Various approaches to losing weight limit certain foods, modifying the diet of the person losing weight. An unbalanced diet with minimal food and nutrients ultimately leads to iron deficiency in the body and other health problems. What does this mean? Let's figure it out together!
One of the reasons for weight stagnation during weight loss may be iron deficiency, since the microelement affects the thyroid gland, which affects metabolic processes. As a result, persistent efforts to lose excess weight lead to exactly the opposite result.
Iron is responsible for important functions in the human body. Microelement deficiency or surplus negatively affects health. However, a lack of a substance is much more common than an excess.
In this article we will look at:
- the role of microelements in human life and daily intake;
- percentage of iron absorption and factors influencing the process;
- what does a detailed table of foods containing iron look like (plant and animal sources);
- what iron-rich foods are suitable for anemia, pregnancy, vegetarian diet.
The role of iron in the human body
Iron is responsible for hemoglobin levels and is part of enzymes that perform the following functions:
- providing oxygen to tissues, cells and organs:
Iron-containing substance (heme) is found in a number of important molecules. Two of them are proteins - hemoglobin and myoglobin, which are involved in the transport and storage of oxygen. Hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells, makes up 2/3 of the iron in the body. Myoglobin helps muscle cells regulate the supply of oxygen needed by muscles.
- hematopoiesis – transportation of important elements into the vascular system;
- maintaining energy metabolism:
Heme is found in compounds essential for cellular energy production (cytochromes). Cytochromes act as electron carriers during the synthesis of ATP (the main substance that stores energy in cells).
- DNA production:
ribonucleotide reductase is an iron-dependent enzyme. It is essential for the process of DNA synthesis and thus makes iron responsible for a wide range of vital functions such as growth, reproduction, healing and immune function.
- antioxidant:
heme-containing enzymes catalase and peroxidase protect cells from the accumulation of hydrogen peroxide, which damages memory. This occurs through a catalysis reaction that converts hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
- formation of nerve fibers;
- body growth;
- maintaining cellular activity;
- assistance in redox processes.
The trace element is involved in protective functions. Foods rich in iron are especially important during pregnancy, since the body lacks the substance during gestation. Deficiency leads to the development of pathologies.
The body's daily requirement for iron
The recommended daily intake of iron for various age categories is:
| Life stage | Age | Men: mg/day | Women: mg/day |
| Babies | 0-6 months | 0,27 | 0,27 |
| Babies | 7-12 months | 11 | 11 |
| Children | 1-3 years | 7 | 7 |
| Children | 4-8 years | 8 | 10 |
| Children | 9-13 years | 10 | 8 |
| Teenagers | 14-18 years old | 11 | 15 |
| Adults | 19 years and older | 8 | 18 |
| Pregnant | Under 18 years old | — | 8 |
| Pregnant | 19 years and older | — | 27 |
| Nursing | Under 18 years old | — | 10 |
| Nursing | 19 years and older | — | 9 |
The total volume of iron in the body is 3-4 g. Location of the substance:
- blood plasma;
- muscles (myoglobin, ferritin);
- liver, spleen;
- tissue depots.
Side effects in case of overdose
Based on the recommended daily intake, iron side effects are rare. Exceeding the recommended dose causes:
- irritation of the gastrointestinal tract;
- vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- The stool is usually darker.
General rules
Iron is an essential trace element that is necessary for the normal functioning of all living organisms. Many processes occur with its participation: hormone , cell differentiation, metabolism .
It is part of respiratory enzymes and takes part in tissue respiration and redox reactions, and its presence in red blood cells ensures oxygen saturation of tissues. The main part of iron (about 65%) is found in hemoglobin and various depots (these include bone marrow, liver, spleen), then myoglobin , tissue enzymes and blood plasma follow in decreasing order of its content.
The need for iron depends on its losses and consumption. An adult man needs to consume 1 mg daily (or 13 mcg per kg of weight), and women need almost 1.5 times more - 21 mcg per kg of weight. In the last trimester of pregnancy , the need for it increases to 80 mcg per kg. The same amount is needed for an infant.
Entered with food, it is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. With sufficient nutrition, 10-20 mg is received daily, but only 2.5 mg is absorbed. This is due to several factors. First of all, food products contain ferric iron (oxidized), and only divalent iron is well absorbed. Partial transformation into an easily digestible divalent form occurs in the presence of ascorbic , succinic and pyruvic acid . In addition, iron absorption decreases after food is cooked, frozen, or stored.
A decrease in iron levels in the body leads to the development of iron deficiency conditions. First, stocks from the depot are consumed. With this disease, the level of iron in the blood, liver, bone marrow and spleen decreases. This entails a disruption in the formation of hemoglobin , red blood cells ( erythrocytes ) and tissue trophic (nutrition) disorders occur.
The causes of iron deficiency conditions are:
- Intensive growth (especially in the first year of life and in adolescence - the pubertal growth spurt), pregnancy and breastfeeding - all these conditions require an increased need for iron, since its consumption increases. If the deficiency is not replenished, anemia develops. From 2-3 years of age, the need for micronutrients decreases until adolescence, when rapid growth again raises the risk of deficiency. It is highest in young girls in whom the menstrual cycle is developing (11-14 years). In pregnant women, anemia develops in 20-80% of cases.
- Blood loss (for ulcers, injuries, malignant tumors, hemorrhoids , diaphragmatic hernia , esophageal varicose veins , diverticulosis , diseases of the respiratory tract and urinary organs, menorrhagia and metrorrhagia ).
- Long-term donation.
- Impaired absorption of iron during resection of the stomach or intestines, decreased gastric secretion, malabsorption syndrome .
- Taking anticoagulants, hormonal contraceptives, long-term use of antibiotics .
- Poor nutrition (such as vegetarianism or anorexia ).
- Excessive physical activity.
- Alcohol intoxication (chronic).
Early symptoms of iron deficiency (latent stage of anemia) do not cause concern in a person, and he considers himself healthy. In the future, in addition to weakness and increased fatigue, disorders of the endocrine, central nervous system and cardiovascular systems are noted. Exercise tolerance is significantly reduced. IDA causes complications in the mother and fetus: anomaly of labor, fetal hypoxia , delayed fetal development. Iron deficiency in young children leads to delayed psychomotor and emotional development.
Treatment should be comprehensive - medications and a diet rich in iron. Considering that iron from food is not completely absorbed, drug treatment is mandatory. Even a complete and balanced diet allows you to cover the physiological needs of the body, but does not eliminate its deficiency in anemia.
Taking iron supplements should be long-term and an improvement in hemoglobin and red blood cells does not indicate restoration of its reserves. Therefore, after normalization of Hb, the medication is continued for 1-2 months, but at half the dose. It should be remembered that almost all tablet drugs have an irritating effect on the gastrointestinal mucosa, causing pain, heartburn , diarrhea , nausea and even vomiting. Possible staining of tooth enamel black. Blood or red blood cell transfusion is used for health reasons (critical hemodynamic condition) in severe anemia.
The patient's nutrition must be complete. The diet contains an increased amount of protein (130-140 g), mostly of animal origin. Protein is necessary for the synthesis of hemoglobin , the construction of red blood cells and the formation of easily digestible iron compounds.
The amount of carbohydrates is within the physiological norm (up to 400 g). This includes complex carbohydrates (cereals, grain breads, muesli, fruits, legumes) and simple ones (sugar, honey, jam).
Since fats inhibit hematopoiesis, their quantity is limited (up to 70 g). They prefer easily digestible fats (all types of vegetable oils and butter). Animal fats, fatty meat and poultry, lard, and fatty sausages are subject to restrictions.
It is necessary to introduce into the diet an increased amount of vitamins that take part in erythropoiesis (group of B vitamins , ascorbic acid ). B vitamins are found in yeast (baker's and brewer's), legumes, liver, kidneys, egg yolks, meat, fish, milk, and cottage cheese. Folacin contains green lettuce, cabbage, green onions, soybeans.
Of course, an iron-containing diet must also include foods high in this microelement:
- meat (beef, rabbit, turkey, chicken);
- fish;
- beef tongue;
- liver (pork and beef);
- kidneys;
- heart;
- cottage cheese;
- chicken egg.
If we analyze food products containing iron, animal meat and poultry are sources of heme iron (only muscle tissue contains it) and its bioavailability is higher. In this regard, they should form the basis of the diet. If we compare animal products according to the content of this microelement, they are distributed (in descending order) as follows: beef tongue, rabbit meat, veal, beef, chicken egg, lamb, turkey, pork, chicken, cheese, cod, pink salmon, cottage cheese.
Iron in food products of plant origin (vegetables, legumes, cereals, tubers, fruits), as well as in milk and fish, is contained in non-heme form, the digestibility of which is much lower. In addition, tannins , soy protein, phosphates, dietary fiber and phytins form insoluble compounds with Fe.
Plant sources of iron include: asparagus, buckwheat, oat and millet cereals, grain bread, beets, sauerkraut, onions, fresh cabbage, zucchini, squash, green vegetables, mint, tops of plants and vegetables (radish, nettle, carrots, turnips) , mustard), dandelion leaves, watercress, apricots, apples, pears, oranges, pineapples, peaches, plums, strawberries, dried fruits, raspberries, strawberries, cherries, black currants.
Animal and poultry meat is a good source of heme iron with high bioavailability
Despite this, the diet should contain vegetables, herbs, and fruits, since they are the only sources of vitamin C , in the presence of which the absorption of this microelement in the duodenum improves (it restores iron and forms well-absorbed chelate complexes with it). It is necessary to eat all green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, sea buckthorn, rose hips, plums, black currants, all sour berries, pears, apples, all types of cabbage, including sauerkraut, carrots, beets, lettuce peppers, pumpkin, tomatoes.
Promote iron absorption and normalize the process of hematopoiesis:
- B vitamins - folic acid and cyanocobalamin - play a great role in hematopoiesis and their deficiency leads to disruption of DNA synthesis in stem cells, and this negatively affects the rate of hemoglobin synthesis. Sources of folic acid (lettuce, spinach, green onions, parsley, lentils, beans, beans, all types of cabbage, asparagus, citrus fruits, pears, apples, apricots, bananas, kiwi, pomegranate, currants, strawberries, grapes, raspberries) must be present in the diet. Suppliers of cyanocobalamin are: animal liver, meat, fish, caviar, fermented milk products, raw chicken egg yolk, yeast, salads, green onions, vegetable tops.
- Copper, which contains liver, cereals, legumes, mushrooms, nuts, raw yolk, strawberries, black currants, watermelons, horseradish, asparagus, beef, wheat sprouts, barley, asparagus, lentils, parsley, rye bread, kefir, yogurt.
- Succinic acid , found in fermented milk products, sunflower oil, sunflower seeds, barley, rye bread, gooseberries (green varieties), apples, cherries, grapes.
- Zinc, which can be obtained by eating yeast, liver, kidneys, legumes, mushrooms, beef, cheeses, eggs. The presence of an additive effect of zinc and iron justifies the need for use during pregnancy.
- Cobalt contains: liver, legumes, kidneys, grains, salad greens, beets, pumpkin, green vegetables, gooseberries, raspberries, apples, black currants, apricots, cherries, pears, nuts, citrus fruits, mushrooms.
- Sulfur-containing foods: onions, garlic and all types of cabbage.
- Spicy herbs - thyme, mint, cinnamon, anise, which can be used to season all dishes.
- “Animal protein factor” - protein increases the absorption of micronutrients and contains myoglobin and hemoglobin.
- Simple carbohydrates (fructose, lactose, sorbitol).
- Amino acids ( histidine , lysine , cysteine ) form easily absorbed chelates.
It is also necessary to take into account antagonistic products that impair the absorption of iron and form insoluble salts with its trivalent form. Such products include:
- Tannin-containing - the main content of tannin in coffee and tea.
- Chocolate.
- Phytin-containing foods (whole grains, rice, soy flour, legumes, bran, walnuts). Soaking cereals, legumes and nuts significantly reduces the phytic acid content;
- Polyphenols of nuts, legumes, tea.
- Oxalates (chocolate, grains, corn, spinach, sorrel, milk, tea).
- Foods high in calcium: sesame, milk, cottage cheese, dried fruits. Calcium can reduce the absorption of heme and non-heme iron.
- Eggs because they contain albumin and phosphoprotein .
- Cereals due to their dietary fiber and phytate . Dietary fiber in the intestines is almost not digested, and iron is fixed on it and excreted in feces.
Alcoholic drinks destroy iron in foods that are consumed with them. Heme iron has a relatively high heat stability, and foods with the non-heme form are not recommended for heat treatment. Meat, liver and fish, with the simultaneous use of vegetables and fruits, increase the absorption of iron from them.
What affects iron absorption
The body is able to absorb about a tenth of the iron it receives. Products and elements that negatively affect microelement absorption:
- phosphates, phytates and antacids;
- soy protein and albumin (egg white);
- milk and dairy products practically do not contain iron and have a detrimental effect on absorption;
- strong tea and coffee reduce absorption due to caffeine;
- phytic acid from cereals and legumes.
To neutralize the negative effects of the above products, it is recommended to additionally take ascorbic or citric acid.
Fully or partially limited products
Excludes:
- Fatty meat and poultry.
- Refractory fats.
- Sausages, smoked meats, canned food.
Limit consumption or consume following certain recommendations:
- Tea as a tannin-containing drink and coffee containing polyphenols. You should not drink them during meals or immediately after them - take a break of 1.5-2 hours.
- Don't go overboard with nuts and legumes due to their polyphenol .
- Eggs because they contain albumin and phosphoprotein .
- Whole grain cereals, rice, soy flour, legumes, baked goods, bran, walnuts due to the content of dietary fiber and phytic acid . Dietary fiber in the intestines is almost not digested, and iron is fixed on them and excreted in feces. Phytic acid reduces the absorption of many microelements, including this one. Based on this, meat and fish should be eaten separately from bread, cereals and pasta.
- Products with a high content of oxalic acid , which interferes with the complete absorption of the microelement, are spinach, sorrel, beets, asparagus, rhubarb, nuts, chocolate, corn.
- Products high in calcium: sesame, milk, cottage cheese, cheeses, dried fruits; calcium can reduce the absorption of heme and non-heme iron.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| vegetables legumes | 9,1 | 1,6 | 27,0 | 168 |
| canned vegetables | 1,5 | 0,2 | 5,5 | 30 |
| swede | 1,2 | 0,1 | 7,7 | 37 |
| canned cucumbers | 2,8 | 0,0 | 1,3 | 16 |
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| canned tomatoes | 1,1 | 0,1 | 3,5 | 20 |
| horseradish | 3,2 | 0,4 | 10,5 | 56 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| corn grits | 8,3 | 1,2 | 75,0 | 337 |
| white rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Confectionery | ||||
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
| cake | 3,8 | 22,6 | 47,0 | 397 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| ketchup | 1,8 | 1,0 | 22,2 | 93 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
| ground black pepper | 10,4 | 3,3 | 38,7 | 251 |
| vinegar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 5,0 | 20 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| creamy margarine | 0,5 | 82,0 | 0,0 | 745 |
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| coffee | 0,2 | 0,0 | 0,3 | 2 |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Percentage of iron absorption from foods
The microelement is not synthesized independently in the body. Products containing iron and pharmaceutical preparations will help replenish your reserves. Hemoglobin is 35% absorbed from food. The substance saturates the blood with oxygen and improves the vital indicators of red blood cells. There are two types of iron:
- Heme (divalent):
found in food of animal origin, providing microelements by 20-25%. Subject to portioned use, rapid absorption occurs.
- Non-heme (trivalent):
enters the body from a plant source - fruits and vegetables, which contain 10% of the valuable element. Recommended for vegetarians, because this group of people most often faces anemia due to the lack of animal food in their diet.
Authorized Products
An iron-containing diet should include:
- Meat, poultry, fish and offal of various culinary preparations, but preference is given to steaming, baking and boiling. Foods prepared in this form are easier to digest and absorb. As for consuming liver, it does contain a lot of vitamins and microelements, but iron is bound by proteins and is not readily available when consuming it. Beef tongue contains more iron, then beef and pork, chicken and rabbit (they contain 8-10 mcg).
- Soups based on broths with the addition of meat. It is known that meat/fish/mushroom broths stimulate appetite, which is often reduced in anemia. To improve appetite, you can eat sauces and salt food, season dishes with pepper, onions, garlic and other spices.
- Cereals - buckwheat, oatmeal, millet in the form of porridges on water and legumes.
- Vegetables - tomatoes, beets, potatoes, greens, carrots, cauliflower, broccoli, sauerkraut, fresh cabbage, bell peppers, pumpkin, asparagus, onions, zucchini, squash and other green vegetables, watercress. In early spring, it is useful to add tops of plants and vegetables (radish, nettle, carrots, turnips, mustard) and dandelion leaves to salads. For better absorption, flavor with vegetable oils.
- Fruits - apple, pomegranate, pear, persimmon, currant, plums, apricots, quince, citrus fruits, blueberries, strawberries, strawberries, peaches, apricots, oranges, pineapples, raspberries, cherries. You need to eat raisins, prunes, and fruit juices.
- Wheat and rye bread.
- Fermented milk drinks, since they contain lactic acid, which, like all organic acids, promotes better absorption of the microelement.
- Eggs.
- Butter and various vegetable oils.
- Drinks: juices (tomato, carrot, beet, peach, apple, apricot), cocoa, rosehip infusion, wheat bran decoction. Fruit drinks and juices that are rich in ascorbic, malic, succinic and other organic acids. And they significantly contribute to the absorption of iron in the intestines. Tea lovers should drink it 2 hours before or after meals and medications.
- Sugar, jam, honey jam.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| spicy vegetables | 2,8 | 0,5 | 5,3 | 36 |
| greenery | 2,6 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 36 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| sauerkraut | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,4 | 19 |
| potato | 2,0 | 0,4 | 18,1 | 80 |
| nettle | 2,6 | 0,3 | 5,2 | 33 |
| watercress | 2,3 | 0,1 | 1,3 | 11 |
| green onion | 1,3 | 0,0 | 4,6 | 19 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot tops | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,3 | 35 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| dandelion | 2,7 | 0,7 | 6,7 | 45 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| beet tops | 2,1 | 0,5 | 5,5 | 17 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
Fruits | ||||
| apricots | 0,9 | 0,1 | 10,8 | 41 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| watermelon | 0,6 | 0,1 | 5,8 | 25 |
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
| cherry | 0,8 | 0,5 | 11,3 | 52 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| figs | 0,7 | 0,2 | 13,7 | 49 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
| plums | 0,8 | 0,3 | 9,6 | 42 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| hawthorn | 0,0 | 0,0 | 14,0 | 52 |
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
| blackberry | 2,0 | 0,0 | 6,4 | 31 |
| irga | 0,0 | 0,0 | 12,0 | 45 |
| viburnum | 0,0 | 0,0 | 7,0 | 26 |
| strawberry | 0,8 | 0,4 | 7,5 | 41 |
| cranberry | 0,5 | 0,0 | 6,8 | 26 |
| raspberries | 0,8 | 0,5 | 8,3 | 46 |
| sea buckthorn | 1,2 | 5,4 | 5,7 | 82 |
| black currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,3 | 44 |
| chokeberry | 1,5 | 0,2 | 10,9 | 55 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
| dried apricots | 5,2 | 0,3 | 51,0 | 215 |
| dried apricots | 5,0 | 0,4 | 50,6 | 213 |
| dates | 2,5 | 0,5 | 69,2 | 274 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jelly | 2,7 | 0,0 | 17,9 | 79 |
| marshmallows | 0,8 | 0,0 | 78,5 | 304 |
| fruit and berry marmalade | 0,4 | 0,0 | 76,6 | 293 |
| paste | 0,5 | 0,0 | 80,8 | 310 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
| sugar | 0,0 | 0,0 | 99,7 | 398 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk | 3,2 | 3,6 | 4,8 | 64 |
| kefir | 3,4 | 2,0 | 4,7 | 51 |
| sour cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,2 | 206 |
| curdled milk | 2,9 | 2,5 | 4,1 | 53 |
| acidophilus | 2,8 | 3,2 | 3,8 | 57 |
| yogurt | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese | 17,2 | 5,0 | 1,8 | 121 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| veal | 19,7 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 90 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken | 16,0 | 14,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Eggs | ||||
| chicken eggs | 12,7 | 10,9 | 0,7 | 157 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| salmon caviar granular | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| punched pollock caviar | 28,4 | 1,9 | 0,0 | 131 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| corn oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| lingonberry juice | 0,1 | 0,0 | 10,7 | 41 |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
Juices and compotes | ||||
| apricot juice | 0,9 | 0,1 | 9,0 | 38 |
| carrot juice | 1,1 | 0,1 | 6,4 | 28 |
| pumpkin juice | 0,0 | 0,0 | 9,0 | 38 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
How to determine iron deficiency in the body
Microelement deficiency is accompanied by general lethargy, increased fatigue, and decreased performance. The skin loses its healthy glow, becomes dry, and flakes. Nails break and peel. The mop of hair thins, “jams” appear in the corners of the mouth, and the skin on the heels becomes rough and cracks.
A systematic lack of iron is a sign of anemia (anemia), which spoils the appearance and has a detrimental effect on health. Medical research shows that even the tissues of the gastrointestinal tract acquire a pale tint. This is a sign of poor blood supply to organs and is not the norm, indicating a failure in receiving nutrients.
Symptoms accompanying substance deficiency:
- dizziness, weakness and fatigue;
- tachycardia, shortness of breath with minimal exertion;
- numbness of the limbs;
- sleep disturbance;
- tendency to catch colds;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- decreased appetite, problems swallowing food;
- craving to eat chalk, raw cereals, desire to sniff paint, acetone.
It is not recommended to make a diagnosis yourself based on descriptions of symptoms on the Internet. The presence of the disease is determined by the doctor after conducting tests. With anemia, the hemoglobin level is reduced: normally in men it is below 130 g/l, in women it is less than 120 g/l.
Spices are the foods that contain the most iron per 100 g.
Since spices and seasonings are not staple foods and are added to dishes in rather modest quantities, we did not include them in our TOP 18 best sources of iron. However, they are the true record holders for iron content per 100 g. Therefore, at the end of the article, we present to you a list of the TOP 15 spices for iron content:
- Thyme, dried: 123.60 mg;
- Basil, dried: 89.80 mg;
- Mint, dried: 87.47 mg;
- Marjoram, dried: 82.71 mg;
- Jeera (cumin seeds): 66.36 mg;
- Turmeric, ground: 55.00 mg;
- Dill, dried: 48.78 mg;
- Celery seeds: 44.90 mg;
- Bay leaf: 43.00 mg;
- Coriander leaves, dried: 42.46 mg;
- Savory, ground: 37.88 mg;
- Anise seeds: 36.96 mg;
- Oregano, dried: 36.80 mg;
- Fenugreek seeds: 33.53 mg;
- Tarragon, dried: 32.30 mg.
What reasons lead to a decrease in iron
The loss and replenishment of iron is a natural process for the human body. When foods containing large quantities of iron are not included in the diet or the microelement is not absorbed, the situation is considered pathological. The risk group includes:
- supporters of strict and “hunger” diets;
- people who eat junk food;
- vegetarians, since the menu does not contain “catalysts” for the absorption of iron;
- women with heavy menstrual cycles.
Anemia of varying severity is considered common. About one billion people on the planet suffer from the disease. The likelihood of developing the disease increases in adolescence and in young and middle-aged women. Anemia can be detected through blood tests, so don't put off visiting your doctor if you notice signs of iron deficiency.
If the numbers are close to the lower limit, then the situation is corrected by adjusting the composition of the products consumed, adding iron-containing ingredients. Switching to proper nutrition restores performance. When hemoglobin drops below 100 g/l, the situation is considered critical. Treatment is prescribed because with anemia there are not enough changes in diet.
It is important to remember that external attractiveness and the desire to get rid of extra pounds should not go against the principles of maintaining health.
Iron deficiency
Unfortunately, insufficient intake of minerals is a common phenomenon in the modern world among both adults and children. Iron deficiency disrupts the functioning of all cells in the body, especially if their functioning requires intense metabolism and oxygen supply. Changes affect the main organs and systems, manifested by a decrease in the activity of all processes and the ability to withstand the negative effects of external factors. A late and already pronounced manifestation of iron deficiency is the development of anemia, in common people - anemia. In this condition, the amount of hemoglobin decreases, and the formation of altered erythrocytes (red blood cells) occurs - they become pale and reduced in size. In humans, the total iron content in the blood serum decreases.
Daily iron requirement for anemia
Iron deficiency anemia is a violation of the absorption of hemoglobin due to a lack of iron. Doctors recommend eating foods with the largest amount of microelements, which will resume the production of hemoglobin in the body. The individual daily dose is determined by a hematologist.
The approximate daily dose for anemia is:
- pregnant and lactating women – 20-25 mg per day;
- adults - 10-15 mg, women need to increase the daily dose due to monthly menstruation;
- children under 18 years old - from 10-15 mg.
Products that increase hemoglobin must be consumed daily.
What iron in foods is needed for anemia
To stimulate hemoglobin synthesis and oxygen saturation of red blood cells, additional consumption of several types of iron is necessary:
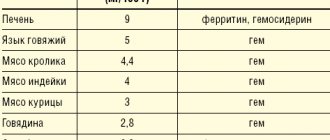
- lactoferrin, transferrin – replenish hemoglobin in the blood;
- ferritin, hemosiderin – support the safety and vital activity of red blood cells;
- cellular iron – improves the transport of oxygen by red blood cells throughout the body.
A consultation with a hematologist after laboratory tests will help determine the type of element required.
Menu (Power Mode)
The range of products is varied, as there are no significant restrictions. Nutrition should be complete and high in calories. You can consume gray and black bread up to 300 g per day, butter and vegetable oil up to 30 g.
Breakfast should be complete and must contain a protein dish (boiled meat, fried or stewed liver, eggs, cutlet, fish) with a side dish of cereals or vegetables. Weak tea with milk, cheese, bread, butter and honey.
The second breakfast includes cheese, fish of any method of preparation, stewed or raw vegetables, milk or rosehip infusion, any juice.
At lunch, the first courses should be cooked in meat, chicken or fish broth with a piece of meat, fish or meatballs. Second courses are also protein (stew, liver, meat or fish cutlets, turkey, rabbit) with vegetable or cereal side dishes, vegetable salads. You can prepare compotes from dried and fresh fruits, juices, and jelly.
The afternoon snack includes cottage cheese dishes, fresh fruits or berries (you can make mousses and jellies from them), tea with milk.
Dinner should also contain two courses. This can include meat and fish dishes with your favorite side dish and cottage cheese casserole with jam and milk.
At night - a fermented milk drink of your choice: kefir, yogurt, yogurt, acidophilus, fermented baked milk.
Daily iron requirement during pregnancy
The need to enrich the body with iron for pregnant women is much higher. Not only the woman, but also the developing fetus needs the microelement. The dosage reaches 27 mg per day.
During childbirth, heavy blood loss occurs; iron consumption is 150 mg. The substance is also lost through breast milk. Pharmaceutical preparations come to the rescue in replenishing the lack of substances.
Iron deficiency in pregnant and lactating women
Even the healthiest women experience iron deficiency during pregnancy due to an increase in the amount of liquid component of the blood and a slowdown in cell growth. This phenomenon is called hydremia and is not a pathology.
With hydremia, there is no deterioration in well-being, there are no signs of a lack of microelements, even hemoglobin is within normal limits. However, sometimes there is still a risk of developing anemia.
When iron is deficient, for pregnant women this is fraught with the development of progressive hypoxia (lack of oxygen), accompanied by metabolic disorders.
For children
Nutrition for anemia in children has a number of features. Iron deficiency in the body of a newborn child is determined by the level of iron supply to the fetus during intrauterine development and the iron content in the mother's breast milk or in formulas after birth. With the standard development of full-term children, depletion of iron reserves occurs by the 4-5th month of life, in premature infants - by the 3rd month of life. From this period, the child’s body depends only on the amount of iron supplied with food.
The best option is to continue breastfeeding the child, since, despite the low iron content in breast milk (1.5 mg/l), its bioavailability is at the level of 60%. This is facilitated by the form of iron-containing protein as lactoferrin .
Along with breast milk, the child’s diet during this period should be expanded through complementary feeding. However, most parents use unadapted dairy products (kefir, milk) for these purposes, which contributes to the development of iron deficiency in the child’s body due to the appearance of microdiapedetic intestinal bleeding. This is especially true for children who are on early artificial feeding with a late (after 8 months) introduction of meat complementary foods.
When artificially feeding, especially in high-risk children (premature babies, twins, low-weight babies), it is recommended to use adapted infant formulas fortified with iron - Similac with iron , Detolact , Nutrilon 2 , Abbott , Nestogen , Samper Baby 1 and 2 . In full-term babies, these mixtures are recommended to be used from the 4th month of life, in premature babies - from the 2nd month.
The inclusion of iron-fortified complementary foods (instant cereals, fruit and vegetable purees, fruit juices) in children's diets significantly increases the intake of iron from food. It is extremely useful to include in the diet of a child from 5-6 months of age meat and vegetable products, complementary foods - canned meat and vegetable products, which are produced by various brands, "Samper", "Gerber", "Beach-Nut", "HiPP", Heinz", "UniMilk", "Kolinska" ").
To cover physiological needs, older children need to receive with food:
- 1-3 years - 1 mg/kg iron per day;
- 4-10 years - 10 mg/day;
- after 11 years - 18 mg/day.
Girls require special attention during pubertal development, which is associated with the onset of menstruation, and for many, poor nutrition due to the desire to lose weight. Therefore, during this period, it is especially important for parents to monitor the child’s diet and include all the necessary food products. At the same time, it is recommended to take iron-containing medications. For young children - in the form of syrup/drops - Lek (syrup), Hemofer (drops), Actiferrin (drops, syrup), Ferrum Maltofer (drops, syrup). For teenagers - Ferrum Lek (chewable tablets at a dosage of 100 mg).
Iron for vegetarians
Plant food sources are rich in non-heme iron. This is not a reason for the microelement not being absorbed. A distinctive feature is high sensitivity to substances that interfere with absorption. The American Dietetic Association states that vegetarians consume even more iron than non-vegetarians. Anemia is no more common among plant-based dieters than among others.
It is important for vegetarians to remember that to increase the absorption of iron, adding products with vitamin C to their diet will help.
Complexes with this research
Causes of hair loss RUR 1,710 Composition
Examination during pregnancy. 1st trimester 10,260 ₽ Composition
Biochemistry of blood. 19 indicators Advanced biochemical blood test RUB 3,510 Composition
IN OTHER COMPLEXES
- Joining IVF RUB 15,090
- Women's check-up No. 1 RUB 11,880
- Examination during pregnancy. 3rd trimester 5,820 RUR
- Female infertility RUB 9,760
- Pregnancy planning. Clinical indicators RUB 3,890