To do or not to do, to take or not to take medicine, to take a test or not to take a test. We are always faced with a choice and are often afraid of making a mistake. Iron can be said that you can’t go wrong with iron.
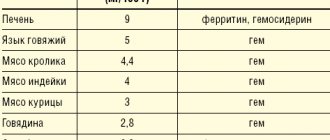
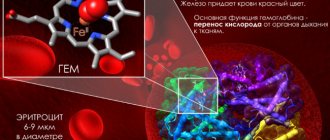
The adult human body contains about 3–4.5 g of iron. More than half of the iron is represented by heme in the composition of hemoglobin, a third is stored in the depot in the form of ferritin and hemosiderin. Moreover, iron deficiency is the most common deficiency condition worldwide, silently leading to anemia.
The main causes of iron deficiency:
Reduced intake of iron into the body due to impaired absorption due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, fasting, refusal, or reduced consumption of foods containing iron.
Increased iron loss during chronic, repeated blood loss (uterine, gastric, intestinal, etc.), as well as during acute massive bleeding.
Increased consumption of iron by the body in children during periods of growth, in women during pregnancy and subsequent breastfeeding of the child.
Factors influencing the decrease in hemoglobin
Most often, changes in the amount of hemoglobin in the blood occur under the influence of the following factors:
- poor nutrition;
- stress;
- serious pathologies of internal organs, tumors, blood diseases;
- large blood losses during injuries, operations, childbirth;
- impaired absorption of iron in the intestine;
- diets for weight loss;
- hormonal changes in the body;
- lack of vitamins B9 and B12.
Also, a decrease in the amount of protein important for our health can be caused by long-term use of certain medications and alcohol abuse.
Low hemoglobin may be a congenital individual feature of the human body. This condition is also typical for older people.
A hematologist will help to identify the cause of anemia and prescribe appropriate treatment. In most cases, it is enough to take a biochemical blood test.
What tests show iron deficiency?
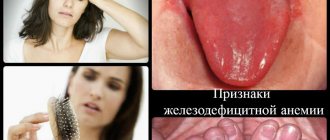
- Be sure to look at a general blood test with a leukocyte formula, since iron deficiency ultimately leads to the development of anemia. Iron deficiency anemia is indicated by a decrease in hemoglobin levels, an indicator of MCV (erythrocyte hypochromia). Often, the examination begins when there are symptoms of anemia (pallor, weakness, dizziness, loss of strength, decreased performance and attention, brittle nails and hair, etc.).
- Decreased serum iron concentration
- Increasing the total iron-binding capacity of serum
- Decreased transferrin saturation coefficient with iron
- Decreased serum ferritin concentration
It is recommended to take tests in the morning, from 8 to 11 am, since the level of iron in the serum is higher in the morning. They should also be taken in the absence of inflammation, which helps lower transferrin levels and increase ferritin levels.
The iron content in the serum is checked 5-7 days after taking vitamin-mineral complexes and dietary supplements containing iron, or short-term use of iron supplements.
Ways to increase hemoglobin levels in the blood
Hemoglobin can also be increased with the help of foods
Anemia is often caused by a lack of certain vitamins and microelements.
In such cases, a balanced diet or taking special medications usually helps to raise the level of hemoglobin in the blood. For various diseases and frequent stress, the doctor prescribes complex therapy.
It is aimed at increasing the content of essential protein in the body and eliminating factors that provoke the development of anemia. Let's look at the most popular ways to increase hemoglobin levels in the blood.
With a special diet
Doctors say that to maintain normal hemoglobin levels in the body, it is enough to include lean meats, a large variety of vegetables and fruits, freshly squeezed juices in your daily diet, and also spend more time in the fresh air.
In most cases, a special diet helps to get rid of anemia, aimed at replenishing the lack of vitamins and microelements that caused the unpleasant condition.
How is iron deficiency treated?
It is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of iron deficiency and adjust nutrition.
If these measures do not help, and iron loss is significant, your doctor may prescribe iron-based medications. Duration of treatment with iron preparations for the purpose of restoration and replenishment of iron reserves in the depot:
- for hidden iron deficiency 1-2 months,
- for mild anemia 3 months,
- with moderate anemia 4.5 months,
- for severe anemia 6 months.
Of course, first of all, iron supplements are used in the form of tablets, drops, capsules, syrups. If your doctor has prescribed you iron supplements, you need to be prepared for long-term and comfortable treatment. This will help by following simple rules.
The dosage of the drug is also determined by the presence of anemia (this is the full therapeutic dose) and the type of iron ion that is included in the drug.
What to do if your child has low hemoglobin
Low hemoglobin in a child under one year old may be a sign of iron deficiency anemia. When to start monitoring hemoglobin levels, is it possible to prevent anemia and correct health indicators without administering medications, said pediatrician and perinatal psychologist Polina Aleksandrovna Kizino.
— Polina Aleksandrovna, red blood cells and hemoglobin are often mentioned in the diagnosis of anemia. How are these three concepts related to each other?
— Hemoglobin is a protein that is found inside an erythrocyte (blood cell). Its main function is to transport oxygen from the lungs to all organs and tissues of the body. The fewer red blood cells, the less hemoglobin, which means the saturation of the body with oxygen is worse. A decrease in the level of hemoglobin, and therefore oxygen in the blood, is called anemia. There are a huge number of types of anemia, and they are caused by different reasons, it is important to understand this.
Causes of anemia
- Low content of red blood cells, increased destruction, slow rate of formation.
- Inability of hemoglobin to bind oxygen.
- Copious blood loss.
- Insufficient amounts of iron, folic acid or vitamin B12 in the body due to an inappropriate diet or malabsorption due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hereditary and others associated with a large number of factors.
— Why does a baby have low hemoglobin?
— The reasons for decreased hemoglobin levels in children are very diverse. More often, hemoglobin falls due to a deficiency of microelements and vitamins, in most cases iron. Iron deficiency anemia is most common in children.
Some of the rarest situations in which low hemoglobin may occur
- Bone marrow pathology.
- Chronic or acute bleeding.
- Hemolysis.
In addition, it has been noted that anemia can occur in children who receive whole milk as their main diet instead of formula. This can be avoided if whole milk is included in baby products - adapted formula, milk porridge, cottage cheese and others.
— How to understand that a child has low hemoglobin?
— External manifestations of anemia are nonspecific. And it is impossible to make a diagnosis without laboratory tests.
The very first signs of low hemoglobin in a child that parents can pay attention to
- Sleep disturbance, shallow sleep.
- Lethargy.
- Fast fatiguability.
- Tearfulness, irritability.
- Paleness, peeling of the skin.
- Less commonly, brittle nails and hair.
Upon examination, the pediatrician can detect a decrease in blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, and sometimes heart murmurs.
Advice: If you suspect anemia in your child, consult your pediatrician. Make a list of questions. Write down your symptoms. Show your food diary for breastfeeding and complementary feeding.
— Why is low hemoglobin dangerous in a child?
— A low level of hemoglobin indicates a low level of oxygen in the blood, that is, hypoxia, which leads to disruption of the functioning of all organs and systems. Of course, the decrease can be of varying degrees, and its manifestations are different, but the closer the hemoglobin level is to normal, the less pronounced the condition.
Degrees of anemia in children
| Anemia I degree (mild) - hemoglobin 110-90 g/l. | Anemia II degree (moderate) - hemoglobin 90-70 g/l. | Anemia of grade III (severe) - hemoglobin below 70 g/l. |
— A mild degree of the disease is more common, since in most cases, babies in the first year of life are constantly monitored by a doctor. And if the baby does not suffer from some serious chronic disease, then, as a rule, it is possible to suspect and begin treatment for mild anemia.
— When is anemia diagnosed?
— The main criterion for diagnosing anemia is a hemoglobin level below 110 g/l. Anything higher is the norm. The disease is diagnosed based on the results of a clinical (general) blood test, which is impossible at home. In this case, the doctor evaluates not only the hemoglobin level, but also other laboratory test indicators. This allows you to determine whether there is anemia or not, as well as to suggest its cause.
A clinical blood test is performed starting at 2 months. It is important to remember about the calendar of examinations for children under one year old and not to miss trips to the clinic in order to see in time and not start the pathological process.
— Polina Aleksandrovna, if a child has low hemoglobin, what should be done to bring the level back to normal?
— The hemoglobin level will not rise to normal levels on its own. We need to work on the cause of anemia. And since the causes are different, the methods of treatment are different. For example, in the most common situation, when a baby’s hemoglobin is low due to iron deficiency, this deficiency is compensated with the help of iron-containing drugs. Everyone knows that hemoglobin is a protein that contains iron. Therefore, by replenishing iron reserves in the body, you can achieve the required hemoglobin level.
You can increase hemoglobin at home without drugs when there is no anemia. For example, a hemoglobin level of 115 g/l is within the normal range, and if it needs to be maintained, a diet will help not to go negative. But iron deficiency anemia can only be treated with medications, not diet. The doctor prescribes medicine and determines how often and in what quantity to take iron, based on data on the level of hemoglobin in the blood of a small patient.
| How to take children's iron supplement | 1.5 hours before meals or 2 hours after meals, washed down with acidified liquid (non-concentrated apple juice, water with lemon). Do not take the tablet with milk, tea, etc. |
| What to eat if a child has low hemoglobin | The diet must include green apples, buckwheat porridge, mainly beef liver, beef, turkey, and possibly oatmeal. |
| What to exclude from your child's diet | Whole cow's milk and whole goat's milk. Children under one year old do not consume baked goods, chocolate, tea, or coffee. |
— What myths are the most dangerous when treating anemia in children?
1 myth. The only reason for low hemoglobin is low iron levels.
— Low hemoglobin levels do not always mean low iron levels. Iron deficiency can be associated with completely different conditions.
2 myth. Hemoglobin levels can be raised by diet.
— The daily intake of iron from food is not enough to produce hemoglobin at pathologically low levels. If, according to the results of the examination, the child has low hemoglobin, it is necessary to contact a pediatrician to find out the cause and receive specific treatment depending on the form and extent of the disease.
— Is it possible to prevent iron deficiency anemia in children under one year of age?
— Diet is important. You should not delay the introduction of complementary foods, because the baby’s endogenous iron reserves are gradually depleted, and by six months it is already difficult to replenish them exclusively with breast milk or formula. So prevention is an adequate varied diet, including through the first complementary foods, the introduction of which is allowed at 4–6 months.
Hemoglobin is not the only indicator by which anemia is diagnosed. It is important not to self-diagnose or self-medicate. If you suspect anemia in your child, consult a doctor for examination. Based on laboratory data, the doctor will confirm anemia or a tendency towards iron deficiency and prescribe the correct therapy.
Pediatrician Polina Aleksandrovna Kizino
*The ideal food for an infant is mother's milk. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. MAMAKO® supports this recommendation. Before introducing new foods into your baby’s diet, consult a specialist.
What iron supplements are there?
Iron in preparations can be represented by a di- or trivalent ion, designated Fe2+ or Fe3+, which is part of salts or complex complexes (for example, polymaltose complex hydroxide).
When using iron salts, you may encounter problems with its absorption. Unfortunately, not all iron from the drug is absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Moreover, this process is poorly controlled, since it depends on the state of the gastrointestinal tract, food taken, and other medications. Therefore, both a lack of incoming iron and an overdose are possible. In addition, not all forms of medication are convenient to use; if some tablets are chewed, the enamel of the teeth is often stained and a metallic taste remains in the mouth for a long time. Trivalent iron preparations usually do not have these side effects.
What supplements should you avoid during pregnancy?
Multivitamin complexes contain almost all vitamins and minerals in safe dosages. And any monovitamins are allowed to be taken only after consultation with a doctor. After all, an overdose of some elements poses a threat to the fetus.
Vitamin A is involved in the development of the unborn baby's immune system. But if too much retinol enters a pregnant woman’s body, the risk of developing congenital anomalies in the fetus will increase several times. Vitamin E is also involved in the formation of immunity and the nervous system. But an overdose increases the risk of premature birth.
Exotic dietary supplements, medicinal herbs, and homeopathic supplements are generally not recommended to be taken during pregnancy. It's better to focus on eating right, getting enough exercise, and minimizing stress. It is imperative to take vitamins prescribed by your doctor. But we must remember that this is not the only condition for a successful pregnancy outcome.
How to increase the effectiveness of treatment
To reduce the likelihood of side effects, iron salts are taken before meals.
The absorption of iron is higher when taken simultaneously with ascorbic and succinic acids, fructose, and cysteine. This property is used in some combination drugs.
Iron absorption is reduced by certain substances from food or medications. Thus, it is reduced by tannin (strongly brewed tea), calcium salts (in milk or medications), magnesium and manganese (in mineral complexes or antacid preparations, such as phosphalugel), tetracycline antibiotics, phosphoric and phytic acids (cereal seeds, legumes). This effect is smoothed out when using preparations based on ferric iron.
Iron absorption is increased in severe iron deficiency. Therefore, you should be more careful about the prescribed dosage. Doctors often rely on a therapeutic dose of 200 mg of iron ion/day. If you understand that an iron supplement is not suitable for you due to the development of adverse reactions, difficulties in taking it, or lack of improvement in your well-being, tell your doctor about this. Under no circumstances should you change the dosage of the drug yourself. Exceeding the dose can lead to overdose and poisoning, reducing the dose can lead to useless use and lack of effect.
How is the effectiveness of treatment assessed?
During the first days of treatment with iron supplements, physical sensations are assessed.
When treating anemia, on the 5-8th day of treatment, a reticulocyte crisis is determined (an increase in the number of reticulocytes compared to the initial value, usually by 2-3% or 20-30‰).
After 4 weeks of treatment, the increase in hemoglobin is assessed. An increase in hemoglobin concentration by 10 g/l by the end of the first month of treatment with iron preparations indicates that the dose has been correctly selected and the effectiveness of therapy. After hemoglobin is restored, therapy is continued to saturate the iron depot, while the dose of the drug is reduced by 2 times.
For hidden iron deficiency, half doses of the drugs are used for 4-8 weeks. Depot saturation is determined using a comprehensive biochemical study (ferritin, transferrin, TLC).
At Lab4U you can take tests to identify iron deficiency and monitor the effectiveness of therapy with a discount of up to 50%.