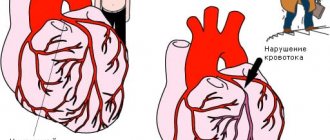
You have had heart surgery - either coronary artery stenting, bypass surgery, or both. What does this mean in the grand scheme of things? This means that modern medical technologies have given you a second chance to find a healthy heart, you again have good blood supply to the myocardium, you can again live without heart pain, not be afraid of physical activity, and our goal is to preserve this second chance given to you for a healthy heart!
Despite surgical treatment and improved blood supply to the heart muscle, which should create favorable conditions for the effective restoration of the patients’ quality of life, expectations are not met - their ability to work and social activity continue to remain low. Many experts recognize the insufficient preparedness of outpatient medical institutions for the rehabilitation of cardiovascular patients. According to one of the leading cardiologists in St. Petersburg, after hospitalization such patients often end up in a network of outpatient institutions that are simply not ready to treat them.
If a patient after heart surgery does not take care of his health and does not visit a cardiologist, then a very high percentage of such patients end up on the operating table again after a few years, because heart disease is chronic and requires constant prevention of relapse!
For example, for 2010-2012 cardiovascular mortality among men 35-74 years old in Germany, Great Britain, Sweden, Belgium, Austria, Italy, Denmark and many other European countries was 100-200 people per 100,000 population. In Russia there are more than 1000 people (Circulation, Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics, 2015), which emphasizes the need for rehabilitation and secondary prevention in cardiac patients.
What is rehabilitation and how should it be carried out?
Rehabilitation - “rehabilis” - lat. restoration of ability.
Who is suitable for cardiac rehabilitation?
- patients with myocardial infarction
- after operations CABG, MCS
- after stenting
- after valve replacement
- after surgical treatment of arrhythmias
Rehabilitation after heart surgery is a set of medical and psychological measures aimed at:
- prevention of further development of the disease
- disability prevention
- improving quality of life
- maintaining the patient's ability to work
- returning him to social activity
Rehabilitation assistance is provided:
- regardless of the duration of the disease
- subject to the stability of the patient’s clinical condition
- in the presence of rehabilitation potential, i.e. physical, psychological, social resources of a person that will help him regain strength
- in the absence of contraindications to various techniques
- based on established diagnosis
Research and specialist consultations required to perform cardiac surgery
Coronary artery bypass grafting
- Coronary angiography, ventriculography (if necessary)
- Transthoracic echocardiography
- Treadmill test
- ECG
- Laboratory research methods
- X-ray of the chest organs
- External respiration function
- Doppler examination of brachiocephalic vessels
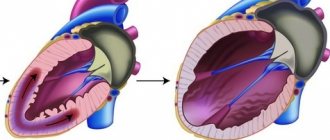
Heart valve surgery
- Transthoracic echocardiography
- Transesophageal echocardiography
- Coronary angiography
- ECG
- Laboratory research methods
- X-ray of the chest organs
- External respiration function
- Doppler examination of brachiocephalic vessels
- Consultation with an ENT doctor
- Dentist consultation
In complicated cases, other examinations may be needed, for example, radionuclide scintigraphy of the myocardium, computed tomography of the brain, computed tomography of the lungs, nuclear magnetic resonance, etc.
Stages of cardiac rehabilitation
There are three stages of rehabilitation after heart surgery and myocardial infarction:
- Stage I – hospital, where stenting/bypass surgery is performed according to indications
- Stage II – sanatorium-resort treatment
- Stage III – outpatient follow-up of the patient after heart surgery or heart attack
is especially important, since it is the longest in time, and, ultimately, determines the further development of the disease.
And if everything is clear with the first and second stages of rehabilitation - a hospital, where the patient is taken by ambulance, and, if possible, a sanatorium, then the third stage of rehabilitation, outpatient, the most important for maintaining health in the future, remains at the patient’s choice.
At the EXPERT Clinic you will be able to undergo the third stage of rehabilitation under the supervision of experienced specialists. In rehabilitation, a multidisciplinary approach is always used, i.e. interaction of specialists of various profiles, namely:
- cardiologist-rehabilitologist
- neurologist
- psychotherapist
- nutritionist
This provides various types of assistance to overcome the consequences of the disease, change lifestyle, reduce the impact of risk factors; assessment of the need and sufficiency, duration, consistency and effectiveness of the participation of each specialist at each specific point in time during the rehabilitation period.
If necessary, at the EXPERT Clinic you will be advised by a council of doctors of various profiles.
Third (outpatient) stage
The “Third Stage of Cardiac Rehabilitation” program at the EXPERT Clinic includes:
- appointment with a cardiologist
- Patient School – group classes with a cardiologist, which discusses the problems patients face and their solutions
- performing ECG, Echo-CG, 24-hour ECG and blood pressure monitoring according to indications
- general blood test, biochemical blood test (lipidogram, coagulogram, electrolytes, homocysteine, CRP, etc.)
- psychological testing
- consultation with a psychotherapist
- consultation with a neurologist
- nutritionist consultation
- genetic analysis of all cardiac markers, including the risk of sudden death, for the patient and his relatives
- genetic analysis of drug doses in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases
Methods for diagnosing heart defects
In order to establish a diagnosis of heart disease, an anamnesis is collected, the presence of diseases that could lead to deformation of the heart valve is revealed: rheumatic diseases, infectious, inflammatory processes, autoimmune diseases, injuries.
- The patient must be examined to identify the presence of shortness of breath, cyanosis, edema, and pulsation of peripheral veins. Using percussion, the boundaries of the heart are identified and sounds and murmurs in the heart are listened to. The size of the liver and spleen is determined.
- The main method for diagnosing valve pathology is echocardiography
, which allows you to identify the defect, determine the area of the opening between the atrium and the ventricle, the size of the valves, cardiac fraction, pressure in the pulmonary artery.
More accurate information about the condition of the valves can be obtained by performing transesophageal echocardiography. - Electrocardiography is also used in diagnostics, which allows one to assess the presence of atrial and ventricular hypertrophy and identify signs of overload of the heart. Daily Holter ECG monitoring allows you to identify rhythm and conduction disturbances.
- Highly informative methods for diagnosing heart defects are cardiac MRI or cardiac MSCT. Computed tomography scans provide precise and numerous sections, which can be used to accurately diagnose the defect and its type.
- Laboratory tests play an important role in diagnosis, including urine and blood tests, determination of blood sugar, cholesterol levels, and rheumatoid tests. Laboratory tests allow us to identify the cause of the disease, which plays an important role in subsequent treatment and patient behavior.
Cardiac rehabilitation results
The positive effects of cardiac rehabilitation at the EXPERT Clinic include:
- eliminating risk factors for coronary heart disease and reducing risk in general
- increasing physical activity
- smoking cessation
- normalization of blood pressure numbers
- weight loss
- improvement of lipid profile
- improving carbohydrate metabolism
- improvement of endothelial function
- slowing down the development of atherosclerosis and its clinical consequences
- improvement of psychophysical condition
- mobilization of patients to cooperate in the process of cardiac rehabilitation.
Dynamic (dispensary) observation is the main form of support for patients with chronic diseases in an outpatient setting. And this does not mean monitoring the natural development of the disease, as, unfortunately, often happens, but carrying out a set of secondary prevention and rehabilitation measures!
After surgical treatment, the patient is recommended to visit a cardiologist in the first days after discharge!
During the first year, visits to the doctor should be made every 4 months. Further, it is recommended to visit a cardiologist at least 2 times a year.
The goal of rehabilitation after cardiovascular accidents is to restore the patient’s physical and psychological health. Rehabilitation is indicated for all patients after surgery, regardless of the severity of the condition, both to gain self-confidence and strength, and to minimize the risk of re-exacerbation. Therefore, do not neglect your health and do not allow the disease to develop! Then you will get a chance to extend your life and improve its quality.
Indications for coronary artery bypass grafting
Indications for CABG are determined by varying degrees of arterial damage and manifestations of coronary heart disease:
As a rule, CABG is not performed:
- severe multiple organ failure;
- during the first months after cerebrovascular accident;
- malignant neoplasms.
FAQ
How long does rehabilitation take after heart surgery?
How long it will take to restore body functions depends on several factors: the severity of the initial condition, age, and motivation of the patient.
However, it is necessary to understand that, in fact, rehabilitation lasts for life, because the whole range of measures is aimed not only at restoring physical and psychological strength, but also at preventing repeated exacerbations of the situation. Without constant prevention, diseases of the cardiovascular system most often worsen.
How to help yourself with heart pain? What medications should you carry with you at all times?
If an attack of angina occurs (pain or burning behind the sternum, shortness of breath during physical and emotional stress, attacks last several minutes), then it is necessary:
- stop physical activity, sit down, calm down
- use nitroglycerin in the form of a spray (Isoket, Nitromint-spray), two or three doses under the tongue
- if the pain does not stop, then after 3-5 minutes you should repeat taking the drug
- If the pain does not go away within 15 minutes, you should chew 1 aspirin tablet with water and call an ambulance.
At what level should blood pressure numbers be maintained?
It is necessary to maintain blood pressure at a level less than 130/80 mmHg. High blood pressure – more than 140/90 mmHg. Art. - indicates the presence of hypertension. More than 180/110 mmHg. Art. indicates severe hypertension.
In order not to lose control of your blood pressure, you must take the medications prescribed by your doctor on time! For this:
- use alarm clock, beep on phone to remind
- Keep the tablets near your toothbrush, razor, or other items you use daily
- Place the tablets in jars indicating the time of administration; for this, you can purchase a special box with compartments at the pharmacy.
What physical activities are possible?
The amount of physical activity can be increased gradually.
6 weeks after surgery , moderate exercise is possible, such as vacuuming, walking the dog, morning exercises, hiking and fishing.
After 3 months, you can increase your activity - swimming, cycling, bowling, tennis, football. Snow removal or gardening at the dacha is allowed.
To maintain good health, moderate-intensity outdoor exercise for 30 minutes 3 times a week is recommended, and those patients who lead a sedentary lifestyle should begin with light exercise programs.
to sexual activity after 9-14 weeks. An exercise test must be performed under the supervision of a physician. If the doctor does not detect any symptoms of overload, then sexual activity is permitted.
How to eat properly if you have heart and vascular diseases?
The main goal of dietary nutrition is to reduce the level of atherogenic lipids in the blood to stop the development of atherosclerosis. Recommended levels of total cholesterol after heart surgery are less than 4.0 mmol/l, LDL - less than 1.8 mmol/l, TG less than 1.7 mmol/l, HDL for women more than 1.2; for men more than 1.0 mmol/l.
It is recommended to eat fruits and vegetables every day, sometimes lean meat, fish, olive and other oils. We allow alcohol in a dose of no more than 2 glasses of red wine per day for men, 1 glass for women. A nutritionist will help you create a detailed nutrition program.
Classification of heart operations
There can be dozens of different diseases in the area of the heart muscle, these are: failure, narrowing of the lumens, ruptures of blood vessels, stretching of the ventricles or atria, purulent formations in the pericardium and much more. To solve each problem, surgery has several types of operations. They are distinguished by urgency, effectiveness and method of influencing the heart.
The general classification divides them into operations:
- Buried - used to treat arteries, large vessels, aorta. During such interventions, the chest of the person being operated on is not opened, and the heart itself is also not touched by the surgeon. That’s why they are called “closed” - the heart muscle remains intact. Instead of a strip opening, the doctor makes a small incision in the chest, most often between the ribs. Closed types include: bypass surgery, balloon angioplasty, stenting of blood vessels. All these manipulations are designed to restore blood circulation, sometimes they are prescribed to prepare for future open surgery.
- Open – carried out after opening the sternum and sawing the bones. During such manipulations, the heart itself can also be opened to get to the problem area. Typically, the heart and lungs must be stopped for such operations. To do this, they connect the artificial blood circulation machine - AIK, it compensates for the work of the “disabled” organs. This allows the surgeon to carry out the work carefully, and the procedure under AI control takes longer, which is necessary when eliminating complex pathologies. During open operations, the AIC may not be connected, but only the desired zone of the heart can be stopped, for example, during coronary artery bypass grafting. Opening the chest is necessary to replace valves, prosthetics, and eliminate tumors.
- X-ray surgery - similar to a closed type of operation. The essence of this method is that the doctor moves a thin catheter through the blood vessels and gets to the heart. The chest is not opened; the catheter is placed in the thigh or shoulder. A contrast agent is supplied through the catheter, which stains the vessels. The catheter is advanced under X-ray control, and the video image is transmitted to the monitor. Using this method, the lumen in the vessels is restored: at the end of the catheter there is a so-called balloon and a stent. At the site of narrowing, this balloon is inflated with a stent, restoring normal patency of the vessel.
The safest are minimally invasive methods, that is, x-ray surgery and closed type operations. With such work there is the least risk of complications, the patient recovers faster after them, but they cannot always help the patient. Complex operations can be avoided with periodic examinations by a cardiologist. The earlier the problem is identified, the easier it is for the doctor to solve it.
Depending on the patient’s condition, there are:
- Planned surgery. It is carried out after a detailed examination, within a specified time frame. Planned intervention is prescribed when the pathology does not pose any particular danger, but it cannot be postponed.
- Emergency are operations that need to be done in the next few days. During this time, the patient is prepared and all the necessary studies are carried out. The date is set immediately after receiving the necessary data.
- Emergency. If the patient is already in serious condition, the situation can worsen at any moment - surgery is scheduled immediately. Before it, only the most important examinations and preparations are carried out.
In addition, surgical assistance can be radical or auxiliary. The first implies complete elimination of the problem, the second - elimination of only part of the disease, improving the patient’s well-being. For example, if a patient has a pathology of the mitral valve and stenosis of a vessel, the vessel is first restored (auxiliary), and after a while valve plastic surgery is prescribed (radical).