Publication date: June 18, 2019
Very often, the cause of headaches (cephalalgia) is lability of blood pressure, which is why such pains are also called “vascular.” Treatment of vascular headache should always begin with eliminating the cause, that is, normalizing the pressure if it provokes the appearance of this symptom. A typical picture of the pathology will look like throbbing or tingling pain, sometimes even a burning sensation.
In a number of cephalgia, headaches with normal pressure are also often encountered, the treatment of which can be very different from vascular headaches. Often such pain occurs against the background of other pathologies and is only a sign, not a disease. The pain mechanism is triggered by the direct impact of various processes on the sensitive receptors of the dura mater and cranial tissue. When cephalalgia appears, it is always worth determining its cause.
The following factors can cause headaches against the background of normal blood pressure:
- traumatic brain injury;
- inflammatory processes both in the head and in other parts of the body (sinusitis, otitis, mastoiditis, etc.);
- neuralgia of the facial trigeminal nerve (usually only part of the head hurts, paroxysmal, tingling);
- brain abscess (temples, frontal part hurt);
- pregnancy;
- flu, colds, adenoviral infection;
- pituitary adenoma;
- frequent stress;
- allergy;
- fistula;
- PMS in women;
- vertebral artery syndrome;
- excessive mental stress (tension cephalgia);
- general fatigue.
All these reasons require a different medical approach, so treatment of headaches with normal blood pressure consists of identifying the factor that caused it and selecting adequate therapy. Sometimes a Paracetamol or Ibuprofen tablet is enough, sometimes normal sleep and rest, in other cases the mandatory help of specialists is required.
What means
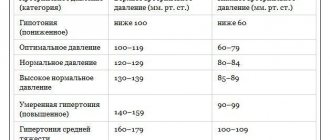
Blood pressure 120 over 80 - what does this mean? To do this, you need to know what these values mean:
- 120 mmHg Art. – systolic pressure, showing the level of blood pressure on the walls of the arteries at the moment of the onset of contractile movement of the myocardium;
- 80 mmHg Art. – diastolic pressure, showing the level of blood pressure on the walls of the arteries at the moment of completion of the contractile movement of the myocardium.
Thus, blood pressure (blood pressure) is an indicator of the force of blood pressure on the walls of blood vessels. Normal blood pressure is considered to be 120/80. But at the same time, for each person there is an individual norm, depending on certain factors. The main ones are:
- the speed at which myocardial contraction occurs;
- the volume of blood pumped by the heart over a certain time period;
- strength of resistance of vascular walls.
It is the stability of the listed indicators that sets the norm of blood pressure. Other factors may also have an additional influence. This is the person’s age group, the presence of chronic diseases, hormonal imbalances, and current psycho-emotional state.
Due to this, blood pressure levels can change throughout life. In a small child they will be quite low, but then - as they grow older - they will begin to rise and reach the accepted physiological (age) group.
Changes in hormonal levels can also provoke surges in blood pressure. That is why frequent changes in pressure during pregnancy and in adolescents are an acceptable norm and indicate an ongoing adaptation of the circulatory system.
During pregnancy, blood pressure readings of 120/80 are considered the absolute norm.
During pregnancy
Blood pressure of 120-127 over 80 during pregnancy is normal, if before pregnancy it was slightly lower. Changes in indicators will occur throughout the gestational period:
- during the first trimester (1–12 weeks), blood pressure may decrease, which is explained by the restructuring of all body systems;
- from the 18th week of gestation, the blood pressure level returns to the pre-pregnancy norm, but may increase slightly;
- By the end of the second trimester (26–27 weeks of pregnancy), blood pressure rises - if a woman does not experience headaches and feels well, then this should be considered as an acceptable norm.
Important! If an increase in blood pressure disrupts general well-being, then the pregnant woman requires medical attention.
Adults and elderly people
The physiological norm of blood pressure in women is somewhat different from that in men. Women's indicators are usually lower by about 6 mmHg. Art. This is due to hormonal fluctuations. For this reason, in old age, female hypertension is somewhat less common. In older people, “healthy” blood pressure levels will be higher. Physiological indicators – 146/158…83/84 mm Hg. Art. A blood pressure of 120/80 means the person is suffering from hypotension.
Children and teenagers
Blood vessels in childhood and adolescence are slightly more distensible than in adults. For this reason, their blood pressure levels are lower and this is a physiological norm. The younger the child, the lower his blood pressure.
Immediately after birth, the baby's blood pressure averages 70/45 mmHg. Art. Minor fluctuations are allowed. Then the indicators begin to gradually increase. At first, babies mature evenly, but when they reach a certain age, blood pressure levels may begin to differ.
For girls this is the age of 3–4 years, 12–14 years. For boys, these ages are 5–8 and 16 years. A blood pressure of 120/80, diagnosed in childhood, cannot be considered normal. But at the same time, in adolescents it will be considered acceptable or slightly increased.
Main reasons
A rapid pulse with low blood pressure is not always a dangerous condition and requires urgent medical intervention. The need for treatment and the effectiveness of therapy depend on why the heart rate has increased, as well as on the inverse relationship. That is, does the pressure drop due to an increase in heart rate or does the opposite happen? First, blood pressure decreases, and the heart rate increases.
Both conditions can be caused by different reasons. But more often, tachycardia becomes a secondary factor, manifesting itself as a compensatory reaction of the body to a sharp drop in blood pressure. A condition where a relatively healthy person’s pulse increases with reduced blood pressure is accompanied by hypovolemia. This means that there has been a decrease in the volume of blood circulating throughout the body.
There are two types of pathology:
- True. It manifests itself with blood loss, dehydration or release of blood plasma into the intercellular space - this reduces the amount of blood in the cavity of the vascular bed.
- Relative. It is characterized by pathological vasodilation, in which the blood volume is no longer sufficient to maintain blood pressure levels in a stable state.
In response to insufficient blood volume and a drop in pressure, the heart reacts by increasing the number of contractions to maintain the blood supply to important organs and systems - this is how a condition develops when the pressure is low and the pulse is fast. In this case, both the upper (systolic) and lower (diastolic) pressure drops immediately.
Dehydration
Losing a large amount of fluid from the body often leads to a decrease in blood pressure and an increase in heart rate. Dehydration occurs as a result of diarrhea (poisoning, infectious diseases, enterocolitis and irritable bowel syndrome). The body also loses a lot of fluid due to vomiting, excessive sweating, and after drinking large amounts of alcohol.
In an elderly person, a drop in blood pressure and increased heart rate are often the result of dehydration due to diabetes and the use of diuretics. Diuretics are prescribed to elderly patients to treat hypertension, which occurs in half of patients over 50–60 years of age; they remove excess fluid from the body. And with diabetes, glucose levels in the blood rise, causing the kidneys to produce more urine.
Blood loss
Blood loss is the most common reason why blood pressure drops during tachycardia. A person can lose blood as a result of injuries and inflammatory diseases, such as gastric and duodenal ulcers, hemophilia, malignant neoplasms of the intestine, esophageal varices, and cirrhosis of the liver.
Release of blood plasma into the intercellular space
Circulating blood volume decreases simultaneously with a drop in blood pressure and an increase in heart rate in the case of certain types of diseases. This happens with inflammatory pathologies of the kidneys, heart failure, liver and biliary tract diseases. Blood effusion also occurs after severe burns to the body and a decrease in protein levels in the blood.
Why can blood pressure decrease with tachycardia?
In many patients, the appearance of a rapid pulse causes a sharp decrease in blood pressure levels, that is, an inverse relationship can be traced. With an increased heart rate, the heart ejects less blood because it does not have time to be fully filled with it, which causes the blood pressure level to decrease.
However, this type of tachycardia, when the pulse affects the pressure, is relatively rare. This phenomenon is diagnosed in patients with signs of ischemia or in adolescents with additional congenital pathways of the cardiac conduction system. However, the pressure does not drop when the temperature rises, after physical activity, fear or pain.
Additional reasons
The following pathological conditions of the body may additionally lower blood pressure and increase heart rate:
- iron deficiency anemia, when the amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells in the blood is reduced;
- panic attacks - attacks of uncontrollable anxiety, fear, panic;
- alcohol abuse and addiction to drugs;
- postprandial hypertension (when blood pressure drops sharply after eating food) and orthostatic hypertension (a jump in blood pressure downward with a sharp change in body position in space, mainly when getting up from a sitting or lying position);
- hypoglycemia – insufficient amount of glucose in the blood plasma;
- arterial valve stenosis;
- ingestion of toxic substances into the body (mercury vapor, lead, cyanide);
- thyrotoxicosis is dysfunction of the thyroid gland when it produces a large amount of hormones.
Often, low blood pressure readings are observed during exacerbation of allergies during grass flowering seasons. A person with a tendency to sensitization may feel weakness, shortness of breath, runny nose, lacrimation, his blood pressure drops, and his pulse quickens due to nervous excitement and swelling of the mucous membranes.
Headache with normal blood pressure
Pressure 120/80 mm Hg. Art. is a physiological norm and headaches accompany it very, very rarely. And if a person has a headache with such blood pressure, then the cause must be sought in other conditions. These may be:
- experienced stress, nervousness;
- the onset of inflammation of the maxillary sinuses (sinusitis);
- complications of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine;
- development of ARVI, influenza, bronchitis;
- poisoning;
- diseases of the ENT organs and others.
To understand the true cause, it is necessary to track changes in well-being and consult a doctor.
How to help a patient
What to do if your heart rate suddenly increases and your blood pressure decreases? The dangerous condition described above requires calling an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, it is necessary to place the person in a horizontal position, raising his legs above his head. You can make the patient sit down by unbuttoning his shirt, loosening his belt and allowing oxygen to enter the room (open the windows).
It is also recommended to give the victim a medicine that will not cause a further drop in blood pressure. For example, sedatives - valerian, motherwort, peony tincture. At the same time, you need to press your eyeballs with your fingers, but without pressure, holding them in this position for 25–30 seconds.
It is necessary to monitor the level of pressure and pulse until the patient’s condition stabilizes.
To make you feel better, you can induce vomiting by pressing on the root of the tongue with a spoon or a clean finger. Then gently influence the areas of the neck where the carotid arteries pass, massaging and stroking them. If a person loses consciousness, they must be washed with cold water and placed on the bed without closing the window - oxygen must be present in the room.
Combination with high heart rate
Pulse is the rate of contraction of the myocardium. Its increase can cause increased physical activity, stressful situations, and neuroses. But if a person’s blood pressure remains within the physiological norm, but the pulse turns out to be rapid, what does this mean?
Blood pressure 120/80 in adolescents is an acceptable physiological norm
Rapid heartbeat - the pulse in this case reaches 100/110 beats per minute or higher - is called tachycardia. It can be caused by various reasons, in particular:
Causes of rapid pulse at normal blood pressure
- binge eating;
- abuse of coffee and caffeinated drinks;
- stressful/hysterical conditions;
- panic;
- being in a hot bath, steam room, sauna;
- climate change - moving from cold to hot;
- diseases accompanied by increased body temperature;
- various diseases of internal organs;
- disorders of the thyroid gland;
- severe poisoning.
Important! Tachycardia that occurs during pregnancy always requires the woman to be hospitalized in a hospital for treatment.
The heart rate rate for all ages will be individual. The following indicators (beats per minute) are considered acceptable:
- 0–5 years – 126…140;
- 5–8 years – 85…98;
- 9–20 years – 75…88;
- 20–60 years – 60…70;
- after 60 years – 64…74.
In case of poisoning, the pulse may exceed 100 beats per minute.
Symptoms of High Blood Pressure
If you feel unwell and don’t have a blood pressure monitor at hand, pay attention to the symptoms
.
They may indicate problems with blood pressure.
Signs of high blood pressure
- Dizziness.
- Weakness.
- Heart pain.
- Headache.
- Numbness of arms and legs.
- Nausea.
- Noise in ears.
- Heart rhythm disturbances.
- Facial redness.
- Swelling.
If you measure your blood pressure and it turns out to be high, it is recommended to repeat the measurement at least within a week. Do this at the same time and record the indicators. If the pressure constantly exceeds the age norm by 15 units or more (for example, does not fall below 135/85 when the norm is 120/80), this is a reason to consult a doctor. Regardless of age, do not allow readings of 140/90 or higher.
If measures are not taken in time, there is a risk of hypertensive crisis - a critical increase in blood pressure that threatens life.
Combination with low heart rate
Hidden heart disease can reduce the pulse to 50–60 beats per minute with normal blood pressure. Many of them at the beginning of development do not have typical manifestations and declare themselves exclusively by a decrease in heart rate. Diseases that provoke the pathological condition can be myocarditis or acquired heart defects.
When measuring blood pressure, it is important to monitor your heart rate as well.
Bradycardia (low number of myocardial contractions per minute) can be caused by an overdose of drugs from the group of beta-blockers and cardiac glycosides. What to do in this case? You should immediately stop taking the medications and consult your doctor.
Blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg. Art. is recognized as a physiological norm. But over time, the heart and blood vessels wear out. As a result, blood pressure indicators change - they, as a rule, increase, but for the current state of the body they remain normal.
Characteristic symptoms
In order to relieve the symptoms of low blood pressure and rapid pulse, it is necessary to promptly recognize a condition that poses a threat to health. Due to circulatory failure, the following symptoms occur:
- fainting;
- lack of coordination in space;
- nausea and vomiting;
- weakness, increased fatigue;
- dyspnea;
- deterioration of visual function.
Dizziness is the most common accompanying drop in blood pressure and increased heart rate
In severe cases, consciousness becomes clouded and generalized convulsions develop, so this condition is considered life-threatening and requires medical intervention. Next, we will talk about first aid measures that need to be provided to the patient before the doctors arrive and the symptoms of tachycardia are relieved.
Diagnostics
Often, an increased pulse with low blood pressure is observed in older people due to age-related changes in the condition of blood vessels and the heart. The walls of the capillaries become brittle and lose elasticity, which is why they cannot fully contract and regulate blood pressure levels on their own. However, similar symptoms are observed in young patients, and an attack of a drop in upper pressure is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, weakness and dizziness.
It is not possible to determine the exact causes of the described condition on your own; you need to contact a specialist. Comprehensive diagnostics usually includes:
- Blood tests - general and biochemical composition. The second method of examination is necessary if poisoning by toxic substances is suspected, and general indicators will make it possible to diagnose inflammatory processes, iron deficiency anemia and other hidden diseases.
- X-ray examination is necessary to detect inflammation of the lungs, the formation of stones in the kidneys, gall bladder, because for these reasons the pulse increases simultaneously with a decrease in blood pressure quite often.
- Echocardiogram – necessary to detect changes in the structure of the heart muscle and valves. It also allows you to evaluate the work of the heart, whether there are signs of damage and impaired contractility. The examination is safe even for a child, since it is carried out using ultrasound.
- A blood test for hormone levels and an analysis for the content of specific immunoglobulins are recommended if problems with the thyroid gland (thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism) and a tendency to allergic reactions are suspected.
Performing an ultrasound of the heart
To track the onset and possible causes of rapid heartbeat against the background of low blood pressure, daily monitoring of indicators is carried out. This allows you to establish the time of heart rate surges and identify predisposing factors (physical activity, anxiety, etc.).