Published: November 27, 2017 Updated: March 9, 2021
Hormonal imbalance can occur for a variety of reasons: due to stress, immune disorders, chronic diseases and viral infections, long-term use of hormonal medications, and even lack of sleep.
In what cases is it necessary to donate blood for laboratory tests? First of all - with an irregular menstrual cycle, heavy menstruation or pain during the cycle, as well as problems with conception. Deterioration of the skin condition - pimples, blackheads, decreased libido - are no less significant reasons to contact CITILAB for testing.
Hormonal screening for women
The choice of hormonal screening, that is, determining which hormones to give a woman, depends on the patient’s complaints, her age and the nature of the menstrual cycle.
From the second to the fifth day of the cycle, the level of pituitary hormones is assessed, which controls the functioning of the ovaries:
- LH (luteinizing hormone);
- FSH (follicle stimulating hormone);
- prolactin;
- AMH (anti-Mullerian hormone);
- inhibin B;
- estradiol;
- progesterone
To measure ovarian hormone levels, the test is performed on the seventh to ninth day of the menstrual cycle. The analysis determines the level of estradiol, testosterone and proteins that bind these hormones: globulin and albumin.
On days 19-22, the concentration of estradiol and progesterone is checked. These hormones should be given to women.
- Estradiol is a beauty hormone; rounded body shapes, timbre of voice, delicate skin, libido depend on it; it plays an important role in a girl’s puberty.
- Progesterone. The task of this hormone is to regulate the menstrual cycle and maintain pregnancy.
If the cycle is disrupted, the procedure for taking tests is selected by the doctor individually. This service can be ordered during your stay at the Mashuk Aqua-Therm sanatorium-resort complex - we conduct research on any day of the menstrual cycle. Our gynecologists treat such problems. The sanatorium has developed treatment programs that can be combined with recreation at a medical facility.
Testosterone
This hormone can be tested in both men and women any day. Testosterone is needed by both spouses, but is a male sex hormone. In the female body, testosterone is produced by the ovaries and adrenal glands. Exceeding the normal concentration of testosterone in a woman can cause irregular ovulation and early miscarriage, and the maximum concentration of testosterone is determined in the luteal phase and during ovulation. A decrease in testosterone concentration in a man causes a decrease in sperm quality.
Reasons for taking gynecological hormone tests
The analysis must be taken at a certain phase or day of the cycle and prepared for it in a special way in order to obtain the most reliable results.
Monitoring hormonal balance in gynecology must be done not only for preventive purposes. It helps monitor the development of the genital organs and age-related changes in the ovaries. Monitor a woman’s condition during pregnancy and after childbirth.
Violation of hormone concentrations has causes and symptoms of deviation. Failures in the endocrine system must be promptly identified and treated; they cause serious diseases, the list of which is impressive.
How to donate blood for hormones. Interpretation of analysis results.
Blood from a vein is used to test hormones.
Depending on the clinical signs indicating a specific pathology, an analysis with tests for specific hormones is usually prescribed.
The most complete picture of your health can be obtained by taking a test for the following hormones.
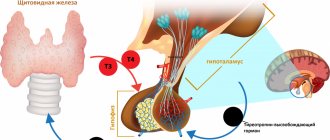
Thyroid hormones:
- T3 (triiodothyronine)
free – stimulates oxygen metabolism in tissues. Normal values: 2.6 - 5.7 pmol/l. - T4 (thyroxine)
– stimulates protein synthesis. Normal values: 0.7-1.48 ng/dl. - Antibodies to thyroglobulin (AT-TG)
are an important parameter for identifying a number of autoimmune diseases. Normal values: 0-4.11 U/ml. - Some others
.
Pituitary hormones:
- TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone)
– stimulates the production of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). Normal values: 0.4-4.0 mU/l. An elevated TSH value usually indicates decreased thyroid function. - FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
. Normal values: in women - depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. Phase I – 3.35-21.63 mU/ml; Phase II – 1.11-13.99 mU/ml; postmenopause – 2.58-150.53 mU/ml; girls under 9 years old 0.2-4.2 mU/ml. In men – 1.37-13.58 mU/ml. - LH (luteinizing hormone)
. Normal values: in women - depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. Phase I – 2.57-26.53 mU/ml; Phase II – 0.67-23.57 mU/ml; postmenopause – 11.3-40 mU/ml; girls under 9 years old - 0.03-3.9 mU/ml. In men – 1.26-10.05 mU/ml. - Prolactin
.
The main function is to stimulate the development of mammary glands and lactation. Normal values: in women (from the first menstruation to menopause) – 1.2-29.93 ng/ml; in men – 2.58-18.12 ng/ml. Increased concentrations of prolactin are called hyperprolactinemia
. There are physiological and pathological hyperprolactinemia. Physiological hyperprolactinemia can be caused by breastfeeding, pregnancy, severe physical activity, and stress. An increased concentration of prolactin in women leads to menstrual irregularities and may cause infertility. In men, hyperprolactinemia leads to decreased libido and impotence. - ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone)
– stimulates the synthesis and secretion of hormones from the adrenal cortex. Normal values: 9-52 pg/ml. - Some others
.
Sex hormones:
- Testosterone
(male sex hormone) is produced by the adrenal glands and in the gonads (in men - in the testicles, in women - in the ovaries). Affects the development of the genital organs, the formation of secondary sexual characteristics, the growth of bones and muscles. Normal values: for men - 4.94-32.01 nmol/l, for women - 0.38-1.97 nmol/l. - Estrogens
(female sex hormones). The main estrogens - progesterone and estradiol - are produced by the adrenal glands and ovaries. Normal values of progesterone in women depend on the phase of the menstrual cycle: Phase I – 1.0-2.2 nM/l; Phase II - 23.0-30.0 nM/l; for postmenopause – 1.0-1.8 nM/l. Similarly for estradiol: phase I - 198-284 pM/l: phase II - 439-570 pM/l; for postmenopause – 51-133 pM/l. Elevated estrogen levels may indicate tumors of the ovaries and adrenal cortex, as well as cirrhosis of the liver. Reduced - for insufficient development and sclerosis of the ovaries.
Adrenal hormones:
- DEA-s (dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate)
is necessary for the synthesis of testosterone and estrogens. The normal range for the concentration of this hormone is: 3591-11907 nmol/l; in women – 810-8991 nmol/l. However, this is the general picture; when processing analysis data, the patient’s age must also be taken into account. - Cortisol
is involved in many metabolic processes and is actively produced as a result of the body’s response to hunger or stress. Normal values: for children under 16 years of age - 3-21 mcg/dl, for an adult - 3.7-19.4 mcg/dl. - Aldosterone
is responsible for regulating water-salt balance in the body. Normal values: 35 - 350 pg/ml.
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
The analysis is taken on the 3rd–8th or 19th–21st days of a woman’s menstrual cycle, for a man - on any day. Strictly on an empty stomach. In women, FSH stimulates the growth of follicles in the ovaries and the formation of estrogen. It promotes the growth of the endometrium in the uterus. Reaching a critical level of FSH in the middle of the cycle leads to ovulation.
In men, FSH is the main stimulator of the growth of the seminiferous tubules. FSH increases the concentration of testosterone in the blood, thereby ensuring sperm maturation. It happens that the hormone works at full strength, but there is no point where it is in demand. This happens when a man's testicles are small or have suffered from some kind of surgery or infection.
Why do you need to examine hormone levels in women?
Hormone tests at different periods of a woman’s life make it possible not only to assess hormonal levels, but also to identify hormonal imbalances. Using the results obtained, it is often possible to diagnose problems in the body and eliminate them in a timely manner.
The doctor will suggest that the woman take hormone tests if any signs of pathology appear in order to eliminate it and normalize hormonal levels.
Hormone analysis is not the most reliable diagnostic method for a woman’s health; it is only an auxiliary technique for assessing the activity of many body systems.
A woman takes tests for sex hormones when there is a hormonal imbalance, which negatively affects the body and its functioning. Having identified a dishormonal condition, the doctor is able to timely diagnose the pathological condition and prescribe the correct treatment.
To obtain reliable results, it is important to take hormone tests correctly: blood is taken at a certain period of the menstrual cycle for each hormone.
A doctor may prescribe a blood test for hormones in different situations:
- for menstrual irregularities;
- with heavy or scanty periods;
- for pain during menstruation;
- for problems with conception and pregnancy;
- with poor condition of skin, hair and nails;
- with decreased libido;
- with increased hair growth;
- in case of violation of the child’s physical development;
- for acne;
- for tumors in the uterus and ovaries;
- for obesity;
- with a tendency to disease;
- with sexual infantilism.
Knowing the hormonal background in all these conditions, you can easily eliminate the problem if the disorders are diagnosed in a timely manner. Normalizing hormone levels by qualified specialists will help you quickly and easily cope with the problem.
LH (luteinizing hormone)
It is given on the 3rd–8th or 19th–21st days of a woman’s menstrual cycle, for a man - on any day. Strictly on an empty stomach. This hormone “ripens” the follicle in a woman, ensuring the production of estrogen, ovulation, and the formation of the corpus luteum. In men, LH stimulates the formation of sex hormone binding globulin and increases the permeability of the seminiferous tubules to testosterone. This increases the concentration of testosterone in the blood, which promotes sperm maturation.
In women, the level of luteinizing hormone depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. The peak concentration of LH occurs at ovulation, after which the level of the hormone drops and “stays” throughout the luteal phase at lower values than in the follicular phase. This is necessary for the functioning of the corpus luteum in the ovary. In women, the concentration of LH in the blood is maximum in the period from 12 to 24 hours before ovulation and is maintained throughout the day, reaching a concentration 10 times higher compared to the non-ovulatory period. During pregnancy, LH concentration decreases.
During the examination for infertility, it is important to track the ratio of LH and FSH. Normally, before the onset of menstruation it is 1, a year after the onset of menstruation - from 1 to 1.5, in the period from two years after the onset of menstruation and before menopause - from 1.5 to 2.
What to do after the examination?
If the problem is identified, you need to contact a specialist. If we are talking about gynecological pathology, you need to consult a gynecologist-endocrinologist. If problems arise in a man, then you need to consult an andrologist. Together with a specialist, the person will undergo additional research and begin appropriate therapy. Hormone therapy is a lengthy process and takes from three to six months. After therapy it is necessary to carry out monitoring.
If there are deviations from the norm in the tests, you should urgently consult an endocrinologist.
What hormones should a woman take?
Let's look at specific situations.
Obesity. There can be two reasons: endocrine and nutritional (food). In this case, the woman should take adrenal hormone tests, for example, check the level of cortisol in the body. If the tests are normal, then the cause of excess weight is food, and not hormonal. An endocrinologist may prescribe additional examination by a nutritionist, urologist, neurologist, gynecologist, and then prescribe therapy.
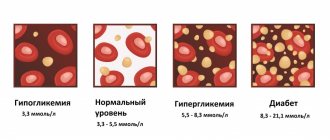
Dry mouth and frequent urination. These are symptoms of diabetes. In this case, the woman should take the pancreatic hormone insulin.
Excessive hair growth on the face, upper lip, male-type abdomen, chest, arms. The cause of all these troubles may be an imbalance of testosterone. Women normally have 15 times less of this hormone than men. Testosterone helps build muscle and speeds up protein synthesis.
Weakness, dry skin, hair loss are signs of thyroid pathology. In this case, give women all thyroid hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and tetraiodothyronine (thyroxine, T4), where 3 and 4 are the number of iodine molecules, and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). If this is an autoimmune disease of the thyroid gland, then we test antibodies to peroxidase.
Increased sweating . Also take thyroid hormones.
Frequent fractures . This may mean that calcium is being leached from the bones. The hormones calcitonin and parathyroid hormone are responsible for this
High blood pressure: Itzeng-Cusheng syndrome, adrenal hormones: cortisol and adrenocorticotropic hormone, which is located in the pituitary gland in order to exclude an endocrine cause of high blood pressure.
A marker for type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease and obesity is the hormone leptin .
Let’s look at what hormones a woman should take for gynecology in a little more detail.
When is a blood test for hormones prescribed?
Hormonal analysis is usually carried out if there is a suspicion of dysfunction of the endocrine glands or if an increase in the size of the glands is detected.
Indications for testing for female sex hormones (estrogens)
are:
- menstrual irregularities;
- infertility;
- miscarriage;
- acne;
- overweight;
- fibrocystic mastopathy (breast disease).
Indications for testing for male sex hormones (androgens)
are:
- suspicion of the development of tumor processes;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- kidney dysfunction;
- overweight (obesity);
- infertility;
- acne;
- in women – excessive growth of body hair.
Hormonal analysis is prescribed during pregnancy if pathological development of the fetus is suspected. An analysis for the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), produced by the cells of the membrane of the embryo, can detect pregnancy already on the 6-10th day after fertilization.
Stool tests:
- Stool examinations should not be carried out earlier than 2 days after an enema, an X-ray examination of the stomach and intestines, or a colonoscopy.
- You cannot take medications the day before, including: - laxatives; - Activated carbon; - preparations of iron, copper, bismuth; - use fat-based rectal suppositories.
- Do not allow urine or water into the sample.
- Conduct stool examinations in women during menstruation
Stool should be collected for examination in the morning. If this is difficult, you can prepare the sample in advance, but no more than 8 hours before submitting the stool to the laboratory. In this case, the sample should be stored in the refrigerator (do not freeze).
Thorough toileting of the external genitalia and anal area. Pre-urinate. Defecate in a dry, clean container: a vessel or a night vase. Transfer a stool sample of 3-5 cubic meters. cm in a pre-prepared, clean, dry container for storage and transportation.
Feces for occult blood
The patient should not eat meat, fish, or tomatoes 3-5 days before the test (they can be replaced with dairy and cereal dishes). The patient should not brush his teeth. The material is collected on the fourth day in a clean, dry container for storage and transportation.