Hemoglobin level is an important indicator of a man’s health, and its decrease is a good reason to see a doctor. After all, this protein performs a number of vital functions, including ensuring tissue respiration. Therefore, when its concentration in the blood decreases, changes in well-being of varying degrees occur, and in severe cases, low hemoglobin can cause the development of serious complications.
What is hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is a complex protein containing iron. Its main task is to add oxygen diffusing into the blood from the lungs and distribute it throughout the body. Giving oxygen to cells, hemoglobin attaches carbon dioxide formed by them in the process of vital activity. Then getting through the bloodstream to the lungs, it gives it away, again making room for oxygen. This is how gas exchange and tissue respiration occur. But, in addition, hemoglobin is involved in maintaining the acid-base balance, in DNA synthesis, and in the occurrence of a number of redox reactions.
To synthesize hemoglobin, the body uses iron, which comes from food and accumulates in the form of ferritin in the liver, lungs, and spleen. There is also a small amount of iron present in the intestinal mucosa. If the diet does not meet the body's iron needs, ferritin is activated. This helps maintain normal hemoglobin levels and organ function. But with prolonged deficiency, its reserves are depleted, and the concentration of hemoglobin decreases.
In men, critically low hemoglobin levels are rare, since they, unlike women, do not experience regular physiological bleeding. For the same reason, the increase in hemoglobin in men occurs faster and more effectively. But if left untreated, there is a serious risk of complications, especially if you have bad habits:
- thrombosis;
- myocardial infarction;
- stroke;
- decreased immunity;
- deterioration of cognitive functions (memory, attention);
- hypoxic coma.
Often, when low hemoglobin persists for a long time, the presence of chronic fatigue syndrome is observed.
Can there be too much iron in the body?
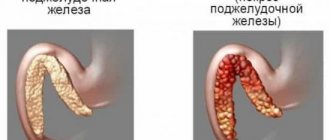
Maybe. An excess of iron is just as harmful to the body as its deficiency. It causes fibrosis of organs and tissues. The pancreas, liver and heart are most often affected. However, it is impossible to achieve an excess of iron through diet alone. The pathology is often due to genetic predisposition and improper or uncontrolled use of iron-containing drugs.
What is an increase in hemoglobin called?
An increase in the number of red blood cells and an increase in hemoglobin is called erythrocytosis. Its characteristic symptoms: nosebleeds, headaches and dizziness, fatigue. Erythrocytosis, in turn, can be a sign of various diseases, which only a doctor can determine.
What does it mean if hemoglobin is elevated?
High hemoglobin levels can be caused by dehydration, smoking, lung cancer, heart disease and other pathologies. Elevated hemoglobin sometimes indicates the presence of a rare disease - polycythemia. When this happens, the body produces too many red blood cells, which can lead to blood clots, heart attacks and strokes. This is a very serious disease that is important to identify and control early throughout your life.
Reasons for decreased hemoglobin levels
The main reasons for a decrease in hemoglobin levels in the blood in men are:
- reduction in the amount of iron entering the body;
- disturbances in the absorption and transport of iron throughout the body;
- a decrease in the number of red blood cells as a result of a violation of their production by the bone marrow or a shortening of life due to various circumstances.
In this case, most often a decrease in hemoglobin is due to iron deficiency in the body. The fact is that the absorption of this microelement from food is limited. Even with proper nutrition, no more than 1-1.5 mg can be absorbed per day, and if there are errors in the diet, the amount of iron entering the body cannot cover the need for it. In such cases, iron depots in the form of ferritin are used to maintain normal life functions. But its reserves are limited, and therefore, when they are depleted, the intensity of bone marrow erythropoiesis decreases. As a result, the number of red blood cells, as well as the level of hemoglobin, decrease, which indicates the development of anemia and is accompanied by the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
Thus, the causes of low hemoglobin in men can be:
- malnutrition;
- insufficient consumption of foods that are sources of iron:
- adherence to a vegetarian diet;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- severe bleeding during injuries, operations, including hidden ones (observed with peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, kidney pathologies, pulmonary siderosis, etc.);
- haemorrhoids;
- malignant tumors;
- chronic intoxication;
- vasculitis;
- systemic scleroderma;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- helminthiasis;
- cystic fibrosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
Statistics show that men are more likely than women to have gastrointestinal diseases caused by Helicobacter pillory, which leads to impaired absorption of iron in the intestines and a decrease in hemoglobin.
A little about the main functions of blood
The main function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen to the cells of the whole body.
All the tasks that the body sets for the blood are carried out thanks to the coordinated work of its following components:
- plasma – the liquid non-cellular part of blood;
- erythrocytes, platelets, represented by various elements leukocytes - cell mass (or suspended formed elements of blood);
- ions of various micro- and macroelements, enzymes, hormones and other substances entering the blood.
All of the above components perform the following functions:
- transport substances necessary for life (hormones, enzymes, nutrients and “fuel” elements) and remove “waste” materials accumulated in the blood (carbon dioxide, etc.);
- regulate the flow of water and electrolytes into the tissue;
- ensure the functioning of the immune system when pathogenic objects (microorganisms, own mutated cells) enter the blood.
A parameter such as blood thickness is determined by the balance between the liquid (plasma) and cellular (formed elements) part of the blood. It is this property that allows it to penetrate the smallest vessels and capillaries. This ensures the necessary delivery of blood to all tissues of the body.
Anemia (or anemia) is accompanied by a decrease in those blood parameters that relate to red blood cells. It is these red cells that carry oxygen, and if their production is disrupted, hypoxia of the tissues of all body systems develops.
Symptoms
The severity of symptoms largely depends on the level of hemoglobin: the lower it is, the more severe the anemia. Therefore, in mild cases, men may not notice changes in their well-being or not attach importance to them, since they are little expressed. In such situations, periodic weakness or increased fatigue may occur, but many attribute this to stress, age and other life circumstances. With a further decrease in hemoglobin, the situation becomes more complicated, the existing symptoms become more intense, and others appear.
Sometimes even a decrease in hemoglobin to 90 g/l is asymptomatic.
In general, a decrease in hemoglobin levels in men may appear:
- drowsiness, weakness, decreased performance;
- shortness of breath, which initially occurs due to physical exertion;
- feeling of heartbeat;
- dizziness that can lead to loss of consciousness;
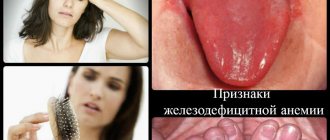
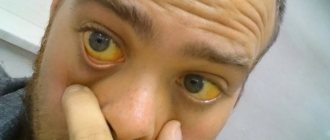
- pallor of the skin and mucous membranes;
- increased irritability, aggressiveness;
- headaches of varying degrees of intensity;
- decreased appetite;
- increased brittleness of nails, the appearance of white spots and bumps on them;
- perversion of taste preferences with the emergence of a desire to eat inedible food, in particular raw meat, chalk, clay;
- developing an addiction to the smells of acetone, gasoline, perfume, etc.;
- ringing in the ears, flickering of spots before the eyes.
A symptom of decreased hemoglobin that is typical for men may be impaired erectile function.
Diagnostics
If the symptoms described above appear, especially if this is accompanied by the presence of factors predisposing to a decrease in hemoglobin, you should take a general blood test and consult a physician with its results. To confirm anemia, a repeat clinical blood test is usually prescribed. This eliminates the possibility of mistakes being made in the laboratory.
If a decrease in hemoglobin levels is confirmed, treatment for anemia is immediately prescribed. And in parallel with this, a comprehensive examination of the body is carried out in order to identify the causes of its development. This is especially important in cases where there are no obvious prerequisites for this, for example, having undergone surgery in the recent past, injuries with large blood loss, etc. For this, the following may be prescribed:
- blood chemistry;
- stool test for occult blood;
- colonoscopy;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and kidneys.
How to increase low hemoglobin
Even a slight decrease in hemoglobin levels requires treatment. Otherwise, the man’s well-being will progressively deteriorate. Therefore, from the moment a general blood test is performed and low hemoglobin levels are established, it is necessary to make adjustments to the daily diet and start taking iron-containing medications. It is impossible to cope with the problem only by changing the diet and increasing the amount of iron sources in the body, since at best, as much of this trace element is absorbed from food per day as is consumed. This will not allow the formation of the necessary depots and eliminate the risk of re-development of anemia in the near future.
It is imperative that in combination with the treatment of anemia, therapy for the disease that provoked its development is prescribed. Accordingly, it will be strictly specific in each individual case.
Nutrition correction
With low hemoglobin, men are advised to increase the amount of iron-rich foods in the daily menu, as well as those containing folic acid, vitamin B12 and ascorbic acid, as they increase the quality of its absorption. These include:
- beef tongue, liver;
- white chicken, turkey, veal;
- various seafood, as well as red and black caviar;
- buckwheat, rice;
- leafy greens, cabbage, broccoli, green beans, spinach;
- legumes;
- pumpkin, tomatoes, beets;
- berries, especially black currants, blueberries, cranberries;
- fruits, in particular pomegranate, persimmon, dried apricots;
- peanut.
But when drawing up a menu, it is worth taking into account the peculiarities of iron absorption. So, you should not combine meat dishes with pasta, bread and cereals. They are recommended to be consumed with vegetable side dishes. It is also necessary to consume fermented milk products and nuts separately from other meals.
Hyperthickness syndrome
Thickening (or hyperviscosity of the blood) worsens the rheological properties of this part of the body. This means that blood begins to move (flow) more slowly through the blood vessels. The following parameters can cause such violations:
- A joint increase in the density of both plasma and blood.
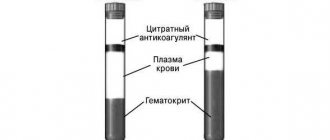
- An increase in hematocrit due to a violation of the ratio of formed elements to the volume of blood as a whole. Normally, the hematocrit is 4:6 (4 – formed part, 6 – plasma). For men, this figure is always slightly higher.
- Increased hemoglobin levels.
- Reduced elasticity and ability to deform red blood cells.
- Increasing the level of a protein responsible for blood clotting, fibrinogen.
- Increased sticking of red blood cells (or aggregation).
- Increased levels of paraproteins - pathological proteins released into the blood during diseases such as myeloma.
Blood density indicators are measured using a viscometer, which compares the speed of movement of this medium in relation to the same indicator of distilled water. Measurements are performed under the same conditions (i.e., same volume and temperature). Normally, blood flows 4-5 times slower than water, and blood viscosity is 1.050-1.064 g/ml.
Blood thickens due to the following factors:
- fermentopathy – conditions leading to incomplete breakdown of food, contamination of the blood with under-oxidized substances that provoke its acidification;
- disorders in the functioning of the liver, which are provoked by an insufficient supply of vitamins, minerals, decreased levels of enzymes and hormones, consumption of large amounts of salty, sweet, smoked, meat and canned foods;
- imbalance between blood cell mass and plasma in tumors of hematopoietic tissue (for example, leukemia);
- dehydration – loss of the liquid part of plasma due to excessive exercise, temperature exposure, taking diuretics, diarrhea, vomiting and poor absorption of water.