The article was checked by a cardiologist, Ph.D. Yakovenko E.I. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
At the Clinical Hospital on Yauza, a preventive and in-depth cardiological examination is carried out to identify heart rhythm disturbances and their causes (ECG, ECHO-CG, bicycle ergometry, Holter, laboratory tests, specialist consultations). We successfully treat arrhythmia using conservative and minimally invasive surgical methods (cardiac resynchronization techniques, radiofrequency ablation of the lesion, operated by Professor A.V. Ardashev).
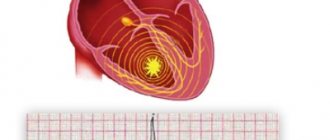
One of the main indicators of effective heart function is the correct rhythm. Disturbances and changes in heart rhythm are called arrhythmia. Their cause can be both cardiac diseases (myocarditis, myocardial infarction, etc.) and non-cardiac pathology (hormonal changes, disruption of the autonomic nervous system, electrolyte imbalance, etc.).
Make an appointment with a cardiologist
Types of heart rhythm disorders
- Tachycardia , that is, an increase in heart rate of more than 90 beats/min. In the case when the increase occurs paroxysmally, they speak of paroxysmal tachycardia.
- Bradycardia . This is the name given to a decrease in heart rate of less than 60 beats/min.
- Extrasystole . This term refers to the appearance of premature and often irregular heartbeats (extrasystoles).
- Atrial fibrillation or atrial fibrillation . Depending on the frequency of ventricular contraction, they speak of a normo- or tachy-form of atrial fibrillation.
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome (WPW) . A change in rhythm that occurs in the presence of an additional impulse conduction bundle.
- Heart blocks . That is, a violation of the conduction of the excitation impulse through the conduction system of the heart.
About the department
In the department of surgical treatment of complex cardiac arrhythmias and cardiac pacing (OHP) of the City Clinical Hospital named after. I.V. Davydovsky carries out all types of interventional procedures for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias (ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias, atrial tachycardia, atrial flutter and fibrillation, atrial and ventricular extrasystole, etc.); implantation of a wide range of devices for the diagnosis and treatment of cardiac arrhythmias (pacemakers, cardioverter-defibrillators, subcutaneous loop heart rate monitors, etc.).
Symptoms of arrhythmia
- Changes in the frequency and quality of the heartbeat. Some patients describe these sensations as “flip”, “somersault”, short-term “freezing”, even “gurgling”. There may be a feeling of increased heartbeat, impact in the shoulder, neck, pulsation in the ears.
- Dizziness up to clouding of consciousness and fainting.
- General weakness, sometimes sweating.
- Rhythm disturbances are often accompanied by chest pain.
- Against the background of arrhythmia, an increase or decrease in blood pressure is possible with the appearance of corresponding symptoms.
Features of treatment of arrhythmia at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
The patient can undergo a full diagnosis, high-quality treatment for arrhythmia (including surgery), and also be under the supervision of specialists (cardiologists, cardiac surgeons) for a year after the operation.
During the period of outpatient observation after surgical treatment, the patient can constantly (if necessary, almost around the clock) be in touch with the doctor.
About cardiac surgical treatment of arrhythmia
Minimally invasive operations with access through a vessel. Duration: 2-3 hours.- High-tech equipment - the non-fluoroscopic mapping system "CARTO" allows you to conduct an intracardiac electrophysiological study directly during surgery to accurately determine the location of the pathological impulse causing the arrhythmia, coagulate it, restoring normal sinus rhythm.
- Hospital stay – 1-1.5 days. Postoperative rehabilitation – 2-7 days.
- Operations can be performed on elderly people (over 65 years old).
- Minimally invasive cardiac surgical treatment is possible even against the background of somatic diseases.
- The department is headed by one of the leading operating arrhythmologists in Russia, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor A.V. Ardashev.
Survey
If arrhythmia is suspected, a cardiac examination should be performed. However, a more or less in-depth, annual examination to detect heart disease is recommended for all patients over 40 years of age.
At the Yauza Clinical Hospital, the following methods are used to study cardiac activity:
- Electrocardiography and echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart).
- 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring (for 24 hours under various conditions).
- Stress tests - assessment of the reaction of cardiac activity to physical activity (bicycle ergometry). Modern equipment (Swiss apparatus from SCHILLER) allows us to conduct research with maximum accuracy.
- According to indications - CT coronary angiography, study of the calcium index of the coronary arteries, MRI of the heart, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring, etc.
Since rhythm disturbances can be caused by various causes, patients with arrhythmias in our hospital are consulted by specialists from various fields. As a rule, a comprehensive examination includes:
- Study of the lipid spectrum of blood.
- Electrolyte metabolism data.
- Analysis of the blood coagulation system.
- Study of the function (hormonal analysis) and structure (echoscopy) of the thyroid gland, if indicated - to exclude other endocrine pathologies.
Make an appointment
Disorders of heart rhythm and conduction (cardiac arrhythmias)
Contractions of the heart muscle are caused by electrical impulses that are generated and conducted into specialized and modified tissue of the heart called the cardiac conduction system. In a healthy heart, excitation impulses arise in the main pacemaker (sinus node), pass through the atria and reach the second-order node (atrioventricular node), after which they spread through the His bundle system and Purkinje fibers to the ventricles of the heart and cause contraction of the muscle cells of the heart. Any deviation from the above procedure must be attributed to cardiac arrhythmias (CHDs) or cardiac arrhythmias. .
Taking into account heart rate, they can be divided into two large groups:
Bradyarrhythmias:
- SA (sinauricular) - blockades,
- SSS (sick sinus syndrome),
- violation of AV (atrioventricular) conduction,
- AV blockade,
- AV dissociation,
- Frederick's syndrome, etc.
Tachyarrhythmias:
- supraventricular and ventricular tachycardias,
- sinus,
- nodal,
- ectopic atrial,
- extrasystole, etc.
Causes of arrhythmias (heart rhythm disturbances)
It is important to distinguish between cardiac arrhythmias caused by organic (irreversible) myocardial damage and functional disorders. As a rule, functional disorders occur in a healthy heart and can be caused by psychogenic, reflex and humoral disorders. Functional heart rhythm disturbances are quite common; it is important to identify and eliminate the causes that cause them, which will save a person from arrhythmia.
Organic disorders occur with: coronary ischemia, hemodynamic defects of the heart and large vessels, heart failure, hypertension. They can appear due to toxic effects (medicines, alcohol, etc.) or infectious toxic effects (rheumatism, viral infections, myocarditis of various etiologies, etc.), hormonal changes. Arrhythmias can be congenital (WPW syndrome, congenital AV block, etc.) or acquired, caused by external influences (myocarditis, heart surgery and trauma, etc.).
Main symptoms (manifestations of arrhythmias)
Bradyarrhythmias:
- Interruptions in heart function, irregular heartbeat, rare pulse (less than 50 beats per minute);
- Occasional dizziness, darkening of the eyes;
- Memory loss;
- Sudden attacks of loss of consciousness (fainting) associated with a rare pulse (Morgagni-Edams-Stokes attacks);
- Increased fatigue, decreased tolerance to physical activity, against the background of a low pulse;
- Periods of falling blood pressure and its instability, ineffectiveness of drug therapy in the treatment of hypertension;
- Manifestation of heart failure (swelling in the legs, shortness of breath) against the background of bradycardia;
- Heartache.
Tachyarrhythmias:
- Sudden onset of palpitations.
- Interruptions in the functioning of the heart.
- Throbbing in the head or throat.
- Dyspnea.
- Pain in the heart during an attack.
- General weakness, decreased tolerance to physical activity, increased fatigue during an attack.
- Development of dizziness or loss of consciousness during an attack.
- Decreased blood pressure (hypotension or unstable blood pressure).
Diagnosis of heart rhythm disturbances (arrhythmias)
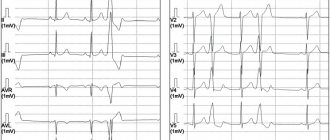
Typically, the diagnosis of arrhythmias is carried out by a clinic doctor, cardiologist or emergency physician. Anamnesis, physical examination, and various instrumental diagnostic methods are important. The most important thing is the registration of NRS on the ECG (for presentation to the arrhythmologist).
Today, in specialized or multidisciplinary clinics, patients are consulted by a cardiac surgeon-arrhythmologist and determine the need and possibility of endovascular interventional (low-traumatic) treatment of cardiac arrhythmias. Our Clinic has all the necessary resources for diagnosing and treating arrhythmias
Methods for diagnosing heart rhythm disturbances include:
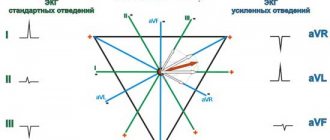
- An ECG (electrocardiogram) allows you to detect tachycardia, bradycardia, or transient SA and AV blockades at the time of treatment.
- Electrophysiological study (EPS) of the conduction system of the heart - is used to confirm the diagnosis in cases where, in the presence of clinical manifestations, it is not possible to detect transient rhythm disturbances using conventional methods (ECG, CM). In some cases, this method makes it possible to verify the organic or functional cause of cardiac arrhythmias.
- 24-hour Holter monitoring (CM—continuous ECG recording) is the most reliable method for diagnosing transient cardiac arrhythmias during the observation period.
- EchoCG (ultrasound of the heart) – reveals myocardial pathology.
- An X-ray examination of the chest allows one to assess the size of the heart shadow and identify signs of venous congestion in the lungs.
- Bicycle ergometry (treadmill test) - allows you to identify coronary heart disease and assess the adequate increase in heart rate contractions during physical activity.
- Tilt test is a test with passive orthostasis. It is carried out on a special rotary table. They will allow you to identify or exclude a connection between the development of fainting conditions and heart rhythm disturbances.
Treatment of arrhythmias: surgical correction of cardiac arrhythmias
At the beginning of treatment of arrhythmias, it is necessary to take into account and exclude such conditions as: the presence of thyrotoxicosis, alcohol abuse, smoking, impaired water-electrolyte status, etc., as well as heart diseases: heart failure, myocardial ischemia, myocardial hypertrophy , inflammatory diseases of the myocardium, disorders of the autonomic regulation of the heart and other diseases that can cause and maintain tachycardia.
In our Clinic, the choice of treatment method for cardiac arrhythmia is made by a specialist, taking into account the clinical picture of the disease, data from instrumental diagnostic studies and recommendations of the Russian Society of Cardiology, the All-Russian Scientific Society of Arrhythmologists.
Self-administration of drugs, self-medication using various methods is highly undesirable and unsafe if the nature, mechanism and cause of the arrhythmia are unknown and not taken into account.
There are several ways to treat cardiac arrhythmias:
- 1. Antiarrhythmic therapy (with constant use of pharmaceutical drugs).
- 2. Electrophysiological techniques:
- cardioversion/defibrillation,
- electrocardiostimulation,
- catheter ablation of the arrhythmia focus.
If there are indications for the treatment of bradyarrhythmias, perform:
- implantation of a pacemaker (artificial pacemaker),
- cardioverter-defibrillator
- devices for resynchronization therapy.
The operation is performed under local anesthesia in X-ray operating conditions and lasts up to 40-55 minutes.
An effective and radical method of treating tachyarrhythmias is catheter ablation (destruction) of the arrhythmia focus. The operation, on average, lasts no more than 1 hour, and after 24 hours the patient can be discharged from the hospital.
Diagnosis of arrhythmia
The main method for detecting arrhythmia is ECG. In most cases, changes in excitability and conductivity are visible during the first study. But with a one-time ECG recording, you can “miss” an episode of rhythm disturbance, so doctors resort to other diagnostic methods:
- ECG with physical activity (“stress test”);
- daily Holter monitoring ー installation of a sensor that will record the electrical potentials of the heart for 24 hours, while the patient spends this day according to his usual routine;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- coronary angiography ー X-ray examination of the heart vessels with the introduction of a contrast agent.
Performed for the first time in Russia
- laser angioplasty for stenotic and occlusive lesions of the coronary arteries of the heart in ischemic heart disease - February 1989
- removal of a foreign body from the lumen of a coronary artery during a complicated angioplasty operation - April 1991
- stenting of the coronary artery for atherosclerotic lesions of the coronary artery – January 1992
- implantation of an original device to close a cardiac septal defect – March 1995
- retrograde recanalization through the collateral canal of a blocked coronary artery – September 2006
- hydrodynamic recanalization for coronary artery occlusion – March 2007
Experience in endovascular operations for coronary artery disease and structural pathologies of the heart - more than 6,000 successful operations!