High blood pressure (hypertension) is a common health problem that affects millions of people around the world. Obesity is also an important public health problem, with its high prevalence and associated risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and kidney disease.
Research has shown that by 2025, about 1.56 billion people worldwide will suffer from high blood pressure. This is 60% more than in 2000. The forecast predicts an epidemic of cardiovascular disease as high blood pressure affects the heart as well as blood vessels, leading to severe damage to various organs such as the kidneys and eyes.
Obesity and high blood pressure
The content of the article
Research has shown that the rise in people suffering from high blood pressure is seen in conjunction with a sharp increase in the prevalence of overweight and obesity. According to the International Obesity Task Force, at least 1.1 billion adults are currently overweight, including 312 million who are obese.
Similar trends are observed in the United States and Europe. For example, in England, 66% of men and 55% of women are overweight or obese.
Waist
But BMI is not the only factor that determines risk. For example, with developed muscles or fluid retention (edema), calculating BMI may lead to an overestimation of the true volume of adipose tissue. BMI may underestimate body fat in older patients and those with loss of muscle mass. This is why waist size is also very important. In addition, excess accumulation of visceral (abdominal) fat also increases the risk of developing diseases. A waist circumference of more than 89 cm in women and more than 101 cm in men is considered significantly higher than normal.
Obesity and heart disease
Obesity is associated with several heart diseases, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, type 2 diabetes, and high blood pressure.
High blood pressure
Approximately 60% of all diabetics are overweight. Further abdominal obesity causes a higher risk due to the high rate of fatty acids and hormones entering the liver from fat deposits in the abdominal cavity.
Accordingly, waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio are surrogate markers of abdominal or visceral obesity and may more accurately predict heart attacks, heart disease, and diabetes than body mass index (BMI).
In addition to the link between obesity and high blood pressure, the co-occurrence of both conditions together also creates a significant economic burden on society.
Data from the most recent National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) for 1999–2000. Shows that although blood pressure control rates have improved much since 1988 from 25% to 31%, they are still low. This resulted in 39,702 cardiovascular events, 8,734 cardiovascular deaths, and $964 million in direct medical costs in the United States. In Europe, these figures are 1.26 billion euros due to the lack of adequate pressure control.
Body Mass Index (BMI)
Body mass index (BMI) is a parameter that determines the relationship between your weight and height. This gives a rough estimate of the total volume of adipose tissue and is associated with an increased risk of a number of diseases. Calculate your exact BMI using the following formula:
BMI=(weight in kg)/(height in meters)
For example, with a weight of 75 kilograms and a height of 1 meter 70 cm, the BMI will be 75/(1.7*1.7)=75/2.89=25.95 kg/m2 From the following table you can find out whether you are overweight ( BMI from 25 to 29.9) or obesity (BMI over 30).
What does your body mass index (BMI) mean?
| Category | BMI | Result |
| Normal weight | 18,5-24,9 | Great! Try not to gain weight |
| Excess body weight | 25-29,9 | You need to lose weight if you have two or more risk factors for heart disease |
| Obesity | Over 30 | You need to lose weight. Lose weight slowly - about 200-900 grams per week. Consult a doctor or dietitian if necessary. |
If your BMI is over 30, then your risk of heart disease is high and you need to lose weight. It is recommended to lose weight for people who are overweight and have two or more risk factors. If you are of normal weight or slightly overweight and do not need to lose weight, you need to be careful not to gain weight. If you need to lose weight, it is very important to do it slowly. Lose weight no more than 200-900 grams per week. Start by losing 10% of your current weight. This is the healthiest way to lose weight and keep it at the required levels for a long time. There are no magic weight loss formulas. You should change your eating style so that you eat fewer calories than you burn daily. How many calories you burn depends on factors such as your body size and how physically active you are (see Examples of moderate physical activity). 450g equivalent to 3,500 calories. So to lose 1 pound, you need to eat 500 fewer calories per day or burn 500 more calories per day than usual. It is best to combine both reducing the caloric content of food eaten and increasing physical activity. And be mindful of portion sizes. It's not just what calories you eat, but how much you eat. As you lose weight, follow a healthy eating plan that includes a variety of foods (such as the DASH diet).
High blood pressure and fat distribution
In addition, the association with high blood pressure is also present when considering the distribution of body fat in obesity. Abdominal obesity has been associated in studies with hypertension.
For example, a study of normative aging found that in men over 18 years of age, the risk of hypertension increased by about three times for every one unit change in the abdominal circumference to hip width ratio.
The Framingham Heart Study found that a 5% increase in weight increases the risk of hypertension by 30% over 4 years. However, weight loss reduces both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Dangers
Obesity is a serious disease that is a disruption of metabolic processes. Excess weight reduces life expectancy.
In hypertension, the fight against fat deposits is included in both treatment and prevention. And this should be taken very seriously, since excess weight in combination with hypertension can cause significant harm to the body.
- With an unhealthy diet, the body receives a lot of high-calorie foods containing large amounts of cholesterol. Its excess in the blood begins to accumulate on the walls of blood vessels and harden over time. This process leads to the formation of cholesterol plaques, which do not allow the blood to move in a normal working rhythm. And the pressure tends to rise at this moment. Also, the vessels lose their elasticity and become very fragile.
- There is a high risk of blood clots that block blood flow, causing severe hypertension and the possibility of developing a hypertensive crisis.
- Atherosclerotic plaques can block coronary arteries, causing a stroke.
Such complications can occur with elevated levels of cholesterol, which enters the body with fatty and high-calorie foods. In combination with insufficient physical activity, smoking, and alcohol consumption, heart overload can occur, which contributes to the development of myocardial infarction.
What does the diet look like?
The diet, during the treatment of high blood pressure, will relieve the patient of excess weight, and will also help restore the tone of the blood vessels and the functioning of the kidneys. In addition, dietary nutrition can be a good prevention of hypertension.
What is the essence of such nutrition?
- It is necessary to reduce the amount of salt, because it retains fluid in the body.
- Eliminate animal fats from your diet because they increase blood cholesterol levels.
- Add plant foods to your diet, because they contain a lot of vitamins and minerals.
- Give up bad habits, do not drink alcohol or smoke, so as not to overload the heart.
These recommendations will help the patient lose extra pounds and reduce blood pressure by about ten millimeters. Thus, atherosclerotic plaques can be split, vascular tone is restored and pressure is normalized.
To lower blood pressure, your diet should be as follows:
- The cardiovascular system is strengthened by consuming potassium and magnesium. They are found in cabbage, beets, carrots and other vegetables.
- To prevent fluid from accumulating in the body in unnecessary quantities, it is better to drink three liters of water a day.
- Avoid fried foods. All foods are best steamed, boiled or stewed.
In addition, add more fresh vegetables and fruits, fish, and dairy products to your daily diet. Fatty meats, sausages, confectionery and sugar should be avoided. In addition, pickles, marinades and preserves should not be consumed.
How does weight affect blood pressure?
Remember the behavior of a person whose weight is several times higher than the permissible norm.
It’s hard for him to move his legs, he’s covered in sweat, his cheeks are purple, he’s short of breath... It’s all due to high blood pressure. Yes, excess weight greatly affects the readings of such a medical device as a tonometer, which is used to determine blood pressure.
The pattern is simple: the more a person weighs, the higher his blood pressure.
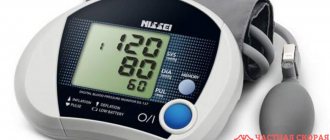
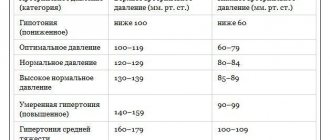
A constant increase in blood pressure is commonly called hypertension . If the blood pressure of a healthy person is 120/80 mm Hg. Art., then in a hypertensive patient it can reach values of 200/100 mm Hg. Art.
The limit when hypertension is diagnosed starts from the upper pressure number in the range of 140 – 159 units.
People who are underweight have the opposite situation - their blood pressure is too low. Chronically low blood pressure is called hypotension .
Hypotension is diagnosed when upper pressure values range from 90 to 99 units.
Sample menu for high blood pressure
The daily menu consists of the standard breakfast, dinner and dinner. A small light snack in the form of fruit or salad is allowed between each main meal. Composition of the daily menu:
- Breakfast - ¾ glasses of cereal, a glass of full-fat milk, a piece of whole wheat bread, 200 g of orange juice;
- Dinner - a salad of fresh vegetables, skinny boiled chicken, no more than 200 g of bacon or vegetable soup;
- 60 grams of lean beef, beans with vegetable oil, 1 potato, 1 apple, 200 grams of non-fat milk.
The digestive dose should not exceed the daily calorie standard. When cooking, avoid frying with oil. It is recommended to prepare dishes by stewing or cooking, which will reduce high-calorie dishes and retain more vitamins and nutrients in food.
What is hypertension?
The word hypertension is used to refer to persistently elevated blood pressure. An increase in blood pressure occurs when there is a narrowing of the arteries and/or their smaller branches, the arterioles. Arteries are the main transport routes through which blood is delivered to all tissues of the body. In some people, the arterioles often narrow, initially due to spasm, and later their lumen remains permanently narrowed due to wall thickening. And then, in order for the blood flow to overcome these constrictions, the work of the heart increases, more blood is released into the vascular bed. Hypertension develops. Very rarely, in approximately one in ten patients, the cause of increased blood pressure is damage to an organ. In these cases we talk about secondary or symptomatic hypertension. In the vast majority of cases, approximately 90% of patients, we are talking about so-called primary, or essential hypertension. Despite the fact that the cause of high blood pressure in these patients has not yet been fully established, there is no doubt that untreated hypertension is a serious threat to their health. The most common complications of hypertension are damage to vital organs such as the heart, brain and kidneys. The main symptom of arterial hypertension is high blood pressure (above 160/95 mm Hg), which may be accompanied by headache, dizziness, flashing before the eyes of spots, spots, circles, and decreased visual acuity. Pain in the heart area, a feeling of palpitations and interruptions in the functioning of the heart are possible. During an increase in pressure, a feeling of heat may occur, the face and other areas of the skin turn red, and then sweat appears on them. The limbs, on the contrary, tend to get cold. In later stages of the disease, symptoms of circulatory failure appear: blueness of the tip of the nose, fingers (acrocyanosis), swelling, shortness of breath during exercise, and eventually at rest. Other symptoms of arterial hypertension do not go unnoticed by the doctor: an increase in the size of the heart, a change in its tones when listening. As the disease progresses, signs of brain and kidney damage appear.
Physical exercise
To prevent the lost kilos from returning again, you should add physical exercise to your diet. People with hypertension need to select all exercises very carefully, because a strong load will have a great impact on the heart and the pressure can rise sharply. That is why all selected exercises should not cause much stress on the body.
The duration of classes at the very beginning should not be long, so you can stop at fifteen minutes a day. Thus, the patient’s heart will get used to small loads, which can later be increased. The training time can be increased every fourteen days by five minutes. You need to walk up to one hour. However, the number of classes should also be increased to six times a week.
You should do exercises constantly, this is the only way to get rid of unnecessary pounds and high blood pressure.
It is better to start your exercises with walking, later you can start doing stretching. The third week can be devoted to exercise cycling and aerobics for beginners.
But when performing, you should carefully listen to your body; if dizziness or rapid heartbeat appears, then the pace should be reduced.
After performing the exercises, you need to measure your blood pressure and report the readings to your doctor. This will help him adjust the course of therapy.
Remember, excess weight has a negative impact on the functioning of the cardiovascular system. In addition to cosmetic problems, various serious pathologies appear. Try to always be in shape so that you can be a healthy and beautiful person all your life.