A reduced level of basophils is called basopenia, but this is a conditional laboratory concept. The concentration of cells is extremely low, and therefore they may simply not be detected in a blood test.
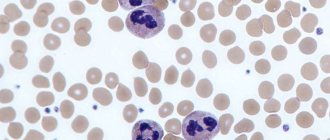
Basophils are called white blood cells. This is a group of granulocytic leukocytes responsible for hypersensitivity reactions. It is through basophils that the body is protected from allergens, toxins and poisons. Due to them, local and systemic manifestations of allergic reactions develop.
Role and functions of cells
Basophils are produced in the bone marrow, after maturation they enter the systemic circulation and after a few hours migrate to peripheral tissues, where they perform a testing and protective function. They recognize foreign protein substances, inactivate them or attract other protective bodies to the entrance gate. Basophils react to food and drug allergens, toxic compounds, toxins of insects, animals, parasites, and plants.
They differ from other granulocytes in their large size, S-shaped nucleus, multiple granules in the cytoplasm, and ability to transport immunoglobulins. Biologically active substances responsible for allergic and inflammatory reactions are concentrated inside basophils:
- interleukins;
- leukotrienes;
- prostaglandins;
- serotonin.
In the highest concentrations they contain two antagonistic (opposite in action) substances - histamine and heparin. The first triggers an inflammatory reaction, increases vascular permeability, and activates blood clotting. The second normalizes smooth muscle tone, prevents thrombus formation, and reduces membrane permeability.
Basophils are prone to chemotaxis - movement towards inflammatory foci, phagocytosis - they can absorb small particles, degranulation - instant release of the contents of granules upon contact with allergens, autolysis - self-destruction after performing their functions. Under their control:
- allergic reactions (including immediate type);
- blood clotting in small capillaries;
- mobilization of other leukocytes against pathogens, including parasites;
- starting the growth of new capillaries;
- accumulation and removal of bioactive substances from tissues (elimination of the consequences of allergies).
Basophils are similar to other proallergic cells - mast cells (mast cells). They are even produced from the same antecedent structures. Previously it was believed that mast cells are fully mature basophils. Later it was proven that the bodies are different, and basophils leave the bone marrow already functionally active, while mast cells are finally formed in the connective tissue.
What are basophils, functions
In the KLA, the indicator is present in the leukogram. Basophils are blood cells from the group of granulocytes. Produced by the bone marrow, they are a type of white blood cell. Viability is maintained from seven to twelve days.
Establishing the level of basophils helps to identify pathological inflammation or the presence of allergic reactions. The resulting focus of inflammation attracts basophils as part of other leukocytes. They are then transformed into heparinocytes, which are involved in the production of histamine, as well as serotonin and heparin. Histamine is designed to combat hypersensitivity, and heparin reduces the ability of blood to clot. Serotonin expands the vascular lumen and increases the ability of the vascular membranes to absorb and release substances.
The cells contain prostaglandins, the purpose of which is to prevent the action of the irritant and neutralize it. At this time, a person feels hyperthermia, becomes weak, and has a fever.
The main purpose of basophils is to take part in immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reactions. The cells are the first to reach the source of inflammation and signal the presence of foreign agents. If the inflammation process lasts longer than three days, more and more basophils are produced in the body.
Main functions:
- trigger the blood clotting reaction;
- participate in the creation of new blood vessels;
- participate in triggering allergic reactions;
- help increase capillary permeability;
- protect the body from infections and parasitic infestations.
A normal indicator is the presence of no more than 1% basophils in the blood. A reduced amount (basopenia) and an increased amount (basophilia) are grounds to suspect an inflammatory process or blood pathology.
Blood levels
The number of leukocytes is determined as part of the general analysis. If you need to find out the size of each group, a detailed CBC is performed with a leukogram or leukocyte formula. The research protocol may indicate only a percentage indicator, or two (relative and absolute). The last value reflects the number of cells per unit volume of blood (liter, milliliter, microliter). Laboratories may use different counting methods and equipment, and therefore reference values (normal values) may differ. Each medical institution indicates the results obtained and physiological values for comparison.
Table - Normal leukogram
| Group of cells | Share, % | Absolute indicator, 10⁹/l |
| Band neutrophils | 1‒6 | 0,04‒0,3 |
| Segmented | 48‒75 | 2,0‒5,5 |
| Eosinophils | 0,5‒5 | 0,02‒0,3 |
| Basophils | 0‒1 | 0,01‒0,065 |
| Lymphocytes | 19‒37 | 1,2‒3,0 |
| Monocytes | 3‒11 | 0,09‒0,6 |
A zero relative basophil index is considered normal. The fact is that the number of these bodies is very small compared to leukocytes of other groups. The upper threshold for adults is 1%; other values are considered normal for children.
Table - Basophil norms for children
| Population category | Reference value, % |
| Newborns | 0‒0,75 |
| 1 month old babies | 0‒0,5 |
| Up to a year | 0‒0,6 |
| Up to 2 years | 0‒0,07 |
| Over 2 | 0‒1 |
It is impossible to determine basopenia by relative indicator. The condition is stated only if the absolute value is lower than 0.01*10⁹/l.
In what diseases are basophils reduced?
A deficiency of corpuscles is determined much less frequently than their excess (basophilia). The reasons for the increased number of basophils are allergic reactions, inflammatory processes, and cancer (see “Elevated basophils” for more details). Basopenia in adults can be accompanied by:
- acute immune responses to the invasion of toxins, infections, parasites, allergens, cell death, or directed against one’s own body;
- chronic exposure to stress;
- physical exhaustion (with long-term and severe illnesses, malnutrition, acute deficiency of vitamins and minerals);
- pathologies of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland;
- treatment with hormonal drugs;
- diseases of the nervous system.
The basophil count drops to a critical level (up to complete absence) with agranulocytosis. This condition is accompanied by a decrease in the number of all granulocyte bodies (segmented neutrophils and eosinophils also decrease).
Agranulocytosis may be of myelotoxic origin (due to damage or malignant degeneration of bone marrow cells). It is caused by radiation, treatment with cytostatics, and some antibiotics (from the penicillin group, Gentamicin, Rifampicin). Immune agranulocytosis can develop against the background of thyroiditis, malaria, polio, influenza, collagen diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma).
During pregnancy
In women, basophils may be absent in a blood test during pregnancy. Most often this is caused by anemia (B12- or B9-deficiency). A temporary decrease sometimes occurs during ovulation, however, this is an irregular phenomenon. In some cases, a slight increase in cell levels is noted. If the CBC shows a normal content of blood cells, except for basophils, one can suspect a natural decrease in their concentration against the background of an increase in the volume of circulating blood.
In children
Basopenia in a child is most often caused by a past infection or severe allergy, which leads to a redistribution of cells in the body. It is also encountered by almost all small patients who undergo chemotherapy or radiation therapy. Since these methods inhibit cell division, a decrease in all groups of leukocytes is observed simultaneously.
Useful information: Bilirubin in urine is increased: more than 3 reasons, what does this mean, normal, treatment in adults and children. What diseases can it talk about?
Approximately 1 person in 100 thousand suffers from Cushing's syndrome. It has been proven that pathology occurs 5 times more often in women than in men. It is diagnosed from 20 to 45 years of age, but there are cases among children. Cushing's disease is caused by hyperplastic degeneration of the pituitary lobes and leads to excessive synthesis of adrenal hormones. The pathology is accompanied by manifestations of hypercortisolism. In childhood, they provoke retardation in mental and physical development, and subsequently lead to disruptions in the functioning of all organs and systems, and severe metabolic disorders.
How to get rid of basopenia
A physiological decrease in protective blood cells (after an illness, for example) does not require drug intervention. Cell parameters return to normal as the body recovers. To monitor the process, it is worth stopping blood tests 1–2 weeks after complete recovery.
If lymphocytes and basophils are low in a pregnant woman, you should not take measures on your own. Immunodeficiency can be caused by hormonal changes, which are aimed at preserving the life of the fetus in the womb. The doctor may prescribe vitamin and mineral complexes to the woman and advise her to rationalize her diet.
When the objective reasons for the decrease in basophil concentration cannot be established (no diseases have been identified, other blood elements are normal), the patient is recommended to optimize the daily routine, diversify the menu, get enough rest and spend more time in the fresh air.
If basopenia accompanies some pathology, treatment is aimed specifically at the disease, and not at abnormalities in the CBC. Autoimmune diseases are treated with hormonal agents, bone marrow lesions are treated with chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and sometimes bone marrow transplantation is used. If the disorders are caused by medications, you will need to adjust the dose or discontinue the offending drugs. In case of severe immunodeficiency, the patient will need to be hospitalized and placed in an aseptic box.
FAQ
Question: If the absence of basophils in the blood is considered normal, why did the doctor say to retake the test in a week?
Answer: Perhaps the specialist was alerted by other indicators of blood cells, or he suspected a violation of the rules of preparation for the study, the influence of the phase of the cycle, which indicates the risk of receiving unreliable information. A repeat CBC is needed to make sure everything is normal.
Question: How to pass the test correctly so as not to retake it later?
Answer: 3 days before a general blood test, you need to stop taking medications, except for vital ones, and avoid alcohol. During the day you should limit physical activity, stress, and mental stress. The doctor recommends giving up unhealthy, spicy, fatty foods and moderating the amount of protein you consume. You need to eat your last meal 12 hours before handing over the biomaterial. On the way to the laboratory, you need to avoid freezing or overheating; it is better to sit quietly for 10 minutes before visiting the manipulation room. Even if all recommendations are strictly followed, it is impossible to guarantee the absence of deviations. In case of significant violations and suspected diseases, the test will still have to be taken again to exclude an error.
Question: How do periods affect the general blood test? Can I take it during menstruation?
Answer: Hormone levels change significantly throughout a woman's cycle. This affects the activity of the immune system and blood clotting. With bleeding, the concentration of leukocytes, red blood cells, hemoglobin, platelets may decrease, and the ESR may increase. Basophils can either decrease to zero or increase. Often deviations do not go beyond the norm, but this possibility cannot be excluded. Doctors recommend taking an OAC between periods, 3-5 days before or after them.
Question: I took the expanded OAC in two laboratories with an interval of 7 days. First, the test showed the complete absence of basophils, and then the lower limit of normal. How do we understand this and is it worth taking the test again?
Answer: Most likely, medical institutions used equipment of different sensitivity, or minor changes actually took place. A satisfactory result of the second test (provided there are no other abnormalities) indicates complete health. If there are no complaints, there is no need to take the UAC again.
Question: What does an increase in lymphocytes and a decrease in basophil levels indicate?
Answer: The level of lymphocytes increases in many diseases. First of all, you need to suspect acute viral infections, because it is these bodies that recognize viral particles and stimulate the formation of antibodies against them. A decrease in the number of basophils may simply be the result of more active synthesis of other leukocyte cells. If the patient is sick or has recently had an acute respiratory viral infection, there is nothing to worry about. If there are no complaints about your health, you should consult a doctor. This state of affairs may indicate a violation of the immune system.
Diagnostics
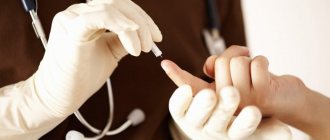
In order to determine the number of basophils in the blood, a general clinical blood test is performed. Fluid for testing is collected from a finger. This procedure is very simple and does not take long, but to ensure the reliability of the results obtained, you must adhere to the following rules:
- do not have breakfast on the morning of the test;
- undergo the procedure in a calm physical and emotional state;
- the day before the OAC, avoid heavy food and alcohol;
- If possible, you should also avoid taking medications that are included in the etiological list at this time.
Determining only the number of basophils from a diagnostic point of view is not very informative, therefore the absolute content of basophils and indicators of other elements of the leukocyte formula are always taken into account.
- Basophils in the blood
conclusions
Basophils are protective blood cells, indicators of allergies, inflammatory and oncological processes. In a healthy person, no more than 1% of white blood cells should be detected among all leukocytes and no less than 0.1 * 10⁹/l. If the number of cells is less, they speak of basopenia. The condition rarely indicates a serious illness, but this option should not be ruled out.
The level of basophils increases in allergic, inflammatory reactions, as well as in oncohematological diseases. Despite the insignificant content of cells in the blood, it is necessary to pay attention to their values so as not to miss serious pathologies. Read more about basophilia in the article: “Elevated basophils - what it is and its causes in adults and children. Is the condition dangerous?
If according to the results of the OAC there are other abnormalities, you need to consult a doctor for help.
Elevated
The normal basophil content should be in the range: from 0 to 0.09 X 109/l (0.09 Giga/liter). If you see 0.2 x 109/l on the test results form, this is no longer the norm, and you need to consult a doctor.
Main reasons for the increase:
- allergic reactions to bites or food;
- vaccinations;
- onset of an inflammatory disease;
- taking medications;
- parasite infection;
- poisoning;
- exacerbation of chronic pathological diseases.
The reasons for the increase in basophils in a child are temporary or appear periodically, for example, in warm weather the number of midges increases and children constantly suffer from allergic reactions to bites.
There are also more serious diseases in which the number of leukocytes increases:
- diabetes;
- chronic sinusitis;
- viral diseases - chickenpox, rubella, influenza;
- gastrointestinal diseases – gastritis, ulcers;
- hepatitis;
- diseases of the urinary system – nephritis;
- anemia;
- hematological diseases – leukemia, erythremia;
- viral hepatitis;
- initial stage of tuberculosis;
- diseases of the thyroid gland - hypothyroidism;
- oncological and tumor processes.
If a child is treated with hormonal drugs, the level of basophils will also be increased. In addition, leukocytes in the blood will increase during surgery. Radiation, even minor exposures such as x-rays, will definitely affect the increase in white cells.