How to prolong and improve life after an ischemic stroke
The period after an ischemic attack is divided into five periods:
- The critical stage is the first 72 hours.
- Acute period – 25-30 days.
- The first stage of recovery is from 3 to 6 months.
- The second recovery period is 12–24 months.
- Residual processes – From 24 months or more.
Life expectancy after an ischemic stroke depends on numerous factors, from the size of the brain lesion to treatment measures.
Providing first aid also affects the outcome of recovery; a simple rule applies here: the sooner, the better. In the first year after ischemic hemorrhage, 65% of patients survive, after 5 years half survive, but after 10 years only a quarter remain alive.
Help to prolong life:
- correct lifestyle;
- diagnostics every 2 – 3 months;
- nutrition;
- restorative gymnastics.
Salt, sugar, fatty and flour foods, smoked meats and sauces should be excluded from the diet. The diet should be dominated by vegetables and fruits, a large amount of fiber and vegetarian soups. Meals should be fractional, 5 meals in small portions.
Timely diagnosis and physical therapy, which improves the quality of blood flow, will help prevent a recurrent attack.
How can you increase your chances?
Each person is individual and their body copes with illness differently. Some stop walking and working, while others simply become less active. Anyone can recover, the main thing is to follow the doctor’s recommendations and listen to your body.
The sooner you start rehabilitation, the faster your brain will recover. In the beginning, gymnastics and massage will help. The rehabilitation program includes exercise therapy and classes on robotic simulators.
Important! Stroke also affects the psyche. Often, the help of a psychiatrist is required.
Taking medications
Life expectancy after a stroke largely depends not only on medical care, but also on the literacy of further rehabilitation. After being discharged home, you should not let the disease take its course. A person must strictly follow the recommendations of doctors. This primarily concerns taking medications. The most commonly prescribed drugs are those designed to improve blood circulation in the brain area. nootropic drugs increase the production of phospholipids and the synthesis of nucleic acids, improve glucose absorption, and reduce excessive activity of nerve cells.
The rehabilitation period includes the use of medications
In addition to nootropics, patients are prescribed antispasmodics, antidepressants, and sedatives. More than 30% of people after an attack have an unstable emotional state, suffer from depression and sleep disorders. This is due to the fact that it can be quite difficult to return to normal life on your own, which is associated with many complications after a stroke.
Important! In the family where the person is after suffering an attack, a positive emotional environment should reign.
Factors influencing life expectancy after stroke
Subsequent life after a stroke will depend on the type of disease, the extent of damage and the presence of additional underlying diseases. There are a number of circumstances that can both facilitate and complicate the course of the underlying disease and the process of restoration of brain cells. So, here are the key factors that have a direct impact on the healing process:
- Stroke on the right side, consequences, how long do they live after it and how is it treated?
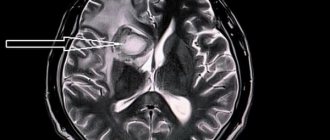
- Damage area. It affects the patient's future life. In the case of extensive damage, the cells are damaged so severely that they can no longer be restored. Because of this, the functioning of the brain is disrupted, which leads to malfunctions of other systems and organs and even to the death of the patient.
- Consequences of a stroke. Patients suffering from paralysis, impaired speech function, sensitivity, and mental disorders are unlikely to be able to lead a normal and fulfilling life. If they manage to recover, it will be only partially. The prognosis is unfavorable because these conditions lead to bedsores, intoxication, and other complications. All these phenomena significantly reduce life expectancy.
- Age characteristics. Older people are least likely to recover from a stroke. The fact is that their cells do not have the ability to quickly renew themselves, they more often develop inflammatory processes, vascular pathologies, and repeated hemorrhages and heart attacks occur. Even if patients manage to survive the attack itself, in case of nervous strain or an attack of hypertension, there is a risk of another stroke. In addition, women have a much greater chance of recovery than men, which is due to their physiological characteristics. Therefore, the general condition of the patient also depends on age and gender.
- Prolonged immobility. When a patient recovers from a stroke, he is often unable to move due to paralysis or paresis. If you neglect to implement the rehabilitation program, the muscles gradually lose their tone and the blood supply to the internal organs deteriorates. This leads to thrombosis, tissue necrosis, and intoxication. Therefore, the condition worsens even more, inflammation, infectious processes, and cardiovascular diseases develop. Such a patient has much less time to live than a person who regularly moves, does exercises and has a positive attitude.
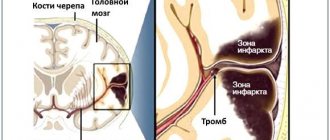
- Localization of the disease. Of course, the prognosis directly depends on the location of the affected areas. Ischemia can affect the tissues that supply blood to the carotid artery, the main and vertebral arteries, as well as their branches. In addition, ischemic cerebral stroke is the most dangerous condition, reducing the chances of survival. Hemorrhagic stroke most often affects the putamen (in 55% of cases), the thalamus, cerebellum, and brain stem.
No one can give an unambiguous answer to the question related to life expectancy after a stroke. This is due to the individual characteristics of each organism. However, according to statistics, about 35% of deaths occur in the first month after the disease, and 50% of patients die during the first year. In any case, you should adhere to one recommendation: lead a healthy lifestyle. It is this that will allow you to avoid complications, prolong life and make it more fulfilling.
Symptoms of a stroke
Stroke leads to various brain injuries, depending on the location of the lesion and the pathological type of cerebrovascular accident:
- disturbances of movement in the limbs: from restrictions (paresis) to complete paralysis. When the lesion is localized on the right, the left limbs suffer; with a left-sided lesion, right hemiparesis is formed; in some cases, movements in all limbs may stop (tetraparesis or double hemiparesis);
- sensory disturbances on one or both sides;
- speech disorders (dysarthria - poor articulation; aphasia - inability to pronounce and understand words, write and read);
- ataxia (impaired coordination of movements, “overshooting”, unsteadiness, imbalance, tremor);
- visual impairment: from blindness to double vision and gaze paresis;
- hearing impairment and dizziness;
- violation of mental functions (consciousness, thinking, attention, memory, will, behavior);
- paresis of the soft palate and pharynx, swallowing disorders;
- disorders of urination and defecation;
- depression of respiration and vascular tone;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- patients complain of headaches, vomiting, hiccups, yawning, shoulder pain;
- consciousness is gradually depressed to the point of coma [1, 3].
Causes of death may include cerebral edema, pneumonia, heart failure, and recurrent stroke. In severe cases, “locked-in syndrome” may develop: the patient is conscious, but cannot move, swallow or speak [3].
How many years do people live after a stroke?
Statistics answer the question of how many years people live after a stroke. As a rule, life expectancy is about 10 years, but in severe cases, death can occur immediately after the attack. Observations of specialists showed:
- some patients (30-35%) die in the first month after the attack;
- After the first year, only half of stroke victims are alive.
In addition, how long people live after an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke also depends on the number of attacks.
Repeated cerebral circulatory disorders are extremely dangerous. So, if after the first attack the life expectancy is approximately 9 years, then the secondary attack reduces it to a period of 2 to 3 years. But what is the overall picture and how long will a person live after a repeated major, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke?
In such circumstances, only 5-15% survive the first year after an attack, and over the next 5 years - about 42% of men and 25% of women. There are many reasons for such sad statistics, but the main thing is that the factors that led to the blow do not disappear anywhere. That is, a predisposition to blood clots, vascular damage due to atherosclerosis, hypertension and heart problems still remain in the body.
Factors influencing life expectancy after stroke
The duration of life after an impact directly depends on such factors.
- The severity of the attack and the extent of damage to brain tissue. Sometimes the severity of the blow is excessive, which leads to death or a global reduction in the life expectancy of the victim.
- Consequences of vascular damage. A person with extensive paralysis is doomed to a lying position, which without proper care is fraught with bedsores and pneumonia.
- Immobility after an impact provokes the formation of blood clots in the lower extremities. Such blood clots, when they break off, often enter the lungs and provoke thromboembolism, which often leads to death.
- Ensuring the safety of a stroke victim. It is necessary to exclude falls caused by dizziness and weakness in the legs, since any fractures, especially the femoral neck, are quite difficult to treat in elderly patients.
- Age. This is an equally important factor, since young people are more likely to survive.
- General health.
Features of the rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation after a stroke
After a vascular lesion of the brain, rehabilitation measures are mandatory, regardless of the severity of the lesions caused by the stroke. The entire recovery period can be divided into two stages: the first days after the attack within the walls of a medical institution and the rehabilitation period in special centers and at home.
Recovery stage in the first month after the attack
As a rule, doctors insist that the victim stay in a specialized department for 2 to 4 weeks. At this point, specialists of various profiles can reduce the entire therapeutic process to a specific system and further recovery. Disturbances in the blood supply to the brain lead to the formation of a focus of dead cells, and nearby cells often exhibit rather weak activity. To restore their normal activity, timely medical care is required.
It is better to remain under the supervision of specialists for some time after a stroke
First, patients are placed in the correct and comfortable position for them, and only then they begin physical therapy. Thanks to regular exercise and medication, brain cells begin to function more actively, which stimulates the restoration of damaged areas of the organ. But positive changes can only be achieved with a daily increase in loads. In the first 14 days, the victim is prescribed only a light massage with stroking and rubbing and procedures using electrical muscle stimulation. If the patient tolerated this stage well, then they begin to restore speech function.
- Life expectancy and consequences after left-sided ischemic stroke
Rehabilitation after discharge
Sometimes all the problems that arise can be eliminated in 2-4 weeks in the hospital, but if this does not happen, then the recovery stage is delayed. It is important for the victim to continue to systematically increase the load over the next two months.
The program of the therapeutic and gymnastic complex, carried out at home, is previously agreed upon with the local doctor. The neurologist develops an adaptation map, based on which all exercises and procedures must be performed. It should be noted that for older people (over the age of 70), a stroke is too severe a trauma, rehabilitation after which is almost impossible.
Who's at risk
After a primary stroke, the body retains mechanisms that provoke the following development of events: intravascular thrombus formation, vascular atherosclerosis. The patient, as a rule, also has a number of concomitant diseases, often in advanced forms: hypertension, diabetes mellitus, arrhythmia, heart failure and others. Preventing recurrent ischemic stroke in such cases is a rather difficult task, but thanks to the efforts of qualified specialists at the Yusupov Hospital, it is feasible.
Repeated ischemic stroke sometimes threatens even patients who are unaware that they have already suffered a vascular accident: patients with short-term disturbances of cardiac or cerebral circulation, the so-called transient ischemic attacks, manifested by the sudden onset of headache, dizziness, numbness of the arm or leg - symptoms which are often ignored, despite the fact that they are the first alarm bells preceding a stroke. The threat of vascular attack increases even more with transient loss of vision, speech, weakness in the upper or lower limb, sudden amnesia and other symptoms.
In this case, the patient should not hesitate; it is recommended to seek medical help as soon as possible at the neurology clinic of the Yusupov Hospital to obtain a doctor’s consultation. You will undergo the necessary examinations: ultrasound examination of large vessels (first of all, it is necessary to examine the carotid arteries), an electrocardiogram, ECHO-CG, detailed blood tests for the lipid profile and the tendency to form blood clots, the level of homocysteine - an amino acid that causes early atherosclerosis and thrombus formation, as well as several times increasing the risk of stroke and heart attack.
A similar examination is also recommended for patients who have suffered a hypertensive crisis, attacks of angina pectoris (pain in the heart area), or arrhythmia. These conditions often precede a stroke and are manifestations of transient ischemic attacks.
Make an appointment
Stroke in old age
How long do older people live after a stroke? In older people, the disease can occur for the following reasons:
- hypertension;
- kidney disease;
- problems with the endocrine system;
- diabetes;
- vascular aneurysms;
- atrial fibrillation;
- rheumatism;
- high cholesterol;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- any viral disease in severe form.
The most common cause of stroke in older people is atherosclerosis, which can provoke a large number of attacks per year, and they may go completely unnoticed by the person. If this process continues for a long time, it is impossible to survive - death occurs.
How long a person lives after a stroke in old age is a complex question. According to statistics, the forecasts are as follows:
- With extensive hemorrhage that occurred in the brain center - death.
- With atherosclerosis and hypertension, survival is possible in rare cases, and the consequences will be very severe.
- With cerebral edema, the prognosis is also poor.
- In case of relapse - death.
The average life expectancy after a stroke that occurs after age 80 is a week. It turns out that the older you are, the less likely you are not only for recovery, but also for survival in general.
First aid
When the first symptoms of a stroke appear:
- Place the patient on the bed.
- Call an ambulance.
- Place the patient on his back or side if vomiting begins or he loses consciousness.
- Unfasten clothes and belt.
- Open the window to allow fresh air into the room.
- Place a cold wet towel or ice in a bag wrapped in cotton cloth on your head.
- Measure the patient’s blood pressure, pulse, and monitor blood pressure and breathing until the doctors arrive.
- If necessary, give medications that were previously prescribed by the attending physician.
- Constantly talk to the patient, try to get answers to questions from him, and do not lose contact.