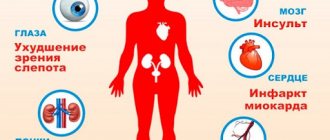
Cardiac arrhythmia is a disruption of its normal activity, manifested in a disorder of the rhythm, frequency and sequence of contraction of this organ. Thus, an increase in heart rate is called tachycardia.
Bradycardia is defined as a slow heart rate and pulse less than 60 beats per minute.
Extrasystole is an untimely contraction of the heart, or its individual parts, which affects the overall function of the organ. With atrial fibrillation, the heart contracts chaotically, which leads to organ hypofunction and negative changes in the general condition of the body.
Physical exercises for cardiac arrhythmia in any of its manifestations help restore the functioning of the heart muscle and are prescribed in the complex treatment of these pathologies.
Benefits of physical activity
The benefits of dosed, well-chosen physical activity for arrhythmia are undeniable. Exercises are prescribed to improve the functioning of not only the heart, but also the entire cardiovascular system.
The main element of exercise therapy for arrhythmia is breathing exercises. It is aimed at preventing attacks of arrhythmia, restoring respiratory rhythm, and normal blood circulation.
At the same time, a special complex is created for those suffering from arrhythmia, which eliminates hypertension of the heart muscle and the body as a whole. Exercises are selected by a physical therapy doctor taking into account the characteristics of existing pathologies.
Charger
In the treatment of arrhythmia, exercise is of great importance, which doctors recommend doing in the morning and evening.
The following exercises can be included in the exercise complex:
- Feet shoulder-width apart, pull up on toes. As you inhale, gently raise your arms up, and as you exhale, lower them down.
- Measured bending as you inhale and straightening your arms at the elbows as you exhale.
- Feet shoulder-width apart, hands at the waist. Turn your body to the right and left, while you need to monitor your breathing and smooth movements. Hands spread to the sides.
- Squatting on two legs. Perform carefully, not jerkily, no more than 5-8 times, with pauses for rest.
You need to start and finish the exercise by walking.
Various techniques
In order for therapeutic exercises and gymnastics to help with arrhythmia, you need to select a complex based on the type and stage of the disease according to the recommendations of the attending physician. Thus, when diagnosing atrial fibrillation, excessive loads in general are strictly prohibited, and starting exercises is allowed only in a hospital setting under the direct supervision of a specialist. Other types of pathology are not prohibitions for therapeutic exercise with a properly selected set of exercises.
According to Bubnovsky
Exercises to restore normal heart rhythm according to Bubnovsky’s method include squats involving all the muscles of the legs and buttocks. The main requirement when performing them is to squat while inhaling and stand up while exhaling. At this time, the body distributes blood evenly from the heart muscle throughout the body, which eliminates heart fibrillation.
During such exercises, special attention should be paid to the physical preparation of the leg muscles, placing the maximum amount of load on them if possible. In such cases, performing squats in compliance with the correct exercise technique can replace cycling, running, and walking in terms of the degree of impact on the body.
You should start classes with 5–10 squats in 1 approach in the complete absence of physical training and from 15–20 in the presence of it. The number of approaches in the first stages of such physical education should not exceed three. Over time, you should increase them, as well as the total number of squats.
It is also recommended that Bubnovsky take heart rate measurements before and after exercise and compare the readings with the norm. Thus, it is possible to check the results of the treatment.
According to Strelnikova
The sinus type of arrhythmia, although one of the safest for health, also requires treatment using breathing exercises. In this case, exercises using Strelnikova’s method are especially effective. Exercises allow you to normalize your heart rate, and in the first stages of arrhythmia, cure it completely.
Like other breathing exercises, Strelnikova’s technique is aimed at activating the cardiovascular and circulatory systems and requires regularity and a gradual increase in load. The exercises should be performed in this order:
- Standing straight, take 5 to 8 shallow breaths. Walk a short distance, taking a short breath with each step. It's worth starting with 8 steps.
- Standing with your arms down and your back straight, you need to clench your fists as you inhale and unclench them as you exhale. It is recommended to perform the exercise at least 6 times with a break.
- Standing with your hands on your waist, lower your hands down as you inhale and return them to their place as you exhale. For the first stages of training, it is recommended to perform the exercise 10–12 times with a break.
- Standing straight, with your legs apart at shoulder level, you need to inhale and tilt your body down and spread your arms to the sides. As you exhale, you need to return to the original position. The exercise should be repeated 12–15 times with breaks.
Regular performance of this set of exercises allows you to quickly get rid of a low or high heart rate. But it should be remembered that deterioration in well-being during exercise requires temporary cessation and a reduction in the pace of their implementation in the future.
According to Buteyko
The Buteyko exercise technique for the treatment of arrhythmia is one of the most common and popular methods of getting rid of this pathology. It is based on training the correct breathing rate, which affects the heart rate. This complex includes the following exercises:
- Standing straight, take shallow breaths, hold your breath for 5 seconds and long exhales. In this case, you need to breathe through your nose, and your chest and stomach should remain motionless while inhaling. It is recommended to repeat the exercise 10 times.
- In a standing or sitting position, inhale, gradually filling the diaphragm and chest, then, emptying them in the reverse order, slowly exhale. At least 10 repetitions of the exercise are also required.
- Alternately take 10 full breaths from each nostril. During breaks between them, you should perform a light massage of the nose.
- Pull your stomach in, take a full breath and hold your breath for 5 - 7 seconds, then exhale slowly. It is recommended to repeat the exercise 10 times with a break after each approach for 5 seconds.
- Take 12–15 exhalations and inhalations for 2–3 seconds.
Active breathing exercises using the Buteyko method will help strengthen the whole body as a whole and improve the functioning of the heart in particular.
Exercise therapy in the treatment of arrhythmia
Exercises in the exercise therapy complex, intended for patients with arrhythmia, have not only a healing purpose. This is a gymnastics complex with a strictly dosed load for a specific patient, which takes into account the state of his health, the severity of the disease and the period of development of the disease.
Example exercises in a lying position:
- Flexion and extension of the legs at the ankle joints.
- Flexion and extension of fingers.
- Abduction of arms bent at the elbows. Move your elbows to the sides - inhale, extend your arms along your body - exhale.
- Inhale, extend your arms along your body, palms up. Exhale – raise your arms and reach your knees with your palms, raising your head and tensing.
- Alternately sliding your feet along the bed without lifting them from its surface. Breathing is smooth, without tension.
- Turns with knees bent at the legs, now to the right, now to the left. Breathing is smooth and spontaneous.
- Alternately abducting the right arms and legs to the side, then the left. At the same time, turn your head in the direction of abduction of the limbs.
- Alternately bending and straightening your legs at the knees.
- Lowering and raising your arms up: on inhalation - up, on exhalation - down.
Sitting on a chair:
- Press against the back of the chair. Hands on knees. Taking a deep breath, raise your arms, bent at the elbows to the shoulders. As you exhale, return to the original position.
- Rolling from heel to toe and synchronously clenching and unclenching your fingers.
- Inhaling, raise your arms up, exhaling, lower them down.
- Sliding your feet along the floor without lifting them from its surface.
- Sitting on the edge of a chair and inhaling, move your right arm and left leg to the sides. As you exhale, lower your arm and bend your leg at the knee. Do the same on the other side.
- Hands along the body, alternately lift the left, then the right shoulder. Breathing is smooth and relaxed.
- Inhaling, spread your arms to the sides, exhaling, use your hands to pull the leg bent at the knee towards your stomach and return to the starting position. Do the same for the other leg.
- Sitting on the edge of a chair, place your hands on your belt and take a deep breath. As you exhale, pull your elbows and shoulders inward.
Starting position standing:
- As you inhale, stretch and clasp your hands. As you exhale, lower your arms.
- Tilt the body to the sides while simultaneously abducting the legs in the same direction. Hands raised up.
- Bend your elbows at chest level and spring your arms back.
- Smooth body rotation left and right.
- Inhale with your arms raised up. Lean forward and reach your knees with your hands - exhale.
- Swing your legs forward and backward. Breathing is voluntary.
- Inhale, squat with your arms extended forward and exhale.
Perform all exercises no more than 10 times, monitor your well-being, breathing, and heart rate.
Attention! If you experience discomfort in the heart area during exercise, you should stop exercising and seek advice from your doctor.
Breathing exercises
Breathing exercises are of great importance in the treatment of arrhythmia. Experts have developed many techniques designed to treat various diseases.
One of them is Buteyko breathing exercises. The complex includes several simple breathing exercises:
- Gradual, slow inhalation through the nose for 4-5 seconds. The abdominal muscles are not involved in breathing. Then exhale the same slow way. Perform 10 approaches.
- The inhalation is longer – up to 9 seconds. At the same time, the chest and diaphragm are filled. Then slowly, calmly exhale. Rest for 5 seconds. Perform 11 approaches.
- Between breathing movements, you need to self-massage the bridge of your nose.
- Now inhalation and exhalation are carried out alternately through each nostril separately. Each of them requires 9-10 approaches.
- The next inhalation and exhalation are performed to the entire depth of the chest. They are executed slowly. When there is a pause between inhalation and exhalation, you need to pull in your stomach for 6-8 seconds.
- The last 12 sets are completed within one minute.
- Then normal breathing is restored.
Rules for performing exercises
Both at home and in the hospital, the patient must adhere to the following rules when engaging in exercise therapy:
If the patient belongs to the first group, then the duration of his training can be 30-45 minutes. For the second group, you cannot load all the muscles in one workout with a duration of no more than a quarter of an hour. After breathing exercises, be sure to rest. Constantly monitor your pulse, the permissible deviation is 10% from the norm. For the third group, exercises are very limited, as they can provoke thromboembolism
It is permissible to train individual muscle groups with partial amplitudes, and the training should not take more than 10 minutes. If your health worsens, for example, patients with hypertension may experience shortness of breath or heart pain, classes should be stopped immediately. It doesn’t matter whether a child or an adult has suffered from coronary artery disease, the doctor will select all the exercises while still in the hospital and give recommendations regarding home exercises.
Yoga for arrhythmia
Practical experience in using yoga exercises has shown their effectiveness specifically for cardiac arrhythmia. They combine not only physical exercises that are beneficial for this pathology, but also proper breathing. Yoga helps restore heart rate and stability.
Exercises are performed in a ventilated room, on an empty stomach, preferably in the morning. After classes, it is not recommended to eat immediately, but only after 40-60 minutes.
Attention! The main conditions for performing the exercises:
- The muscles of the body should be relaxed.
- Breathing movements must be performed at a slow, calm pace.
Recommended set of exercises
- Lotus pose. The backs of the hands touch the heels. Take a slow breath, tighten your stomach and bend over so that your forehead touches the floor. Exhaling slowly, sit back in your previous position. At first, this exercise is performed once a day. After 2-3 weeks, you can perform it twice a day, taking into account all the recommendations.
- Lie on the floor or carpet with your head facing east. Alternately, raise your legs: right – inhale, left – exhale. The duration of repetitions is 5-7 minutes at an even, calm pace.
- Slowly raise your arms up and back, while taking a deep breath. Exhalation is accompanied by the return of the hands to the starting position. But at the same time you need to lift your body from the floor and touch your legs with your hands.
- Lying on the floor, make sure that your arms lying parallel to your body do not touch the floor with your elbows. Raise your head and legs from the floor to a distance of 15-20 cm and stay in this position for 2-3 seconds. All this is done with a slow, deep breath. As you exhale, you need to return to the starting position.
- Lying down, bend your knees so that you can grab your ankles with your hands. At the same time, you need to take a deep breath. As you exhale slowly, lower your limbs. This exercise can be repeated 7-8 times and performed twice a week.
Useful exercises to strengthen the myocardium
In diseases of the cardiovascular system, it is the loads that can increase the resistance of the myocardium to oxygen starvation that bring benefits. These include walking, running, swimming, dancing. Breathing exercises have a similar effect on the heart muscle. Methods for carrying it out may differ, but the most important rule is that the exercises must be performed at an individual, comfortable level.
First aid for arrhythmia
The method of restoring heart rhythm using breathing is based on the fact that a measured rhythm of inhalation and exhalation, which a person can control, normalizes the rhythm of contractions of the heart muscle. Therefore, any option with counting the duration of respiratory movements helps with arrhythmia.
To do this, you can inhale for 2 - 3 counts and exhale for 4 - 6 counts. In this case, you need to be in a sitting position with a straight back. It is recommended to gradually stretch your inhalations and exhalations, focusing on your sensations.
After mastering this exercise, the following type of pulmonary exercises is recommended to prevent attacks:
- Left hand behind back.
- The right hand is located near the face.
- Close your right nostril with your right thumb.
- Inhale through the left nostril.
- Close the left nostril with your ring finger and exhale through the right nostril.
After 8 - 10 breathing cycles, you need to change hands. The duration of the first lesson should not exceed 2 - 3 minutes, then you can slowly increase it. The duration of inhalations and exhalations is determined by comfortable sensations.
For cardiac aneurysm
The use of any load for training, even breathing, with an aortic or cerebral aneurysm, is possible only after consulting a doctor, since stress can provoke intense internal bleeding and death.
If there is a small and stable aneurysm or an operation has been performed to remove this vascular defect, then the doctor may allow you to do gymnastics, including breathing. In this case, any low-intensity and slow movements with simultaneous inhalation and exhalation are indicated:
- spread your arms to the sides - inhale, hug yourself by the shoulders with them - exhale;
- with the pelvis stationary, turn the chest to the right - inhale, return to the starting position - exhale;
- in a position lying on your back, inhale with your stomach for 2 counts, raising the abdominal wall; for 4 counts, exhale, drawing in your stomach.
Watch the video about doing exercises for the heart and their benefits:
httpv://www.youtube.com/watch?v=embed/aNUu4Fhvkts
After operation
From the second day, with an uncomplicated postoperative course, patients begin breathing exercises under the guidance of a doctor to prevent congestion in the lungs. To do this, it is recommended to spend 5-6 times a day for 5 minutes:
- exhale through closed lips (movements like when blowing out a candle);
- inflating balloons or rubber toys;
- exhaling air through a straw into a glass of water.
After 5-6 days it is allowed to sit on the bed and walk within the ward. At this time, breathing exercises are carried out in an expanded mode. Recommended:
- deep belly breathing with accentuated exhalation,
- smooth stretching of the exhalation length,
- inhale for 3 counts and exhale, and then 2 more short exhalations.
With tachycardia
To slow down your heart rate you need maximum relaxation. This can be achieved by changing the ratio of the duration of inhalation and exhalation, as well as by pausing after exhalation. In the first lessons, the ratio of these phases is 3:5:2.
Every day they are increased by 1 count, if discomfort appears, they are stopped until a stable result is obtained, and then you can continue to stretch each breathing movement. If at first it is difficult to breathe like this, then after 3-4 cycles they return to normal breathing; after its restoration, it is recommended to extend the lesson.
To improve blood vessels
To normalize vascular tone and increase performance, the following exercise is performed: after a normal (non-forced) inhalation, you need to exhale sharply and briefly, while drawing in your stomach as you exhale. This is followed by a passive inhalation and a sharp exhalation.
Do 10 cycles of the right nostril with the left one closed, change sides, also take 10 inhalations and exhalations, then with both nostrils 15 times.
Other types of physical activity
For cardiac arrhythmia, physical exercise should be moderate, but daily. Their intensity is increased gradually so that the body can adapt. At first, this may be a short walk with mandatory heart rate monitoring. Then you can alternate walking with running at a slow pace.
When heart rhythm disturbances occur, swimming is very effective, but without stress, which can be done in a pool or in calm natural bodies of water. Riding a bicycle or an exercise bike is not contraindicated. In winter, you can make ski trips on flat slopes without descents or ascents.
(
2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Doctors' opinion
Numerous studies have confirmed a direct connection between the occurrence of atrial fibrillation and how intensely a person exercised. The most common type of disease, atrial fibrillation, has recently been diagnosed more and more often in young people who spend a lot of time in the gym. Although, according to generally accepted opinion, it is the “prerogative” of elderly people, patients with heart defects and arterial hypertension.
This suggests that with cardiac arrhythmia, prolonged physical activity can be life-threatening. Moreover, patients with such a diagnosis will probably be banned from professional sports by a cardiologist.