Knowing the MSN in a blood test, a discrepancy with the norm, a shift in any direction, it will not be difficult for the doctor to suggest a probable diagnosis, the degree of development of the disease and exclude pathological changes. Having the result in hand, the doctor receives a complete picture of the possible causes that provoked the imbalance of the formed elements.
If you complain of poor health, weakness, hyperthermia and other signs of discomfort, the therapist prescribes a general blood test - an indicative way to establish a diagnosis. Each number in the results has its own acceptable limits and deviations are an alarming sign.
What does MCH mean?
Having recorded picograms of MCH, it is possible to determine the content of average hemoglobin in the blood structure. Violation of permissible limits consistently leads to transformation in bone marrow cells and red blood cells. To understand what exactly provokes a change in blood composition, it is worth finding out what MSI is.
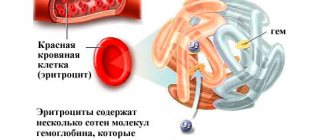
Analysis - records the hemoglobin content in the red blood cell. The final figures are calculated using the formula, dividing the total hemoglobin by the resulting volume of red blood cells.
Within acceptable limits, data is limited to 24 - 35 picograms. For children of different ages, the values may differ.
A discrepancy in MCH values occurs under the influence of various factors, which has an impact on the average blood CP value. It is the result obtained that is the basis for diagnosing anemia.
Indications for analysis
The study of material for MCH and MCHC is usually not carried out to determine only this indicator. The significance is paid attention to when undergoing laboratory blood tests, along with others.
Doctors often prescribe a complete blood count to check for MSI in patients with signs of anemia, especially in the acute period. The situation is quite serious, since loss of strength and lack of vital energy have a negative effect on the usual way of life, physical and psycho-emotional health. Sometimes it is enough to make some adjustments to the way of life, change gastronomic habits in order to positively affect the functional processes in the body.
Normal indicators
To obtain accurate data and decipher a blood test for MCH, doctors use tabular data with prescribed norms of the erythrocyte index for different ages. According to the MCH norm, deviations are determined and a provoking factor is found that disrupts natural processes in systems.
Hemoglobin in the blood is a variable unit and it changes throughout the life cycle. It differs depending on gender type, and the difference is significant in children and adults.
Comparing the MCH rate in a blood test at different stages, the following is noticed: the maximum numbers are recorded in children at birth - 30 - 37 picograms. At one year of age, the values decrease to 24 – 30, and in adolescents – 26 – 32. Having crossed the 15-year mark, normal values vary between 26 – 34.
If pathological changes do not bother you with symptoms and are not detected at all, with the onset of 18 years, the permissible limits do not change until the age of 65.
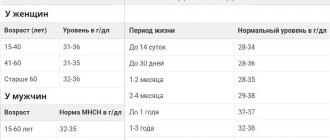
Acceptable MCH standards in adults
The MCH indicator in a blood test is considered in a general context, together with other components, and is practically not prescribed separately.
| FLOOR | AGE/YEARS | HEMOGLOBIN CONTENT IN 1 ERYTHROCYTE MSN/PICOGRAMS |
| Men | 15 — 18 | 27, 0 – 32, 0 |
| 18 — 45 | 27, 0 – 34, 0 | |
| 45 — 65 | 27, 0 – 35, 0 | |
| 65 -120 | 27, 0 – 34, 0 | |
| Women | 15 — 18 | 26, 0 – 34, 0 |
| 18 -45 | 27, 0 – 34, 0 | |
| 45 — 65 | 27, 0 – 34, 0 | |
| 65 — 120 | 27, 0 – 35, 0 |
Normal MCH in adolescents
| TEENAGE CATEGORY | AVERAGE HEMOGLOBIN CONTENT IN 1 ERYTHROCYTE MSN/PICOGRAMS |
| Children 9 – 15 YEARS OLD | 26 — 32 |
Normal MCH in children
| CHILDREN OF DIFFERENT AGES | HEMOGLOBIN CONTENT IN 1 ERYTHROCYTE MSN/PICOGRAMS |
| 1 day from birth | 30, 0 – 37, 0 |
| 1 month | 27, 0 – 34, 0 |
| Six months | 24, 0 – 30, 0 |
| Year | 22, 0 – 30, 0 |
| 16 years | 25, 0 – 31, 0 |
| 7 – 12 years | 26, 0 – 32, 0 |
Changes in coagulogram and clinical blood test parameters
Changes in the coagulogram of a pregnant woman are a natural physiological process associated with the appearance of the uteroplacental circulation. It is due to the fact that the pregnant woman’s body prepares for an increase in blood volume during pregnancy and for possible blood loss during childbirth.
During normal pregnancy, the activity of the blood coagulation system increases. This means that already in the 3rd month of pregnancy, fibrinogen increases, which reaches its maximum values on the eve of childbirth. Therefore, gynecologists reasonably recommend monitoring this indicator during pregnancy (once per trimester, if there are deviations in these indicators, more often, once a week).
Simultaneously with the increase in fibrinogen, the activity of the internal blood coagulation mechanism also increases, while the analysis shows a shortening of the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). Other parts of the blood coagulation system, such as the coagulation blocker antithrombin III, also change during pregnancy. But as pregnancy progresses, there is a gradual decrease in the activity of this indicator.
But lupus anticoagulant should not be produced normally in a pregnant woman.
Pregnancy also affects the results of a general blood test. Indicators such as hemoglobin and hematocrit may decrease in the second half of pregnancy, and leukocytes, on the contrary, may increase.
How to prepare for the examination
Any laboratory blood test is performed on an empty stomach.
The distance between eating food and pricking a finger is maintained from 8 to 12 hours, and also:
- per day, you should give up alcohol-containing drinks;
- It is worth excluding coffee and tea;
- before the procedure it is necessary to refrain from physical activity and psycho-emotional shocks;
- It is recommended not to smoke 30–60 minutes before the procedure.
The correct decoding of MCH can be the starting point in establishing a diagnosis and compliance with the rules must be approached with the utmost seriousness.
How is the analysis carried out?
Blood monitoring for MCH and MCHC is carried out in the same way as a general analysis - after taking material from a finger. The manipulation does not take much time and there is practically no discomfort. By observing all preparatory measures and requirements for the procedure, the most accurate result is obtained.
Why is MCH elevated in a blood test?
An increase in the concentration of hemoglobin in an individual red cell leads to an increase in MCH - the color indicator rises by 1.1.
Changes are recorded in fairly serious pathologies, which has a logical explanation.
You should also know that when the MCH rate in children at birth is higher than normal, then by adulthood the indicators may stabilize and not cause concern. At the same time, if MCH is elevated in an adult, then this is a serious signal from the body about the onset of pathological processes.
Anemia
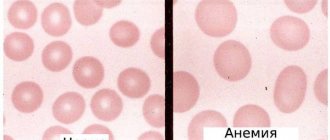
In the vast majority of cases, hyperchromic and megaloblastic anemia lead to transformation. Oversaturation of Hb and the formation of voluminous cells cause an abnormal change in the transport function of the blood. Excessive accumulation of hemoglobin disrupts the movement of blood in the small vessels of vital organs, which negatively affects functional activity. The cells are modified, are not considered complete and die faster than expected.
Hypothyroidism
Thyroid hormone in low concentration inhibits the functionality of the bone marrow, which promotes an increase in hemoglobin concentration, and accordingly increases MCH levels.
Oncological diseases
Pathologies of the red bone marrow, digestive organs, and lungs consistently lead to changes in red blood cells and to the fact that MCH in the blood test is increased.
Liver pathologies
Protein molecules are produced in liver cells. With cancer and hypertrophy, their synthesis increases. Due to the high content of red blood cells, the Hb volume and color index increase significantly. The frequency of cases is predominant by gender - women are diagnosed less often than the stronger sex. If a deviation in MCH values is detected in the blood test of a child or adult, leukemia is most often diagnosed. Cancer diseases increase the index tenfold.
Fluctuating numbers upward is an indicator that the blood is trying to correct the situation and performs its functions to the best of its ability. It's worse if the MCH value is lowered.
What is it used for?
This indicator is one of the most constant in blood tests. In this regard, it is used to identify errors during laboratory tests. The MCHC red blood cell index is used in the following cases:
- when assessing the effectiveness of anemia therapy;
- in the differential diagnosis of anemia;
- when diagnosing hypochromia.
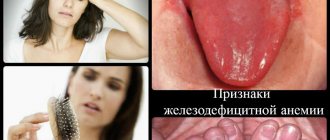
Signs of iron deficiency anemia
Iron deficiency anemia is a common pathology in our time. It is caused by insufficient intake of iron from food or its difficult absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, and may also be associated with some chronic diseases and blood loss. Characterized by a decreased level of red blood cells, it occurs due to severe bleeding, increased destruction of red blood cells or impaired formation of blood cells. Anemia is popularly called anemia. To diagnose it, an analysis to determine the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin is usually not enough. The following blood parameters are usually examined, which together give a more complete picture:
- mean red cell hemoglobin concentration (MCHC);
- average hemoglobin content in one red blood cell (MCH);
- red blood cell distribution width (RDW);
- mean erythrocyte volume (MCV);
- color index (CP).
Why is MCH low in blood tests?
If the average hb content in the erythrocyte is reduced, this suggests a diagnosis of hypochromic anemia. Mostly the situation is aggravated by a lack of iron in the blood structure. Usually hemoglobin is not accepted by the body due to pathological changes in organs and systems:
- inflammatory process;
- dysfunction of metabolic processes;
- hypovitaminosis;
- lead poisoning.
A reduced MCH in a blood test has a detrimental effect on biochemical reactions and negatively affects the patient’s condition. The clinical picture is clearly expressed and creates significant discomfort.
Iron deficiency
A decrease in MCH MCHC in a blood test is often associated with a loss of iron concentration. When the reading is less than 5 mg, doctors look for the cause in internal bleeding, diseases of the digestive system, and an unbalanced diet. Lack of iron leads to unprofitable hemoglobin production. Iron deficiency anemia is predominantly diagnosed in women due to the characteristics of physiological development.
Hereditary pathologies
A decrease in MCH in children indicates pathologies of a hereditary type. During the development of the disease, the synthesis of structural elements of hemoglobin is disrupted. Hb, which carries alpha protein chains, leads to hypoxia of blood cells, as oxygen delivery is disrupted. The disease is diagnosed from the first months of life, which allows urgent measures to be taken.
Vitamin B6 deficiency
Adermin is involved in metabolic processes and is part of the enzymes that synthesize valuable amino acids. Its importance in fat metabolism is undeniable. In its natural state, its amount should be 2 mg, but the value tends to fluctuate. If the concentration of the substance is disturbed in the bone marrow, then the process of building Hb polypeptide chains subsequently changes - the reason for low MSHC and MCH. The condition is more often observed in the fairer sex.
Indications for testing
MSI in a blood test is a highly informative indicator, thanks to which it is possible to assess the current state of the body, confirm the diagnosis, conduct differential diagnostics and study the dynamics of prescribed therapy. Typically, this test is prescribed at the MedArt clinic for:
- Preventive and clinical observation, including for pregnant women.
- Baseline examination during patient hospitalization.
- Suspicion of anemia (of any type).
- Diseases of the hematopoietic system.
- Infectious and inflammatory processes.
- Evaluation of the effectiveness of the started treatment.
It is important to understand that the MCH is not an independent indicator. To evaluate it, a detailed blood test is prescribed, reflecting the most complete picture of the bloodstream at the moment.
How to stabilize MCH performance?
To restore the correct indicators, it is necessary to reconsider the usual way of life and pay attention to eliminating the root cause.
To increase the body’s resistance to diseases, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, introduce moderate physical activity, and control the psycho-emotional state. You can have a positive effect on your blood composition by including healthy foods rich in nutrients in your diet. A properly formulated diet includes essential amino acids and molecular iron in the required volumes. Pomegranate, liver, apples, seafood should be present in every family's food basket.
During pregnancy, the body experiences a double load, therefore, it is important to strengthen the diet with healthy foods. In addition, you should take multivitamins.
Monitoring of MCH in the blood is carried out throughout the entire life cycle so as not to miss a serious pathology.