Causes of hypercalcemia
Many reasons can cause an increase in calcium levels in the blood. Among them:
- Improper use of vitamin D – with violations of recommended doses.
- Changes in the functioning of the endocrine system, when the parathyroid gland begins to work in an overly active mode.
- The occurrence of malignant tumors. This condition is especially typical for cancer of the breast, lungs and blood.
- Kidney failure.
- Uncontrolled consumption of foods containing high concentrations of calcium, as well as taking vitamin kits without doctor’s recommendations.
- Tuberculosis.
- Severe dehydration.
In addition, a sedentary lifestyle caused by forced immobilization of limbs, such as fractures or paralysis, also causes high calcium levels in the blood.
Shortage for pregnant women
The pregnancy period is a crucial one for a woman.
At this moment, the mother’s body gives all the nutrients to the developing fetus for the normal formation of the most important systems and organs of the future human being. Therefore, hypocalcemia is a normal situation for pregnant women. Most often, the main signs of the presence of pathology are:
- Goose bumps on the skin.
- Preeclampsia.
- Occasional convulsions.
- There is aching in the bones, especially in the lower extremities.
An increased lack of nutrients leads to the formation of serious pathologies. These consequences include:
- Swelling of the lower extremities.
- Dental diseases.
- Dry skin.
- Long and severe toxicosis.
- Loss of large amounts of hair.
- Brittleness of the nail plates.
- Unreasonable irritability and insomnia.
Calcium deficiency in most cases occurs in the last stages of gestation. Due to lack of treatment, children born with this pathology are often susceptible to rickets.
Every pregnant woman should not only take urine and blood tests, but also monitor her own health. If such signs are detected, you should contact your gynecologist for additional treatment.
How does hypercalcemia manifest?
Pay attention to your health and find out the level of calcium in the body if the following symptoms begin to appear for no apparent reason:
- refusal of food due to loss of appetite;
- difficulty defecating, especially on a regular basis;
- constantly tormenting thirst;
- lack of strength in the limbs, due to muscle weakness;
- exacerbation of anxiety and tendency to depression;
- unexplained vomiting or persistent nausea.
Dehydration, which develops due to high calcium levels, is caused by increased activity of the kidneys, which respond to an excess of this element. In this regard, secondary symptoms may be:
- feeling of dry mouth;
- dark color of urine;
- lack of saliva;
- general weakness and drowsiness.
At the first sign of dehydration, you should immediately call for medical help, as this condition can be fatal. Before the doctor arrives, the patient should be given plenty of warm drinks.
If you don't have enough calcium
WOMEN HEALTH
Calcium is a macronutrient that is involved in the formation and strengthening of bone tissue, teeth, hair and nails. It is found in blood, cells and tissue fluids. Calcium affects the permeability of foreign bacteria, viruses and allergens through the walls of blood vessels.
The effects of calcium on the body are enormous. And its deficiency can provoke such troubles as ailments and various diseases.
Frequent seizures
One of the signs of calcium deficiency may be increasingly frequent cramps in the calves. Less common are contractions in the arms, armpits and thighs. They usually occur at night or in the morning. They are accompanied by acute pain and cannot be controlled in any way.
Calcium is important in transmitting nerve impulses to muscles and is responsible for their contraction. If the calcium level in the blood is low, a spasm occurs.
Calcium may not be absorbed due to a lack of vitamin D and B vitamins. If you think that you consume enough foods containing the macronutrient calcium, then you should pay attention to other foods that should contain vitamins B and D.
Brittle nails
The normal calcium content in the nail plate in women is from 900 to 4500 mcg per 1 g of dry weight; in men this figure is lower - from 450 to 1500 mcg/g. Fluctuations in this indicator, both down and up, indicate an imbalance of the macronutrient throughout the body.
The reasons for calcium deficiency can be different:
- its low content in food;
- adolescence – at this time there is an increased consumption of macronutrients for bone mineralization;
- pregnancy – the skeleton of the unborn baby is actively being built and calcium is being washed out of the mother’s body;
- menopause in a woman;
- various diseases of the body that prevent the proper absorption of calcium from food.
With a lack of calcium, nails can become:
- softer;
- less durable;
- stratified;
- brittle.
White stripes and spots, familiar to many, may be associated with calcium deficiency. This is a violation of the keratinization of the nail plate, which contributes to the formation of voids between its layers. And they already lead to fragility.
The body seeks to compensate for the lack of calcium by taking it from “non-essential” parts of the body. With a deficiency of this mineral, hair becomes brittle and thin, nails peel (a very unpleasant sight), and even teeth make themselves felt. All these signs should alert you.
Dry skin
Calcium plays a significant role for human skin. Its main functions:
- restoration of the protective function of the epidermis and regulation of lipid production;
- it is he who “stitches” the lipid layers of the skin together, ensuring their density and enhancing the moisture-resistant function of the skin;
- regulation of keratinization processes;
- participates in the process of sebum secretion;
- enhances the antioxidant role of the skin, keeps elastin and collagen fibers intact;
- regulates the tone of capillaries and blood vessels and helps carry out skin lymphatic drainage.
If the foods and dishes consumed by a person are not rich enough in calcium, then over time this will lead to the following deviations:
- increasingly slow cell renewal, difficult maturation of keratinocytes leads to dryness and thinning of the skin layer;
- a decrease in the activity of fibroblasts leads to a decrease in the firmness and elasticity of the skin, a decrease in the synthesis of structural elements of the skin and its depletion;
- weakness of capillaries.
All these changes will gradually lead to irreversible skin aging processes. Therefore, preventing and eliminating calcium deficiency is very important.
Tooth decay
The lack of calcium in the human body is compensated by its gradual leaching into the blood from the skeleton. If such a deficit is replenished in a timely manner, then no dangerous consequences will occur.
If the process of deficiency is chronic, then deviations from the norm arise, which the body gives us with the following symptoms:
- bleeding and gum disease;
- tooth decay.
Calcium is involved in the endless process of restoring tooth enamel. Since it does not stop for a second, the teeth need this macronutrient continuously.
Have you noticed similar problems in yourself or a loved one? Review your diet and, if necessary, include foods rich in calcium.
In addition to eating foods with sufficient calcium, you can add medicated toothpaste with this element as an additional source.
Insomnia
The macroelement calcium is directly involved in the synthesis of melatonin. Calcium levels in the body increase during deep sleep. And the lack leads to its violation. This element helps the brain use the amino acid tryptophan, which enters the body with consumed proteins. And it has a positive effect on the production of the hormone melatonin, which affects the quality and duration of sleep and, as a result, a person’s mental health.
If you start to sleep poorly, then first of all you need to look at your diet. Analyze the calcium and protein content in the dishes and products you eat and make adjustments.
All the symptoms listed in the article may indicate not only a lack of calcium, but may be based on completely different reasons.
The first thing you should do is pay close attention to your diet, analyze what and in what quantities you eat. Adjust if necessary. At the same time, it is necessary to take a biochemical blood test and look for calcium macronutrient deficiency.
Doctor - hygienist
State Institution "Center for Hygiene and Epidemiology"
Frunzensky district of Minsk"
Gapanovich Valentina,
What complications can it lead to?
When high calcium levels are accidentally detected, immediate action must be taken to avoid complications. Ignoring metabolic disorders can lead to:
- Osteoparosis. Lack of adequate treatment leads to calcium being released from the skeleton into the bloodstream. This becomes the main cause of thinning of bones and joints, which means bone fragility increases. Spinal curvature is observed in 85% of patients with hypercalcemia.
- Formation of kidney stones. The kidneys are a paired filtering organ that purifies the blood, which means they also accumulate calcium. Unfortunately, it is impossible to identify stones at an early stage. They make themselves felt when the situation has already started and blockage of the ducts or the movement of stones through the ureters begins, which is always associated with unbearable pain.
- Dementia and other central nervous system disorders.
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
The musculoskeletal system and kidneys are usually the first to suffer. If you have a frequent urge to urinate, you need to check not only your bladder, but also your blood for calcium levels.
Why is calcium needed in the body?
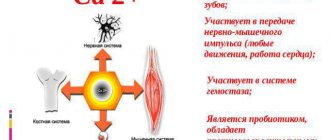
Calcium, like no other trace element, is necessary for the functioning of the entire body. It is required primarily for the formation of strong, strong bones. Calcium is a structural component of the entire human skeleton. In addition to this trace element, it is also present in soft tissues.
A biologically significant element takes part in many functions of the body: enzymatic, metabolic, neuromuscular, hormonal. The following beneficial qualities are identified that the nutrient provides in the human body:
- Normalizes sleep.
- Acts as a preventive measure against the formation of mutation cells during the development of cancer, and also prevents the preconditions for the formation of polyps on the inner walls of the intestine.
- The vitamin affects lymph clotting.
- Normalizes the functioning of the myocardium and circulatory system, maintains the pulse, stimulating contractions of the heart muscle.
- Regulates the normal functioning of metabolism.
- Participates in neuromuscular conduction.
- Necessary as a prophylaxis against the occurrence of an allergic reaction.
- Controls the performance of intestinal motility, thereby reducing the frequency of situations in which obstruction of stool through the pipes occurs.
- Regulates the production of parathyroid hormones.
If the presence of calcium in the body decreases, then the internal systems and organs begin to borrow the required amount from bones or tooth enamel. As a result, dental pathologies begin to develop; with minor bruises, cracks or fractures are recorded. The consequences of nutrient deficiency are the formation of more serious diseases such as osteoporosis.
How to Diagnose Hypercalcemia
If excess keratin or liver dysfunction can be determined by the yellowish color of the skin, then excess calcium cannot be diagnosed by eye. You can find out your calcium level through a simple biochemical blood test. If the laboratory notes an excess of the element, an additional examination will be prescribed, which is already aimed at identifying the cause of the metabolic disorder.
Women are advised to have a mammogram to rule out breast cancer. At the same time, it is important to undergo a chest x-ray. In order to find out how much the bones have lost their strength, a magnetic resonance imaging scan is shown. It will show the density of the skeleton and identify particularly depleted areas.
If the patient takes any medications on an ongoing basis, you should definitely inform your doctor about this so that he takes this into account when interpreting diagnostic materials.
Blood test for ionized calcium
Ionized calcium is calcium that is not bound to any substances and circulates freely in the blood. It is the active form of calcium that is involved in all physiological processes. A blood test for ionized calcium will assess calcium metabolism in the body. This test must be given to patients in the following cases:
- Treatment after resuscitation, surgery, major trauma, burns.
- Diagnosis of cancer, hyperfunction of the parathyroid gland.
- Carrying out a hemodialysis procedure.
- Taking the following medications: bicarbonates, heparin, magnesium, calcium supplements.
A blood test for ionized calcium is carried out in conjunction with determining the level of total calcium and blood pH. The value of ionized calcium is inversely related to blood pH: the level of ionized calcium increases by 1.5 - 2.5% for each decrease in pH by 0.1 unit.
Treatment of hypercalcemia
In certain cases, drug treatment is not prescribed. This applies to cases where the calcium level does not greatly exceed the permissible normal limits. In such a situation, it is enough to discuss the correction of the diet, including the list of prohibited foods, which include:
- milk;
- cheese;
- cottage cheese;
- yogurt;
- kefir;
- nuts.
After a certain period of time, the patient will be scheduled for a repeat blood test. It will show whether its composition has returned to normal or not.
In more severe situations, diuretics may be prescribed, provided that kidney function is not impaired and the body is not at risk of dehydration. It is important to strictly adhere to the dosage, because such drugs lead to a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
If the excess calcium is caused by a serious health problem, the patient will be hospitalized for medical attention.
List of foods high in calcium
If hypocalcemia was detected in the initial stages of manifestation, then the pathological condition of the patient is compensated by the introduction into the body of foods that are saturated with calcium. The following ingredients are identified to be included in the diet of a patient suffering from nutrient deficiency.


![Rice. 1. Functioning of the glymphatic system of the brain (according to [11]) 1. Glymphatic system functioning (according to [11])](https://expert35.ru/wp-content/uploads/ris-1-funkcionirovanie-glimfaticheskoj-sistemy-mozga-po-11-fig-1-330x140.jpg)

