Palpitation is a sensation of fluttering or pulsating in the area of the heart. The feeling of palpitations can be caused by a stressful situation, physical activity, medication, or, in rare cases, a person's health condition.
Although the sensation of heart palpitations can be distressing, it usually does not pose a risk to human health. In rare cases, palpitations may be a symptom of a more serious heart condition such as an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), which may require treatment.
Psychological reasons
The main psychosomatic causes include:
- emotional stress;
- depression;
- panic attacks;
- stress.
Indeed, in an anxious state, a person’s heart begins to work faster, and consequently, symptoms such as sweating, tremors, shortness of breath appear, and, of course, the body gives a signal in the form of a palpable heartbeat.
If you feel your heart beating and all possible diseases have been ruled out, there is another way to solve the problem - eliminating stress and conflicts. If the cause of your palpitations is psychosomatics, then you should change your lifestyle. Give up stressful work, change or expand your social circle, try to eliminate any stress.
Consider adopting new healthy habits, such as walking in the fresh air, playing sports, or visiting health resorts. If possible, go to the sea to breathe the salty air. Take a course of massage, electrophoresis. Give up bad habits: smoking, drinking coffee or tea, energy drinks that stimulate the nervous system, and, of course, overeating. If your heart palpitations are caused by illnesses such as a panic attack or depression, consult a psychiatrist. These ailments are treated with medication.
How to treat palpitations with normal pulse and blood pressure
To eliminate the feeling of palpitations with normal pulse and pressure, you need to identify the cause and fight it:
- If heart problems are established, heart-supporting medications are prescribed to normalize the rhythm. These are, for example, Digoxin, Corglicon, Bisoprolol or Concor, Atenolol, Novodigal.
- In case of hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, medications are selected that reduce the production of hormones. These may be Mercazolil, Propicin, Tyrosol or glucocorticosteroids.
- For neurotic origins of increased heartbeat, Glycine, Valerian Extract, Motherwort Forte, Novo-Passit are prescribed. But they can also prescribe stronger sedatives from the group of antidepressants and tranquilizers.
- Infectious diseases are treated with antibiotics. Along with them, medications that restore normal heart rhythm and vitamins may be prescribed.
- If the cause of the problem is anemia, its nature is identified and iron supplements are prescribed. These are Sorbifer, Maltofer, Aktiferrin, Fenyuls. They also adjust their diet and lifestyle in general.
Whatever the cause of increased heartbeat, medications and their dosage should be selected by a specialist. Self-medication can quickly and seriously worsen your health.
Normal heart condition
Before we look at the main medical reasons why a person can feel their heartbeat, it is worth deciding how many heartbeats there should be on average per minute. The heart is a biological engine for the distillation of blood. In order to saturate the cells of organs with oxygen, the heart works continuously throughout life. It has three states: relaxation, atrial contraction and ventricular contraction. Normal heart rate is approximately 60-80 beats per minute.
Going beyond these indicators is a deviation. There are external reasons why the number of heart beats may increase or decrease. You can feel the heart beating just by putting your ear to your chest, or using a phonendoscope. You need to measure your pulse at rest. Before this, you need to clarify the patient’s well-being and his diagnosis. The pulse depends on the time of day, temperature and humidity, the mood and mental state of a person, and age.
As already mentioned, in an excited emotional state, the number of heart beats per minute in a person increases. When the temperature rises, the heart rate also increases, and when the temperature drops, it slows down. Children tend to have a much faster pulse than adults. It can be up to 120 beats per minute, but with age it decreases and at the age of 15, during teenage puberty, it returns to normal - 60 beats.
How to calm a loud heartbeat without affecting the pulse using traditional methods
Loud heartbeats with a normal pulse can be made more moderate by taking:
- Decoctions of motherwort, hawthorn, rose hips, St. John's wort. They strengthen the heart muscle, soothe, contain vitamins, and have a pleasant taste. The course of using one of the herbs is 10-14 days. You should drink liquid 2-4 times a day.
- Decoctions of lemon balm, mint, chamomile. These herbs also calm and strengthen the nerves and relieve intoxication. You can mix them and brew them like tea, adding honey to the warm liquid before drinking.
Herbs are especially useful for neurotic origins of heartbeat, when a person feels the pulse throughout the body. They also provide an effect for heart problems, fatigue, and infections, but do not replace medications.
Atrial fibrillation
The most common abnormality in the field of cardiology is atrial fibrillation. It is determined by the following symptoms: the heart either stops, then starts beating sharply, as if you had just run a cross-country race. A person hears the sound of a heartbeat. The main symptoms also include difficulty breathing, dizziness, and chest pain. Often the disease is asymptomatic, which is a more dangerous condition for a person, because not diagnosed in time can cost health or even life.
If we talk about the physiological features of this disease, then instead of a full contraction of the atria, fibrillation occurs, that is, incomplete contraction, while the ventricles of the heart contract to 160 beats per minute. This is very dangerous for the heart, as it experiences incredible overload. The first symptoms may occur during times of stress. The consequences of the disease manifest themselves in the form of strokes, heart attacks and various heart diseases. If the sound of the heartbeat is noticeable even at rest, this is a serious signal from the body.
The main causes of arrhythmia are hereditary or congenital heart disease and valve disease. Another cause is coronary heart disease. Also, improper functioning of the organs responsible for hormones affects the heart muscle.
Like any disease, arrhythmia is better prevented than treated. Heart health is affected by a person's lifestyle. Play sports, get rid of bad habits that have a detrimental effect on the heart, worry less and you will never know what it means to feel your heartbeat in a calm state.
Complications
If the palpitations are not caused by heart disease, the risk of complications is low. Possible complications of heart palpitations caused by heart disease:
Fainting. If your heart beats fast, your blood pressure may drop, causing you to faint. This most often occurs when there are heart problems, such as congenital heart disease or certain heart valve diseases. Heart failure. In rare cases, heart palpitations can be caused by life-threatening arrhythmias and can reduce the efficiency of the heart. Stroke. If your heart palpitations are caused by atrial fibrillation, a condition in which the upper chambers of the heart tremble instead of beating properly, blood can pool, causing blood clots to form. When a blood clot breaks loose, it can block a cerebral artery, causing a stroke. Heart failure. This can cause the heart to work ineffectively for a long period of time due to arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation. Sometimes controlling your heart rate for an arrhythmia that is causing heart failure can normalize your heart function.
Treatment of atrial fibrillation
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to determine the source of the disorder, namely with the interruption of which valve or ventricle it is associated with. It is necessary to completely examine the entire cardiovascular system. The course of treatment consists of lifelong observation by a cardiologist, drug treatment, and, in some cases, surgical procedures. Most often, arrhythmia is classified as a chronic pathology, and surgical intervention is rarely required. It is necessary for people with congenital heart disease and is performed in children under 14 years of age when drug treatment is ineffective.
Are heart murmurs dangerous? When to sound the alarm?
Heart murmurs can be not only pathological, but also functional – i.e. be an absolutely normal consequence of increased load. Functional noises can occur due to disturbances in blood flow and changes in blood parameters. Their appearance is caused by fever and pregnancy. Pathological noises can be associated with various disturbances in the functioning of the organ itself, pathologies in the functioning of the thyroid gland.
What are the risk factors?
There are many physiological reasons why heart murmurs may occur. These include:
- Causes that are not related to cardiac activity, but have a direct impact on the functioning of the heart. An example is the change in vagal tone observed in vegetative-vascular dystonia.
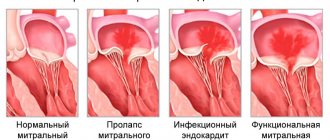
- Anomalies in the structure of the heart. These are not always dangerous pathologies. In some cases, these are small differences in the anatomical structure of the organ, which are formed in the prenatal period. Possible abnormalities include mitral valve prolapse, accessory chordae of the left ventricle, or the presence of a patent foramen ovale located between the atria. Anatomical deviations can affect large bronchi, which will create compression of the aorta and pulmonary artery, as a result of which blood flow will be slightly impaired.
- Metabolic disorders. A classic example is anemia, when increased work of the heart is necessary to compensate for signs of lack of oxygen. Accelerated blood flow causes noise. Most often, murmurs are auscultated at the apex of the heart.
- Changes in blood viscosity and tachycardia are observed in cases of disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system (thyrotoxicosis) and in febrile conditions.
- A state of prolonged fatigue caused by various types of stress: physical, mental, mental, can lead to disturbances in the functioning of the ventricles.
- During pregnancy, the occurrence of noise is normal, as there is an increase in the volume of circulating blood. However, such heart murmurs can be considered normal only in cases where the patient was examined earlier and no pathologies were identified.
8
24/7
Pathological causes
- When heart murmurs are detected, the causes may lie in defects. These are disorders that can be either acquired or congenital, affecting the heart and its vessels, in which abnormalities are observed in the anatomical structure of the organ and a predisposition to destruction of the heart valves. Valve damage can manifest as stenosis, insufficiency, or a combination of both. Heart murmurs in adults often develop against the background of tonsillitis or scarlet fever.
- Cardiomyopathy. Dilation of the chambers of the heart or thickening of the myocardial walls, caused by prolonged toxic effects on the heart muscle of thyroid or adrenal hormones. Other causes include hypertension and myocarditis.
- Rheumatic or bacterial endocarditis is accompanied by an inflammatory process of the endocardium and an increase in bacterial vegetation on the valves. The result is heart valve murmur.
- Acute pericarditis is inflammation of the pericardium, which will also be accompanied by the appearance of noise.
Symptoms
Symptoms may vary, since heart murmurs are caused by different reasons. In this case, only a doctor can detect the noise by auscultation.
Possible symptoms accompanying the appearance of noise may include:
- paleness of the skin, general weakness and fatigue (this is how anemia manifests itself);
- increased irritability, aggressiveness, rapid weight loss, tremors (thyrotoxicosis);
- dizziness, emotional lability, fatigue (may indicate VSD).
The following signs may indicate pathology:
- heartbeat disturbances;
- the appearance of shortness of breath at rest and after exercise;
- swelling of the lower extremities;
- dizziness and loss of consciousness;
- chest and chest pain.
Diagnostics
Noises can be determined using the following diagnostic measures:
- auscultation of heart murmurs (listening) is the most effective diagnostic method;
- angiography (allows you to assess the condition of blood vessels);
- chest x-ray;
- EchoCG;
- ECG;
- cardiac catheterization;
- load tests.
8
24/7
The strength of noise is determined using special tests:
- assessment of breathing patterns at the moment of inhalation and exhalation;
- Valsalva maneuver (the patient exhales forcefully, while closing the nose and mouth).
Treatment
Depending on the cause, treatment may be medication or surgery. The preparation of a treatment plan is carried out by a doctor, taking into account many factors: existing medical history, previous diseases, additional symptoms, and the patient’s age.
Drug treatment often involves the use of the following drugs:
- Anticoagulants. They thin the blood and are intended to prevent the formation of blood clots in blood vessels.
- Diuretic drugs. They help bring high blood pressure back to normal, relieve swelling and excess fluid accumulation in the body.
- ACE inhibitors. Used to lower blood pressure.
- Statins. Regulate blood cholesterol levels.
- Beta blockers. Regulate heart rate and lower blood pressure.
It is not possible to manage with one drug during treatment. As a rule, it is necessary to prescribe a whole range of medications. This is due to the fact that disturbances in the functioning of the heart lead to disruptions in the functioning of other body systems. Therefore, specialists of different profiles can participate in treatment.
Drug treatment can reduce the load on the valves, but in case of serious pathologies it is not enough and surgical intervention is required.
The following types of operations can be performed:
- Valvuloplasty. During the operation, a catheter is inserted, at the end of which a balloon is attached. The balloon is inflated, it increases in size, expanding the space around it.
- Annuloplasty. The essence of the intervention is to install a special ring that strengthens the area around the valve. The operation is performed to restore the mitral valve.
- Surgery on the valve or its supporting tissues. Used when it is necessary to repair valves that do not close correctly.
- Another surgical option is valve replacement. It is used when it is impossible to restore the valve due to existing defects.
The operation can be carried out in 2 ways:
- Open heart surgery. During the intervention, a mechanical or biological valve can be installed. Each of them has its own characteristics, so it is selected depending on the overall health situation. A mechanical valve will last longer, but may cause blood clots to form. Its installation will accompany lifelong medication use. Taking anticoagulants is mandatory - it will reduce the risk of stroke.
- Transcatheter replacement. There is no need for open heart surgery. The new valve is installed using a catheter. The catheter is inserted into a vessel located, for example, on the leg and passed to the heart.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the cause of the noise, the degree of development of the pathology and the treatment performed.
Noises associated with anemia and thyroid diseases can be completely eliminated with treatment.
A conditionally favorable prognosis accompanies the situation with acquired valve defects caused by a prolonged inflammatory process (after surgery).
In case of congenital anomalies of the anatomical structure, active compensatory work is required to maintain the functionality of the body. Because of this, heart failure often develops, which is quite difficult to treat. If congenital defects are detected, treatment must be carried out necessarily. First, they increase the risk of sudden death. Secondly, the organ is at greater risk of developing bacterial endocarditis.
Prevention
Measures should be taken regardless of the age at which a heart murmur is detected.
If a heart murmur is detected in a child, it is necessary to carry out regular examinations in the future.
In adolescence, heart murmurs are most often caused by physiological changes in the body and the growth of the chest. In this case, physical activity and active sports are recommended. To prevent the development of rheumatism, which will have a detrimental effect on the condition of the heart, adequate (if necessary, with the use of antibacterial drugs) treatment of inflammatory processes in the throat, sore throats, pharyngitis, etc. is necessary.
If pathology is detected in patients for whom surgical intervention is contraindicated, it is necessary to pay attention to nutrition: avoid fatty foods, giving preference to fresh vegetables and fruits. This will reduce the risk of developing vascular atherosclerosis. In addition, it is necessary to give up bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol.
You should not select complexes for physical education without consulting a doctor. The permitted amount of physical activity must be agreed with your doctor.
If a heart murmur occurs against the background of pathologies of other organs and systems (diabetes, endocrine system disorders), it is necessary to carry out treatment for existing diseases.
Early diagnosis of cardiovascular disease is extremely important. This will avoid the development of life-threatening complications. Therefore, preventive examinations are recommended - visit a specialist once a year to assess how the heart is working.
8
24/7
Tachycardia is the main cause of severe pounding in the chest
The second most common heart disease is tachycardia. Normally, at rest in an adult, the number of beats per minute should be up to 80 times. But if you find that the number of beats is 100, then quickly make an appointment with a cardiologist. Due to intense work, the heart beats harder and, as a result, is more noticeable to a person.
If the number of beats exceeds this norm, this is one of the signs of tachycardia. Naturally, the disease negatively affects the functioning of the heart - the ventricles do not have time to fill with blood, so there is a deterioration in the blood supply to organs and tissues, and as a result, there is a lack of oxygen.
As a rule, the cause of tachycardia and a constant feeling of palpitations are excessive physical exertion, sunstroke, and diseases of the body, both infectious and viral. Treatment is very simple if you consult a doctor in time. If the necessary drug treatment is provided, heart problems should not arise. After a certain period, tachycardia, if left untreated, becomes chronic, which leads to a worsening of the condition, a person feels the heart beating more strongly, heart disease and inflammation of the myocardium appear.
To summarize, we determine that tachycardia is the main cause of a strong heartbeat, as a result of which a person can hear his own beats. From this we conclude that normally a person should not hear his own heartbeat.
Feeling of palpitations with a normal pulse - what is it, the main reasons
The sensation of palpitations with a normal pulse is a condition that requires investigation, caused by one of the reasons:
- Arrhythmia. With this heart disease, the heart beats unevenly, but the heart rate may remain the same. Or increase, but not fall outside the norm.
- Infectious myocarditis or endocarditis. These are inflammatory diseases of the myocardium and inner lining of the heart, caused by viruses or bacteria. One of the symptoms of both is increased heartbeat.
- Cardiosclerosis. Here, normal heart tissue is replaced by connective tissue due to metabolic disorders or previous illness, high loads, problems with hematopoiesis, and thyroid gland. Therefore, the conductivity of impulses is disrupted, and arrhythmia can form.
- Myocardial dystrophy. When the disease occurs, the myocardium undergoes negative changes, as a result of which its functions are also impaired. This results in oxygen deficiency, shortness of breath, rapid heart rate, loud heart sounds and extraneous noises. The pulse may not fall outside the normal range. That is, he seems to be normal, but the person feels bad.
- Heart disease. There are many options here, and not all of them are congenital; there are also acquired ones. Some defects present at birth may become apparent over time.
- Arterial hypertension. With increased pressure, the functioning of the ventricles of the heart is disrupted. This and other changes lead to tachycardia.
If it seems that your heart is beating faster than usual, or there are other signs of deterioration in health (headache, heaviness in the chest, shortness of breath, nausea, fear), you should see a doctor.
Other reasons
Non-cardiological causes of palpitations in the chest also include:
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- anemia;
- neurosis;
- menopause;
- elevated temperature.
These diseases are accompanied by the following symptoms: dizziness, shortness of breath, suffocation, increased fatigue, sweating, chest pain. Treatment of these diseases is carried out by a specialist.
How to get rid of palpitations
In addition to special cases, there is general treatment. First of all, go to your local clinic and see a general practitioner, who will refer you for a general blood and urine test. After conducting these examinations, he can identify pathology in other organ systems, after which he will refer you to a cardiologist. He will conduct the following tests:
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- ECG;
- ECG with stress.
If abnormalities are detected, the doctor may refer you for the next test - heart monitoring for several days. The device will measure your pulse, blood pressure and breathing rate for 2-3 days, after which a diagnosis will be made based on the data.
It is also necessary to exclude complications of diseases, determine and make an accurate diagnosis. It is important to comply with therapy. If your health worsens, you should consult your doctor again. Most often, corticosteroids and cardio medications are prescribed for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Speaking about the most popular tablets that are used to treat cardiovascular diseases, we need to name “Aspirin”, “Captopril”, “Nebilet”, “Panangin”. All medications should be taken only after a doctor's prescription. As for non-pharmaceutical methods of treating the heart, examples of effective herbal medicine are a decoction of valerian herb, mint tinctures and tea with chamomile flowers.
If your heart is beating loudly: diagnosis
When the pulse is normal, but the heart is beating strongly, you should first consult a physician. After all, heart rate norms have wide boundaries for each age. And for one person a pulse of 80 is optimal, while for another the same value is accompanied by a deterioration in well-being, as it is a symptom of an illness. The following methods will help to identify it or ensure the patient’s health:
- ECG,
- Ultrasound of the heart,
- blood test for hormones,
- general blood test.
It is also important to measure your blood pressure several times throughout the day and keep a diary. If the above diagnostic methods reveal a problem, they may additionally prescribe a chest x-ray, MRI, as well as consultation with specialists.