rupture (before examination) and a further increase in physical activity.
Elastic compression is used, which requires constant wearing of compression hosiery. But in case of chronic vascular diseases of the lower extremities, this is done with extreme caution. And if there is a systolic pressure on the tibial artery of less than 80 mmHg, compression is strictly prohibited.
Anticoagulant therapy is also practiced. It consists of administering anticoagulants in a therapeutic dosage. It is prescribed to all patients with deep vein thrombosis. Thrombolysis is also used.
Surgical treatment consists of surgery. It helps restore the lumen of blood vessels to normal size, improve blood permeability and prevent dysfunction of venous valves.
The choice of technique, volume and form of intervention depends on the location of the thrombosis, the extent of the lesion, the severity of the disease and the presence/absence of additional pathologies.
Thrombosis of the popliteal vein: treatment with folk remedies
At the first pain and symptoms of thrombosis, immediately consult a doctor. It is important to remember that untimely treatment or its absence leads to the fact that normal blood circulation in this area can be lost irretrievably, without restoration.
Some people choose traditional medicine to combat blood clots. Indeed, selected recipes passed down from generation to generation gave in some cases positive results. It is not recommended to experience the power of ancestral knowledge without consulting a doctor. Traditional recipes can act as a counterweight to traditional medicine and interfere with the main treatment. We talk about the methods that are considered the most popular among the people.
You can try verbena infusion. Brew a spoonful of verbena in a glass of boiling water, then strain and drink in small sips all day long.
Baths with marsh dried dried herbs can relieve pain. To do this, pour 200 g of the plant into a bucket of boiling water and infuse. Take a warm bath for sore feet for 30 minutes. Regular procedures are distracting.
!
Combine such procedures with the main treatment, after consulting with your doctor.
Instead of swampy cucumber, you can use regular cucumber. Preparation for the procedure is the same, only you need to keep your feet in the infusion for no more than 20 minutes.
A popular traditional medicine in the treatment of popliteal vein thrombi are compresses based on a decoction of thistle. They relieve pain and have a healing effect.