Acceptable pressure levels during breastfeeding
Even children know the correct blood pressure indicator - it is 120/80 mm Hg. But not all people correspond to this value, because everyone has always been a little higher, a little lower, a little lower. This is what you should follow. Normal blood pressure is considered a person who feels well.
The period of breastfeeding is a very important time in the life of every young mother, because it is responsible not only for your health, but also for the well-being and development of your baby. That's why a nursing mother should be careful and think that everything is fine. You cannot underestimate your condition, because only when the mother feels comfortable, the child is calm and joyful.
If the pressure increases to 135/85 mm Hg, there may not be any negative consequences.
When it increases above - 140/90 and much more, and the well-being of the deterioration of the deterioration of the deterioration of privacy, this is already treatment in the clinic.
Breastfeeding - questions and answers
What to feed a newborn?
At different times, different answers were given to this question. However, the latest recommendations of Russian and foreign specialists - neonatologists, pediatricians, nutritionists - once again prove: the new is the well-forgotten old. Scientific research has confirmed that the best food for a child is mother's milk. It contains all the nutrients a baby needs in the first six months of life.
Why is breastfeeding good for a baby?
Breast milk contains in an optimal combination all the proteins, fats and carbohydrates, vitamins, water and minerals a baby needs. Unlike mixtures, it is completely absorbed and provides immunity to the newborn.
Children who receive breast milk are less likely to catch colds, suffer less from otitis media and infections, from diarrhea and allergies than children who are bottle-fed. Breastfeeding gives the baby a feeling of closeness to the mother, warmth and comfort.
Why is breastfeeding good for a mother?
Breastfeeding helps build closeness with your baby. Attachment to the breast immediately after childbirth helps to contract the uterus, timely separation of the placenta, and prevent bleeding. A woman who breastfeeds is at lower risk of anemia (anemia), osteoporosis, ovarian (adnexal) and breast cancer. If a number of conditions are met, breastfeeding also helps prevent another pregnancy. This method of family planning is called lactational amenorrhea (LAA).
What is natural (exclusive breastfeeding) feeding?
Natural feeding involves feeding the baby ONLY breast milk in the first months of life. No water, no juice, no complementary foods. During the first six months of life, a healthy baby does not need any other food other than mother's milk.
The baby gives the mother a “signal” to produce milk; “request” to change the composition of milk when he is sick; "request" to increase the amount of milk when he is growing rapidly.
The mother gives the child ideal food, the composition of which changes depending on his needs; antibodies that protect it from infections and diseases; love, warmth and tenderness; feeling of comfort and security.
Breastfeeding is a process of two-way communication between mother and child. The more often and longer the baby suckles, the more milk the mother produces.
What special breast care is required during breastfeeding?
Almost none. If you shower daily, you should not wash your nipples before or after feeding. Soaps and disinfectants can dry them out and make them sore. There is also no need to lubricate the nipples with a solution of brilliant green (brilliant green) or ointment. It is good to leave a little milk on the nipples after feeding. Your milk contains various antibacterial substances, and therefore is the most reliable hygiene product.
When should you start breastfeeding? How often do you put your baby to the breast?
You should start breastfeeding within the first hour after birth. First, the breast secretes the colostrum the baby needs, which is very nutritious and rich in vitamins and antibodies. Colostrum is the first natural vaccination for a newborn against infections. Even one drop of colostrum contains everything a newborn needs. After two to three days, milk begins to be produced. Feed the baby as required, but with a break of no more than three hours during the day and no more than five at night. Put your baby to your breast frequently. The more often the baby suckles, the more milk the mother produces. If a baby gains weight of at least 500 grams per month and urinates at least six to eight times a day, then he is getting enough milk.
How should a nursing woman eat?
There is a widespread myth that breastfeeding women need special foods. In fact, your body can produce multi-component breast milk from so-called “simple” foods: bread, potatoes, carrots and apples. The main thing is that the food of a nursing mother is varied. It is advisable to include meat, fish, legumes, vegetables, fruits, and dairy products in your daily diet. Forget talk of “forbidden foods.” You can eat everything, provided that neither you nor the child’s father is allergic to any specific product. Forget also the stories about “uneven” or “thin” milk, supposedly a consequence of poor nutrition of the mother. Research shows that even with a very poor diet, the content of fat and some vitamins in milk can only slightly decrease. The amount of proteins remains unchanged. In any case, low-fat milk is better than the “good” complementary foods!
To reduce pain attacks in a baby, a nursing mother should first of all limit the consumption of whole milk in any form - do not add it to tea, porridge, etc. If possible, replace whole milk with lactic acid products. And also eat those vegetables and fruits that grow and are typical for the region of residence.
It is important NOT to eat foods that increase gas formation - cucumbers, cabbage, grapes, corn, kvass, fresh yeast bread, etc. Products that provoke the development of colic in a baby are fatty pork, salads with mayonnaise, fried and salty foods, seasonings and marinades.
Does going to work or school prevent you from continuing breastfeeding?
No. Milk is expressed and can be stored at room temperature for eight hours, in the refrigerator for three days, and in the freezer at -18 degrees for up to three months. The quality is not lost.
There are several ways to express milk: manually, with a breast pump, with a breast pump-syringe, or with a “warm bottle”. Your health visitor or other trained specialist will tell you more about these methods. The technique of expressing milk is useful for all mothers to learn to relieve the feeling of pressure during fullness or engorgement of the breast. In addition, you can always leave your milk for your baby if for some reason you have to be separated from him for a while.
Why does milk disappear, and what to do in such cases?
As a rule, milk disappears because the mother does not allow the baby to suckle enough, or rarely puts him to the breast, or, worrying that “the baby is malnourished” or “the milk is bad,” introduces complementary foods. As soon as the child receives complementary feeding, he begins to suck less on the mother's breast, and the less the child sucks, the less milk the mother's body produces. Therefore, if you are worried about a lack of milk, try feeding your baby more often (10-12 times a day). Make sure it is attached correctly to your chest. And be prepared for the fact that the results will not be noticeable immediately: after changing your diet, four to seven days must pass before more milk begins to be produced.
Is it possible to breastfeed after a caesarean section?
Yes. Everything is done exactly the same. The only difference is that your milk sometimes comes in a little later, and you may need more help from your healthcare team when latching on. The main thing is to find a position in which the baby could suck without causing you pain or discomfort. For example, the baby can be “thrown” over the shoulder or fed while lying down, etc.
What other problems may arise and how to solve them?
Breastfeeding is a skill and it takes time to master. Not everything will work out right away; difficulties may arise. Don't be scared and don't give up! Almost all problems that arise during breastfeeding are quite easily solvable. Painful or injured nipples are a consequence of improper attachment of the baby to the breast. In this case, there is no need to stop feeding. Rinse your nipples with warm water and let them dry. Place your baby on the breast that is less irritated. Try different feeding positions. Applying a drop of breast milk to the nipple before and after feeding also promotes healing. Engorgement is a painful fullness of the breast with milk. This can happen within two to three days after birth, when milk production begins. Frequent feeding and, if necessary, pumping will help you cope with this problem.
How to breastfeed correctly?
1. Take a comfortable position, sitting or lying down. Bring your baby to your chest so that his head and body are in the same plane. The baby should face the breast, with his nose opposite the nipple. 2. If you wish, you can support the breast from below with your whole hand or place four fingers under the chest on the chest, and the fifth, large, on top. 3. Touch the nipple to your baby's lips, and when he opens his mouth wide, allow him to take the breast into his mouth, holding his body tightly to you (bring the baby to the breast, not the breast to the baby!).
If the baby is attached to the breast correctly, he will capture with his mouth not only the nipple, but also most of the areola (the dark spot around the nipple) with the tissue located along it. In this case: - the child’s chin touches the chest; - his mouth is wide open; - you can see most of the halos above the upper lip, and not under the lower one; - you do not experience any discomfort in your chest. As a rule, the baby releases the breast on its own, satisfied and sleepy. Remember that breastfeeding is a wise investment in your baby's health.
High blood pressure during breastfeeding
High blood pressure during breastfeeding is not uncommon today. This phenomenon is associated with the stress on the myocardium during pregnancy, when the muscles of this organ are very taxed to ensure the proper functioning of the body of the woman and her child. Also, changes in the hormonal levels of a pregnant woman contribute to heart disease.
Therefore, at every visit to the appetite clinic, the doctor who notices it measures the blood pressure. Its cost shows to what extent the stern woman's circulatory clamshell is able to function properly.
To alleviate the condition of the elderly, a mother can have an experienced doctor who can prescribe such drugs so as not to harm the child.
The course of treatment for hypertension during breastfeeding will be significantly differentiated, in this case including only approved medications and respectful diets.
Why does breastfeeding mothers have high blood pressure?
High blood pressure in the paragraph is caused by the following factors:
- Excessive dependence on coffee, tea, licorice root tincture;
- overwork, stress, lack of sleep;
- smoke;
- hereditary predispositions that reveal themselves after pregnancy;
- take medications that increase smooth muscle tension - oxytocin, methylerometry;
- various cardiovascular disorders;
- diabetes;
- Difficult childbirth or complications after it;
- Problems with the endocrine system.
If excess pressure begins to develop, blood pressure readings gradually increase. Regardless of the reasons that led to hypertension, medical care is necessary to prevent the development of the disease. If nothing is done in this direction, after a while you may notice that it is taking effect and finally leading to pathological changes in the body.
Normal pressure
Both during the period of bearing a child and after his birth, if a young mother practices breastfeeding, the pressure should be within normal limits, this means that the body can fully cope with the loads, and no pathological changes occur in it. In healthy people, blood pressure should not be lower than or exceed the normal range of 90/60-140/60. Blood pressure can fluctuate within acceptable values; such changes depend on the characteristics of the body, age, weight and many other factors.
Enter your pressure
Move the sliders
120
on
80
Signs of high blood pressure
When the pressure increases, the feeding mother feels the following symptoms:
- Headache;
- nausea;
- Black spots before her eyes;
- chills;
- Fast impulse;
- Breathing and breathing;
- Problems with vision.
Even some of the above-mentioned symptoms indicate improper functioning of the cardiovascular system. It often precedes pregnancy, but even after pregnancy, symptoms of hypertension can persist during breastfeeding.
Symptoms
| Pressure | Symptoms |
| Increased |
|
| Decreased |
|
Diagnostic methods
Since this disease is very serious and can cause both heart attacks and strokes, the dieter must necessarily undergo research to determine the causes in which hypertension occurred so that doctors can prescribe effective treatment.
Complex diagnostics includes the following methods:
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Blood chemistry. They use it to test for anemia from iron deficiency.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG).
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland, heart and abdominal cavity.
- Echocardiography.
- Computed tomography of the kidneys and adrenal glands.
- Urography and aortography.
Carrying out the necessary tests will not only reveal the fact of hypertension in a nursing mother, but also determine its causes and begin effective treatment.
Lactostasis due to high blood pressure
Lactostasis is a blockage of the milk duct. Most often it occurs in first-time mothers in the first days after starting breastfeeding.
This condition can be caused by high blood pressure, but the problem is complex. Inability to express milk and non-compliance with the frequency of feeding the newborn, as well as tight underwear. The thoracic ducts can become worse due to stress and exposure to cold. All these factors also lead to breast swelling.
Therefore, you should take care of yourself and make sure that inattention and high blood pressure do not cause galactorrhea in the mammary glands.
First aid
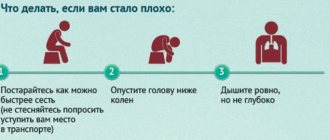
In case of a sharp increase in blood pressure, you should immediately try to normalize it and seek medical help. If this is not the first time a nursing woman finds herself in a dangerous condition, you need to get a tonometer and have it at hand.
If the ambulance has not arrived yet, in this situation you should:
- Lie down comfortably so as not to put your health at greater risk;
- ask others to open the windows and let cool, fresh air into the room;
- lower your blood pressure with medications (if this is not the first time and the doctor has previously prescribed them for hypertension)
- Place a hot water bottle on your feet to warm them up if you feel shaky;
- stay calm or drink valerian extract to find emotional balance.
After doing all these steps, wait until the doctor tells him about the medications you took.
How to measure?
Correct measurement of pressure will allow you to make a reliable diagnosis.
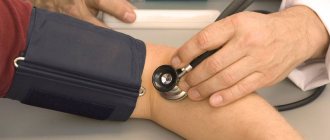
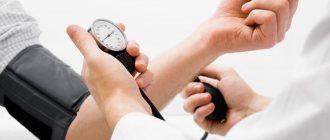
Before measuring blood pressure, you should sit down and relax. Place a cuff on the arm, above the bend of the elbow, fixing the stethoscope on the inside where the large vein passes. Next, we pump up the air with the bulb so that the cuff fits snugly to the arm. Then the air slowly descends, and the tone is listened to through a stethoscope. The first beat shows the systolic pressure, and the last beat shows the dystolic pressure. For ease of use and obtaining accurate data, it is recommended to use an electronic tonometer. This will help avoid data inaccuracies, and the procedure will not bring any difficulties to a person who does not know how to measure blood pressure.
Permitted and prohibited drugs
In this situation, the question arises, what can be taken for blood pressure while breastfeeding, since most of the drugs pass into milk?
There are such drugs. Here they are:
- Nifediline.
- Methyldol.
- Verapomil.
- Dolegit.
Although these drugs are not absorbed into breast milk, they may cause decreased milk supply. To normalize blood pressure, the tablet is placed under the tongue. The doctor prescribes the drug, determines the duration of its use and dosage.
There are also drugs that are completely prohibited for use by nursing mothers:
- Beta-blockers (Atenolol, Nadolol).
- ACE inhibitors.
- Atgiotensin receptor blockers (reserpine).
- Diuretics (furosemide).
- Antispasmodics (No-shpa, Dibasol, Papaverine).
A nursing woman bears full responsibility for her health and the health of her child, so she should not take medications without the participation of a specialist.
Herbal treatment
One way to reduce high blood pressure is by consuming medicinal plants.
The calming properties of herbs give a good effect. They are observed when consuming a decoction from the entire list of herbs.
To prepare it, take:
- Juniper cones (2 tablespoons);
- lemon balm (2 tablespoons);
- fennel seeds (1 tbsp.);
- allspice (3 tablespoons);
- Peppermint (3 tablespoons).
Mix all ingredients in the quantities indicated above and pour 2 tablespoons of the mixture into a thermos. Pour boiled water (1 liter) over these herbs. Set aside for 3 hours, then strain. Drink 0.5 glasses twice a day - morning and evening half an hour before meals.
Feeding the child during this treatment cannot be stopped.
Traditional medicine recipes
In nature, there is a large list of plants that affect blood pressure, but many of them are not recommended during lactation. Herbs are a potential source of allergies for a baby, because components from plants can also pass into the mother’s milk. If a nursing mother periodically faces the question of how to raise her blood pressure, then her menu can include dishes with juniper berries. In case of arterial hypotension, they can be eaten either fresh or used in the preparation of drinks. Just 5 berries can significantly raise blood pressure, so you shouldn’t eat them in larger quantities.
Wormwood has similar properties. The dry plant is infused in boiled water in the proportions of 1 glass of water to two tablespoons of herb until completely cooled and drunk in small sips. Honey will help smooth out the not-too-pleasant taste.
You can also use a medicinal mixture of hops, motherwort and valerian. The plants are taken in equal parts - one tablespoon at a time - poured into a glass of boiling water, filtered after infusion and drunk in small portions several times a day. This healing drink will improve the functioning of the nervous system, restore sleep and heartbeat, and bring blood pressure back to normal.
Herbs, in particular motherwort, can be used to increase blood pressure during breastfeeding, but with great care to avoid harm to the baby.
An even larger list of herbs and plants can be used during lactation, but with caution - angelica, thistle, St. John's wort, hawthorn and others. When consuming healthy decoctions, teas and tinctures, be sure to monitor the baby’s reaction. At the first sign of a negative reaction from the child’s body, it is better to stop taking such folk remedies.
Therapeutic baths
Therapeutic baths are effective as one of the additional measures that help a nursing mother relax and reduce blood pressure.
They are available in 2 versions:
- With the addition of a solution of valerian or sea salt. Give a bottle of sedative or 1 tablespoon of salt in water. Treatment can be continued for up to 15 minutes.
- Clay baths. Add 3-4 handfuls of white clay to the water. Grind until completely dissolved and lumps disappear. Add chopped garlic (1 head). The session should last up to 30 minutes. After bathing, dry with a hard towel.
Methods to combat low blood pressure during breastfeeding
Most often, a decrease in pressure (hypotension) does not require correction, since with normal rest and nutrition, indicators are restored independently due to compensatory mechanisms.
Main symptoms of hypotension:
- weakness;
- sleep phase disturbances (nighttime insomnia and pathological daytime sleepiness);
- apathy - lack of desire to do anything, lack of interest in anything;
- diffuse headache;
- visual impairment (double vision, blurred contours);
- dizziness.
Reduced blood pressure disrupts the blood supply to organs and tissues, including the mammary gland, so long-term persistence of these symptoms is accompanied by the risk of a decrease in milk supply.
How can you raise a woman’s blood pressure during lactation?
The period of breastfeeding is characterized by the presence of many restrictions in the mother's lifestyle, therefore traditional methods of blood pressure correction are prohibited.
The safest methods to raise the blood pressure of a nursing mother are presented in the table below.
| Way | Mechanism of action |
| Increased drinking regimen (up to 2.5 liters per day). Allowed: compote, juice (natural), uzvar, fruit juice, clean water | Increasing the volume of circulating fluid in the vessels |
| Balanced nutrition (daily caloric intake of at least 2500 kcal) | Adequate intake of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and mineral salts with foods ensures the normal functioning of the vascular wall and endocrine glands responsible for blood pressure levels |
| Physical activity (morning exercises, special fitness for women in labor) | Increased blood flow in working muscles increases vascular tone throughout the body |
A common cause of low blood pressure in women after childbirth is dysfunction of the thyroid gland. In this case, you can raise the values by systematically using iodized salt or iodine preparations (after preliminary consultation and laboratory tests with a doctor).
How to relieve discomfort during hepatitis B due to low blood pressure at home?
Sudden signs of hypotension, which significantly worsen a woman’s condition and complicate child care, require immediate correction.
A nursing mother can raise her blood pressure at home using several methods:
- drink a cup of coffee. One mug of weak coffee a day will not affect the quality of milk (large quantities make it bitter), but will improve the mother’s condition;
- drink a cup of strong black or green tea with sugar;
- use tincture of ginseng or lemongrass (1 tablespoon, dissolved in a glass of water). The products can only be used after consulting a doctor;
- shake your abs (for women during the first month after a caesarean section or complicated childbirth - it is strictly contraindicated).
Drug treatment using pharmacological drugs is carried out only against the background of concomitant pathology and pronounced changes. Often, women must stop breastfeeding during therapy.
Diet
Nutrition during pregnancy should also be adjusted. A nursing woman should avoid excess salt, fried, fatty and smoked foods. You should also avoid hot and spicy spices and even sweets. Both the child and his mother are harmful.
Instead of junk food, eat more fruits and vegetables, fresh or minimally heated.
Nursing mothers should prohibit smoking and drinking alcohol. Coffee and tea have a negative effect on the health of women with hypertension; it is advisable to limit them. It is extremely important to maintain optimism and peace of mind.
What to do if a nursing mother has low blood pressure
Having learned that high blood pressure is dangerous, it is necessary to deal with low blood pressure. Blood pressure below normal is also common, so the following recommendations will help normalize it:
- A woman should get plenty of rest. Her sleep should be 8 hours a day. You can avoid stress by taking herbal teas that contain sedatives.
- If low blood pressure occurs due to anemia, it is necessary to raise the hemoglobin level to normal using special medications.
- In case of hypotension associated with a lack of iodine in the body, it is obtained from iodized salt. In addition, many of them contain algae and fish.
If your blood pressure is low, a nursing woman should lie down for a while. When he gets better, he will need unsaturated sweet black tea with something nutritious.
First aid measures in case of a sharp rise in pressure
If a woman breastfeeding her baby feels unwell, she must:
- Lie down to avoid fainting. If this is not possible in the current situation, sit down or at least find a fulcrum and rest your head.
- Drink a mug of strong sweet tea, eat a sandwich with butter and cheese (this is an option for raising blood sugar levels, even with diabetes).
- Apply light pressure to the temples or massage the cervical vertebrae. This will improve blood circulation.
- Wash your face with cold water, make a compress on your forehead with a dampened towel.
- Take valerian/motherwort tincture - just a couple of drops.
Even if all the methods described helped improve your well-being, you should not delay visiting a therapist. If a nursing mother knows the true cause of such attacks, it will be easier for her to eliminate them. Preventative measures will help avoid pressure surges in the future.
Causes of low blood pressure
A condition in which blood pressure is low is called hypotension. In this condition, the upper limit falls below 90. In a woman with HD, many nutrients are transferred to the growth and development of the child. Therefore, iron deficiency anemia is considered one of the causes of hypotension.
Another deficiency of thyroid hormones is hypothyroidism.
There are also factors that contribute to lower blood pressure, such as postpartum depression, stress, and overwork.
conclusions
A decrease in blood pressure in a woman during breastfeeding is a common occurrence, which is accompanied by characteristic complaints. Traditional correction methods using large amounts of coffee, alcohol, and medications are contraindicated during lactation. Doctors recommend that a nursing mother drink strong tea, a lot of compote or juice for blood pressure. The main ways to correct the condition are proper rest, balanced nutrition and adequate physical activity. The methods will help not only raise blood pressure, but also speed up recovery after childbirth.
Symptoms
You can recognize low blood pressure by the following symptoms:
- lack of breast milk;
- general weakness and drowsiness;
- weight loss;
- blue circles under the eyes:
- dizziness;
- apathy.
Low blood pressure can be recognized by these symptoms. This is a fairly dangerous condition and can lead to fainting if not handled correctly.
Low blood pressure during breastfeeding increases with drinking more fluids. During breastfeeding, a woman should consume more as it is necessary for milk production.
Consequences of high and low blood pressure during lactation
If we compare low and high blood pressure, the latter condition is much more dangerous because it can cause swelling of the mammary glands, that is, lactastasis. In this case, the woman’s reproductive health will suffer, in particular, refusal to breastfeed.
In addition, arterial hypertension can cause the following consequences:
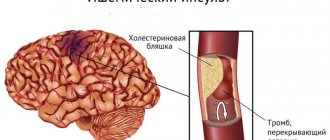
- stroke or heart attack;
- atherosclerosis;
- complications of diabetes;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- heart failure.
Therefore, monitoring their well-being is the responsibility of every nursing woman, because we are talking not only about her health, but also about the well-being of the newborn.
Prevention
There are simple and inexpensive preventive measures that can reduce the risk of hypertension in breastfeeding women:
- To do this, if the pressure has already risen many times, you need to monitor its values using a tonometer.
- Move more, breathe fresh air, be physically active.
- Avoid nicotine and alcohol.
- Eat a healthy diet.
- Maintain psychological balance.
Although the diagnosis of hypertension in nursing mothers is quite serious, you should not be afraid, because if you follow the recommendations of specialists, the prognosis is favorable. It is enough to monitor your health and, if necessary, undergo therapy.